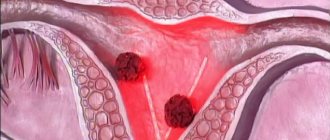
Glaucoma is a pathology of the organ of vision, accompanied by increased intraocular pressure, a disturbance between the production and outflow of intraocular humor, deterioration of vision and atrophy of the optic nerve.
For treatment, in some cases, you can get by with eye drops, following recommendations for doing exercises, taking vitamins and nutrition, and additional folk therapy. In other cases, only surgical or laser treatment is indicated.
Glaucoma cannot be completely cured. When the first symptoms appear, the condition may stabilize. In advanced forms of the disease, the eyeball is deformed, the optic nerve atrophies, and the resulting deterioration of vision or blindness is not corrected.
Is it possible to treat glaucoma on your own?
Fighting glaucoma on your own without the consultation and help of an ophthalmologist is ineffective. Treatment of the disease includes:
- diagnosing the form;
- identification and, if possible, elimination of the provoking factor;
- stabilization of intraocular pressure using instillation of eye drops;
- regulation of the balance between the production and outflow of intraocular fluid;
- inhibition of dystrophic and atrophic processes;
- prescribing additional medications for the treatment of underlying diseases that provoked glaucoma;
- compliance with preventive measures, performing eye exercises and taking multivitamin complexes.
Is it possible to completely cure glaucoma without surgery?
It is impossible to completely cure glaucoma without surgery for two reasons.
Firstly, therapy is aimed at maintaining the functionality of the eye, reducing IOP, and restoring the balance between the production and outflow of moisture. Secondly, the disease causes irreversible processes - atrophy of the optic nerve, deformation of the eyeball, blurred vision and blindness.
Drug treatment of primary glaucoma
Conservative treatment of glaucoma is carried out using medications in 3 areas:
- Ophthalmic hypotensive therapy to reduce intraocular pressure;
- Improving blood supply to the internal membranes and intraocular segment of the optic nerve;
- Normalization of metabolic processes of eye tissues to inhibit the degenerative processes of glaucoma.
It is immediately necessary to stipulate that the key issue in the treatment of the disease is the issue of normalizing the level of intraocular pressure (IOP). The remaining methods are only auxiliary in nature. To these can also be added the organization of the correct work schedule for a patient with glaucoma and his daily life.
When starting regular use of antiglaucoma drops, the patient should know what options exist for their effect on intraocular pressure:
- IOP decreases after a single application (instillation) of the drug. Each repeated instillation regularly repeats this effect;
- The effect of the drug is delayed. At first it is weakly expressed, but intensifies in the following days of regular instillation of the drug;
- There is resistance to the drug from the very beginning, and it has no effect on intraocular pressure;
- The drug has an unexpected effect, i.e. the pressure after instillation does not decrease, and sometimes even increases quite significantly. Therefore, a test is required for each antiglaucomatous drop.
In this regard, prescribing medications to lower IOP levels is the prerogative of the doctor. An ophthalmologist, when choosing the drug needed in a particular case, is able to take into account many factors that are completely unknown to the patient. Therefore, you cannot prescribe or stop antiglaucoma medications on your own! Even if the frequency of instillation is changed, it is necessary to consult with your doctor.
When prescribing a certain regimen of instillation of antiglaucoma drops, the patient must be observed by an ophthalmologist for 2-3 weeks dynamically. Further, treatment monitoring should be carried out every three months. Every 1-2 years, it is recommended to change medications, with appropriate monitoring.
Medicines used in the treatment of glaucoma are divided into two groups: drugs that accelerate the outflow of intraocular fluid and drops that inhibit its production.
Treatment of acute glaucoma
In case of an acute attack of glaucoma and a severe form of the disease, the use of folk remedies is unacceptable. Unconventional methods can only be an additional measure to the main treatment prescribed by a specialist.
