Classification
Nevi are divided into several types, depending on location.
- Located on the retina. Such neoplasms are considered benign. They are localized on the back wall of the eyes. Not accompanied by the development of characteristic symptoms. The spot has characteristic clear outlines and a flat shape. Does not change its size over time.
- Iris. The pigment that is responsible for color has an important function in it. With various violations, it can create such points.
- Conjunctiva. Nevus, which is located on the conjunctiva, is very rare. It is easy to spot due to its unusual location.
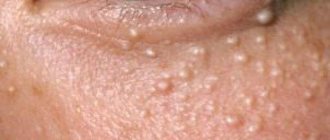
- Around eyes. In ophthalmological practice, such cases occur frequently. In this case, moles are located on the eyelids and nearby integuments. The color of nevi can be light or dark brown.
In addition, such neoplasms are divided into stationary and progressive.
- The presence of a progressive nevus tends to increase in size and change shape over time. Characteristic is the presence of fuzzy outlines. Dystrophic changes may be observed in the retina. The risk of retinal detachment increases. Against this background, a decrease in visual acuity develops, cloudy spots may appear before the eyes, and a fuzzy, distorted image appears. This group of nevi is dangerous because it poses a risk of malignant tissue damage. It can be diagnosed in the dynamics of development.
- The typical appearance of these neoplasms consists of flat or protruding nevi. They have a round shape. The color is usually grey. They do not have clear outlines or boundaries. Characteristic signs are lack of growth and persistent color. There are no retinal changes or visual impairment.
Only a doctor can determine the type of such neoplasms after a full diagnosis. It is impossible to independently determine the classification. Sometimes it is visually impossible to notice the presence of moles. Therefore, they are discovered by an ophthalmologist after a special examination.
Types of nevi of the choroid of the eye
Pigmented nevus is classified as follows:
| View | Description |
| Stationary (typical) | This type of mole on the choroid of the eye is a flat formation, sometimes protruding slightly above the iris. Its shape is round or oval, and its color varies from gray to gray-green. The sizes are small - from 1 to 6 millimeters. A stationary neoplasm does not increase in size over time and no inclusions of other colors are observed on its surface. Visual functions are not impaired. |
| Progressive | It often changes shape, grows, the clarity of the boundaries changes, and inclusions of other shades appear. The retina is deformed, the choroidal vessels are compressed. Sometimes even retinal detachment is diagnosed. A progressive nevus can provoke visual impairment, the appearance of glare in front of the eyes, and disturbances in the integrity of the visual image. Doctors consider this type of nevus dangerous, since there is a possibility of degeneration into a malignant formation. When a progressing mole is detected, a series of studies are carried out in order to exclude a cancerous nature, and then treatment is resorted to. |
Symptoms
A mole on the choroid of the eye grows without pain symptoms, but can affect the sharpness of vision.
A stationary mole on the uvea of the eye occurs asymptomatically. It is invisible not only to its owner, but also to the people around him. It is discovered during a routine visit to the ophthalmologist or in cases where the nevus grows. In this case, the patient complains of the following symptoms:
- blurred vision;
- feeling that there is a foreign object (sand or dust) in the eye;
- narrowing of the field of view.
Causes of formations
Nevi in the eye appear for the same reason as other moles, that is, due to the concentration of melanin. Leads to this:
changes in hormonal levels, stress, infections, inflammation, hormonal contraceptives, genetic factors.
Scientists believe that a mole in the eye appears more often in people with light hair and skin, since there is less pigment in their body. Despite the fact that nevi are formed before birth, they appear most often as they grow older. But in men and women they occur in the same number of cases.
Why does pathology appear?
Choroidal nevus of the eye, like other moles, occurs due to increased melanin content. The following factors can provoke this condition:
The pathology often occurs in people living under stress.
- hormonal imbalances;
- constant stressful situations and nervous overstrain;
- inflammatory diseases;
- infectious diseases;
- genetic predisposition.
Diagnostics
Basically, the presence of a nevus can be detected through a random examination of the fundus. If the presence of such a neoplasm is suspected, the doctor conducts dynamic examinations.
Observes the development of the mole. For this purpose, special color filters are used. After this, a final diagnosis can be made.
You can very clearly see the presence of a nevus in a red color. When exposed to green color, it tends to disappear. In this way, the doctor can only detect pathological changes in the layers of the retina.
