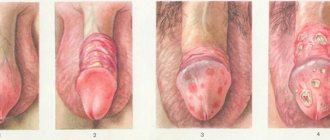
Hemospermia or hematospermia is a type of pathology accompanied by the presence of blood in the ejaculate. Due to the excess number of red blood cells, the seminal fluid may be red or pinkish in color. This pathology can occur in men of different ages. In young patients, hemospermia is most often benign in nature and does not require special treatment, while in patients over forty years of age, the appearance of blood in the semen is a signal of a possible neoplasm in the prostate. Often this type of pathology manifests itself in sexually active young patients. It is difficult to detect if sexual life is conducted without the use of barrier contraceptives. At a young age, only 2% of cases of hemospermia indicate the presence of chronic or malignant diseases, but by older age this figure increases to 14%.
Hematospermia does not necessarily require treatment. Blood in the seminal fluid may appear after a vasectomy or biopsy of the prostate gland and scrotal organs. Typically, within one to four weeks, the sperm becomes normal in appearance and no medical intervention is required.
Hemospermia can be false or true. The true one is accompanied by the ingress of blood into the sperm, forming directly in the seminal fluid, while the false one is mixed with it during its passage from other organs or as a result of injury or inflammation of one of the sections of the seminal tract.
Symptoms
In most cases, hemospermia signals problems with male health, so if bloody inclusions are detected in the semen, you should immediately contact a urologist. He will conduct a diagnosis and prescribe tests to identify the root cause. This phenomenon affects not only a man’s ability to bear children and the performance of his sexual functions, but also the condition of the body as a whole.
Thus, in men under the age of 35, hematospermia indicates the presence of inflammatory processes in the prostate gland, epididymis, and seminal vesicles. Symptoms may be as follows:
- nagging pain in the lumbar region;
- protein in urine;
- pain in the scrotum, groin, testicles;
- discomfort when urinating;
- elevated body temperature.
If the problem is caused by inflammation of the prostate, in addition to blood inclusions in the semen, other signs are added:
- frequent urge to go to the toilet, but little urine comes out;
- premature ejaculation;
- the quality of sexual life decreases, the severity of orgasm decreases;
- Body temperature rises to 37.2-37.5.
If at least one sign is present, you need to consult a specialist, which will help you avoid more serious problems.
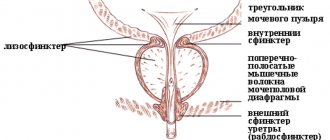
Anatomy and physiology
Sperm is a liquid containing male reproductive cells (sperm) and auxiliary substances.
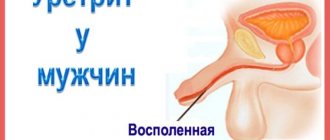
The cells gradually mature in the testicular tubules, after which they enter the epididymis and seminal vesicles. The liquid part of sperm, consisting of acids, vitamins, nutrients, immunoglobulins and other components, is formed in the seminal vesicles and prostate gland. At the end of sexual intercourse, all components of the ejaculate are mixed and fluid is released through the urethra. Infections, malignant changes, injuries and other pathologies can affect the condition of the organs responsible for the release of sperm. Typically, pathological hemospermia is associated with the prostate, since tumors can form in this gland. Also, the discharge of blood along with semen sometimes indicates inflammation of the prostate and seminal vesicles. Other causes may be related to medical interventions and trauma.
Causes
Hematospermia can be provoked by various diseases of the genitourinary system in men. This is usually inflammation of the seminal vesicles, medically called vesiculitis. It precedes chronic prostatitis. Also, blood in semen indicates problems with the prostate gland, another organ responsible for the production of seminal fluid. Vesiculitis is accompanied by general weakness, nagging pain in the lower abdomen and when urinating. Besides semen, blood is also present in urine.
Hemospermia is often caused by STIs (sexually transmitted infections), epidymitis, urethritis, and other inflammatory processes that are not clearly expressed. With urethritis, purulent discharge from the urethra is added to weakness and pain when urinating. Epididymitis has the following symptoms: frequent urge to go to the toilet, inflammation of the epididymis, swelling, soreness of the scrotum, pus from the urethra. Hemospermia can also be caused by intense, frequent sex life if there is congestion in the male genital system.
In men over 40, blood in the semen may indicate the presence of a prostate tumor, including a benign one. The danger of the disease is that in the initial stages it is asymptomatic. But modern medicine has already found a solution to this problem - an antigen test, which makes it possible to diagnose tumors in the early stages. Blood in semen can also appear as a result of injuries, mechanical damage, or taking a biopsy sample. The condition may persist for 1-4 weeks, after which it resolves. In such situations, treatment is not required.
Other causes of hematospermia include:
- stones in the urethra;
- obstruction of the vas deferens;
- polyps in the urinary canal;
- tumors of other organs;
- seminal vesicle cysts.
To determine the exact cause of the deviations, a thorough examination is necessary.
How is hemospermia diagnosed?
