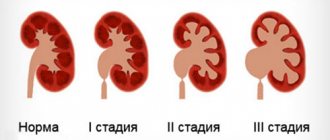
The reasons for changes in acetone levels in urine can be very diverse. After all, it is a product of the body’s vital activity. And its level is influenced by many factors. The level of acetone can always be monitored at home using easy-to-use test strips. An increase in acetone in a child’s urine may be a signal of serious illnesses that will require examination by a specialist. Also, acetone in urine increases in pregnant women, as a result of dehydration due to toxicosis and frequent vomiting. Acetone in the urine is a constant companion of diabetes mellitus, namely, the stage of decompensation. For people suffering from diabetes, acetone will serve as a direct ticket to hospital treatment.
Diagnostic methods
Every pregnant woman who registers with the antenatal clinic in a timely manner knows that it is necessary to take a urine test before each visit to the doctor (in the final stages - weekly).
This is done in order to diagnose pathological processes at the earliest stages and promptly correct them. In the case when ketonuria is detected for the first time, and there is no history of any diseases of the urinary tract, there is no need to panic. Very often, repeated testing does not reveal any deviations from the norm.
If, in a repeated urine test, there is an increase in the level of ketones, then it is worth thinking about malfunctions in the pregnant woman’s body.
With ketonuria over 40 mg/dL, the woman requires hospitalization, and further examination is carried out in a hospital setting.
When the level of ketone bodies fluctuates between 20-40 mg/dL, an outpatient study is performed, which includes:
- blood test, including biochemical, with determination of creatinine, urea, bilirubin fractions, electrolytes and other indicators (if necessary);
- determination of glucose concentration and sugar curve;
- Ultrasound of the urinary system;
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland and other studies as indicated.
For women prone to ketonuria, there are special test strips, thanks to which she can independently determine the average level of ketone bodies in her urine. Conducting research does not require special skills. To do this, a ready-made test strip is dipped into the morning urine sample, and the results obtained are assessed based on the color of the indicator (their values are written on the box with the test strips).
Test strips for determining the level of ketone bodies in urinary sediment can be purchased at the pharmacy chain
Diagnostic methods
Standard chemical reactions are used to detect ketone bodies in urine. The test can be performed in a laboratory or at home.
In the laboratory, urine is examined using a special analyzer; at home, test strips from different manufacturers are used.
Such tests are available at pharmacies without a prescription and can detect ketone bodies in morning urine without visiting a clinic. The only disadvantage of the test systems is the impossibility of determining the exact values of ketone bodies (as in the laboratory); only the range is determined.
Types of test strips:
- 1Acetonetest (Normal)
- 2Visual test strips Bioscan.
- 3Ketoglyuk-1 (for determination of ketones and glucose in urine), Uriket-1 (Biosensor-AN LLC).
- 4Ketofan, Diafan (Lachema, Czech Republic).
- 5 Strips for assessing several parameters, including the level of ketone bodies: Multistix (Bayer), Uripolian-11 (Biosensor-AN), Bioscan-Penta, Decafan Laura (Lachema), Uristik-Dirui (Korea), Multichek (Canada).
The principle of operation of all test systems is a chemical reaction that occurs between the reagent applied to the strip and the components of urine. The result of the reaction will be coloring of varying intensity, proportional to the concentration of ketone bodies (the higher their level, the stronger the color). The sensitivity of the tests depends on the manufacturer and proper storage.
For the test, a pregnant woman needs to dip a test strip into her morning urine sample and, after a certain time, compare the resulting color with the table on the jar.
Attention! In case of intense coloring (bright pink color and ketone concentration more than 1 -1.5 mmol/l), you should immediately consult a doctor!
Table 1 - Comparison of test strip scales from different manufacturers
Consequences
What to do if ketone bodies are found in a child’s urine?
Without accurate diagnosis, treatment with diet and medications, ketonuria during pregnancy can have dire consequences. The breakdown products of acetone and acids poison the body of the mother and fetus, complicating the process of pregnancy. Even if the pregnancy goes through and is resolved successfully, toxic substances can provoke long-term complications in the development of the child.
High levels of ketones in urine that persist for a long time and are not corrected can cause:
- dehydration and poisoning of the body of the pregnant woman and the fetus;
- kidney diseases associated with impaired urine excretion;
- osteoporosis and associated symptoms (joint pain, limited movement, muscle cramps, frequent fractures);
- the development of diabetes in pregnant women in the 3rd trimester (gestational), which is dangerous because it can subsequently turn into the classic insulin-dependent diabetic form;
- complications of pregnancy and delivery (frozen pregnancy, miscarriage, premature birth);
- delayed physical and intellectual development of the child due to constant intrauterine poisoning with toxic substances;
- ketoacidotic coma is an extreme degree of intoxication with acetone.
Ketoacidotic coma is a dangerous condition that can lead to death. It develops with a sharp increase in protein breakdown products and inadequate utilization of sugars by the liver. It is especially common in diabetic patients who neglect insulin therapy. Acetone coma leads to serious disruptions in the functioning of vital organs - the heart, lungs, even stopping. Without treatment, this condition causes swelling of the brain and death.
However, coma does not develop immediately, but over several days; signs of poisoning (nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting, smell of acetone from the mouth) and dehydration (dry skin, lethargy, low blood pressure and body temperature) increase. If signs of diabetic coma develop, you should immediately call an ambulance and take the patient to the hospital for treatment and observation.
Treatment of the disease
The appearance of ketone bodies in urine during pregnancy
Treatment of ketonuria is prescribed after laboratory tests and identification of the exact cause of the disease. Main methods of therapy:
- Drug treatment.
- Following a special diet.
- Active lifestyle.
If the pathology is caused by diabetes, therapy is used aimed at normalizing blood sugar levels. In the most severe cases, insulin administration is prescribed.