Rarely, an ultrasound examination may be necessary. This method allows you to study the condition of the fundus vessels. To do this, a contrast agent is used, which can be used to detect the presence and location of moles. Typically used for stationary diagnosis. There are no changes in the blood vessels.
If the presence of a nevus progresses, doctors install a special substance. It passes through the walls of the blood vessels that are adjacent to the mole. This is observed in a progressive form. In this way, doctors observe the dynamics of development.
How to recognize and treat nevus of the choroid and iris? – ODSIS Medical portal
It is melanin that gives the shell of the eye a certain color and its saturation. These same cells are the cause of the formation of moles, which form in a limited area of the body.
Nevi occur on the conjunctiva or choroid. The first is a transparent tissue covering the outside of the eye. And the second is the choroid of the eye.
Causes of formations
Nevi in the eye appear for the same reason as other moles, that is, due to the concentration of melanin. Leads to this:
- changes in hormonal levels,
- stress,
- infections,
- inflammation, inflammation
- hormonal contraceptives,
- genetic factors.
Scientists believe that a mole in the eye appears more often in people with light hair and skin, since there is less pigment in their body. Despite the fact that nevi are formed before birth, they appear most often as they grow older. But in men and women they occur in the same number of cases.
Kinds
Formations are divided into stationary and progressive. The first type does not change its color and size. This type is not prone to the appearance of new tumors. In most cases, they do not pose any threat to health.
Progressive ones change their size and color. Nevi usually have a yellowish, variable border and can lead to blurred vision.
Conjunctival mole
This type of mole occurs in 5% of people. It appears outside or inside the film.
The localization of the nevus is different: cartilage, eyeballs, transitional folds, lacrimal month. In one case they rise above the surface, in the other they are flat.
Photo of iris nevus on the eye
There are several types of conjunctival nevi:
- Nevus growths. They appear as pinkish or red spots. They consist of capillaries and pass through the entire shell.
- Pigmented nevus of the conjunctiva. They are similar to a mole. They occur due to an excess of melanin.
- Cyst-shaped. Formed during the fusion of lymphatic vessels. When magnified, it begins to resemble a honeycomb.
Choroidal nevus
This type is found in 2-10% of people. More often susceptible to degeneration into a malignant aggressive tumor.
Moles are formed from cells of the supravascular plate, but over time they can spread to deeper layers.
The localization of the nevus is most often behind the widest part of the eye, but in rare cases it forms in the equator region. The typical species has clear or irregular outlines, dimensions up to 0.6 cm, and a uniform color of gray or gray-green.
Progressive may be of a different shade; compression of the choroidal vessels occurs. This type is divided into typical, suspicious or atypical. Only the latter type requires urgent treatment.
Sometimes choroidal melanocytoma is detected during diagnosis. This is a large cell nevus localized on the optic nerve head.
The prognosis for this form is favorable. In 90% of patients, the diagnosis is incidental, but with large tumors there is slight visual impairment and an increase in the blind spot.
What is the danger of pigmented nevi in the eye?
For many years, the nevus did not manifest itself. But under certain circumstances they can transform.
If you have the following symptoms, you should contact an ophthalmologist as soon as possible:
- limitation of the field of vision or reduction in its quality,
- the appearance of a sensation of a foreign body in the eye,
- change in color and size of the nevus.
According to statistics, in 1 case out of 500 there is one cancerous transformation. Medical supervision is required for formations with a thickness of more than 2 mm, in the presence of subretinal fluid, when orange pigment appears, or when the nevus is located on the posterior disc of the apple.
Many people are interested in: is it possible to prevent a mole from transforming into a malignant tumor? This is easy to do if you undergo annual examinations and avoid exposing your eyes to ultraviolet radiation.
Treatment methods
For benign lesions, treatment is usually not prescribed. For progressive nevus, electroexcision is used. This is a surgical method of exposure that involves an electric scalpel. Simultaneously with the procedure, plastic surgery of the defect is performed.
In modern private clinics, laser is often used. This method is good when you need to remove hard-to-reach formations. If the manipulation must be carried out urgently, then microsurgery is performed.
In children, nevi are treated only in extreme cases, if there is a process of intensive progression.
