An important indicator of tests during pregnancy and after it is protein in the urine. Normally, urine has no traces of protein. Its presence (proteinuria) indicates an inflammatory process in the body or a violation of the integrity of the membranes of the glomeruli and tubules of the kidneys. A general urine test is mandatory for patients who have recently given birth. Doctors closely monitor this indicator, because it is the first signal of the disease.
What does the appearance of protein bodies mean in the analysis of a pregnant and parturient woman?
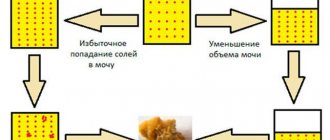
The main function of the kidneys is to filter the blood and remove metabolic products and excess fluid from the body. The kidney filter is designed in such a way that water and substances with low molecular weight dissolved in it enter the urine. The protein molecules are too large to pass through the basement membrane of the kidney filter under normal conditions.
The appearance of protein in the urine indicates a violation of the integrity of the renal barrier or an increase in its permeability. Most often, an increase in protein in the urine is accompanied by an increase in protein in the blood. It can also appear as a result of error - due to improper collection of material for analysis.
Protein in the urine may increase slightly for physiological reasons: excess protein intake from food or intense physical activity shortly before the test.
Protein in the urine before childbirth may appear due to nervous tension
This explains the reasons for the presence of protein in a woman’s urine immediately after childbirth. If she gives birth naturally, she has to endure a heavy load. Normally, protein in postpartum urine should disappear within 1-2 days. If this does not happen, you should pay attention to the condition of her kidneys.
Protein in the urine before childbirth may appear due to nervous tension and stress of the expectant mother.
Reasons for detecting protein in urine after childbirth, what to do
Protein is one of the three main components needed by the human body. In some diseases, the body begins to lose it through the kidneys. The appearance of protein in the urine is especially dangerous during pregnancy and after childbirth.
The appearance of protein in a general urine test in women after childbirth and pregnant women can signal a number of serious problems that require timely treatment.
It should be remembered that the range of drugs for the treatment of kidney diseases in pregnant women and women in labor is limited. This means that the earlier the disease is detected, the more effective the treatment will be.
A general urine test (UCA) is one of the main tests for pregnant women and women in the postpartum period. Protein metabolic products found in the TAM may signal a serious kidney pathology that requires immediate treatment.
Women, starting from the twentieth week of pregnancy, should have their urine tested at every appointment with a gynecologist in order to promptly identify serious diseases. Women after childbirth take the OAM at least three times - the day after childbirth, on the day of discharge from the maternity hospital and a month after childbirth at a scheduled appointment with a gynecologist.
If a woman in labor is bothered by pain or prolonged discharge from the genital tract, or she had kidney disease before pregnancy, the test will have to be repeated several times.
Taking a urine test correctly
To avoid inaccuracy in the analysis results, a woman needs to learn how to correctly take the OAM:
- on the eve of the test, you must follow a diet and exclude foods rich in proteins: meat, legumes, eggs;
- the day before the test, you need to limit physical activity;
- material is collected in the morning, immediately after sleep;
- before collecting urine, you must wash yourself thoroughly without using soap or other hygiene products, carefully close the entrance to the vagina with a sterile gauze or cotton swab;
- Next, you should collect an average portion of urine in a sterile disposable plastic container;
- The urine must be brought to the laboratory within two hours.
In some cases (with profuse lochia after childbirth, severe condition of the woman in labor), it is not possible to collect urine correctly, then the analysis is collected by a nurse using a catheter. In this case, accidental ingestion of protein-containing substances is excluded.
Norms of protein in urine for pregnant women and women in labor
Protein in the urine less than 0.033 g/l is considered normal and does not require treatment. If the amount of protein does not exceed 0.08 g/l, the doctor will order a retest to rule out violation of the rules when collecting urine. Proteinuria exceeding this level indicates pathology; the woman needs to undergo additional examination, often in a hospital setting.
If the level of protein metabolic products in the urine is increased, the cause should be looked for. First of all, eliminate the possibility of protein getting into the urine along with vaginal discharge if the material is collected incorrectly. It must be remembered that after heavy physical exertion or stress, protein in the urine may be increased. This happens, for example, on the first day after birth. But if all collection conditions are met, it is necessary to look for the disease and conduct additional research.