Medicinal treatment methods include prescribing medications:
- saline solutions - to rehydrate the body;
- sorbents - for poisoning;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs – for the treatment of inflammatory diseases;
- antiemetics – for severe vomiting leading to dehydration.
In order to prevent dehydration, patients are advised to drink plenty of fluids - still mineral water, a weak chamomile decoction, dried fruit compote.
Treatment
You can get rid of ketones in the urine by correcting the underlying disease, diet and changing the lifestyle of the expectant mother.
First of all, the most dangerous conditions are excluded: decompensation of diabetes mellitus, early toxicosis and gestosis, acute infections. If no apparent cause is found, then treatment measures begin with changing the lifestyle and nutrition of the pregnant woman.
A slight excess of the level of ketone bodies does not lead to any negative consequences. There should be no cause for concern in this case.
It is important to remember that acetone is a strong toxin that can cause disruption of placental permeability, damage to the baby’s nervous system and developmental abnormalities.
5.1. Diet
Nutrition should be complete, enriched with vitamins and microelements, contain proteins (50%), fats (20%) and carbohydrates (30%) in a balanced amount.
It is necessary to limit confectionery, flour products, spicy, salty, smoked, fried and fatty foods. It is advisable to drink a sufficient amount of clean drinking water (in the absence of edema syndrome).
5.2. Lifestyle
It involves a full night's rest (about 8 hours a day), moderate physical activity, positive emotions, and regular walks in the fresh air.
Exhausting physical training, hard work, mental overstrain, stress, fasting and refusal to eat are contraindicated.
5.3. Drug therapy
Should be aimed at improving liver and kidney function, reducing blood pressure readings, normalizing blood sugar and acetone in the urine.
Conditions such as late gestosis, eclampsia, early moderate and severe toxicosis with repeated vomiting, overt diabetes in pregnant women with high glycemic levels must be treated in a hospital setting using infusions and injections.
Regular urine screening throughout the entire pregnancy period contributes to timely diagnosis and treatment.
Video Photo Tables
Main causes of acetonuria
Reasons for high levels of acetone in urine in children and how to reduce the level
Acetonuria is the excretion of acetone in the urine. Most often, this phenomenon is observed in children, but can also occur in adults.
Where does acetone come from in the human body? It would seem that this is a dangerous substance that can cause poisoning. In fact, this is true. But the fact is that acetone is a type of ketone bodies, which may be needed in certain situations.
When eating food, a child and an adult receive glucose with it, which is necessary to meet energy needs. Some of the glucose is converted into energy immediately, and the unclaimed is stored in the form of glycogen. In extreme situations, for example during fasting or heavy physical exertion, it breaks down again into glucose, compensating for energy costs.
Glycogen reserves are concentrated in the liver, skeletal muscles, and muscle tissue of internal organs. There are no glycogen reserves in the brain, so timely snacks are important for successful mental work.
If the glycogen supply is depleted or is initially insufficient to cover the body's needs, another substrate in the form of fats is used to obtain energy. They break down into ketones, which serve as alternative energy sources.
Acetone is a type of ketone body.
Ketone bodies are needed to provide energy support to the brain in extreme situations. In large quantities they are toxic to the body. First, acetone will appear in the blood. Later it will be excreted by the kidneys in urine.
Acetone in urine in children
Acetone accumulates in a child's body faster than in adults. Glycogen reserves in children under 7–8 years of age are small, so situations when there is not enough of it arise more often.
Acetone is detected in the urine of a child in the following cases.
- Violation of the diet when the baby receives too much fatty food, as well as foods containing preservatives, additives, and dyes. In childhood, the ability to absorb fats is reduced.
- Starvation. Children have much less glycogen than adults, so fat breakdown processes begin faster, and acetone is detected in urine more often.
- Infectious diseases that are accompanied by a rise in temperature and serious condition. Acetone in children in this case is the result of decreased appetite and dehydration due to illness.
- Type 1 diabetes mellitus, when the baby's pancreas does not produce insulin. It is responsible for transporting sugar from the blood to the tissues. In diabetes mellitus, glucose remains in the blood. The child’s body is forced to use other sources of energy in the form of fat reserves.
- Vomiting and loose stools during infectious and exacerbation of chronic diseases. The child’s acetone will increase due to the same glucose deficiency. She simply will not be able to assimilate. Due to severe vomiting and serious condition, the baby will simply refuse to eat and drink.
Acetone in urine in adults
In adults, acetonuria is less common and is often a sign of metabolic disorders, deterioration of diabetes, malignant tumors, poisoning, and coma.
Acetone may also appear in the following situations.
- Prolonged fasting, following diets with limited carbohydrates.
- Excessive consumption of protein and fatty foods.
- Increased physical activity during sports training or at work.
- Severe infectious or chronic diseases
- Alcohol abuse.
Acetonuria during pregnancy
The body of a pregnant woman is configured to bear and give birth to a child, so all metabolic processes proceed much more intensely. Acetone in the urine of pregnant women appears in the situations described above, but they need to be taken more seriously and not ignored.
In the early stages of pregnancy, acetonuria can be caused by toxicosis with uncontrollable vomiting, when the body simply does not take food. Naturally, to meet the needs of the mother and fetus, fat reserves are used, and acetone appears in the urine.
In later stages, gestational diabetes becomes the cause of the appearance of acetone in the urine. It is typical only for pregnant women and disappears after the birth of the baby.
Ketone bodies in urine
In the process of general metabolism, as a result of glucose synthesis in the human liver, three breakdown products are formed:
- beta-hydroxybutyric acid;
- acetoacetic acid;
- acetone.
In medicine they are called ketones or ketone bodies. Their presence in microdoses of 20-50 mg has been detected in the body of every healthy person. In laboratory urine screening, such indicators are practically invisible. Ketones are excreted by peripheral tissues, as well as in the urine.