During an attack of acute glaucoma, the following drugs are prescribed:
- miotics, or drugs for constriction of the pupil, lowering IOP and spasm of accommodation (Pilocarpine up to 3-6 times a day, for diagnosis every 10-15 minutes);
- beta-blocker Timolol 0.5% or 0.25% to reduce IOP, normalize the outflow of intraocular humor and reduce its formation in the morning and evening;
- Diacarb to reduce blood pressure and reduce swelling - 0.25 mg tablet three times a day;
- if other drugs are ineffective - Lasix or Furosemide once a day, preferably in combination with Asparkam or Panangin tablets to replace calcium;
- it is possible to replace or supplement drugs with Dorzolamide (Dorzopt), Brinzolamide (Azopt) and other eye drops, used 1-2 times a day depending on the medication;
- Fotil and Fotil forte are combination drugs containing Pilocarpine and Timolol.
All medications are used as prescribed by a doctor in recommended dosages and are sold in pharmacies with a prescription. Self-medication during an acute attack of glaucoma is unacceptable. It is the specialist who diagnoses the cause of the disease, accompanying factors (increased IOP or normal, increased production of intraocular fluid, impaired outflow) and selects groups of medications.
Laser treatment of glaucoma
Laser glaucoma surgery is used to eliminate intraocular blocks that occur when intraocular fluid drains from the eye.
Lasers in glaucoma surgery began to be widely used in the 70s of the last century. Today, argon laser systems (with wavelengths of 488 and 514 nm), as well as neodymium YAG lasers (with a wavelength of 1060 nm) or semiconductor (diode) lasers (with a wavelength of 810 nm) are most often used.
When exposed to a laser, a local burn is applied to the trabecular area, which subsequently causes atrophy and scarring of its tissue (coagulation), or a microexplosion is performed, with tissue rupture by a shock wave (destruction).
There are many laser operations, however, only two are most widespread:
- Laser trabeculoplasty.
- Laser iridotomy (iridectomy).
Laser surgeries have their advantages and disadvantages. The benefits of laser treatment include:
- Restoring the outflow of intraocular moisture naturally;
- Carrying out the intervention under local drip anesthesia without the use of general anesthesia;
- Performing the operation on an outpatient basis;
- Short rehabilitation period;
- Absence of complications inherent in traditional glaucoma surgery;
- Relatively low cost.
The disadvantages of laser treatment for glaucoma include:
- Limited effect of the operation and its reduction in advanced cases of the disease;
- The occurrence of a reactive syndrome, with an increase in intraocular pressure immediately after laser intervention, as well as the subsequent development of the inflammatory process;
- Risk of damage to the tissue of the posterior epithelium of the cornea, iris vessels, and lens capsule;
- The occurrence of synechiae (adhesions) in the iridotomy area (angle of the anterior chamber).
When performing laser iridectomy (iridotomy), a small hole is created in the peripheral part of the iris. The operation is prescribed if there is a functional pupillary block, and its implementation allows you to open the angle of the anterior chamber and equalize the pressure in each of the chambers of the eye. The use of iridotomy is possible in the case of angle-closure glaucoma (primary, secondary), or in a mixed form of the disease. Sometimes it is required after surgery for glaucoma.
Laser iridectomy is often performed on the second eye for prophylactic purposes during an acute attack of primary angle-closure glaucoma.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia (introducing a solution of lidocaine, inocaine, etc. into the eye). A special goniolens is placed on the eye, which allows laser radiation to be focused on a selected area of the iris. Iridectomy can be performed in any quadrant and is performed in several stages in different sectors of the iris in thinned areas.
In some cases, it is not possible to obtain a through hole in the iris, or it closes very quickly due to the formation of synechiae and pigment deposition. In this regard, repeated intervention is required.
Laser trabeculoplasty is performed by applying a series of burns to the inner trabecular surface. This effect improves the permeability of the trabecular diaphragm for aqueous humor and reduces the risk of Schlemm’s canal block. The mechanism of action of the operation is characterized by tension and shortening of the trabecular diaphragm due to wrinkling of tissue at the burn site, with widening of the trabecular slits in the areas between burns.
The operation is prescribed in the surgery of primary open-angle glaucoma, when drug therapy is ineffective. The procedure is performed using local anesthesia. During this procedure, a goniolens is placed on the eye. According to the particularly popular technique of linear trabeculoplasty today, one row of burns is performed in the area of Schlemm’s canal.
Gymnastics for the eyes
Eye exercises are an unconventional way to improve the quality of vision, reduce the adverse effects of excessive visual stress on the eyes and relieve fatigue.
After each exercise, you need to blink for 50-70 seconds.