Locations
Birthmarks form in different areas of the eye:
- external and internal areas of the protein;
- tearful month;
- semilunar fold;
- iris or retina;
- limbo.
Location of conjunctival nevi
An ocular nevus forms on the inner and outer parts of the conjunctiva. Birthmarks are detected on the inner corner of the eye, the periphery of the cornea, the lacrimal month, and the semilunar fold. Sometimes neoplasms appear on the inside of the eyelid. Although moles are located near the pupil, they do not block the view or impair vision.
Treatment
If the doctor has confirmed the presence of a typical type, then drug therapy is not necessary. Regular monitoring and frequent visits to the ophthalmologist will be required. It is enough to carry out an inspection several times a year. If the nevus begins to grow and its structure changes, then surgical intervention is necessary to remove it.
At each examination, the ophthalmologist must record the condition of the nevus and keep a photo report. This will help monitor any changes. Therapeutic treatment can be prescribed taking into account the location of the tumor, its size and the development of the process.
Each patient must be registered with a doctor.
It is important to control the dynamics and intensity of growth of such neoplasms. If necessary, they are simply excised. This procedure is safe and is performed exclusively in a hospital setting. To do this, use the following methods:
- Electroexcision. This excision consists of removing the pigment spot. This method helps to carry out the removal as accurately as possible. In addition, the patient undergoes plastic correction of the defect of the conjunctiva and cornea.
- Laser therapy. This technique is most often used to remove nevi. This carries a low risk of injury. This will also help remove moles that are located in hard-to-reach places.
- Surgery. Prescribed in case of emergency. This usually occurs with benign tumors. Emergency help is needed when large nevi develop.
- Surgical intervention. Used when severe symptoms of a malignant nature develop, especially when visual acuity decreases. The operations are not dangerous or painful for the patient.
It is impossible to get rid of such unusual moles on your own. The patient needs a full examination and diagnosis by an ophthalmologist.
Nevus of the choroid and iris: photo, danger, diagnosis, treatment, prognosis
Choroidal nevus resembles a birthmark, which is located in the deep structures of the eye. This formation is identified by an ophthalmologist during an examination of the patient. Approximately 8-10% of people suffer from nevus, and its development is more often observed in people with blue eyes and fair skin. The choroid does not have nerve endings, therefore the processes developing in it do not cause pain to the patient.
ul
How to detect
Melanoma of the eye includes several types: iris, conjunctiva, ciliary or vascular body, eyelid.
Retinal melanoma is a malignant neoplasm that occurs at the site of pigment cells that produce melanin
Tumor on the eyelid
The most dangerous option is a tumor on the eyelid, but it is rare. The tumor spreads from weakly pigmented and pigmented spots, in some cases it goes to the conjunctiva. The main symptom is the presence of a pigmented formation with a stalk, resembling a mushroom. It may be covered with cracks or papillae.
Metastases go to the brain, liver, skin. Melanoma in the eye of the presented type is treated with close-focus radiotherapy. Then the affected areas are removed using an electric knife. No biopsy is performed! If discoloration or increased pigmentation is observed, the prognosis is poor.
Distribution of patients with intraocular tumors by age group (n)
Tumor of the conjunctiva
Melanoma in this type of eye occurs against the background of conjunctival pigmentation as multiple or single nodes. Development is superficial. The tumor is located in the eye at the limbus, near the semilunar fold, near the lacrimal caruncle. If the neoplasm develops from a nevus, it has a dark color and an uneven surface. Large tumors can be pinched between the eyelids.
The neoplasm, located in the conjunctiva of the sclera, often goes deep into the eye. If it is in the lacrimal caruncle, there is a risk of spreading into the orbit. There is a risk of metastases.
Choroidal tumor
The presented melanoma in the eye most often develops in people aged 50-70 years. It appears very rarely in childhood and adolescence. The disease is one-sided. It can have one of two types - planar, nodal.
A neoplasm located in the conjunctiva of the sclera often goes deep into the eye
Planar formation poses a great danger. The diameter of the tumor is approximately 6 mm, the color is brownish to grayish. The spread goes outward; among the symptoms, it is worth highlighting visual impairment. If the tumor is located behind the macula, there may be no symptoms. Then, a year later, the patient may complain of a dark spot in his field of vision.