Ketones perform a number of vital functions in the human body:
- maintain energy balance;
- are a source of energy;
- nourish most tissues.
If a high level of acetone is detected, including during pregnancy, the doctor diagnoses ketonuria, that is, an increased content of ketone bodies.
There are a number of factors that increase the production of ketones in a situation of relative norm:
- intense physical exercise;
- strict (protein) diet, fasting;
- dehydration;
- alcohol intoxication;
- hot weather for a long time;
- surgical interventions;
- stress, high psycho-emotional stress.
Ketonuria of this etiology is not dangerous to human life, but requires a more attentive attitude to your body and lifestyle in general.
Methods for diagnosing ketonuria
All diagnostic methods for studying the level of ketones in the body can be formally divided into:
- at home, when they can be carried out independently;
- laboratory
Through the former, ketonuria during pregnancy can be determined mainly in its expressed form. The main symptoms are a strong odor of acetone in the urine, vomit, if any, and during breathing.
A related method is the use of indicator test strips impregnated with a chemical reagent. The way they work is by reacting a chemical with the ketones present in the urine. As a result of the interaction, the color of the indicator strip changes, and you receive information about the level of acetone.
There is also an alternative method for determining ketonuria. For this you will need ammonia. Add a couple of drops of alcohol to a container with freshly collected urine and watch the dynamics. The urine will become a rich red color if ketone bodies exceed the permissible limit.
Laboratory tests for diagnosing ketonuria are more reliable and indicative, which is especially important during pregnancy. If you have been sent for testing to a laboratory, follow a number of rules:
- Approximately one day before collecting biomaterial, give up fatty, salty, smoked foods;
- perform genital hygiene;
- collect exclusively morning urine;
- Use a sterile container for collection.
In laboratory conditions, the level of ketone bodies is recorded using the Lange test using the “+” and “-” signs:
- "-" - negative result;
- “+” – insignificant presence of ketones;
- “++”, “+++” – positive reaction to the presence of ketone bodies;
- “++++” – ketones in the urine sharply exceed the norm.
Additional examinations in case of detection of ketonuria during pregnancy include:
- general, biochemical blood tests;
- glucose tolerance test;
- blood test for glucose concentration;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs, thyroid gland.
Ketonuria is a rapidly progressive disease, so during pregnancy it is important not to delay in finding out the causes of its occurrence. Any delays can cause irreparable harm to the child.
Reception is strictly by appointment only!!!
Doctor Plus LLC License No. LO-77-01-004801
Registration at the clinic by phone
Make an appointment at the clinic
- +7 (495) 125-49-50
- Addresses of clinics in Moscow
- Daily
- call me back
Acetone in urine
- this phrase means the identification of ketone compounds in the test results. Ketones are the result of metabolic processes in the liver. In a healthy person, they are present in such small quantities that they do not affect the results of laboratory tests of urine. With impaired metabolism, the synthesis of ketone compounds in the liver increases, which leads to the occurrence of diseases.
Ketone compounds include acetoacetic acid, acetone, and beta-hydroxybutyric acid. Initially, their appearance and increase in concentration begins in the blood, and, as a result, in the urine. If an unpleasant odor appears during urination, and a specific taste of acetone appears in the mouth and breath, then this is a cause for concern.
Early toxicosis and gestosis in pregnant women
As mentioned above, pathological conditions such as early toxicosis and gestosis can lead to the appearance of ketones in the urine.
In 90% of cases, it manifests itself as vomiting, although other symptoms are also possible: increased salivation, cholestasis, dermatoses, disorders of the nervous system. The risk group for the development of toxicosis in the early stages includes women with a history of somatic and mental illnesses.
The basis of such disorders is the abnormal attachment of the trophoblast to the uterine endometrium, triggering subsequent pathological reactions:
- 1 The entry into the blood of a large number of substances that affect the processes of normal contraction of the vascular wall.
- 2 Vascular endothelial dysfunction.
- 3 Activation of interleukins, proteases.
- 4 Violation of LPO (lipid oxidation).
- 5 Generalized spasm of the arteries.
- 6 Reduced blood supply to internal organs (heart, kidneys, liver, brain).
- 7 Increased peripheral vascular resistance.
- 8 Increased blood pressure with subsequent pathological abnormalities in the functioning of the internal organs of a pregnant woman.
- 9 Laboratory abnormalities: protein, ketones in urine (rarely glucose), increased coagulation parameters.
The main causes and signs of ketonuria in pregnant women
The reasons for the increase in ketone levels during pregnancy can be different, since during this period a complete destabilization of the main metabolic processes occurs in the woman’s body. However, this factor is only one of many, and the full list of possible causes of ketonuria is as follows:
- poor nutrition;
- systematic stress;
- overwork;
- smoking;
- sedentary lifestyle.
Of all the factors mentioned above, nutrition plays a dominant role. It is the food entering the body or its absence that is the source of all problems. Abuse of smoked meats, canned food, semi-finished products, snacks and overly fatty foods inevitably leads to the appearance of ketone components. At the same time, other factors only contribute to the deterioration of the situation, significantly increasing the level of by-products and complicating their complete removal.
Toxicosis plays a certain role in the development of ketonuria. Often, the redistribution of metabolic processes provokes a kind of push, promoting the production of half-life products. At the same time, other reasons only enhance the initial effect, which leads to a sharp increase in their concentration.
Exceeding the concentration of ketone bodies in the body has a pronounced toxic effect on the body, contributing to a significant deterioration in human well-being. Their systematic influence on tissues and organs leads to the appearance of negative signs, among which the following are most often diagnosed:
- constant fatigue;
- nausea;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- apathy.
