A woman expecting a child may experience impaired renal function, as a result of which the body accumulates calcium salts - oxalates, which over time can form stones in the genitourinary system.
Oxalates in urine during pregnancy are normal for a healthy woman if the salts are formed in small quantities. If the analysis shows a significant concentration of such substances, we may be talking about a serious pathology.
What are oxalates in urine during pregnancy?
These are derivatives of oxalic acid and occur in the form of crystals or esters.
WARNING! The information on the site is provided for informational purposes and cannot be used to make a diagnosis or make treatment decisions. Where do oxalate crystals come from? They form when calcium, sodium, potassium, iron or magnesium react chemically.
As a result, stone formations form in the intestinal area. Excreted through the kidneys and urinary system.
About 10% is absorbed and enters the bloodstream.
This does not have a serious impact on the health of a pregnant girl.
Problems begin with chronic high levels of this substance in the body. In this case, some functions may be impaired or fail altogether, which happens quite often.
In this case, sharp stabbing pains in the abdomen may be felt.
Almost every woman experiences oxalates in urine during pregnancy, but the danger lies in their high concentrations.
What are oxalates
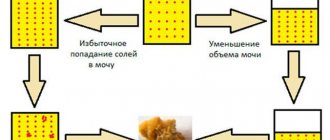
Calcium salts - oxalates - along with other substances (such, for example, include the combination of pure calcium salts with orthophosphoric acid - phosphate) are a product of natural metabolic processes in the body, dissolved by fluid passed through the kidneys, excreted along with urine. A woman’s health depends on the balance of this substance - the concentration is a little more or a little less, and the condition will deteriorate, triggering the pathological process of development of the most serious diseases. If the kidneys cannot cope with the load, the salts are not excreted and begin to crystallize and turn into stones.
In the body of a healthy person, calcium is processed and excreted in a timely manner, in optimal volumes, so oxalate salts are found in the urine in a minimal amount. This balance can be upset by a number of factors:
- taking large amounts of vitamins;
- abundant consumption of vegetables;
- genetic predisposition;
- regular stress;
- diabetes mellitus;
- inflammatory and infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- deficiency of magnesium salts.
Pregnancy is a difficult test for the female body - all the mother’s resources are directed to maintaining the development and protection of the fetus, all her organs and systems work on this task, often to the detriment of the woman herself, so even ordinary allergies can become a problem. For the development of a child, a large amount of calcium is required, which is produced by the mother's body. If the mother's kidneys do not function properly and do not provide enough water to dissolve and excrete the salts, this is the reason for their crystallization and precipitation in the urine.
Why do salts appear and why are they dangerous?
The causes of oxalate in urine during pregnancy vary.
In some cases, the disease progresses due to dysfunction of the thyroid gland and poor nutrition.
During a medical study, specialists identified the factors that cause the disease most often:
- constant stress;
- physical exercise;
- toxins in the body due to taking antibiotics or other medications;
- excess vitamins;
- food containing large amounts of oxalic acid;
- urolithiasis disease;
- pathologies of the excretory system;
- lack of moisture (dehydration);
- magnesium deficiency;
- diabetes;
- consequences of operations on the intestines.
Crystals in urine during pregnancy can lead to some complications. In the chronic stage and to developmental problems in the embryo.
They occur due to the fact that some beneficial microelements do not reach the baby. On this basis, conditions for the suppression of mental and physical activity in the future develop.
The presence of oxolates in the urine of a pregnant woman may indicate the development of inflammatory diseases, diabetes mellitus and Crohn's disease.
The most dangerous complication of the appearance of oxolates in the urine during pregnancy can be the formation of kidney stones. These are one of the most difficult types of crystals to remove, which, when moving, can provoke not only renal colic, but also a number of complications during pregnancy and childbirth.
Causes of oxaluria
There are many reasons why a person may develop oxaluria. These may be hereditary factors that provoke the primary form of the disease, and pathological processes in the gastrointestinal tract. The nutritional factor also plays a role.
The main reasons that, according to doctors, sooner or later lead to oxaluria are:
- congenital defects of enzymes responsible for the process of absorption and excretion of calcium oxalate from the body;
- excessive consumption of foods containing calcium oxalate - pepper, rhubarb, sorrel, cocoa and chocolate;
- chronic disease of the gastrointestinal tract - Crohn's disease;
- pathological processes in the intestines - deficiency of lactobacilli, ulcerative colitis;
- surgical intervention performed on the intestines, temporarily or permanently inhibiting its functions;
- abuse of vitamin preparations, in particular ascorbic acid;
- lack of vitamins B6 and/or A in the body;
- living in an area with unfavorable environmental factors.