Possible pathologies in pregnant women
The most serious pathology, accompanied by the appearance of protein metabolism products in the urine, remains preeclampsia (formerly known as gestosis). The disease can appear as early as the second half of pregnancy. Preeclampsia poses a huge risk to the health of the mother and fetus. The disease is accompanied by an increase in blood pressure above 140 mmHg and the appearance of edema, often in the lower legs.
Due to the enlargement of the uterus during pregnancy, another serious disease occurs - pyelonephritis. Pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the urinary tract and cause inflammation of the renal collecting system. In this case, the woman exhibits symptoms of intoxication - nausea, vomiting, high fever, and pain in the lumbar region, often one-sided. Protein fractions appear in the urine in large quantities. When cystitis occurs, frequent urges and pain when urinating appear.
Glomerulonephritis may first appear during pregnancy and may also cause protein in the urine. The disease is autoimmune and is not usually associated with infection. With glomerulonephritis, blood pressure increases, blood and protein appear in the urine. Less commonly, the disease is asymptomatic.
With many chronic diseases, kidney failure of varying degrees of severity can occur, which can also lead to the appearance of protein in the urine.
Possible ailments for women in labor
In the early postpartum period, protein in the urine is most often associated with persistent preeclampsia. A characteristic symptom of gestosis after childbirth is severe headache. After intensive therapy with saline solutions, thrombolytics and anticoagulants, the amount of protein decreases.
The second most common cause of increased protein levels in the urine is glomerulonephritis. After childbirth, a woman’s body is weakened, creating ideal conditions for the debut of this disease.
In the postpartum period, urolithiasis often manifests itself for the first time. When the pressure of the enlarged uterus on the ureters disappears, kidney stones move freely through the urinary tract, injuring their wall. As a result, blood and protein appear in the kidneys, and then in the urine.
Pyelonephritis and nephropathies after childbirth are less common, mainly after difficult births, accompanied by ruptures of the birth canal and manual separation of the placenta.
Non-pathological causes of deviations
The presence of a small amount of protein in the first days after birth is absolutely normal. Childbirth is a heavy load for the whole body, during which a large amount of energy is released and a lot of protein is broken down. The kidneys help remove excess protein. In addition, after childbirth, postpartum secretions (lochia), rich in protein fractions, may enter the container for analysis.
What do they do if protein is detected in the urine?
If protein is detected in the urine after the test is repeated, an in-depth examination is carried out. An absolutely harmless method for pregnant women and women in labor is ultrasound of the kidneys. Ultrasound can detect enlargement of the kidney and disruption of its structure.
For a more accurate diagnosis, MRI and CT are used, which can show difficulty in the outflow of urine and other functional disorders in the kidneys.
After collecting an anamnesis and examination, the doctor will determine whether the increased amount of protein in the urine is associated with pregnancy (as, for example, with gestosis) or with kidney damage and, based on this, will prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Doctor's advice
If a pregnant or postpartum woman has protein in her urine, first of all, it is necessary to adjust her diet. Protein-rich, spicy, and salty foods are temporarily excluded to avoid fluid retention in the body and stress on the kidneys.
Medicines are selected depending on the cause of the appearance of protein in the urine. The doctor takes into account the safety of the drug for a pregnant woman and for a breastfed child.
For pyelonephritis, broad-spectrum antibiotics remain the drugs of choice. They act on pathogenic bacteria and promote normal filtration of urine in the glomerular apparatus of the kidneys. Modern antibiotics do not harm the fetus and can be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding. For glomerulonephritis and nephropathies, corticosteroids and analgesics are used. Before using drugs, the balance between the risk for the child and the benefit for the health of the mother is assessed.
In severe cases, if the disease is autoimmune in nature, antitumor drugs - cytostatics - can be used. When using them, breastfeeding stops.
In case of preeclampsia, thrombolytics, anticoagulants, and blood pressure lowering drugs are used. If the protein in the TAM does not disappear and complications arise (eclampsia), the only treatment option is emergency delivery followed by intensive care.
Advice from a traditional healer
During pregnancy, a woman can prevent the development of kidney disease. For this, folk remedies are used - medicinal herbs, herbs and teas. Lingonberry leaves, bearberry, and birch buds improve blood flow, filtration in the kidneys and help eliminate toxins. Herbal preparations, for example “Brusniver,” have a complex effect on the body.
