Every person's blood contains red cells. In medicine they are called red blood cells. Often, when they penetrate into another biological fluid (urine), hematuria is diagnosed. But at the same time, it is necessary to take into account the quantity, and also understand whether they are accurate.
If red blood cells in the urine are elevated, the reasons in men may lie in age-related changes in the body. Normally, if a representative of the stronger sex is from 18 to 45 years old, there should be a number of them, calculated by the formula (4.2-5.6 * 10)12 per liter of blood. At the same time, the indicator should not lean upward. Up to these age limits, a deviation of 0.2 is permissible.
Functions in the body
Red blood cells are fairly small, biconcave, round-shaped cells that are also called red blood cells. There are 2 types of these cells in the body - changed and unchanged.
The former almost always arise as a result of some disease, do not contain hemoglobin and are ring-shaped. They are not present in the systemic circulation. In most cases, they appear in biological fluids and are pale in color.
Unchanged red cells have a regular shape and contain hemoglobin, and are colored bright red. They are present in human blood and, with various abnormalities, can appear in other biological fluids.
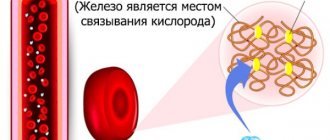
It is worth noting that in the human body, red blood cells occupy almost 25% of the total volume of all cells.
Red blood cells perform several important functions in the human body:
- They supply hemoglobin and oxygen to the tissues, due to which metabolism is carried out.
- They help transport carbon dioxide from cells, which facilitates gas exchange and speeds up metabolism.
- They normalize the acid-base balance in the body, which prevents various diseases associated with its disturbance.
- They stimulate the formation of important enzymes and other substances in the body that ensure normal metabolic processes.
- Relieves symptoms of intoxication and prevents re-development of the condition.
- They help transport nutritional components supplied with food to cells.
Thanks to the complex effects of cells, many processes take place in the human body, which is very important for the normal functioning of internal organs.
How and under what conditions are they produced?
Unchanged red blood cells in the urine cannot appear without the production of cells in the body. Every few seconds, red bone marrow produces more than 2 million red blood cells. Normally, they are in the systemic circulation for 100-120 days, after which they are absorbed by macrophages, and newly formed cells enter the blood.
The formation of red blood cells occurs in the red bone marrow of large bones, such as the pelvis, vertebrae, ribs and even the bones of the skull. This process requires normal functioning of the organ.
It is worth noting that cell formation occurs in several stages, each of which follows from the previous one:
- The initial stage is accompanied by the formation of erythroblasts. These cells resemble red blood cells in appearance, but are larger in size and have some differences in the membrane.
- Erythroblasts form pronormocytes, which are smaller in size, but also do not resemble full-fledged red blood cells.
- Basophilic normocyte is the next stage of cell formation. These cells already have an uneven pinkish color.
- In polychromatophilic normocytes there is a high concentration of hemoglobin.
- Oxyphilic normocyte is more reminiscent of an erythrocyte in shape and size, and has a bright pink color.
- The reticulocyte is the precursor of a full-fledged red blood cell, but has a different color.
- A mature red blood cell is called a normocyte. It is these cells that enter the systemic circulation and perform various functions.
After all functions are completed, cell absorption occurs in the liver and spleen. This process is normal, but can be disrupted by various diseases.
Diagnostics
So, in order to accurately determine how many red cells are present in urine, it must be transported to a clinical laboratory. The main warning sign indicating the need to visit a specialist is a change in the color of the urine, which, if blood gets in, will have variations of red shades.
With a low concentration of red blood cells in the urine, it has a brownish color. If a man develops small blood clots in his underwear, this indicates the development of cancer. In the case of a pronounced scarlet color, kidney disease will most likely be detected.
Rules for collecting biological fluid for laboratory research. Source: med-explorer.ru
If a burning sensation in the urethral canal is added to the changed color, hematuria is diagnosed. Moreover, this condition can occur against the background of urolithiasis, or after the penetration of infections into the body. With frequent urination, a constant desire to defecate, but not being able to do so, we will be talking about prostatitis. To confirm or refute pathologies, ultrasound screening and blood tests are indicated.