A complex of gymnastics for the eyes for glaucoma:
- slow rotation of the eyeballs clockwise, then in the opposite direction;
- initial position – completely relaxed eyes, then close your eyes tightly for 3-5 seconds, then return to the starting position and repeat 5 times;
- acupressure of closed eyes, temples, eyebrows;
- draw a bow using eyeball movements - to do this, first look at the upper right corner without turning your head, then at the lower right, upper left and complete the drawing at the lower left, slowly do 5-8 repetitions.
It is important not to make sudden movements when performing eye exercises.
Stages of pathology
There are several sequences of disease development:
- At the first stage, a slight increase in intraocular pressure appears. The patient may feel almost nothing. A similar situation occurs, for example, during inflammatory processes (conjunctivitis, blepharitis).
- Intraocular tone at the second stage leads to disruption of local blood flow, and this, in turn, causes oxygen deficiency. The person begins to feel a decrease (narrowing) of the visual field.
- At the third stage, symptoms progress sharply. Currently, the patient's field of vision is represented by only small areas with optimal visibility. The nerve endings responsible for the conduction of impulses are compressed under the pressure of increased tone and are gradually destroyed and die.
- At the fourth (terminal) stage, a person no longer has objective vision. All he can do now is distinguish between light and dark. Usually, complete blindness follows when the last nerve endings cease to function.
Vitamins
For eye health, preventing the progression of glaucoma and other ophthalmological diseases, it is necessary to receive beneficial microelements and vitamins:
- lutein;
- zeaxanthin;
- anthocyanins;
- selenium;
- vitamin C;
- B vitamins;
- vitamin E and A.
This can be done in two ways: enriching the diet with useful substances, taking multivitamin complexes. Pharmacy organizations offer drugs and supplements - Vitrum Vision, Blueberry forte regular and with lutein, Complivit ophthalmo, Visionace, Myrtilene and others.
Dietary recommendations
A diet rich in beneficial microelements and vitamins and minimizing harmful foods that affect the health of the eyes and the body as a whole are the keys to successful prevention and treatment of glaucoma.
Prohibited products:
- alcohol;
- fatty, salty, smoked foods;
- strong tea;
- concentrated meat broths;
- pickled, soaked foods;
- baked goods, chocolate, sugar, other fast carbohydrates.
We recommend reading: Nutrition for glaucoma
It is advisable to include in the diet:
- fruits and berries, fresh vegetables (especially blueberries, blueberries, rose hips, cabbage, spinach);
- various oils (olive, sunflower, flaxseed, hemp, corn, peanut);
- fish;
- nuts;
- cereals, yeast;
- meat.
Folk remedies
Recipes for alternative and traditional medicine are new in the treatment of glaucoma, when conservative therapy is unaffordable or ineffective. However, they should be used after consulting an ophthalmologist, if there are no restrictions or contraindications, and the benefits outweigh the possible risks.
Calendula
Take dry grass in bulk or in filter bags in the amount of 1 bag or 2 tbsp. l., pour a glass of boiling water and leave for 90 minutes, strain. Use the resulting solution for eye rinsing and lotions. You don’t have to throw away the brewed bags with medicinal herbs, but put them on your eyelids for 2-3 hours before going to bed.
Honey
Bee products, in particular honey, are included in many traditional medicine recipes for glaucoma. Before use, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of an allergic reaction to the component.
Mix honey and onion juice in equal proportions and drop them into your eyes. This method should be used in the absence of contraindications and allergies to components.
Another recipe is to dissolve candied honey (1 tsp) in a cup of cooled strong tea and drop the prepared solution into each eye twice a day. The next day, prepare a new solution for instillation. You can make compresses at night by dissolving 1 tsp. honey in the same amount of water.
Then soak cotton pads with the resulting product and apply to closed eyes. Do it every evening before bed for up to 2 weeks; repeat after a 5-day break is possible.
Chickweed
Pass fresh chickweed grass, or woodlice in other words, through a meat grinder or juicer to obtain thick juice. Dilute the resulting component with purified alcohol, taking 1000 ml of juice and 100 ml of alcohol. Place the tincture in the refrigerator for a couple of days, take 50 ml twice a day.