Possible diseases
Elevated protein is a symptom. The increase in the level of protein bodies in the urine itself does not threaten health, but it indicates that the kidneys are not coping with their function due to illness.
Protein in the urine can appear with the following diseases:
Recommended topic:
Bacteria in urine during pregnancy
- inflammation of the stromal component of the kidneys (pyelonephritis);
- inflammation of the kidney parenchyma (glomerulonephritis);
- inflammation of other organs of the genitourinary system (ureteritis - ureters, cystitis - bladder, urethritis - urethra);
- gestosis (late or prenatal toxicosis of pregnant women);
- nephropathy - impaired kidney function;
- large area burns (burn disease).
In the process of diagnosing these diseases, attention is paid to other components of the analysis. In case of kidney pathology, in addition to protein in urine, red blood cells, white blood cells and glucose will be found.
What consequences to expect
Consequences from the appearance of protein in the urine should be expected not because of the protein itself, but because of the factor that provoked its appearance. If the alarm bell was noticed on time and treatment was started in a timely manner, then the occurrence of complications is unlikely.
The negative consequences of such diseases arise due to the fact that the patient did not seek help from specialists in time when any symptoms appeared or due to the negligence of health workers monitoring the indicators of the woman in labor.
That is why pregnant women and those who have already given birth undergo a general urine analysis much more often than other diagnostic procedures.
An unfavorable consequence of increased protein in the urine during pregnancy is gestosis. This pathology is characterized by impaired blood flow in the kidneys and brain, resulting in swelling and intoxication with protein breakdown products. The normal functioning of the placenta is also disrupted. The child receives less nutrients and oxygen, which in some cases leads to developmental pathologies, premature birth or miscarriages.
If the protein in the urine after childbirth is elevated for 3 or more days, you should be wary of the development of kidney failure. When the functioning of the renal filter deteriorates, swelling, fever, and intoxication are observed. When toxic metabolic products are no longer excreted from the body, they begin to poison all other organs - multiple organ failure develops.
To prevent such consequences, it is necessary to follow all the doctor’s instructions on time: take tests, undergo a course of treatment.
Recommended topic:
Leukocytes in the urine of a child
The influence of infusion preparation for cesarean section on hemostasis parameters
About the article
1506
0
Regular issues of "RMZh" No. 1 dated January 14, 2005 p. 15
Category: General articles
Authors: Arzhanova O.N. , Kulichkin Yu.V. , Kiselev A.G. , Lekareva T.M.
For quotation:
Arzhanova O.N., Kulichkin Yu.V., Kiselev A.G., Lekareva T.M. The influence of infusion preparation for cesarean section on hemostasis parameters. RMJ. 2005;1:15.
In recent years, developments in prenatal obstetrics have led to a significant increase in operative delivery by cesarean section. The frequency of operations ranges from 10 to 20% or more for various complications of pregnancy and somatic pathology. For many years, endotracheal anesthesia was preferred for cesarean section due to hardware support of the respiratory system. At the same time, a strong impression of reliability and safety was created. It has now been convincingly proven that only regional anesthesia for caesarean section can be considered relatively safe. When carrying out this method of pain relief, it is necessary to monitor hemodynamics and prevent hypotension. In modern obstetrics, epidural anesthesia is being replaced by combined spinal-epidural anesthesia, which has significant advantages in creating muscle relaxation in the surgical area. However, one of the significant disadvantages of a spinal block is a decrease in blood pressure, which requires timely infusion of appropriate volumes of fluid. In order to reduce the volume of preload, preparations of hydroxyethylated starches (HES) have recently begun to be used. The use of drugs in this class significantly reduces the frequency of vasopressor use, does not interfere with fetal blood flow and does not cause significant hemodynamic disturbances in the newborn. It is known that it is the hemodynamic disturbances that occur during the period of fetal extraction that lead to a decrease in the Apgar score, creating the effect of hemodynamic hypoxia.