Table of indicators is normal
Normally, for each age group, the number of red blood cells in the urine is slightly different. Deviation from the norm is considered a disorder that requires treatment.
| Age group | Norm of red blood cells in urine |
| Newborns and children up to 3 years old | From 2 to 5 cells in the field of view |
| Patients from preschool and school age | No more than 4 cells in the field of view |
| Men | Up to 1 unit in field of view |
| Women | No more than 3 units in the field of view |
The absence of cells in the test material is not considered a deviation, but exceeding the permissible norm is a reason to visit a doctor.
The number of red blood cells in urine in men
Deteriorating health and the approaching midlife crisis in men cause a constant change in the number of red blood cells. The norm of red blood cells in the age category 18-45 years is (4.2-5.6 * 10)12 per liter of blood. Moreover, this figure should not be inclined upward or downward. Before 18 and after 45 years, the norm deviates by 0.2 in each direction.
A change in indicators is considered an alarming sign. Repeated analysis is carried out for reliability. But in any case, you should contact a medical specialist, because changes in the number of red cells in the urine may be temporary. An increase in red blood cells may occur due to a decrease in immunity levels. Everything returns to normal after 2 days. If the high level of red blood cells in urine continues to persist, then you should immediately make an appointment with a doctor.
Symptoms of increase
Unchanged red blood cells in the urine can appear against the background of absolute health of a child or adult. However, as the condition progresses, the disorder necessarily manifests itself with various symptoms, the severity of which depends on the organism and the characteristics of the pathological process.
Externally, the disorder can be manifested by pallor of the skin, dark circles under the eyes, as well as skin moisture, which is associated with increased work of the sweat glands. In addition, hematomas may appear on the patient’s body even with light pressure or bruising. This indicates a vascular disorder, causing capillary fragility and hemorrhage under the skin.
In addition, patients experience weakness and fatigue. Depending on the cause of the appearance of red blood cells in the urine, the patient may report pain in the abdomen, as well as in the kidney area.
In medicine, the appearance of unchanged red blood cells in urine is called hematuria . It may be accompanied by pain in the bladder area, as well as discomfort when urinating.
Additionally, many patients experience an increase in body temperature, possible pain in the heart, and a decrease in blood pressure. If the appearance of cells in urine is associated with pathologies of the reproductive system, pain appears in the lower abdomen, which intensifies when urinating. This symptom is typical for men suffering from prostatitis and other diseases.
In women, the menstrual cycle is disrupted, and pathological vaginal discharge may appear. Additionally, almost all patients with hematuria experience weakness, fatigue, and headache. The child's condition with this disorder usually does not worsen.
There may be a slight decrease in motor activity and an increase in body temperature. Only when the disorder lasts for a long time does the child develop general symptoms in the form of weakness, dizziness and loss of appetite.
The nature of the symptoms and the severity of the manifestations depend on the cause that provoked the hematuria.
Treatment
Depending on what pathological process was identified, the most appropriate treatment tactic for a particular clinical case is determined. When pathogenic bacteria or infections that cause inflammation are actively spreading in the body, an antibiotic treatment regimen is developed. Amoxicillin is most often prescribed for treatment.
If internal bleeding occurs, then the patient must be hospitalized and all subsequent actions are carried out exclusively in a hospital setting. The main treatment tactic is surgery, and the use of hemostatic medications is also indicated. For inflammation in the bladder, healing instillations are prescribed.
The principle of performing healing instillations. Source: yunost-kmv.ru
Also, identified tumor formations and polyps are subject to surgical treatment. For cystitis, taking antibiotics would be most justified. If there is stagnation of urine in the body, then additional diuretics are prescribed. In most cases, preference is given to the drug Canephron.
It is important to understand that the main part of pathological processes is characterized by a hidden nature of the course. That is why all representatives of the stronger sex are recommended to undergo regular preventive examinations with a urologist, as well as treatment for concomitant diseases.
Reasons for the increase
Unchanged or changed red blood cells may appear in the urine of patients as a result of various reasons.
The most common of them are the following:
- Injuries to the kidneys and bladder of varying severity.
- Bruises of internal organs, causing deterioration in the functioning of the liver, kidneys, and digestive tract.
- Diseases of the genitourinary system in patients of different ages. Red blood cells in urine can appear with pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, urethritis, cystitis, prostatitis, prostate adenoma. In women, the symptom may be associated with endometritis, endometriosis, fibroids, cycle disorders, and inflammatory pathologies of the appendages.
- Pathologies of the red bone marrow, in which the process of production of red blood cells is disrupted, and immature cells enter the systemic circulation.
- Malignant neoplasms of internal organs.