Aloe
This medicinal plant is found in almost every home; it has many medicinal properties and is used for glaucoma. To do this, tear off 3-4 fresh leaves from the aloe and pour in 0.2 liters of water, put on fire, bring to a boil and cook for 5 minutes after boiling.
Cool and strain the resulting broth, use for up to 2 weeks three times a day to wash the eyes.
Nettle and lily of the valley
The product is used for compresses in the morning and evening for 10-15 minutes. To do this, grind half a glass of nettle shoots and the same amount of lily of the valley leaves. For one use, mix a teaspoon of crushed raw materials, add cold water and leave for a day. The next day, soak cotton pads in the solution and place them on closed eyelids.
Motherwort
The herb has a beneficial effect on blood vessels, heart, blood pressure and nervous system. You can use fresh raw materials or buy crushed herbs in bulk or bags at the pharmacy.
2 tbsp. l. motherwort, pour 250 ml of boiling water and leave for an hour, strain through cheesecloth. Drink the resulting infusion three times a day, one tablespoon at a time, for a month, repeat if necessary after a 10-day break.
Potato
Grate the potato tubers on a fine or medium grater, add a spoonful of apple cider vinegar. Stir the mixture and leave for half an hour. Then apply to gauze or cotton cloth, wrap the cloth on both sides, apply to closed eyelids and press with your hands for better contact.
The compress relieves pain and pain in the eyes, applied for 20-30 minutes until 10-14 days until the symptom disappears.
Dill
Take linen, canvas or cotton bags and place 1 tablespoon of dill seeds in each. Boil water, place the bags inside and bring to a boil. After cooling, use as compresses on the eyes.
Another way to use dill for glaucoma to reduce intraocular pressure is to prepare a decoction for oral administration. For this, 2 tsp. dill seeds pour 500 ml of water, boil for 10 minutes, remove from heat and leave to infuse for 30-60 minutes. Strain the resulting broth and take 50 ml three times a day half an hour before meals.
Store the prepared solution in the refrigerator for up to a week, making sure that the solution does not change the smell, taste, color and other properties.
Drug therapy for glaucoma
Data on disability and blindness from glaucoma show that in Russia this nosology ranks first among the causes of irreversible vision loss. If we consider an unselected group of glaucoma patients registered for the first time, then only 55-60% of them can be effectively treated with medications, subject to a rational and, most importantly, individual approach to the use of antihypertensive drugs. Considering the complexity of this problem, in April 1998, the V Russian National Congress “Man and Medicine”, after almost a year of discussion, adopted the federal program “Rational treatment of glaucoma” (authors A.P. Nesterov and E.A. Egorov), which contains sufficient detail All issues of drug treatment of glaucoma are considered. This article will present some aspects of this program that are of interest to doctors not only in ophthalmology, but also in other specialties. Antiglaucomatous drugs include miotics,
a2 - adrenergic agonists, adrenaline preparations, b - blockers, prostaglandins F2a and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors.
Antihypertensive drugs can be divided into two groups according to their effect on the hydrodynamics of the eye: drugs that improve the outflow of aqueous humor (AH) from the eye, and drugs that inhibit its production.
Drugs that improve outflow Cholinomimetics
The main advantage of cholinomimetics lies in the pathogenetic validity of their effect on intraocular pressure (IOP).
By narrowing the pupil and pulling the iris root away from the angle of the anterior chamber, they improve the access of IVs to the drainage system of the eye. At the same time, the trabecular diaphragm stretches, its permeability increases, and Schlemm’s canal expands. At the same time, their continuous use can lead to fibrous degeneration of the intraocular muscles, irreversible miosis, increased permeability of the vessels of the anterior eye, changes in the composition of the EV, and the formation of posterior synechiae. Pilocarpine
is a plant alkaloid obtained from the Pilocarpus pinnatifolius Faborandi plant.