All forms of HES improve the rheological properties of blood and microcirculation. By improving the rheological parameters of the blood, transport and provision of oxygen to tissues is improved. HES of medium and high molecular weight are highly effective in preventing and stopping capillary bleeding [1,3]. Over the past decade, many studies have emerged demonstrating the ability of HES to repair damaged endothelium. Apparently, HES solutions allow, in conditions of generalized endothelial damage, to maintain normal levels of perfusion and life support until autoregulation processes begin, restoring normal endothelial permeability. Positive results have been reported from the use of HES solutions in patients with multiple organ failure (sepsis, septic shock, severe forms of gestosis) [3]. A decrease in intravascular fluid volume is the main symptom of severe forms of preeclampsia, eclampsia, and general reactive inflammation syndrome. Many factors are responsible for the occurrence of this phenomenon, including an increase in the capacity of the venous bed and the deposition of blood in it, generalized damage to the endothelium with an increase in capillary permeability [1,2]. Swelling of the perivascular and perilymphatic spaces occurs, which impedes the outflow of albumin, dextrans and water from the interstitium. Oncotic pressure sharply increases in the interstitium and in extravascular spaces, which leads to an increase in extravascular hyperhydration in general and interstitial pulmonary edema in particular, and worsens tissue oxygenation, since it complicates the transport of energy substrates and metabolites [4]. Clinical observations indicate the effectiveness of therapy for gestosis and disorders of the uteroplacental circulation with solutions of hydroxyethyl starch. No negative effects on the condition of the intrauterine fetus were noted. Voluven (Frezenius Kabi, Germany) is a 6% solution of hydroxyethyl starch (HES) with a molecular weight of 130±20 kDa. According to the classification, Voluven belongs to medium molecular weight HES, but only formally. The drug is fundamentally different from other medium molecular starches in that it has significantly less side effects. The development of a new type of HES was aimed at achieving certain pharmacokinetic characteristics. Standard European pentastarch has been modified to reduce the average molecular weight to 130,000 Da and the degree of substitution to 0.4. It was assumed that this would make it possible to obtain small, osmotically more efficient molecules. In studies, Voluven has been shown to increase blood plasma volume by 100% of the administered volume of HES. The duration of the effect exceeds the duration of infusion by 4–6 times. A clinically important advantage of Voluven is its weaker effect on the blood coagulation system [2]. Purpose of the study: To study the effect of intraoperative infusion of the drug "Voluven" on indicators of systemic hemodynamics, the state of the hemostasis system in pregnant women who underwent delivery by cesarean section; and also to determine the severity and frequency of side effects of the drug (effects on the liver, kidneys, the formation of allergic reactions) in this group of patients. Materials and methods The study included adult pregnant women who were planning to deliver by cesarean section. Exclusion criteria were diabetes mellitus, liver and kidney dysfunction. By random selection, 2 study groups were formed: the main group (n=35) and the control group (n=30). In the main group, during the operation, a 6% solution of the drug Voluven, as well as crystalloid solutions (0.9% NaCl solution, Trisol, Disol, Acesol, 5% glucose solution) were used to replace the volume of blood volume. In the control group, crystalloids were administered, in 2 cases the administration of the drug “Gelatinol” was required, and also in two cases - fresh frozen plasma. 1 day before surgery, after transfer to the ICU and 1 day after surgery, hemodynamic parameters (heart rate, blood pressure), clinical blood test parameters (hemoglobin, hematocrit, erythrocytes, leukocytes), parameters characterizing the state of the hemostatic system (prothrombin index, APTT, thrombin time, fibrinogen, platelet count), biochemical parameters (total protein, bilirubin, creatinine, glucose, potassium, sodium). The relative density of urine, the volume of intraoperative blood loss, daily diuresis on the day of surgery, and the total volume of intraoperative infusion were also taken into account. In all cases, planned delivery was carried out by cesarean section in the lower segment of the uterus according to a set of obstetric indications. Transsection was performed using a transverse Pffannenstiel incision, and the uterine wound was sutured with a single-row vicryl suture. Combined spinal-epidural anesthesia was used for pain relief. The condition of the newborns was assessed using the Apgar score and did not differ significantly in both groups. The volume of blood loss during surgery was 637.5±15.7 ml and 611.1±30.0 ml in the main and control groups, respectively (p>0.05). Results When using Voluven during surgery, hemodynamic parameters remained stable. The average heart rate in the intervention group was 85 beats/min before surgery and 77 beats/min immediately after transfer to the ICU; in the control group these indicators were 84 and 81 beats/min, respectively, p>0.05 (Fig. 1). Coagulation parameters in all cases remained within normal limits (Table 1). The prothrombin index decreased slightly