Further pressure on the eye and pain are noted. At the next stage, the presented symptoms disappear abruptly. Eye mobility decreases, metastases appear in the bones, liver and lungs. This is how the final stage begins.
Iris melanoma
The tumor can appear in any part of the iris. Forms – planar, diffuse, nodal. The coloring is uneven, various brown shades predominate. The course of the disease lasts for more than one year, and the anterior chamber, the surface of the iris, and the ciliary body may be involved in the process. There are no metastases.
Orbital tumor
Symptoms in this case include optic nerve atrophy, pain, impaired mobility of the eyeball, and loss of visual acuity. The initial stage is rare, the secondary form is metastasis.
The tumor can appear in any part of the iris
Tumor of the ciliary body
This tumor is characterized by an asymptomatic course. Changes occur only after the tumor has grown - the anterior chamber may be uneven, the ciliary vessels on the sclera are dilated, the pupillary edge of the iris is flattened. Often the cause of the disease is benign tumors that come from the ciliary body.
ul
Diagnostic methods
To detect melanoma, the following steps are taken:
Angiography
In this case, the doctor gains knowledge of what the blood vessels around and inside the tumor look like. Dye is injected into a vein in the arm and goes directly to the vessels of the eye. The camera detects the dye and takes a photo of the vessels every couple of seconds.
Biopsy
In this case, a tissue sample is taken. A thin needle is inserted into the eye and suspicious cells are transported with it. But, as a rule, there is no need for this method.
Distribution of patients with orbital tumors by age groups
Eye examination
In this case, melanoma in the eye is detected by a simple method - the doctor looks inside the eye using a bright light and a lens. This method is called ophthalmoscopy.
The earlier the diagnosis is made, the better the prognosis
Application of ultrasound
Reviews about this method are positive. High frequency sound waves are used. They are emitted by a transducer. The doctor applies it to the eyelid, and the device produces a clear photo.
The earlier the diagnosis is made, the better the prognosis.
ul
Determination of stage
The stage of melanoma in the eye is determined by the following methods:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
- Blood test for liver function.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- Chest X-ray.
- CT scan.
Treatment is carried out in various ways. The most radical is surgical excision
You can also learn how to identify and treat uveal melanoma.
ul
Treatment of melanoma
Treatment is carried out in various ways. The most radical is surgical excision. But, as a rule, doctors strive to save the eye. In view of this, organ-preserving operations are widely used.
- Cryodestruction. Melanoma in the eye is destroyed using a laser.
- Radiation therapy – internal and external. The tumor is irradiated, as a result it decreases in size, and the affected cells die.
- Diathermacoagulation. The treatment involves the use of high temperatures, which are created by electricity.
Melanoma can even form in the eye. The disease is painful and poses a great threat to the patient’s life.
The presence of a tumor is determined both visually and using modern methods - ultrasound and angiography. The sooner the disease is noticed, the greater the chance of restoring vision and saving the eye.
Cryodestruction, diathermacoagulation, and radiation therapy are used as treatment.
ul
Classification
Depending on the location, the nevus is divided into the following types.
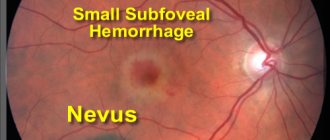
- Nevus of the retina, choroid. Choroidal neoplasms are usually benign and affect the posterior uvea of the eyes. This type of pathology is asymptomatic. Distinctive features of a choroidal nevus: the spot has clear edges and a flat shape, its size remains unchanged for a long time.
- Nevus of the iris. At this point, the amount of melanin determines the color of the formation in the iris.
- Nevus of the conjunctiva. It is rare, affecting about 5% of people. Easily diagnosed due to its specific location.
- Nevus around the eyes. In the practice of ophthalmologists, such a deviation in health occurs quite often, when the formation of moles occurs on the eyelids and nearby integuments, and is easily diagnosed. The color of such nevi ranges from light to dark brown.
Source: https://dermalatlas.ru/razdely-meditsiny/onkologiya/nevus-horioidei-i-raduzhki-glaza-foto-opasnost-diagnostika-lechenie-prognoz/
How is a choroidal nevus formed?
The term choroid refers to the choroid, which runs under the sclera at the back of the eye, maintains intraocular pressure at a constant state and provides nutrition to the cones and rods of the retina.
The choroid consists of several layers, each of which contains pigment cells. The nevus develops from the cells of the supravascular outer lamina, and then can spread to deeper tissues.