This is the most well-known and used antiglaucoma drug. Available in the form of eye drops of 1, 2 or 4%, containing in 1 ml of solution 0.01, 0.02 or 0.04 g of pilocarpine hydrochloride or pilocarpine nitrate, packaged in dropper tubes of 1.5 ml or in bottles of 5 , 10 and 15 ml. Scheme of distribution of antihypertensive drugs at points of application
| Group | Subgroup | Name of main drugs |
| Products that improve outflow | ||
| Cholinomimetics | M-cholinomimetics | Pilocarpine |
| Sympathomimetics | a- and b-stimulants | Epinephrine, dipivalyl epinephrine |
| Prostaglandins | Prostaglandin F2a | Latanoprost |
| Product inhibitors | ||
| Sympathomimetics | a2-stimulants | Clonidine |
| Adrenergic blockers | a- and b-blockers | Proxodolol |
| b1-blockers | Betaxolol | |
| b1, 2-blockers | Timolol maleate | |
| Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors | Dorzolamide hydrochloride | |
| Combination drugs | Fotil, timpilo | |
The most commonly used are 1 and 2% solution concentrations. A further increase in concentration does not lead to a significant increase in the hypotensive effect, but significantly increases the risk of adverse reactions. The duration of the hypotensive effect with a single instillation of pilocarpine solution varies individually and ranges from 4 to 8 hours. In prolonged pilocarpine eye drops, 0.5 or 1% methylcellulose solution, 2% carboxymethylcellulose solution or 5–10% polyvinyl alcohol solution are used as a solvent, which allows increase the duration of action with a single instillation to 8 - 12 hours. Among the side effects of pilocarpine, miosis should be noted, which occurs 10 - 20 minutes after instillation and lasts up to 6 hours. With long-term use, miosis persists constantly. This is important in elderly patients with phacosclerosis or incipient cataracts, since against the background of a narrow pupil they note a significant decrease in visual acuity. It should be noted that a relative spasm of accommodation appears 10 to 30 minutes after using the drug. In this regard, maintaining a constant high concentration of the drug in the tissues of the eye is impractical, since this creates conditions for a decrease in effectiveness and also leads to persistent spasm of the ciliary muscle. The functional state of the ciliary muscle is very important for the “gymnastics” of the eye. Microcontractions of this muscle constantly massage the trabecular apparatus, shaking and cleansing it, improving blood supply. Therefore, periodic (for 1–3 months) withdrawal of pilocarpine and its replacement with non-miotic antiglaucoma drugs are desirable throughout the year. Sensitive patients may notice a transient headache after instillation, especially when using high concentrations of the drug. With long-term use, some patients experience the occurrence of follicular conjunctivitis. The use of pilocarpine is contraindicated in iritis, iridocyclitis, and iridocyclitic crises. Its use is also undesirable for other inflammatory diseases of the anterior part of the eye. a- and
b -stimulants
This subgroup includes epinephrine and epinephrine dipivalyl, which are direct stimulators of a- and b-receptors of various localizations.
Epinephrine
(adrenaline) is one of the first sympathomimetics for the treatment of open-angle glaucoma.
In the treatment of glaucoma, high concentrations of epinephrine are used - 1 and 2% solutions. The mechanism of the hypotensive effect of epinephrine consists of two active factors. Firstly, epinephrine improves the outflow of explosives from the eye through the drainage system, and secondly, it briefly and slightly inhibits its production. According to some data, epinephrine is able to somewhat improve the outflow of fluid along the uveo-scleral pathway. Local side effects with long-term use of epinephrine include conjunctival hyperemia, chronic allergic conjunctivitis, and lacrimation. Such reactions can occur in more than half of patients. Another common complication is dark pigmentation of the edges of the eyelids, conjunctivitis and, less commonly, the cornea. A very serious complication of epinephrine treatment is the occurrence of macular edema, which occurs in aphakic eyes. General side effects include increased blood pressure, tachycardia, arrhythmia, pain in the heart, and cerebrovascular disorders. The use of the drug is contraindicated in case of angle-closure and mixed glaucoma, hypersensitivity to epinephrine, arterial hypertension, severe atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis. You should also limit the use of epinephrine eye drops during pregnancy. Dipivalyl epinephrine
is the modern dosage form of epinephrine.
It is available in the form of eye drops with a concentration of 0.1% solution of the active substance in plastic dropper bottles with a capacity of 10 ml. Dipivalyl epinephrine is a precursor that, when passing through the cornea, is biotransformed into epinephrine. Epinephrine dipivalyl is highly lipophilic and penetrates the eye tens of times more easily. The hypotensive effect of a 0.1% solution of dipivalyl epinephrine corresponds to the effect of a 2% solution of epinephrine. Usually the drug is prescribed 1 - 2 times a day. Local side effects are less pronounced than when using epinephrine. Pigmentation of the anterior part of the eye and eyelids, as well as toxic maculopathy, are much less common. Due to the low concentration of dipivalil epinephrine eye drops, its indications for use are expanding in elderly patients and people suffering from arterial hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases. Prostaglandin F 2 a
Latanoprost is a precursor to prostaglandin F2a, developed in recent years specifically for the treatment of glaucoma.