in both study groups, indicating that the drug under study had no effect on this indicator. APTT decreased slightly in the control group and remained unchanged when using the drug (Fig. 2). Thrombin time increased slightly in the control group; in the main group it remained virtually unchanged. The fibrinogen level significantly decreased in the Voluven group on the second day after surgery (Table 1). This property of the drug can theoretically contribute to the prevention of thromboembolic complications during surgical delivery. The number of blood platelets tended to decrease in both groups immediately after surgery and on the second day, but these fluctuations were within normal limits (Fig. 3). With regard to clinical blood test parameters (Table 2), a slight decrease in the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin was noted in both study groups, which also indicates the absence of an effect of the drug on these parameters. The number of leukocytes in both study groups increased, but in the intervention group this increase was less pronounced, which indicates a less severe reaction of the body to surgery and administered drugs. During the work, the dynamics of total blood protein in the patients included in the study was monitored. It was found that in postpartum women who underwent Voluven infusion before surgery, the level of total blood protein on the 2nd day after the intervention was significantly higher than in the control group (p It is known that one of the most dangerous complications of the use of HES drugs is the development of acute hyperoncotic syndrome renal failure. This circumstance required us to monitor renal function - the level of blood creatinine. Fluctuations in this indicator in both study groups were identical and fell within the normative parameters (Fig. 5). Conclusions When using Voluven during cesarean sections, hemodynamics remain stable, not there is a significant change in the parameters of the hemostatic system. Considering the decrease in the level of fibrinogen in the study group, we can talk about the possible effect of the study drug in terms of the prevention of thromboembolic complications (Fig. 6). The use of hydroxyethyl starches leads to a decrease in the severity of inflammatory processes (the increase in the number of leukocytes in the treatment group after surgery was significantly lower than in the control group). During the study, no significant adverse reactions were observed, including cases of acute renal failure or allergic reactions. In none of the cases of Voluven use, a blood transfusion was required during surgery. However, in 2 cases during surgery there was an increase in local bleeding, which was stopped by the administration of dicinone and had no effect on the amount of surgical blood loss. Thus, Voluven has a minimal hypocoagulation and disaggregation effect, does not have a negative effect on the condition of the fetus, and can be used for preinfusion in pregnant women in preparation for regional anesthesia. Literature 1. Endothelial dysfunction. causes, mechanisms, pharmacological correction // ed. N.N. Petrishcheva – St. Petersburg: Publishing house of St. Petersburg State Medical University, 2003, – 184 p. 2. Dyugeev A.N., Fomin M.D., Zavarzina O.O. Principles of intensive therapy for severe atypical forms of late gestosis // Russian Medical Journal. – 1999. –№1 3. Shifman E.M., Tikanadze A.D. – Infusion therapy in the perioperative period: what, to whom and how much? Petro 2001 – 40p 4. Zikria BA et al – Hydroxyathylstarch macromolecules reduce myocardial reperfusion injury. Arch surg – 1990, V125 P930–934
Content is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Share the article on social networks
Recommend the article to your colleagues
How to collect analysis correctly
Properly collected material for analysis is an important component of diagnosis. To exclude an erroneous result and avoid unnecessary repetitions of tests, you need to adhere to the rules for collecting a urine test:
Before collecting urine for analysis, you need to wash your external genitalia.
- clean dishes without traces of detergents (it is better to purchase a sterile jar for collecting urine at the pharmacy);
- Morning urine is taken for analysis; you should not have breakfast before collecting it;
- Before collecting urine, you need to wash the external genitalia; you should not use antiseptics (they destroy the protein);
- It is better to cover the vagina with a tampon, so the discharge will not get into the urine;
- an average portion of urine is collected (you need to start urinating in the toilet, then bring the container, not collecting until the end).
By following these guidelines, you can prevent foreign protein from entering your assay.
Protein norm in the analysis of pregnant and parturient women
In healthy people, protein should not be detected in the urine at all. In this case, there is a value or deviation that is not considered as a pathology - 0.08 g/l (according to some sources, 0.033 g/l). This amount of protein may be evidence of a physiological process or neglect of hygiene procedures before collecting urine. However, this may be early evidence of the development of an inflammatory process in the kidneys. Therefore, if protein is detected even in the smallest concentrations, a repeat analysis is carried out the next day.
For a pregnant woman, the limit value for protein in the urine is 0.14 g/l. But even with such figures, the patient is monitored with mandatory testing in a couple of days.