A nevus usually begins to develop at the birth of a child, but at this time it is not noticeable. Pigmentation usually begins before the onset of puberty, around 11-14 years of age, with the next burst of pigment accumulation occurring in adulthood. The formations are not pigmented in all patients.
The causes of nevi and their pigmentation are unknown. It occurs in equal numbers in men and women. Often a nevus forms in only one eye.
Nevus
Nevus is the most common benign intraocular tumor, localized in the posterior part of the fundus (89%), about 11% of nevi are located in the equator and preequatorial zone.
Ophthalmoscopically, nevi are detected in 1-2% of the adult population; in older people, the frequency of their detection increases. And at autopsy, according to P.Hale (1965) and J. Hass (1974), the percentage of detection of nevi in the choroid increases to 6.5-20%.
G.Brown et al. (1981) it was suggested that the frequency of nevi is much higher, since about 5% of them are represented by a difficult to diagnose non-pigmented clinical form. Indeed, a thorough ophthalmoscopic examination of a large population group (3654 people) using a single protocol revealed 6.5% of choroidal nevi, 6% of which were weakly pigmented.
Weakly pigmented or non-pigmented nevi are usually localized in the equator and preequatorial region. Most nevi appear from birth, but their pigmentation appears much later, and they are usually discovered by chance after 30 years. In men and women, nevi are diagnosed equally often; the frequency of damage to the right and left eyes is equal; cases of bilateral nevi are not uncommon.
Clinic
For a long time, choroidal nevi are asymptomatic and are the subject of accidental findings during ophthalmoscopy. In the fundus they are represented by flat or slightly protruding foci (up to 1 mm) of a faint gray or gray-green color with feathery but clear boundaries, their diameter ranges from 1 to 6 mm (Fig. 6.16).
Rice. 6.16. Stationary nevus of the chorinoid
The featheriness of the borders, according to J.Shields (1983), is due to the translucency of the red-orange vessels of the choroid in the area where the pigmentation edge intersects. Pigmentless nevi have an oval or round shape, their borders seem smoother, but less clear due to the lack of pigment. In 80% of patients, single drusen of Bruch's membrane are detected.
A similar clinical picture, observed over many years, made it possible to identify such nevi as stationary. As the nevus grows and its size increases, dystrophic changes in the retinal pigment epithelium intensify, which leads to an increase in the number of drusen of Bruch's membrane, the appearance of weak subretinal exudate, and a yellowish halo appears around the nevus (Fig. 6.17).
Rice. 4.17. Progressive nevus of the chorinoid. a - juxtapapillary; b - paramacular
The appearance of these symptoms is associated with tumor growth, compression of adjacent choroidal vessels and the occurrence of stagnant changes around the nevus. The color of the surface of the nevus changes to more intense, its boundaries become less clear.
In some cases, during this period, single fields of orange pigment can be seen on the surface of the tumor. The described picture is regarded by us (1980) as a progressive nevus. When assessing the progression of a nevus localized in the macular zone, one should take into account the possibility of involutional dystrophic changes in the overlying retina in individuals in the 7th decade of life.
In such a situation, ophthalmoscopy of the fundus of the fellow eye helps: the presence of dystrophic changes in it confirms the involutional nature of changes in the retina and pigment epithelium.
Morphogenesis
Melanocytes involved in the development of choroidal nevus are distributed in the choroid, ciliary body, and iris stroma.
They may be visible in the sclera (scleral emissaries, episcleral tissue). G Naumann (1966) believes that melanocytes take part in the formation of several forms of nevi:
1) the spindle cell type is represented by melanocytes with small nuclei and small intraplasmic pigment granules; 2) the egpithelioid cell type is distinguished by large melanocytes containing melanin in the cytoplasm, but there are no signs of polymorphism in the nuclei and nucleoli, which distinguishes nevus from melanoma; 3) balloon nevus is characterized by large spherical melanocytes with foaming, vacuolated cytoplasm. Type 1 nevi are more often present in the choroid. Balloon nevi are quite rare and are clinically distinguished by the yellowish color of the tumor surface.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of nevus is based on a typical ophthalmoscopic picture.