However, the main sign of ketonuria is a specific odor associated with increased removal of by-products from the body by all available means. Saliva, sweat and urine are characterized by a persistent odor of acetone, which is sharp and rich. In turn, with a decrease in the concentration of negative elements and normalization of metabolic processes, it gradually evaporates, leaving no trace behind.
Increased ketones in urine during pregnancy: reasons
Before talking about possible diseases that lead to an increase in ketone bodies in the urine, it is necessary to list physiological and non-life-threatening conditions that can change this indicator:
- unhealthy diet with a predominance of fatty and meat dishes in the diet;
- long-term lack of carbohydrates in food;
- excessive physical activity;
- prolonged severe stress;
- dehydration.
If ketone bodies in pregnant women are elevated due to any of these reasons, then their value quickly returns to normal after eliminating the trigger factor:
Even more interesting:
- review of diet;
- organizing healthy sleep and rest;
- prescription of sedatives.
Other more serious reasons requiring mandatory medical examination and intervention:
- diabetes;
- intoxication of various origins;
- prolonged fever;
- infectious diseases;
- liver diseases;
- dysfunction of the pancreas.
The reasons for the increase in ketone bodies in urine during pregnancy may be different. If you suspect any of the above, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. High levels of ketones are dangerous for women and children.
Ketone bodies in pregnant women with gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a condition that occurs in the body of a pregnant woman, which is manifested by an increase in blood glucose (hyperglycemia) and completely disappears on its own after delivery.
This is one of the most common pathologies leading to increased blood sugar during gestation. Ketone bodies appear in the urine of pregnant women due to impaired carbohydrate and fat metabolism. To diagnose this condition, blood is taken from a finger, a glucose tolerance test is taken, a urine test is taken, and, if necessary, the level of glycosylated hemoglobin is assessed.
If a pregnant woman is diagnosed with Gestational Diabetes and adequate treatment is prescribed in a timely manner, there will be no threat to the fetus. Some experts believe that women with a history of gestational diabetes need to monitor their glucose levels in the future in order to notice pathological changes in time. Scientists point to the relationship between the development of gestational diabetes in pregnant women and the delayed development of diabetes mellitus.
Table 2. Norms of blood and urine parameters to exclude GDM
| Index | Norm |
| Fasting blood glucose | 3.3-5.5 mmol/l |
| Ketone bodies in urine | none |
| Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1C) | 4,5-6,5% |
Increased performance in the third trimester
Ketones in urine are increased in a pregnant woman in the third trimester for the same reasons as in earlier stages. Usually, after the 17th week, the urinalysis results return to normal. Therefore, if this has not happened by the third trimester, we cannot talk about physiological reasons.
You need to know about this: In the 3rd trimester, a situation may arise that an actively developing fetus consumes glucose from the mother’s body overnight. This triggers the mechanism for the breakdown of fats in the mother's body. The result is that in the morning the concentration of ketone bodies in the urine of a pregnant woman is increased.
If an increase in ketones during pregnancy occurs for this reason, then the situation can be easily resolved. A woman is recommended to have an additional snack made from foods with “slow carbohydrates” before going to bed.
Why do ketone bodies increase in late pregnancy?
In the third trimester, first of all, it is necessary to exclude 2 causes: improper or unbalanced nutrition and gestational diabetes mellitus. The latter sometimes occurs hidden, there may be no symptoms.
Ketone bodies in urine in late pregnancy may appear due to intoxication or infectious diseases, but changes in the composition of urine will not be the only symptom of these pathologies. Associated with: fever, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, general weakness, lethargy. Manifestations depend on the specific cause of ketonuria, which will be accompanied by symptoms of the underlying disease.
How to diagnose and treat acetonuria in expectant mothers
To control the level of acetone, you need to undergo regular tests and examinations. If acetone is detected in the urine, you need to find out the amount of the substance and, accordingly, the severity of the pathology; Depending on this, the doctor chooses one therapy or another.
Diagnostics
At the antenatal clinic, where a pregnant woman registers, she should come for screening - prenatal diagnosis - once every trimester.
Planned and additional tests
For the first time, the expectant mother undergoes a general urine test when registering for pregnancy. Afterwards, if gestation proceeds without pathologies, he brings a jar of liquid waste to the clinic according to the following schedule:
- in the 1st trimester - once a month;
- in the 2nd trimester - twice a month;
- in the 3rd trimester - once a week.
Acetonuria is detected using a standard test. When the test for acetone is positive, laboratory workers issue a conclusion with pluses, the number of which is used to judge the level of a toxic substance in the urine. So:
- one plus - there is very little acetone;
- two pluses - the level is increased, but only slightly - this happens during toxicosis or with poor nutrition;
- three pluses - the situation is much more dangerous, most likely the cause of acetone in the urine is fasting;
- four pluses - high levels of the substance, a symptom of gestational diabetes mellitus or other serious pathology.
A diagnosis of “++++” is a good reason to hospitalize the expectant mother in order to carry out therapy in a hospital setting - otherwise the treatment will be useless.
It happens that there are advantages in the expert’s conclusion, but the pregnant woman’s well-being is normal. Then the doctor sends the woman for re-testing.
To clarify the cause of the pathology, the doctor prescribes additional tests and examinations for the patient, including:
- blood test for biochemistry - to determine glucose levels and confirm or deny diabetes; liver health is also assessed using a biochemical blood test;
A biochemical blood test is considered one of the most reliable; 5 ml of fluid is taken from the ulnar vein of a pregnant woman for testing in the laboratory - blood test for hormones - to investigate possible dysfunctions of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands;
- pressure measurement - to diagnose gestosis or infectious inflammation in the body.
The patient may also be referred for an ultrasound of internal organs, for example, the thyroid gland.
Test strips
A woman can detect acetonuria at home. To do this, go to the pharmacy and buy special strips for express diagnostics. Each strip contains litmus and is impregnated with a special composition.