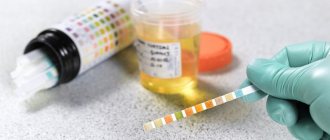
Once hemospermia is identified, a series of diagnostic tests are performed to determine the source of bleeding or the cause of blood in the semen. Some of the most commonly performed diagnostic procedures are:
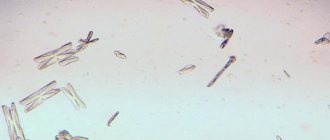
- spermogram;
- sowing ejaculate for flora and sensitivity to antibiotics;
- testing for sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- general urine analysis;
- urine culture for flora and sensitivity to antibiotics;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys, bladder with determination of the amount of residual urine, prostate gland, seminal vesicles, scrotal organs.
If necessary, a magnetic resonance examination of the pelvis (MRI of the pelvis) is performed, which can identify benign or malignant formations of the pelvic organs in a man.
Diagnostics
To identify the primary source of hemospermia, a whole range of measures is carried out. First of all, the doctor conducts a detailed survey: when did the patient first discover blood, how often does this phenomenon repeat, were there any injuries or medical procedures that could have caused the bleeding. Depending on the answers, the doctor determines a scheme for further diagnostic procedures.
As part of the examination, a bacterial culture test is required, since infections often provoke the appearance of blood in the semen. Next, it is necessary to check for the presence of inflammatory processes, so a spermogram is done. Before donating sperm, you should not smoke, drink alcohol, or have sexual intercourse for 3 days. To complete the picture, the doctor prescribes a blood test for coagulation and antigen (PSA), which is necessary to identify tumors and other pathologies of the prostate.
An important place in the diagnosis is occupied by ultrasound, including transrectal ultrasound, which allows visualization of the prostate gland. An ultrasound examination of the scrotum and testicles shows the full picture. Men over the age of 40 undergo an MRI aimed at diagnosing oncology.
Classification of hemospermia
Depending on the causes of occurrence, primary and secondary hematospermia are distinguished.
The primary form is said to be when the appearance of blood in the ejaculate is not caused by any infectious diseases or inflammatory processes, that is, it is not associated with any organic changes in the body. Primary pathology rarely reoccurs and does not require seeing a doctor.
Secondary hemospermia is systemic in nature. It is a consequence of surgical intervention in the reproductive system or organic changes in the body. It often manifests itself in prostatitis, cirrhosis, tuberculosis, and parasitic infections. In approximately 25% of cases, the pathology occurs due to prostatitis, the treatment of which is indicated by taking antibiotics.
Treatment
Since hemospermia itself is not a disease, but only signals the presence of one, treatment is prescribed based on the results of the examination. Before the tests are ready, urologists usually prescribe drug therapy using anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents. Since in most cases it is infections and inflammation that provoke this condition.
Further treatment depends on the cause of the blood in the semen. When identifying neoplasms, oncology, the choice of technique is determined by the stage and nature of the formations.
In most cases, men under 40 years of age who have red blood cells in their seminal fluid for a short time do not require therapy. Supervision by a specialist is sufficient.
Additional symptoms
If hemospermia is caused by a disease, there is a high probability of other pathological signs appearing. Studying symptoms helps specialists clarify the diagnosis with the help of a small number of examinations.
Possible symptoms and signs:
- painful urination;
- discomfort during ejaculation;
- weak erection;
- pain in the perineum and pubic area;
- increase in body temperature;
- dizziness and weakness;
- blood in urine;
- redness and swelling of the scrotum.
If the above symptoms are detected, you should definitely undergo examination. Acute infection of the prostate gland can cause purulent complications.
Probability of conception
Hemospermia often becomes the cause of male infertility, since in this condition the number of living sperm is negligible or they are absent. Therefore, the pathology requires a course of treatment aimed at improving the quality of sperm. Usually this is vitamin therapy. If indicated, it may be accompanied by the use of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs. The course of taking vitamins before conception is 3 months. This is how long it takes to form new sperm capable of fertilization. Thus, vitamin B, folic acid, promotes the production of high-quality sperm, E - increases the vitality of sperm, and C - increases the production of testosterone.
The vitamin complex must be prescribed by a doctor!
What to do if blood appears during ejaculation
As we have already said: “Sperm with blood is not a death sentence.” But it’s worth making it a rule that any problems with the genitourinary system should be examined by doctors.
Blood during ejaculation is still not normal. Remember that only in 98% of cases this does not mean anything terrible, but 2% remains that this is a sign of cancer.
A very important factor that helps not to make a mistake and not cause a false alarm is the erroneous opinion about the presence of sperm with blood. Before seeking treatment, you should make sure your assumptions are correct.
Masturbation with ejaculation on a light surface will help you with this. This way you can definitely identify the problem. Take this seriously and do not resort to the help of a sexual partner.
Treatment of hemospermia
Treatment can be completely different for various diseases of the genitourinary system.
As a rule, treatment begins with a course of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. If symptoms return after a while, then a detailed examination is necessary to accurately determine the causes of this phenomenon.