Fundus examination with color filters helps in diagnosis. With ophthalmoscopy in red light, the choroidal nevus becomes especially clearly visible, while when examined in green light, the stationary nevus “disappears”, only changes in the retinal pigment epithelium with a progressive nevus remain visible. Fluorescein angiography
(FA)
is one of the most important diagnostic methods for choroidal nevi. Stationary nevi are characterized by hypofluorescence throughout the entire study; there are no changes in the surrounding vessels or in the choroid, especially when their localization is limited to the outer parts of the choroid.
With progressive nevus, when changes occur in the adjacent choroidal vessels, leading to perifocal stasis, fluorescein leakage appears. On the posterior surface of the retinal pigment epithelium, as the nevus progresses, drusen appear, which penetrate into the pigment epithelium, lift it, forming microdefects.
This contributes to spotty staining of the surface of the nevus; within the 1st minute of angiography, drusen begin to fluoresce, their glow persists throughout the entire period of the study. Fluorescent drusen are located both on the surface of the nevus and along its circumference. As a rule, angiography reveals a significantly larger number of drusen than ophthalmoscopy.
Angiography with indocyanine green largely shows the absence of fluorescence of the nevus at all stages of the study. Visual disturbances with choroidal nevi are usually absent. Secondary changes in the retina can only be detected with precision methods for studying the visual field. Ultrasound diagnostics is not very informative.
Differential diagnosis
Despite the typical clinical picture inherent in choroidal nevi, they still have similar symptoms to a number of diseases. First of all, we are talking about the differential diagnosis of a progressive nevus with initial choroidal melanoma, metastatic carcinoma, choroidal osteoma, delimited choroidal hemangioma, congenital local hyperplasia of the retinal pigment epithelium, reactive hyperplasia of the retinal pigment epithelium, subretinal and subchoroidal hemorrhage.
Treatment
Stationary nevi do not require treatment, but require dynamic monitoring, as they can grow during the patient’s life, moving into the stage of progression and even initial melanoma.
Progressive nevi, taking into account their potential for malignancy, are subject to treatment. For small sizes (up to 8 mm in maximum diameter and elevation up to 1.5 mm), laser coagulation is effective, which should be carried out simultaneously, using the basic principle of tumor treatment: delimiting and destructive coagulation. The exception is progressive nevi located in the central zone of the fundus, when high visual acuity can be impaired during laser coagulation.
In such cases, it is necessary to take into account the patient’s age, the nature of the work he performs, and the possibility of qualified control over the behavior of the nevus. In this case, it is necessary to photograph the fundus in dynamics, noting its size, the nature of the color, its uniformity, and changes in the surrounding retina.
Dynamic FA, ultrasound biometry, central vision examination, and perimetry to identify relative and absolute scotomas are shown. The appearance of the latter, even in the absence of obvious enlargement of the nevus, indicates the beginning of tumor growth.
Forecast
With a stationary nevus, the prognosis is good for both vision and life.
A progressing nevus should be considered as a potentially malignant tumor. Long-term observations (from 5 to 20 years) indicate the possibility of malignancy of the nevus. According to J. Oomley and G. Comstoc (1973), 1 out of 4000-5000 nevi necessarily turns into melanoma. At the same time, observations by Z.L. Stenko and P.A. Vein (1986), G. Naumann (1971) indicate the possibility of malignancy of progressive nevi in 1.6% of cases. A J. Mims (1978) emphasizes the importance of the size of the nevus during its transition to melanoma.
As a rule, up to 10% of nevi exceeding 6.5 mm in diameter and 3 mm in height with changes in the underlying retina become malignant. The role of progressive nevi in the development of choroidal melanoma is indicated by V.V. Vit (1987), M. Yanoff and L. Zimmermann (1987) and this, naturally, worsens the prognosis for both vision and life.
Prevention
There are no specific rules for preventing the development of such neoplasms. Until now, the etiology of such moles is not known. To avoid the development of negative consequences, you should consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Timely diagnosis will help determine the presence of such neoplasms and help get rid of them, especially if the nevi are malignant. Therefore, every person should visit an ophthalmologist 1-2 times a year.
In addition, do not forget to monitor eye and eyelid hygiene. If suspicious symptoms develop, you should consult a doctor. Progressive nevi can affect visual acuity. If the patient observes clouding or distortion of the image, then it is necessary to contact an ophthalmologist.