This test determines the presence of acetone, as well as the level of the substance in the urine. In the package you will find instructions that tell you in detail how to use the strips.
Urine is collected in a sterile container in the morning. The strip is lowered into the yellow liquid to the level specified in the instructions. After 2 seconds, take out the test, which, depending on the amount of acetone, will turn different colors after two minutes. If the strip turns light yellow, you are lucky - the acetone is normal (that is, present in the form of “traces”); purple color indicates a pathologically high level of a toxic substance in the urine. A detailed table of values is provided in the instructions.
The color of the test strip after it has been in the urine determines the presence or absence of acetonuria
Rules for using test strips to detect acetone in urine:
- Avoid touching the sensor elements of the indicator;
- after removing the strip from the package, use within one hour;
- the container with strips must be tightly closed;
- Use urine for testing within two hours;
- carry out the test at a room temperature of +15 to +30 °C.
Sometimes test strips are painted in colors that are not on the scale in the instructions - this means the test is defective. If the strip is colored only on the sides, it may be due to substances from medications contained in the body.
In any case, for an accurate diagnosis, as well as for the causes of acetonuria detected by test strips, you still need to go to the doctor.
Therapy
Profuse vomiting is one of the signs of acetonuria; leads to dehydration of the body, and also increases the already high level of acetone in the urine.
How to compensate for fluid deficiency in the body
First of all, a woman should switch to an increased drinking regimen; juices and sweet carbonated drinks are not suitable for this - we drink clean water, green tea, up to two liters a day. It is not recommended to drain a glass or cup in one gulp, otherwise you will provoke another attack of vomiting. Pour the liquid into yourself slowly, in small sips.
Water compensates for the lack of fluid in the body after severe vomiting; swallow little by little, intermittently
Together with liquid masses, when vomiting, electrolytes are removed from the body - calcium, potassium, sodium, magnesium salts. These substances are responsible for the functioning of the nervous system - they transmit nerve impulses. Violation of the water-salt balance threatens organ failure. The pregnant woman feels completely exhausted, sometimes unable to even get up from the sofa; thoughts are confused. The baby in the womb also suffers due to the poor health of the mother.
To quickly restore electrolyte balance, a woman will need a rehydration solution. Solutions that are taken orally are sold in pharmacies. Here are some that are safe for those who are pregnant:
- Rehydron - powder in bags for preparing a solution, contains the necessary salts, as well as dextrose, which helps the elements to be absorbed; one sachet is dissolved in a liter of boiled, cooled water, drunk during the day, in small portions, without any additives; course of treatment - 3–4 days; in case of severe dehydration or severe bouts of vomiting, you should not drink Regidron; an overdose threatens confusion and cardiac dysfunction;
- Gastrolite is a powder packaged in sachets; in addition to electrolytes, it contains chamomile extract (to fight inflammation) and glucose (which is not very good for diabetics); a packet of Gastrolit is designed for a glass of warm boiled water; you need to drink 4–5 glasses a day - about a liter in total; Duration of treatment: 3–4 days; prohibited for renal failure and allergies to components;
- Citroglucosolan is a powder in sachets of different dosages: 2.39 g is dissolved in 100 ml of warm water, 11.95 g in 500 ml, and 23.9 in a liter of water; drink in small portions, within the first half hour - up to 900 ml; Every 40 minutes, the drug is repeated, up to 80 ml of healing liquid is taken per day per kilogram of body weight;
- Glucosolan - available in two types of tablets - with salts and with glucose; to take, take 1 tablet of salts and 4 tablets of glucose, dissolve in 100 ml of water; drink in the same way as Tsitroglucosolan; Both drugs have one contraindication - allergy to the components.
Rehydration agents should be taken at the first signs of dehydration (weakness, dizziness after vomiting); in general, the amount of electrolyte fluid drunk should be one and a half times greater than what the body has lost.
Rehydron in Russian pharmacies is the most popular remedy for restoring electrolyte balance in case of dehydration
Diet
When the cause of acetonuria is gestational diabetes mellitus, the expectant mother will have to bring her glucose level to normal. Exclude from the diet:
- chocolate and other confectionery products;
- carbonated sweet drinks;
- fried foods;
- semi-finished products;
- fatty dairy products;
- eggs.
If acetone in the urine appears as a result of fasting, eating with carbohydrates is not prohibited. However, it is important to remember that during pregnancy, fatty, salty, fried foods, to put it mildly, are not good for the health of the mother and the unborn child.
In all cases of acetonuria, the patient is recommended to eat:
- vegetable soups where you can put lean meat;
- boiled, baked or stewed lean meat (chicken, turkey);
- porridge - it is not forbidden to add a small piece of butter to the plate;
- low-fat cottage cheese;
- dry cookies;
- apples.
After 3-4 days of such a diet, you are allowed to gradually include other dairy products in the menu.
Photo gallery: dishes and products for diet for acetonuria
Don't eat a lot at one sitting; sit down at the table more often than usual - 4-6 times a day, put small portions on your plate.
When to resort to medications
In case of a slight increase in the level of acetone in the urine, diet and solutions with electrolytes will be sufficient for treatment. But if the vomiting does not stop, the same Regidron is useless; in this case, the woman is admitted to the hospital and given IV drips with saline solution. Contains pure water, as well as sodium and chlorine ions. Saline solution is recognized as harmless for pregnant women; Not even cases of allergies were detected. Intravenous administration of the drug eliminates the lack of valuable minerals and removes toxins.
To stop vomiting and restore normal intestinal motility in a hospital setting, patients with acetonuria are administered the drug Cerucal intravenously. The medicine weakens the sensitivity of the nerves that transmit impulses to the vomiting center located in the brain, and also increases the tone of the stomach and intestines. Since Cerucal has a lot of side effects, it is prohibited to use it in the 1st trimester, and in the later stages it is used only if a threat to the woman’s life is detected.