- Blood diseases accompanied by impaired blood clotting.
- Infectious pathologies accompanied by a febrile state.
- Damage to the kidneys by the tuberculosis bacillus, rupture of the ureters, bladder.
- Severe urolithiasis.
- Overheating of the body as a result of prolonged exposure to open sunlight, in a bathhouse or sauna.
- Stressful situations in which all metabolic processes in the body are disrupted.
- Poor nutrition with a lot of spicy, fatty and sour foods in the diet, as well as abuse of alcoholic beverages on an ongoing basis.
- Excessive and constant physical activity.
Various factors lead to the appearance of cells in the blood. Their number also depends on the pathology and the degree of its neglect.
Causes of pathology
The reason for a small deviation from the norm is considered abnormal and is of a very different nature:
Kidney cancer
- lack of treatment for infectious diseases;
- heart failure, which appeared due to the individual course of an infectious disease;
- mononucleosis, which is diagnosed only in hospitals;
- severe hemophilia, which prevents blood from clotting, causing the second to enter the urine;
- a pathogenic process that occurs through stagnation of urine in the bladder, which leads to the proliferation of bacteria;
- surgical interventions and trauma, due to which the inflammatory process began in the kidney area;
- formation of polyps in the genitourinary system;
- the development of bacterial inflammation that arose due to advanced cystitis;
- kidney cancer and diseases of the genitourinary system;
- blood in the discharge, which is often caused by bleeding in the urinary tract.
Increased red blood cells in urine with prostatitis
An increased level of red blood cells occurs with a disease in men such as prostatitis. But the figure does not jump the line: no more than 3 units.
If, during observation by a medical specialist, the figure increases, then additional studies are carried out. Cytology and urine culture are prescribed.
Active development of bacteria is observed when urine is inoculated. This process occurs as a result of bleeding and all sorts of complications. Cancer is detected by cytology. The diagnosis of prostatitis requires constant intervention from doctors, because the disease can develop into a cancerous tumor, which causes terrible pain. Red cells increase in number when:
Recommended topic:
Normal urine diastase
- there is smallpox or fever;
- prostate function is impaired;
- cardiovascular disease develops;
- inflammation throughout the body;
- heart function is disrupted;
- the body is attacked by an acute viral disease.
Why do doctors recommend giving up junk food the day before the tests? Because all this affects the final results, including excessive physical activity. Therefore, to avoid an erroneous diagnosis of prostatitis, you should listen to medical specialists.
Physiological reasons
The excess of red cells in the urinary secretions of men can also be considered a physiological reason. The red blood cell count increases when an adult male:
Excess of red cells in men's urinary secretions may occur due to stress
- consumed a large dose of alcoholic beverages;
- ate a lot of spicy or salty foods;
- was in the sun for a long time and got sunstroke;
- took a steam bath;
- became interested in prolonged physical activity;
- suffered severe stress.
Doctors wrote a whole treatise on the topic: “What can’t be done before tests?” It reveals all the reasons for erroneous analyzes. A patient who neglects the advice of doctors harms the results of the tests. A repeat experiment is ordered.
Indications for the study
In some cases, the appearance of cells in the urine is a temporary problem that does not require treatment. But more often the condition requires diagnosis and treatment in order to prevent complications.
Main indications for the study:
- A large number of cells in the urine, increasing as the disease progresses.
- Severe pain in the kidney area or lower abdomen.
- Foreign impurities in urine in the form of pus, sand.
- Deterioration of general condition.
- Fever.
- The appearance of complications from internal organs.
These indications are considered a reason to immediately visit a doctor. As a rule, it is recommended to contact a therapist who will prescribe a test.
How to determine
Unchanged red blood cells in the urine are determined by clinical examination of urine in the laboratory. Other methods are not used, since general analysis is the most informative and reliable.
Unchanged red blood cells in urine
If necessary, a clinical blood test is prescribed, which allows you to get a complete picture of the patient’s general condition and determine the need for other studies.
Establishing diagnosis
The number of red cells in urine can only be calculated through laboratory tests. A person notices changes in the color of urine when there is blood in it. The low blood content in urine explains its brownish tint. Blood lumps on underwear indicate cancer.
Kidney bleeding is diagnosed when the urine is scarlet in color. The diagnosis of hematuria is made when a burning sensation is added to the color of the urine. And hematuria, in turn, is caused by urolithiasis or infection.