After a full diagnosis, the doctor will be able to determine the classification of formations and the method of eliminating them. As an additional prevention, you should adhere to a healthy lifestyle. Sleep should be complete, nutrition balanced and rich in vitamins. It is necessary to give up bad habits.
Indications and treatment of uveal nevus
If the nevus is benign in nature, then therapy in the vast majority of cases is not required. However, when a mole is examined once every six months, and then once a year, and during the examination an increase in size is diagnosed, then they resort to electroexcision, which is a method of surgical intervention during which the nevus is eliminated using a special electric scalpel. After the intervention, they resort to plastic surgery.
If the choroidal nevus is progressive, then laser therapy is often used. The formation is exposed to a laser beam, during which the cells evaporate. Photocoagulation is also used, which is a method of getting rid of a mole by destroying the tissue with a light source.
Treatment of choroidal moles in children is carried out only when they begin to increase in size, which is fraught with deterioration of vision.
What is the danger?
Pigment spots can degenerate into a malignant tumor, and choroidal nevus is no exception. The danger is that under the influence of ultraviolet light, nevus cells transform into cancer cells and melanoma is formed. The formation changes size and color. A pigmented nevus of the conjunctiva usually limits the field of vision, in which case the patient is advised to remove the mole with a laser.
Is there any danger?
When the formation of the choroid appears, it does not manifest itself in any way. It can remain unnoticed for many years. However, there is a risk of its degeneration into a malignant tumor. When this happens, a person experiences the symptoms described above. If at least one of them appears, it is important to visit a doctor who will conduct a series of examinations, determine the nature of the mole and prescribe the correct treatment or removal of the tumor.
Doctors say that 1 in 500 nevi transforms into a malignant formation. Constant medical supervision should be carried out when a mole rises above the eyeball by more than 2 centimeters, if it contains subretinal fluid, its color changes, orange spots appear, and when it is localized behind the eyeball. In order to reduce the likelihood of transformation of a benign uveal nevus, it is important to undergo examinations by an ophthalmologist every year and reduce eye contact with ultraviolet radiation. Doctors recommend wearing sunglasses even in winter, since exposure to ultraviolet radiation overtakes you even in cloudy weather. If a person wears glasses for vision, then he should purchase another one with sun protection lenses.
Get your uveal mole examined for a threat to your vision or cancer.
Moles! Who knows their meaning?
I have a mole under my nose on the left side (((I don’t like it, I want to remove it! I don’t know what it means!
Natalia
The interpretation of the location of moles and their influence on a person’s fate is closely related to the science of “reading a person’s face,” physiognomy, which originated in the east. Initially, all moles were assigned a negative meaning, but long-term observations made significant, factually confirmed adjustments. Codes with lists of meanings have developed, by reading which you can learn a lot about yourself and look at your life differently. General characteristics Pay attention to bright, noticeable moles. Small moles scattered throughout the body play virtually no role. If a mole stands out strongly or rises above the skin, this is a lucky sign that mitigates possible unfavorable meanings. For dark-skinned people, black moles are more important, for light-skinned people - convex ones. It is also important which side of the body the mole is on. For men, the right side is favorable, for women - the left. The appearance of new moles, the disappearance or increase in size of existing ones, reflects actions committed by a person that affect future life and, possibly, change fate. Moles on the face Moles on the face are of decisive importance. A mole on the right eyebrow indicates an early marriage, on the left - the likelihood of a late or unsuccessful marriage, celibacy. Above the right eyebrow - energy, enterprise. In the corner of the eye it means passion, jealousy, irritability. A mole under the right eye speaks of marital fidelity, as well as sensuality and generosity. Under the left eye - about experiences in married life. On the right eyelid - about a penchant for intellectual professions. On the left eyelid - about excellent memory and diplomacy, down-to-earthness. On the left side of the forehead - about the wastefulness and weakness of the owner. A mole in the middle of the forehead means numerous victories on the love front. A woman is always surrounded by admirers, and a man is most likely Don Juan! The “third eye” point is a sign of strong intuition, reason, and mysticism. Owners often suffer from headaches. A mole on the nose indicates sociability. On the tip of the nose - a craving for complicating love relationships and everything forbidden. Under the right nostril - the owner has an extraordinary destiny, a mystical mindset. In the center between the nose and upper lip - an indication of independence, love of pleasure. On the bridge of the nose there is a hint of a love of travel, as well as a developed imagination and a penchant for creativity. On the cheekbone - determination (especially if the mole is on the right side), oratory abilities. Under the lower lip is a sign of a fragile psyche and health. Above the upper lip - cruelty, imperious character. On the red border of the lips - weakness of will, inability to take responsibility for one’s actions. In the language - longevity, suspiciousness. On the chin - the desire to have a strong family, conservatism. On the temple - inconstancy, frequent mood changes, variability in views. On the right side - subtle intuition, the gift of foresight, bright individuality. On the right cheek for men - eccentricity, for women - increased male attention. On the left cheek - a sign of innate talent, good memory, for a woman - natural charm.