Latanoprost reduces ophthalmotonus by stimulating uveo-scleral outflow through the ciliary body into the suprachoroidal space and then into the episcleral veins. The effect of the drug is associated with interaction directly with prostaglandin F receptors. Latanoprost is available as a 0.005% solution in 2.5 ml dropper bottles. It is recommended to instill once a day. The hypotensive effect of latanoprost with long-term use corresponds to the effect of a 0.5% solution of timolol maleate. Of the side effects identified to date, it should be noted that 3 months after the start of treatment, there is an increase in pigmentation of the iris from blue to brown. Data also appeared on the development of anterior uveitis and macular cystic edema during treatment with latanoprost. Agents that inhibit the production of a 2 -Stimulants
Clonidine is available in the form of eye drops in concentrations of 0.125, 0.25 and 0.5% in 1.5 ml dropper tubes and 5 and 10 ml bottles. Clonidine helps reduce the production of intraocular fluid. Iphthalmotonus decreases rapidly under the influence of clonidine. The hypotensive effect appears within 30 minutes, its maximum occurs 3 hours after instillation and lasts up to 8 hours. It is recommended to instill 2 - 4 times a day. Local side effects manifest themselves in the form of complaints of burning in the eye, foreign body sensation, dry mouth (about 20% of patients), nasal congestion, hyperemia and swelling of the conjunctiva (15% of patients), chronic conjunctivitis.
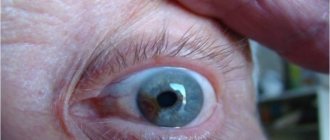
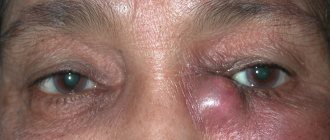
Red eye syndrome in the practice of a therapist. Ocular manifestations of systemic diseases.
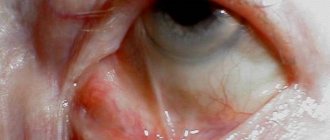
Iritis in Behçet's disease. Red eye, beginning hypopyon (pus in the anterior chamber of the eye)
Scleritis in rheumatoid arthritis. Pain in the eye area, dilatation of superficial and deep vessels of the sclera, swelling of the conjunctiva
Episcleritis in rheumatoid arthritis. Only the superficial vessels of the sclera and conjunctiva are dilated. There may be no pain.
Hypopyon. Causes: Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, sarcoidosis, Behçet's disease, tuberculosis (from Diagnostic picture tests in clinical medicine, GSJ Chessell, et al. and Oxford textbook of medicine. Ed. DJ Weatherall)
Adverse reactions of a general nature manifest themselves in drowsiness, slowing down the speed of mental and motor reactions. Less often, patients report nervousness and anxiety. Bradycardia, constipation, decreased ventricular secretion, and impotence may occur periodically. It should be noted that even when applied topically as eye drops, clonidine can reduce systemic systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Contraindications for the use of clonidine are increased individual sensitivity to the drug, inflammatory diseases of the anterior part of the eye and some general diseases, such as severe cerebral atherosclerosis, severe sinus bradycardia, occlusive diseases of the peripheral arteries, and depression. a- and
b -adrenergic blockers
Proxodolol is available in the form of eye drops with a concentration of the active substance in solution of 1 and 2% in glass bottles of 5 ml and in dropper tubes of 1.5 ml.
It is recommended to use 2 - 3 times a day. The hypotensive effect is quite pronounced. The maximum reduction in IOP is about 7 mm Hg. Art. from the initial level. The effect after a single instillation lasts up to 8 - 12 hours. The mechanism of reducing ophthalmotonus is manifested in the inhibition of intraocular fluid. Side effects include bradycardia, arterial hypotension, and bronchospasm in patients sensitive to proxodolol. In this regard, the drug is contraindicated for use in patients with bronchial asthma, other chronic lung diseases, heart failure, severe bradycardia, and arterial hypotension. b 1 -blockers Betaxolol
is a selective b1-blocker of prolonged action.