An increase in red blood cells in the urine is often associated with a male disease - prostatitis. A pronounced symptom is a constant desire to go to the toilet, while the discharge will be scanty in quantity.
Modern research methods help to identify a specific diagnosis of a pathological condition: ultrasound, blood tests.
Preparing and conducting analysis
Special preparation for collecting biological material is not required, but doctors recommend following certain rules. 10-14 days before urine collection you should not drink alcohol. 3-5 days before, it is better to give up sour, salty, spicy foods, which can negatively affect the condition of the kidneys and also distort the diagnostic result.
It is important not to overwork and also avoid stressful situations. The collection of material must be carried out in the morning when you first visit the toilet and after washing the genitals with warm water and soap.
Experts recommend not collecting urine for the first 2 seconds after the start of urination, and starting collecting urine after 2 seconds. The urine container must be dry and clean. It is better to give preference to sterile pharmaceutical jars with a lid, which are designed for the material.
After collection, urine should be sent immediately to the laboratory. But if necessary, you can store it in the refrigerator. Doctors recommend examining the material directly on the day it is collected, which makes the result more accurate.
In laboratory conditions, urine is examined under a microscope, the number of pathological cells and other components normally present in the material is calculated.
Urine collection rules
Urine analysis readings will be informative with proper preparation and urine collection. A special container is purchased at the pharmacy or a glass jar is prepared at home.
- The dishes must be prepared in advance, washed, sterilized and dried. Do not wipe, especially inside.
- The day before the test, you should not drink alcohol, overheat, or eat spicy, especially salty foods. It is not advisable to put too much physical strain on yourself. If your doctor has prescribed you to take medication regularly, you should tell your urologist about this.
- Before donating, you need to wash your external genitalia with warm water without soap or gel so that excess secretions do not get into the tests.
- For dinner, you should not eat spicy or heavily colored foods. Such as beets and carrots, garlic and beans. Avoid fatty fried meats.
- In the morning before the test, it is advisable not to have breakfast. On an empty stomach, the indicators are more accurate, especially since the level of sugar, leukocytes, proteins and other substances in the urine is simultaneously determined. As a last resort, refrain from coffee, strong tea, and drinks with dyes.
Women should not be tested during their period. Natural bleeding will distort the readings.
Decoding the results
The results of the study can be obtained the very next day after submitting the material.
Normally, it contains the following parameters:
- The volume of test material, which depends on how much urine the patient has collected.
- The color should normally be straw yellow, but with a significant number of red blood cells it can be pink or even red. In addition, urine is normally clear.
- Density normally ranges from 1002 to 1025. With deviations, the indicator may change in one direction or another.
- Normally, there is no glucose in the analysis.
- The amount of protein normally does not exceed 0.03 g/l.
- Ketone bodies and bilirubin are normally absent. In pathologies it can appear in different quantities.
- Normally unchanged red blood cells depend on age. For children under one year old - no more than 5 cells in the field of view, children of preschool and school age - up to 4 cells in the field of view, women - up to 3 cells in the field of view, men - up to 1 cell in the field of view. If this indicator increases, we can talk about hematuria of varying degrees of neglect.
- The amount of squamous epithelium is insignificant or moderate. If the analysis indicates “many”, most likely the patient has some kind of disease.
- White blood cells are normally 1-4 units per field of view. An increase in level indicates the development of inflammation.
- Modified red blood cells should not be present in the material.
- Bacteria, fungi, salts, mucus, columnar epithelium are normally absent.
When studying the result, you should rely on normal indicators. Their deviation indicates illness.
When to see a doctor
Independent study of the study results helps to detect deviations, once the patient is approximately aware of the norm for his age. If any point does not correspond to the norm, but is significantly or slightly elevated, it is worth visiting a therapist.
The doctor will conduct an examination and prescribe additional diagnostics to identify the cause of the deviation. Usually a consultation with a urologist, gynecologist, cardiologist, gastroenterologist, or endocrinologist is required.
How to get it back to normal
Unchanged red blood cells in the urine appear as a result of various factors. However, in most cases, the disorder is associated with pathologies of the genitourinary system. Treatment is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease.
Medications
Various medications are used in treatment, depending on the specific disease and the presence of complications.
The following groups of funds are considered the most effective:
- Ibuprofen is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug that is used to relieve pain, relieve symptoms of inflammation and reduce body temperature. The patient is prescribed from 1 to 3 tablets per day, the course of treatment lasts up to 7 days. The drug effectively eliminates severe manifestations and significantly alleviates the patient’s condition.