A mole under the eye or on the lower eyelid - what does it mean?
A mole under the eye means that its owner has a soft and pleasant character, calmness and balance. He is pleasant to talk to, a good friend and a good colleague. The positive energy of such a person makes him a welcome guest. He is distinguished by optimism and the ability to listen; communicating with such a comrade is always interesting.
Such individuals love animals and children. They are able to take care of even a casual acquaintance who gets lost in a strange city, loses his wallet, or gets into other troubles. They do not allow themselves to be deceived, because they value the results of their work too much and are distinguished by their frugality.
A mark under the eye indicates that you are marked by the goddess of fortune. You will be lucky throughout your life. Troubles are a rare guest on your life path. Most likely, you are unpretentious, and your average income is enough for your comfort. However, money issues will not be a problem either; owners of such moles are able to earn a good fortune.
If the mole near the eye is on the left side, closer to the temple, then caring may border on self-sacrifice. These qualities are combined with confidence and perseverance, so it is almost impossible to convince a friend with such a characteristic mark on his face to stop picking up street animals. These people often find themselves in charity, choose the profession of social workers, and engage in volunteer activities. If they have the financial means, they become philanthropists.
Among the meanings of a mole under the left eye, there is also popularity among members of the opposite sex. You know how to win someone you like. Such people make faithful wives and husbands who are able to provide for their families and create comfort in the home. A mole located on the opposite side of the face also speaks of a person’s sensuality and attractiveness.
If the location of such a mark is under the right eye, then we are talking about a person who is distinguished by a rare sense of purpose. He is able to move in the direction of his dreams throughout his life. Such people almost always achieve what they set out to do. Even where others give up and move on to another goal, they continue to move forward.
–>
If there is a mole under the eye, what does it mean?
You need to pay attention even to what part of the face they are located on. If on the left, this means that throughout life a person faces many small unpleasant situations that have to be dealt with. It also means a long life and a comfortable old age.
Women who have moles located on the right side of the left eye often face misunderstanding and betrayal from loved ones. Sexual people prone to cheating have nevi in the inner corners of the eyes.
Pigmented formations, namely moles under the right eye in women, are a symbol of attractiveness and easy fate. It also matters what part of the face they are located on.
What does a mole under the left eye mean?
If a pigment formation is located under the left eye on the inside of a woman, this indicates her wealth. Any business that a lady undertakes brings her profit. The owners of such spots are very smart and also have a creative nature.
A nevus located near the left eye in the inner corner is a sign of a flighty, fickle nature.
A mole under the left eye testifies to the modest nature of the hostess and her promiscuity in everything. She does not attach much importance to household chores and fashionable clothes. Such a woman pays special attention to feelings and experiences. If the spot is located closer to the ear, then such an owner is capable of self-sacrifice for the sake of another.
If such a spot is located closer to the nose, it is a symbol of passionate and jealous women. They are selfish, and there is constant chaos and movement around them.
The sign of a career woman has always been a nevus located under the right eye, right in the middle. Such women achieve heights at work, but in love affairs they have difficulties - it is difficult to find a good, reliable partner, although they are faithful and sensitive. Such people can become your most loyal and devoted friend for life. If you are lucky enough to meet people with these markings, hold on to them with both hands and appreciate them.
If the mole is located under the lower eyelid of the right eye, you are looking at a real optimist. This cheerful person with a good mood is always the center of attention. People with these spots are very energetic and kind to others. Communication with them brings only pleasure and makes you smile.
A cute mark under the eye in the cheek area is a symbol of a passionate person who always has chaotic relationships with the opposite sex.