Immediately after childbirth, the protein in a woman’s urine may be very elevated (especially if the birth was difficult). On the first day, this is normal, because the woman has suffered severe physical and nervous stress. But 2 days after birth, the indicators should normalize (up to 0.08 g/l). If this does not happen, it is necessary to carry out additional diagnostic measures and begin therapy.
Protein in urine after childbirth - normal and pathological
During pregnancy, a woman is constantly monitored and undergoes regular tests. There is no more common test during pregnancy and after childbirth than urine testing. Protein in the urine during pregnancy is often a sign of an inflammatory process that does not disappear after childbirth.
Protein in urine: description and diagnosis
Proteins are very important, as they take part in many processes that occur in the human body.
Protein is present in the body in large quantities. It is the basis of all fabrics. Proteins are involved in metabolism and are building materials for the body. Proteins in the blood are normal, but in the urine they are not, since protein in the urine indicates that the kidneys have begun to let in not only harmful substances, but also useful ones, that is, the body has begun to lose valuable proteins.
A general urinalysis (UCA) helps monitor kidney function. A woman takes it multiple times during pregnancy and after childbirth. Protein in the urine can be a sign of a dangerous pathology, so doctors always treat such indicators with caution. It needs to be rechecked several times, and if protein appears constantly in the urine, a more detailed examination of the genitourinary system should be prescribed.
Urine testing is familiar to everyone and is very simple: in the morning you need to collect urine and take it to the laboratory within an hour.
However, not all women know that there are rules for preparing for analysis that will help avoid the false appearance of protein in the urine:
- On the eve of the analysis, it is not advisable to eat a lot of protein foods: eggs, meat, mushrooms. Such foods increase the amount of protein in the blood and urine. It is not necessary to follow a strict diet; it is recommended to limit the consumption of protein foods.
- It is advisable for a woman to insert a tampon into her vagina. After childbirth, a woman begins to bleed, which lasts up to a month. The discharge is quite abundant, it can be included in a urine test and the result will show protein. You can insert a tampon only with your doctor's permission. If there are stitches or damage, you just need to try to collect the urine carefully.
- Before collecting urine, be sure to wash yourself, and wash and sterilize the container itself the day before, and also dry it thoroughly. An insufficiently clean container often causes false protein to appear in the urine.
Explanation: norm and deviation from the norm
Proteinuria – increased protein content in the urine
Normally, there should be no protein in the urine, but there are reference values of 0.08 protein fractions for the entire volume of urine. However, some doctors consider even such a small amount of protein as an incipient infection, so they recommend duplicating the analysis.
Some doctors believe that a value up to 0.08 (0.033 and above) still requires attention. After childbirth and during pregnancy, you need to be especially careful about possible inflammatory processes. They don’t talk about the lower limit of normal, since even the complete absence of protein is normal.
A slight excess of the norm indicates an inflammatory process of the genitourinary system, a strong excess of the norm indicates a serious kidney pathology.
The doctor cannot make a diagnosis based on OAM alone. To begin with, he will recommend that the woman give urine again, observing all the rules of hygiene. The reasons for the appearance of protein in the urine after childbirth can be different:
- Incorrect urine collection. With heavy postpartum discharge, it is not always possible to collect urine correctly. The discharge partially ends up in the urine, and protein is detected in the analysis.
- Increased stress on the body. During labor, a woman experiences enormous stress. If you donate urine the next day, a small amount of protein may be found in the urine, indicating physical overexertion. When repeating the analysis after 1-2 days, the protein usually disappears.
- Impaired kidney function. If kidney function is severely impaired, protein will be found in the urine in significant quantities both during pregnancy and after childbirth. In this case, it is necessary to check the kidneys, undergo an ultrasound procedure, and take blood tests.
- Preeclampsia. This is the most dangerous cause of protein in the urine during pregnancy, as it can lead to the death of the mother and child. A woman’s blood pressure increases greatly and vascular permeability is impaired. Even after childbirth (with gestosis through cesarean section), signs of gestosis and protein in the urine persist. The woman is observed for some time in a hospital setting.
Signs and possible diseases
Most often, an increased level of protein in the urine indicates inflammation of the kidneys.
If the amount of protein in the urine is too high, then most likely there is a serious kidney or genitourinary disease. With a constantly elevated protein content in the urine, the disease is rarely asymptomatic. Severe kidney damage is accompanied by characteristic symptoms corresponding to a particular disease.