You can cure a man using folk methods. The main traditional medicine against hemospermia is the red root. You can prepare a decoction or infusion from it. To prepare the decoction you will need 25 g of red root and 1 liter of boiling water. The red root needs to be crushed and poured with boiling water. The decoction should be infused for an hour. You need to take the decoction three times a day for 30 minutes. before meals.
The infusion is prepared from 50 g of red root, filled with a bottle of vodka. The infusion will be ready in 7 days; it should be stored in a dark place. Take 3 teaspoons of infusion before meals. Can also be added to green or herbal tea. The course of treatment with the balm is 3 months.
You can also use propolis, namely its extract, to obtain which you need to evaporate 40 g of propolis in 200 ml of alcohol. Cocoa butter should be added to the resulting substance in a ratio of extract to oil of 1:20. From the resulting substance you need to roll up suppositories for rectal use and place them rectally until improvements appear.
Any of the traditional methods of treatment can be highly effective, but also have certain contraindications, so you should not resort to them without first consulting a doctor.
https://youtu.be/s1njHo_Jqbg
Thus, the presence of blood in semen, as a rule, is a sign of one or another disease of the male genital organs. It is necessary to consult a doctor as early as possible, since any disease is easier to treat in the early stages.
Hemospermia is a serious but treatable disease. A competent, qualified approach to the diagnostic process, which our clinic can provide, is the key to a successful treatment outcome. Modern methods of treating a disease such as hemospermia can be both therapeutic and surgical methods of treatment.
The decision about what kind of treatment should be prescribed in a particular case depends both on the results of diagnosing the disease and on a number of other reasons. To do this, it must be determined how often a man experiences hemospermia, how long the period of the disease lasts, as well as the age of the patient.
The final decision on which treatment method should be used is made by the urologist andrologist based on a thorough analysis of the examination results, in which the causes of hemospermia should be identified.
The course of treatment is aimed at helping the patient completely get rid of the disease and recover. If the result is successful after treatment, the man no longer experiences pain, and in this case, medical supervision is not required. However, if the disease has become chronic and its symptoms have been observed for more than two months, then additional examination, detailed consultations, which can be carried out by a qualified urologist andrologist, and a more thorough course of treatment are required.
The accuracy of the diagnosis and the quality of the examination determines how effective the course of treatment will be.
In some cases, hemospermia will be treated with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs. In 95% of cases antibiotics are prescribed:
- Augmentin;
- Trifamox;
- Ampiside;
- Ceftriaxone;
- Suprax;
- Levofloxacin;
- Gatispan;
- Streptomycin;
- Doxycycline;
- Monural.
Antibacterial therapy eliminates the main causes of inflammation. Reduces the risk of complications, as well as progression of existing diseases of the genitourinary system.
How to treat hemospermia at home?
No disease can be treated without a doctor’s opinion and establishing the cause of the pathology. Therefore, the first thing a man needs to do if he finds blood in his semen is to consult a urologist. Then, undergo all the necessary examinations and, after determining the cause of hemospermia, begin treatment.
Based on the results of tests and diagnostic measures, the doctor may decide to treat the disease of the primary type of hemospermia (false) with the help of antibacterial therapy. The diagnostic complex is:
- Ultrasound;
- Blood chemistry;
- Sperm analysis;
- Prostate examination;
- Tests for the presence of PSA antigen;
- Venereal diseases.
However, in 50% of cases with this method of treatment, suppression of symptoms is observed only at the time of taking the pills. After completion of the course, the disease may recur. Therefore, it is necessary to treat under the supervision of a urologist and monitor the condition of the genital organs over time. Hemospermia itself does not affect the organs, but is only the main manifestation of the main pathology.
Hemospermia treatment with folk remedies is also popular for a number of reasons: it is inexpensive, accessible and effective in cases where the etiology is known.
Traditional methods of treatment:
- Grind the penny root (red) in an amount of 25 grams. Pour 800 grams of boiling water, wrap in a warm towel, and let cool. Divide the liquid into two parts and take 48 hours before, regardless of meals. You need to treat with this method for at least a month. After reduction or elimination of symptoms, repeat the course after 3 months.
- Infusion of ginseng and red root. Prepare 0.5 liters of vodka. Grind 50 grams of dry red root, 50 grams of dry ginseng. Mix with vodka and place in a dark place for 10 days. Then take it out and strain it in a special way: put a tablespoon of thick propolis in gauze and put it on the bottom of the watering can. Strain slowly so that the vodka seeps through the thick layer of propolis. Take 1 tablespoon three times a day for 2 weeks. 1 week break, then again two weeks. It is necessary to treat in this way until the symptoms are completely eliminated.
Hemospermia and its treatment depend on the factors that provoked this disease. The causes, symptoms and etiology are individual for each individual patient. Both pathogenic bacteria and mechanical damage can cause a pathological disorder. However, it is necessary to treat in any case, the disease does not go away on its own, but only “overgrows” with chronic diseases of the urethra or prostate.