The antiemetic drug Cerucal is administered to pregnant women carefully, only for health reasons.
Sorbents such as Smecta and Enterosgel help rid the body of toxic substances, including acetone. They are excreted from the body unchanged, carrying away the absorbed toxins. The instructions for the drugs indicate that they are safe for expectant mothers. However, it is contraindicated to drink sorbents without a doctor’s approval.
The effective sorbent Smecta binds and safely removes harmful microbes and toxins from the body
For the treatment of diseases and conditions that are accompanied by acetonuria, the following is used:
- for diabetes mellitus - medications that lower glucose levels; if the result is weak, start insulin therapy;
- with high blood pressure, magnesium droppers will help;
- for thyroid pathologies - synthetic hormones.
To replenish the fetus's depleted reserves of nutrients, the pregnant woman in the hospital is given IV drips with glucose and vitamins (if there are no contraindications).
In some cases, even hospital therapy does not help patients - then there is nothing left to do but induce early labor.
Reasons for appearance
The metabolism of carbohydrates in the body is extremely important, as they are necessary to nourish all internal organs and muscle tissue. If the synthesis of sugar in the body is disrupted, this leads to the carbohydrate balance being disturbed.
If the normal glucose concentration is not restored, then the amount of ketones will increase. The following reasons may lead to the development of such a situation:
Untimely feeding. Frequent skipping meals contributes to disruption of metabolic processes, including a pathological decrease in blood glucose. Insufficient intake of carbohydrates from food. Any hypocarbohydrate diet can provoke carbohydrate metabolism disorders
It is important to note that the caloric content of the diet of the expectant mother should exceed the caloric content of the diet of an ordinary woman by 20-25%.
- Excessive physical activity. During pregnancy, habitual household activities can also lead to a decrease in blood glucose. After a general cleaning of the apartment, a pregnant woman may have traces of ketones in her urine.
- Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus. Severe forms of this disease are accompanied by disturbances in carbohydrate metabolic processes. The insulin-dependent variant of diabetes mellitus is especially dangerous. Hypoglycemic coma is a critical condition manifested by the appearance of a specific symptom - the smell of acetone from the mouth.
- Severe gestosis. Frequent attacks and vomiting provoke the development of a decrease in blood glucose. If the course of gestosis is protracted, this can lead to persistent ketonuria.
- Infections caused by or viruses. Severe infectious diseases accompanied by high fever can lead to the development of carbohydrate metabolism disorders.
- Prolonged psycho-emotional stress. Excessive suspiciousness or worries over trifles lead to the fact that the expectant mother’s body begins to malfunction. Constant depression, in which the pregnant woman remains for a long time, also leads to the development of metabolic disorders.
- Increased thyroid function. Hyperthyroidism is a fairly common pathology that occurs during pregnancy. This condition is characterized not only by an increase in thyroid hormones in the blood, but also by a disruption of general metabolic processes. Quite often this situation is transient and normalizes after childbirth.
- Disturbance of metabolic processes. This situation occurs in many pathologies. In this case, not only disturbances of carbohydrate metabolism are formed, but also fat metabolism.
Now we recommend watching a video in which Dr. Komarovsky will talk about where acetone in urine comes from.
Clinical picture of acetonuria
When ketone bodies are present in the urine, characteristic symptoms occur. Since the condition often develops as a result of other diseases, signs of the underlying pathology predominate.
The appearance of acetone in the urine may be associated with physical and nervous fatigue
Symptoms of acetonuria include:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- refusal to eat;
- dry skin;
- coating on the tongue;
- lethargy, fatigue, general weakness;
- thirst;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- abdominal pain;
- the smell of acetone, reminiscent of the aroma of rotten fruit;
- sometimes diarrhea.
It is not necessary to show all the signs. The clinical picture depends on the level of acetone, the sensitivity of the body, and the main cause of acetonuria. With prolonged acetonemic syndrome, the following symptoms are added:
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- increased and weakened pulse;
- liver enlargement.
In laboratory indicators, leukocytes exceed, there is an increase in ESR, a decrease in glucose and chlorides in a biochemical study. In case of poisoning of the body or kidney disease, epithelium may appear in the urine.
In severe cases, the toxic effect of ketone bodies leads to depression of brain function. In a child, this is manifested by drowsiness, apathy, loss or confusion, and convulsions. If treatment is not prescribed in time, coma and cerebral edema may develop.
How to recognize pathology, threats to mother and fetus
Like most pathologies, acetonuria occurs in three forms - mild, moderate and severe. Each has its own symptoms:
- with a mild form, the clinical picture is blurred: dizziness, minor headaches, nausea - all this accompanies any pregnancy; additional signs - frequent trips to the toilet “in small ways” and thirst;
- the average degree already has specific symptoms - the urine begins to smell like acetone; headache is difficult to bear, vomiting is possible, health worsens;
- severe acetonuria is accompanied by severe vomiting with the smell of acetone; the head hurts unbearably, you feel weak, the skin becomes dry; sometimes the right side bursts open - due to an enlarged liver.
Acetone freely “walking” throughout the body poisons organs and tissues; Not only does a pregnant woman suffer from vomiting, but in severe forms of the pathology, the woman’s health and even life are at risk, since:
- the functioning of the liver and digestive tract is upset;
- the body is dehydrated, immunity is reduced;
- the blood becomes too thick, which leads to the formation of edema and blood clots in the vessels;
- blood pressure increases, cardiac activity is disrupted;
- in rare cases, cerebral edema occurs;
- acetone negatively affects brain cells, sometimes leading to hemorrhage;
- the activity of the central nervous system sharply decreases; failure of the central nervous system to perform its functions leads to death.