Available in the form of a 0.5% solution in plastic dropper bottles of 5 ml. The decrease in IOP under the influence of a single instillation of betaxolol lasts up to 12 hours. When using it, miosis, spasm of accommodation, and visual impairment are not observed. It is usually recommended to use 2 - 3 times a day. Local side effects include short-term discomfort in the eyes and lacrimation that occurs immediately after instillation. Rarely, a decrease in the sensitivity of the cornea, its spotty coloration, and anisocoria are detected. General adverse reactions with topical use of betaxolol are minimal and rare. However, betaxolol should be used with caution in patients receiving additional oral b-blockers, reserpine, adrenergic psychotropic substances, diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis, and bronchial asthma. b 1,2 -Adrenergic blockers
Of the drugs in this subgroup, timolol maleate is the most widely used in our country.
Timolol maleate
is the most famous representative of non-selective beta-blockers for the treatment of glaucoma.
Available in the form of eye drops in two concentrations of 0.25 and 0.5%, with 1 ml containing 2.5 and 5 mg of active substance, respectively. Packaged in glass or plastic bottles, equipped with droppers, with a capacity of 5 ml. The mechanism for reducing ophthalmotonus of timolol maleate is to inhibit the secretion of EVs. With long-term use, tonographic studies show a moderate improvement in the outflow of fluid from the eye. The hypotensive effect occurs 20 minutes after instillation, reaches a maximum after 2 hours, and lasts for at least 24 hours. The reduction in IOP is about 35%. Timolol maleate is instilled 1-2 times a day. Timolol maleate, when applied topically, does not affect the diameter of the pupil, does not cause a spasm of accommodation, and does not significantly change blood circulation in the anterior part of the eyeball. Local adverse reactions manifest themselves in dry eyes, irritation of the conjunctiva, swelling of the corneal epithelium, pinpoint superficial keratitis, and allergic blepharoconjunctivitis. There are, although very rare, quite serious side effects of a general nature. In case of hypersensitivity to timolol maleate, even a single instillation can cause a drop in blood pressure up to collapse. Quite often, especially at the beginning of treatment, bradycardia, arrhythmia, dizziness, and muscle weakness are observed. Recently, data have been provided on the inhibitory effect of the drug on mental status. It can cause depression and psychoasthenia. Timolol maleate
is contraindicated for use in patients with corneal dystrophies, dry keratitis, hypersensitivity to it, bronchial asthma, chronic pulmonary diseases, sinus bradycardia, heart failure.
Should be used cautiously in patients with diabetes mellitus, especially those with a labile course. Timoptic-depot
is a new prolonged dosage form of timolol maleate.
Available in two concentrations (0.25 and 0.5%) in bottles equipped with dispensers designed for 1 drop of solution. The drug is used only once a day, since the duration of its hypotensive effect with a single use exceeds 24 hours. Thus, the total amount of the drug entering the body is reduced by 2 times. Due to this, the tolerability and safety of the drug increases, and general adverse reactions decrease. Economic calculations have shown that the use of timoptic depot is more cost-effective for the patient than the use of conventional non-extended timolol maleate. The combination drugs Fotil, Fotil-Forte and Timpilo
are a combination of timolol maleate and pilocarpine.
By acting on various points, they enhance the hypotensive effect. Fotil and timpilo are a combination of a 0.5% solution of timolol maleate and a 2% solution of pilocarpine, with 1 ml containing 5 mg of timolol maleate and 20 mg of pilocarpine hydrochloride. Fotil-forte contains a combination of 0.5% timolol maleate and 4% pilocarpine solution, active substances in 1 ml - 5 mg timolol maleate and 40 mg pilocarpine hydrochloride. After instillation of the drug, an effective decrease in IOP occurs starting from the second hour, the maximum effect occurs after 3 - 4 hours, the duration of the hypotensive effect is about 12 hours. It is recommended to use Fotil and Fotil-Forte 1 - 2 times a day. Local adverse reactions are more pronounced when using Fotila Forte due to the higher concentration of pilocarpine. They manifest themselves in a quickly passing burning sensation, pain in the eye, blurred vision, and conjunctival hyperemia. With continued treatment, these phenomena decrease. Systemic adverse reactions correspond to reactions characteristic of both drugs separately. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors Dorzolamide hydrochloride
is a new topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitor used as eye drops and is a 2% aqueous solution of dorzolamide hydrochloride, packaged in 5 ml dropper bottles.