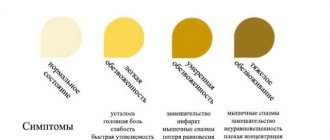
Symptoms
The most common symptoms due to which you can independently suspect the presence or absence of this pathology in pregnant women are:
- Frequent painful urge to go to the toilet (more than 15 times a day).
- Constant feeling of fatigue, drowsiness.
- Headaches, possible loss of consciousness and dizziness.
- Change in urine color.
- Sharp, short-lived pain in the lower abdomen, which is sometimes mistaken for colic.
- Slightly elevated temperature.
It is important to note the fact that such changes are often accompanied by a sudden change in diet.
With the slow development of the disease, the above symptoms may be mild or not expressed at all.
In such cases, there is a possibility that the disease will develop hidden. Late diagnosis and untimely treatment will not contribute to successful treatment.
Types of diagnostics
Diagnostic measures are aimed at the need to promptly detect the cause of the disease and first get rid of it, simultaneously removing its negative impact on the mother’s body.
The first symptoms of pathology are detected in the results of a general urine test. They are manifested in increased protein content, reflected in the results of the study.
The following procedures are prescribed as additional diagnostic measures:
- biochemistry of urine;
- general and biochemical blood test;
- Ultrasound.
As treatment progresses, follow-up studies are prescribed. They are necessary so that the doctor can see the response of the woman’s body to the therapy and determine the extent of the effect of the drugs on the child.
The main thing is to identify the cause and take timely measures to eliminate it in order to protect mother and baby from various health problems.
Kinds
The detection of oxalates during pregnancy often indicates pathological processes occurring in a woman’s body that affect the urinary system. The condition is dangerous because it practically does not manifest itself symptomatically, therefore it is detected only on the basis of a urine test and the results of instrumental examinations (ultrasound).
Several types of oxalates are commonly found in urine, each formed from salts of different types of substances. The most common are calcium oxalates, but concretions of crystallized potassium, ammonium and sodium salts combined with oxalic acid are also released. The formation of such stones is influenced by various factors - from improper diet to an excess of vitamins taken.
Recommended topic:
Symptoms and treatment of urolithiasis in women
Treatment
In most cases, treatment takes place on an outpatient basis.
A pregnant woman is sent to a hospital only in case of acute health problems that entail a danger to the development and life of the child. If the amount of oxolates in the urine is not greatly exceeded, then treatment recommendations include adherence to dietary table No. 7, as well as the drinking regime.
A special place in oxolate therapy is occupied by regular physical activity. Moderate exercise helps their movement from the kidneys and removal from the body of the expectant mother.
In severe cases, drug therapy or surgery using laparoscopy is prescribed.
Prevention
If you have problems with the urinary system and the presence of elevated levels of oxolates, the following products should be limited in the menu:
- berries with a high acid content (plum, currant, strawberry, cherry);
- beans;
- coffee;
- tea;
- sorrel,
- bell pepper;
- parsley;
- potato;
- beet;
- onion;
- eggs.
Depending on the individual characteristics of the body, a pregnant woman should exclude broths from fatty meats, poultry or fish.
If there are increased crystals in the urine during pregnancy, then it is necessary to help the body remove them as soon as possible, and the following will help to cope with this:
- cereals;
- fermented milk products;
- watermelons;
- unsweetened compotes;
- drinking purified water.
It is highly not recommended to use special diuretics during pregnancy.
It is also recommended to limit salt intake, as it “binds” water in the body and prevents the excretion of oxolates from the kidneys.
Before taking folk diuretics, you need to consult a specialist and determine the absence of allergic reactions.
Preventive measures should not harm the health of the mother and child, so you must follow the instructions of the gynecologist and nutritionist.
Author: Maxim Dmitrievich, obstetrician-gynecologist Specially for the site kakrodit.ru
Diet and drink are the main methods of treatment
Since during pregnancy the main reason for the increase in the volume of calcium salts excreted in the urine is impaired kidney function, treatment of this condition consists of the following measures:
- diet - exclusion from the diet of foods containing oxalates in both significant and small quantities (cocoa, chocolate, any sweets, beets, lettuce, sorrel and spinach, citrus fruits, currants and rose hips, fatty broths);
- drinking regime - the volume of liquid should exceed 2-2.5 liters, you should drink mineral water, compotes, fruit drinks, herbal decoctions, infusions and preparations.
In addition to the listed measures, on the recommendation of doctors, pregnant women can take vitamin and mineral complexes:
- vitamin B6;
- magnesium oxide;
- citric acid;
- sodium and potassium citrate.
Recommended topic:
Treatment of uric acid diathesis (urate) in adults
All therapeutic measures must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor and in strict accordance with his prescriptions - self-medication can harm the expectant mother and her child, as well as aggravate problems with the genitourinary system.