- Spasmalgon is a drug that has analgesic and antispasmodic effects. Used for cystitis and other pathologies of the genitourinary system, it helps alleviate the condition, as well as urination. This allows pathogenic microorganisms that lead to the appearance of red blood cells in the urine to be removed from the organs. Take 1 tablet 2 times a day, repeat the dose for 5-8 days in a row.
- Azithromycin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that alleviates the patient’s condition when identifying infectious, bacterial diseases of the bladder, kidneys, urethra, and other internal organs. Tablets are taken orally, 1 piece 2 times a day for 3-6 days, depending on the severity of symptoms.
- Urolesan is a herbal remedy in capsule form, which is actively used to eliminate microbes from the urinary system. Capsules are taken 3 times a day, 1 piece for 10-20 days, depending on the severity of symptoms.
- Monural is a very effective antimicrobial medication in powder form, which is often prescribed for hematuria resulting from damage to the kidneys or bladder. The product is taken once in the amount of 1 sachet. The powder is dissolved in 100-150 ml of water, and the solution is taken orally. If necessary, repeat the dose after 5-7 days.
- Dicynone is a drug to stop bleeding, which is prescribed when a large number of red blood cells are found in the urine on an ongoing basis. In this case, the drug is used in courses of 3-7 days, daily the patient is administered 2 ml of the drug intramuscularly 2-3 times a day. This helps stop bleeding, which is associated, for example, with damage to the bladder wall from a stone.
- No-spa is an antispasmodic medication that is used for damage to the kidneys, bladder, liver or urethra. Helps relieve spasms and relieve pain. Tablets are taken 3 times a day, 1-2 pieces for 10 days.
- Cycloferon is an antiviral medication that is prescribed to patients when the appearance of red blood cells in the urine is associated with a protracted course of a viral disease. The patient is administered intramuscularly 2 ml of the drug per day for 10 days. In some cases, an individual regimen is used, which involves breaks between injections.
The treatment regimen in each case may differ, depending on the disease and possible complications. It is important not to self-medicate, as the risk of complications is increased.
Traditional methods
Folk remedies do not help to completely cure the patient, but they can significantly alleviate his condition.
A decoction of nettle leaves is considered one of the most effective natural remedies for stopping bleeding. For 500 ml of water you need to take 5 g of dry leaves of the plant, cook for 3 minutes, leave for 1 hour to infuse. After this, the filtered decoction is taken orally, 50 ml 2 times a day for 5 days.
Another effective remedy is douching with calendula decoction. This method can only be used by women when bleeding is associated with inflammatory pathologies of the reproductive system.
For 1 liter of water, take 20 g of dried flowers of the plant and cook for 10 minutes. After cooling, filter the product and use it in the evening for douching. Repeat the procedure 10 days in a row.
Traditional methods can worsen the course of the underlying disease, so their use should be agreed with a doctor.
It is strictly forbidden to visit saunas, baths, or take hot baths if red blood cells appear in the urine.
Other methods
Additional methods of therapy include physiotherapy and surgery. Physiotherapy is used in cases of hematuria associated with kidney damage. Electrophoresis is considered a popular and effective procedure. In this case, special electrodes are applied to the kidney area, which affect the organ and stimulate tissue restoration.
The course consists of 10-15 procedures, once every 3 days. The manipulation lasts up to 30 minutes.
If the ureter is ruptured, bladder tumors are detected, internal bleeding or large kidney stones are detected, surgery is performed. The method is most effective in this case. The features of the operation and the recovery period depend on the disease.
Today, the operation can be performed openly or using endoscopic instruments and performing a minimally invasive procedure. Each case requires an individual approach.
Possible complications
Lack of therapy will certainly lead to various complications, so do not put off visiting a doctor.
The most common consequences:
- Worsening of symptoms of the underlying disease.
- Massive blood loss.
- Anemia due to the loss of a large amount of blood.
- Spread of the inflammatory process.
- Damage to the kidneys or bladder as a result of stone movement.
- Tumor growth into nearby organs, if the cause is cancer.
Complications also depend on the underlying disease that caused the hematuria.
Unchanged and changed red blood cells can appear in the urine of a child and an adult. The causes of this disorder vary, and in some cases no treatment is required. However, more often the patient needs to immediately consult a doctor to prevent complications.