For the unborn child, the appearance of acetone in the mother’s body threatens to result in:
- disorders of the development of the nervous system, which leads to serious pathologies;
- intrauterine growth retardation;
- in exceptional cases - poisoning with acetone, which is contained in maternal blood; as a result, the fetus dies;
- miscarriage or premature birth.
Ketone bodies in urine
In the process of general metabolism, as a result of glucose synthesis in the human liver, three breakdown products are formed:
- beta-hydroxybutyric acid;
- acetoacetic acid;
In medicine they are called ketones or ketone bodies. Their presence in microdoses of 20-50 mg has been detected in the body of every healthy person. In laboratory urine screening, such indicators are practically invisible. Ketones are excreted by peripheral tissues, as well as in the urine.
Ketones perform a number of vital functions in the human body:
- maintain energy balance;
- are a source of energy;
- nourish most tissues.
If a high level of acetone is detected, including during pregnancy, the doctor diagnoses ketonuria, that is, an increased content of ketone bodies.
There are a number of factors that increase the production of ketones in a situation of relative norm:
- intense physical exercise;
- strict (protein) diet, fasting;
- dehydration;
- alcohol intoxication;
- hot weather for a long time;
- surgical interventions;
- stress, high psycho-emotional stress.
Ketonuria of this etiology is not dangerous to human life, but requires a more attentive attitude to your body and lifestyle in general.
Methods for diagnosing ketonuria
All diagnostic methods for studying the level of ketones in the body can be formally divided into:
- at home, when they can be carried out independently;
- laboratory
Through the former, ketonuria during pregnancy can be determined mainly in its expressed form. The main symptoms are a strong odor of acetone in the urine, vomit, if any, and during breathing.
A related method is the use of indicator test strips impregnated with a chemical reagent. The way they work is by reacting a chemical with the ketones present in the urine. As a result of the interaction, the color of the indicator strip changes, and you receive information about the level of acetone.
There is also an alternative method for determining ketonuria. For this you will need ammonia. Add a couple of drops of alcohol to a container with freshly collected urine and watch the dynamics. The urine will become a rich red color if ketone bodies exceed the permissible limit.
Laboratory tests for diagnosing ketonuria are more reliable and indicative, which is especially important during pregnancy. If you have been sent for testing to a laboratory, follow a number of rules:
- Approximately one day before collecting biomaterial, give up fatty, salty, smoked foods;
- perform genital hygiene;
- collect exclusively morning urine;
- Use a sterile container for collection.
In laboratory conditions, the level of ketone bodies is recorded using the Lange test using the “+” and “-” signs:
- "-" - negative result;
- “+” – insignificant presence of ketones;
- “++”, “+++” – positive reaction to the presence of ketone bodies;
- “++++” – ketones in the urine sharply exceed the norm.
Additional examinations in case of detection of ketonuria during pregnancy include:
- general, biochemical blood tests;
- glucose tolerance test;
- blood test for glucose concentration;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs, thyroid gland.
Ketonuria is a rapidly progressive disease, so during pregnancy it is important not to delay in finding out the causes of its occurrence. Any delays can cause irreparable harm to the child.
Why do expectant mothers find acetone in their urine?
Acetone becomes one of the end products of metabolism in the human body. Ladies who have long forgotten their school chemistry lessons, nevertheless know that a solution of the substance perfectly helps remove nail polish.
Acetone is a colorless volatile liquid with a rather pungent odor; an organic substance representing a class of ketones. One of the most popular solvents - used in construction, food industry, pharmaceuticals; In significant doses, acetone causes narcotic poisoning and damage to the central nervous system in humans.
The mechanism of entry of the substance into urine
During pregnancy, a woman’s body switches to an enhanced “work schedule”: systems and organs work hard - blood flow, heartbeat, and metabolism accelerate. The liver intensively produces glycogen, a polysaccharide, a source of glucose; The baby in the womb requires energy to develop, so glycogen consumption increases. When for some reason the reserves of a substance run out, the body looks for alternative sources of energy and eventually begins to break down accumulated proteins and fats, which normally should not be consumed. As a result of the breakdown of adipose tissue, toxic substances are formed:
- acetone;
- acetoacetic acid is an unstable organic compound;
- Beta-hydroxybutyric acid is an intermediate product of fatty acid oxidation.
These toxins enter the blood plasma, circulate throughout the body and finally end up in the kidneys, and after the blood is processed by the paired organ, in the urine.
It should be noted that acetone is present in the urine of every expectant mother, but its level is negligible - up to 50 milligrams per liter; Not every urine test will confirm such a small amount. That’s why the term “traces of acetone in urine” arose - that is, the reagent seemed to detect the substance, but it makes no sense to include it in the composition as a full-fledged component.
And only when the acetone content in the urine is from 50 to 500 milligrams per liter, is it time to talk about acetonuria - an alarming symptom of diseases caused by metabolic disorders. If the level of ketone bodies in the urine exceeds 500 mg/l, a life-threatening condition occurs.
Causes of acetonuria in pregnant women
The detection of acetone in urine signals the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus, something that appears exclusively during gestation - the word “gestation” means pregnancy - and goes away after the child is born. Such diabetes occurs in later stages; Impaired carbohydrate metabolism reduces the body's ability to produce insulin, a hormone that controls the synthesis and breakdown of essential substances. The mother’s disease threatens the fetus:
- hypoxia - oxygen starvation, which leads to intrauterine growth retardation, and in severe cases to death;
- macrosomia - overweight; a child is born with underdeveloped systems - cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive; mortality among such infants is high;
- premature birth.
Another disease that appears in pregnant women in the later stages - gestosis, or late toxicosis - is also accompanied by an increase in the level of acetone in the urine. An increase in blood pressure, inevitable with gestosis, causes a deficiency of oxygen in the cells; the body tries to get energy from a reserve source - the breakdown of fats, with the inevitable release of acetone. In exceptional cases, gestosis threatens the life of the pregnant woman (convulsions, cerebral edema, coma appear); the child may also die or be born premature, with developmental abnormalities.