The maximum hypotensive effect begins 2 hours after instillation of the drug and lasts 12 hours. Dorzolamide hydrochloride combines well with almost all antihypertensive drugs, giving a potentiation of the therapeutic effect. The local carbonic anhydrase inhibitor dorzolamide hydrochloride is used for complex additional therapy 2 times a day, when used separately - 3 times a day. During the observation of the patients, no serious side effects were noted, with the exception of a slight short-term burning sensation in the eye immediately after instillation, which was noted by 80% of the subjects, and bitterness in the mouth (15%). A rational approach to the prescription of antihypertensive drugs
A rational approach to antihypertensive treatment of glaucoma is determined by the clinical form of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient. The drugs of first choice are currently b-blockers (timolol maleate), as well as a cholinomimetic (pilocarpine). The combination of a beta-blocker and a cholinomimetic makes it possible to influence both the production of explosives and its outflow (combined drugs timpilo, fotil, fotil-forte). The remaining ophthalmic hypotensive drugs (anticholinesterase drugs, sympathomimetics, prostaglandins, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors) are second-choice drugs. They are prescribed for intolerance or insufficient effectiveness of b-blockers and/or pilocarpine. To reduce the negative effect of the addictive phenomenon, it is advisable to annually replace medications for 2 - 3 months, using second-choice drugs for this. Temporarily replacing the drug with another allows you to restore its hypotensive effect. It should also be borne in mind that each antihypertensive drug not only reduces IOP, but also affects various natural metabolic processes in the eye. Periodic change of medications helps maintain normal metabolism.
Treatment of an acute attack of glaucoma
A special place is occupied by the treatment of an acute attack of glaucoma, which is one of the emergency conditions in medicine. In other words, first aid in this situation must be provided by a doctor of any profile without fail. The recommended technique is to prescribe pilocarpine every 15 minutes during the first hour, then 2 times every hour and subsequently every 4 hours. At the same time, timolol maleate is instilled 2 times a day. Orally, the patient receives acetazolamide (0.25 g 4 times a day) and glycerol (at the rate of 1 g per 1 kg of body weight 1 time a day). Among the general procedures, hot foot baths are used; in the field, a saline laxative can be given. In the future, the patient should be urgently referred to a specialized ophthalmological appointment for hospitalization and further management. An attack that cannot be controlled within 24 hours is subject to laser or surgical treatment.
The effectiveness of home treatment
Traditional methods and adherence to recommendations are effective at the initial stage of glaucoma and in the complex treatment of advanced forms. The following must be observed:
- drinking regimen - no more than 3 liters per day, preferably in small quantities at a time to prevent increased IOP and edema;
- avoid high temperatures, do not visit baths and saunas;
- minimize strong physical activity, heavy sports;
- do not tilt your head forward for a long time, avoid washing by hand in this position, washing floors, etc.;
- food should be as healthy as possible, exclude alcoholic beverages, salty, fatty and fried foods.
Compliance with home treatment methods allows you to delay complications of the disease, in particular visual impairment and blindness.
Prevention
The best prevention of glaucoma is its detection in the early stages and comprehensive treatment. It is prevention that will help maintain excellent vision and eliminate early blindness. In the early stages, the disease is extremely difficult to detect due to its almost asymptomatic course. Therefore, doctors recommend regularly visiting a doctor for examination. After forty years, it is necessary to visit an ophthalmologist every six months.
The doctor may prescribe a course of treatment with drops. They will reduce internal pressure and excessive moisture release. But during treatment, you should strictly follow the doctor’s instructions. You should not skip taking medications, as then the whole process will not be beneficial.
In addition, in the initial stages, the doctor may prescribe restorative treatment. Its nature and duration depend on the individual characteristics of the person. This treatment is recommended to be carried out regularly, approximately every two to three years. If the patient is at risk, then he should take care of his body and reduce physical and psychological stress.
An elderly person needs to know the causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention of glaucoma. This will allow him to quickly begin therapy when the disease occurs.