Protein in the urine itself is not a reason to interrupt breastfeeding, but if drug treatment is prescribed, you should consult a specialist about lactation.
Protein in the urine during pregnancy and after childbirth can signal the following diseases:
- Pyelonephritis. An infectious disease accompanied by inflammation of the kidney tissue. This is a serious disease, which is often accompanied by severe pain and significant deterioration. In the last stages of pregnancy, pyelonephritis can cause an emergency caesarean section. Characteristic symptoms of pyelonephritis: severe lower back pain, fever, chills, nausea and vomiting, swelling, frequent urination.
- Glomerulonephritis. This disease affects the glomeruli (glomeruli) of the kidneys. It can develop against the background of infection or systemic diseases. Main symptoms: the amount of urine excreted decreases, the urine itself becomes dark, lower back pain, nausea, vomiting, high blood pressure and body temperature, and swelling appear. Pain does not always accompany the disease, so during pregnancy some symptoms go unnoticed.
- Nephropathy. This is a collective term that refers to kidney dysfunction and connective tissue proliferation. The symptoms are different, but most often they are lower back pain, difficulty urinating, nausea, swelling, increased blood pressure, weakness, and headache.
This is not the entire list of possible diseases that are accompanied by protein in the urine. It can appear with cystitis, kidney stones, and tumor processes.
Treatment method
Drug treatment for proteinuria depends on the cause of its occurrence.
Protein in the urine is a diagnostic sign and not an independent disease. Treatment will depend on the cause of protein in the urine. First of all, you need to make a correct diagnosis. If there is a suspicion of improper collection of material, the urine will be collected with a sterile catheter.
A special glomerular barrier in the kidney, which filters urine, is responsible for the appearance of protein in the urine. If protein appears in the urine, then the permeability of the barrier is broken and needs to be restored.
Diseases that lead to the appearance of protein in the urine are usually treated with medication, and the doctor may also recommend a gentle diet and bed rest.
Features of treatment:
- Corticosteroids. Prednisolone-based drugs constitute a group of hormonal drugs that have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. They are prescribed for various inflammatory infectious diseases. The doctor will select medications that will be as safe as possible for the baby and do not require interruption of breastfeeding.
- Antitumor drugs. These drugs are prescribed infrequently and only for tumor processes. A doctor may prescribe them if protein in the urine is caused by a tumor in the kidney. Cytostatics have a large number of side effects and contraindications, so they can only be taken with the permission of a doctor and in case of emergency.
- Drugs that prevent the formation of blood clots. Drugs are often prescribed to normalize the functioning of blood vessels and prevent the formation of blood clots. They improve microcirculation in the kidneys and pelvic organs.
- Antibiotics. Antibiotics are prescribed for inflammation caused by bacteria. Antibiotics are taken in courses simultaneously with probiotics to maintain intestinal microflora. Not all doctors advise interrupting breastfeeding while taking antibiotics. You should consult your pediatrician about feeding.
- In some cases, diuretics and herbs are prescribed to improve urine flow. Not all medications are suitable for breastfeeding. It is recommended to take them only after consulting a doctor and a thorough examination.
More information on how to “read” a general urine test can be found in the video:
Read: Urine analysis: how to prepare, collect and what to take?
Treatment method
If high protein is detected in the urine, it is necessary to treat the disease that led to this condition. Therefore, before starting therapy, it is necessary to establish an accurate diagnosis. If the renal barrier is broken, it needs to be restored, as well as eliminate the inflammatory process and possible infection.
The main method of treatment is medication. The following groups of drugs are recommended:
The main method of treating high protein is medication.
- hormonal anti-inflammatory (corticosteroids) – have antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects;
- blood thinners (anticoagulants) - to prevent blood thickening and blood clots;
- antimicrobial agents (antibiotics) – eliminate pathogens of infectious diseases of a bacterial nature;
- probiotics and eubiotics are taken in combination with antibiotics to prevent dysbiosis;
- diuretics;
- vitamin complexes to improve general condition.
In addition to taking medications, it is recommended to temporarily reduce protein intake from food, drink more fluids and stay in bed until complete recovery. Drug therapy should be administered with caution if a woman is breastfeeding. There are medications that pass into breast milk, so only a doctor should prescribe the drug and its dosage. And the entire treatment process must be carried out under his control.