But in the 1st trimester, acetonuria appears as a result of toxicosis. The main culprit is vomiting, as a result of which the pregnant woman rapidly loses nutrients. It’s impossible to get new ones - every meal is accompanied by another urge to “turn yourself inside out.” Therefore, the body is forced to compensate for the lack of carbohydrates with “unscheduled” consumption of adipose tissue - and where to go when the embryo requires energy for growth and development. So a dangerous sign is found in the urine of the expectant mother - acetone.
Toxicosis in the early stages, as well as food poisoning, cause serious bouts of vomiting, which causes fluid and beneficial elements to leave the pregnant woman’s body.
Other diseases in pregnant women, the symptoms of which are acetonuria:
- infectious inflammation - some microbes (beta-streptococci, influenza viruses) provoke metabolic failure, including energy metabolism; and immunity also comes into play in the fight against infection - the production of antibodies increases, which requires significant energy expenditure; when there is not enough glycogen, fats serve as “fuel”;
Infections during pregnancy disrupt metabolism, which leads to acetonuria - diseases of the thyroid gland (for example, Bazedova) - accompanied by metabolic failure and breakdown of fats;
- pathologies of the adrenal glands, which are characterized by increased synthesis of the hormone cortisol, causing increased breakdown of glucose; and again the source of energy is the reserves of adipose tissue;
- diseases of the digestive system, in which the absorption of nutrients through the walls of the digestive tract slows down; as a result, there is not enough glucose and the breakdown of fats starts;
- fatty hepatosis or fatty liver - accompanied by a violation of protein-fat metabolism;
- intoxication of the body with mercury, phosphorus, lead - leads to metabolic disorders; and the appearance of acetone in the urine is caused by anesthesia using chloroform.
Acetonuria is also provoked by a woman’s dietary and lifestyle habits, for example:
- poor food - not enough carbohydrates enter the body; when a pregnant woman goes on a strict diet, this is generally beyond the bounds of reason; to produce energy, the body begins to “eat” fat reserves, intensely releasing toxic ketone bodies;
- abuse of fatty foods or foods high in protein (eggs, smoked meats, fried foods); the acid-base balance is disturbed - in favor of acids - which leads to a slowdown in metabolism;
The expectant mother's love for fatty cakes results in a disruption in the balance of acids and alkalis in the body; there is a threat of acetonuria - food poisoning - causes vomiting, dehydration, resulting in loss of carbohydrates;
- increased stress (hard work, sports); Carbohydrate consumption increases to compensate for energy production; the body spends fats.
Expectant mothers who are exposed to stress, hormonal imbalances, and with weakened immune systems are also at risk. It is better for pregnant women to get out of environmentally unfavorable areas whenever possible - a polluted environment poisons the body, which ultimately threatens a slowdown in metabolism and the appearance of diseases that accompany acetonuria.
Why is the rate increased?
Ketones in the urine of a pregnant woman are a phenomenon caused by several factors, including both dangerous diseases and minor physiological abnormalities. Among the latter are:
- a diet with a significant amount of meat and excessively fatty foods;
- lack of norms for carbohydrates in food;
- heavy physical activity;
- dehydration due to toxicosis.
Other reasons that provoke the occurrence of ketonuria:
- prediabetes and diabetes;
- intoxication of the body;
- the presence of infectious diseases;
- pancreatic or liver dysfunction.
These problems require medical intervention, as otherwise the level of ketones will only increase, which will negatively affect the woman’s health.
Ketone bodies in gestational diabetes in pregnant women
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a disease that occurs only in pregnant women and is characterized by high levels of glucose in the blood.
If the value exceeds 5 mmol/l when donating blood on an empty stomach, GDM is diagnosed.
During the period of bearing a child, a large load appears on the pancreas, which may stop properly producing insulin. Without it, glucose entering the body is not absorbed, so it accumulates in the blood. Excessive amounts of it cause diabetes. Against the background of poor absorption of carbohydrates, the concentration of ketones in the urine increases.
GDM can be dangerous for the baby due to congenital diseases and even premature birth. Therefore, patients with this diagnosis need to be constantly under medical supervision.
In order to timely detect the development of gestational diabetes, a glucose tolerance test must be taken at 16-24 weeks of pregnancy. This test is required for all women, not just those at high risk for diabetes.
GTT is carried out by donating venous blood. First stage: on an empty stomach (do not eat for 12 hours before the examination). The second stage: with a load on the pancreas (glucose dissolved in water) - carried out 1-2 hours after taking the substance.
Elevated ketones in the third trimester
Normally, ketone bodies in urine during pregnancy should stabilize by the third trimester. If in the early stages their presence was explained by a restructuring of the body or an incorrect regimen, then in later stages this indicates the presence of a disease. An increase in indicators can threaten both the development of GDM and the appearance of late toxicosis.
By the third trimester, the amount of ketones in the absence of pathologies may increase, as active fetal development occurs. The baby uses up the mother’s glucose in just one night, which is why fats begin to break down. For this reason, acetone bodies can be found in morning urine.
It is worth checking whether the increase in ketones occurred once or whether there are abnormalities in the mother’s body by retaking the test. The day before diagnosis, you need to adhere to a diet that excludes fast carbohydrates.
Gestational diabetes
Another common pathology during pregnancy is GDM (gestational diabetes mellitus), which occurs in 7% of women during pregnancy.
The disease is accompanied by changes in carbohydrate metabolism and is characterized by an increase in venous blood glucose levels, first detected during this period (usually at 24-26 weeks).
A pregnant woman's blood sugar levels will differ from those of a non-pregnant woman (Table 2 below).
Table 2 - Criteria confirming the diagnosis of gestational diabetes