What is strabismus?
In this article
- What is strabismus?
- Why does strabismus occur in children?
- Strabismus in infants. Characteristics of the pathology
- How to determine strabismus in newborns. What types are there?
- True strabismus. Its types
- Recommendations
To understand the reason for the appearance of strabismus in a newborn, let’s understand the term and features of this pathology. So, strabismus (strabismus) is an abnormal phenomenon of the visual organs in which some eye muscles do not work properly. This is where the incorrect location of the eyeballs comes from: they “look” at each other or in different directions (depending on the type of strabismus). Most often, pathology is detected in children and is considered the absolute norm until a certain age (three years). That is, until all the eye muscles learn to work synchronously. Strabismus is usually diagnosed in the first days of life. It is very important to start treating the disease at an early age, before the muscles have become stronger. Sometimes the pathology occurs in adults, but rarely. In this case, experts see the reason in external factors. Or it is an advanced form of strabismus that was not treated in childhood. Important: since adaptability is lost with age, strabismus in adults is diagnosed along with double vision.
Causes of nystagmus in a newborn baby
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! An effective remedy for restoring vision without surgery or doctors, recommended by our readers! Read more…
Nystagmus is a disease in which spontaneous vibrations of the eyeballs occur. Such movements are not controlled by either the brain or the optic nerve. The effect of a constantly running gaze is created and the child is not able to fix visual objects. Nystagmus in newborns develops over time.
After all, after birth, babies’ vision is still poor, and their gaze is still wandering. Only after the first month of life does the child learn to fixate on objects. If the gaze has not clearly formed, doctors can make a preliminary diagnosis - nystagmus. At 3 months the disease is confirmed and observed for up to a year.
After all, such a deviation in most cases is considered temporary and can go away on its own if no pathology is detected.
Causes of nystagmus
Most often, this type of eye disease is diagnosed a year during the first preventive examination in a children's clinic. It is at this age that involuntary fluctuations of the eyeball and the inability to focus on an object or object are considered a pathology. The following factors provoke nystagmus in children:
- hereditary predisposition of the child;
- congenital disorders of the nervous system or their appearance as a result of injuries during birth;
- myopia;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- infection in the ear and, as a result, illness;
- taking medications by the expectant mother that are prohibited during pregnancy;
- parental use of drugs and alcohol before conception and during the entire course of pregnancy by the mother.
In an adult, the disease can be provoked by stress and nervous tension. Therefore, it is so important to conduct an examination not only with an ophthalmologist, but also with a neurologist at the first symptoms.
What types of nystagmus are there and how does it manifest?
In ophthalmology, the following types of eye diseases are distinguished:
- Horizontal nystagmus. With this shape, the eyes move from right to left;
- Vertical. In this case, the eyeballs move alternately from bottom to top and back;
- Pendulum-shaped. The eyes move with the same amplitude in all directions;
- Dissociated. Eyes move in different directions.
Another classification of nystagmus divides it into acquired and congenital. Acquired is more common in adults. In children, the disease has a congenital form.
In the first year of life, a child will not be able to explain what is bothering him. Parents should closely monitor the baby themselves.
Signs of congenital nystagmus, in addition to a shifting gaze, are increased photosensitivity and decreased level of vision.
Also, the disease of the visual apparatus is manifested by the following symptoms:
- constant dizziness;
- attacks of nausea;
- hearing impairment;
- lack of coordination in space and the sensation of objects moving around.
The manifestation of all signs of the disease depends on the stage of nystagmus. For example, if the disease is at the very beginning of its development, it is not at all noticeable to others. When the eye is motionless, there are no vibrations.
They appear only when the child’s eyes are strongly moved to the left or right. The average degree of the disease is characterized by already visible movements of the eyeballs when the baby looks straight.
In the most severe form, oscillations occur even during slow abduction of the eye to the sides.
With congenital nystagmus in newborns, fluctuations are observed in the second month of life. Involuntary movements and poor focusing on an object for up to a year are the norm. But it is necessary to consult with a specialist so as not to miss the possible pathology that causes the disease.
How is nystagmus diagnosed?
In order to ensure the accuracy of the disease and exclude others, the patient must undergo a complete examination. The diagnosis is made by a neurologist after the following studies
- amplitude of rotation of the eyeball;
- complete examination of the retina;
- Brain MRI.
In addition, an acuity check with an ophthalmologist and consultation with him are prescribed. If necessary, the child is referred for examination to an otolaryngologist.
We recommend!
To treat eyes without surgery, our readers successfully use a proven method. Having carefully studied it, we decided to offer it to your attention. Read more…
How is nystagmus treated?
As a rule, treatment of nystagmus in children is a whole complex of long-term procedures, also aimed at getting rid of the pathology and disease that causes eye disease.
Glasses are prescribed only to those children whose nystagmus has caused myopia or farsightedness. Modern medicine carries out therapy using special devices, the action of which is aimed at stimulating the level of vision in the baby. This course is held a couple of times a year and lasts three weeks. Through surgery, doctors reduce the amplitude of eye oscillations to a minimum.
Throughout the treatment, the child is registered in a special institution from the moment the disease is diagnosed until the age of 15. During this long time, doctors try to improve vision as much as possible and reduce the amplitude of eye rotation. Treatment is effective at an earlier age. This is why it is so important to identify nystagmus as soon as it appears.
A fairly common occurrence is the development of one eye disease into another - myopia. This happens at the moment when the baby is just learning to keep his gaze on individual objects.
Prevention of nystagmus in children
It is quite difficult to protect the baby from such an eye disease. But it is up to parents to promptly treat diseases of the ENT organs, and also to prevent the development of serious diseases throughout the child’s body. Try to examine the child’s brain and nervous system as often as possible so as not to miss pathological formations.
If, as a result of visual impairment, the child was prescribed glasses, be sure to buy them and let the child wear them, find the right words, tell them how important it is. Most importantly, teach your child not to be embarrassed about wearing glasses, so that complexes do not arise in the future. If you do not adhere to this doctor’s recommendation, the baby will soon develop nystagmus.
Congenital nystagmus in a newborn is almost impossible to prevent. It is impossible to completely insure a baby against injuries during childbirth and infections. But a woman is able to significantly reduce the risk of developing pathology if she monitors her health during pregnancy, trying to constantly strengthen her immunity.
Any child can suffer from nystagmus due to certain reasons. This does not make him some kind of weak-minded; his physical development does not lag behind his peers. The baby will just need to undergo certain procedures and, if necessary, wear glasses for vision correction.
Why does strabismus occur in children?
There are many reasons for strabismus. These may be congenital diseases or injuries received during childbirth, heredity, infectious diseases, inflammatory processes occurring in the eyes, advanced cases of myopia, farsightedness or astigmatism, severe physical activity and stress on a regular basis, and poor visual hygiene.
Only a specialist can identify the cause and begin competent therapy, taking into account the patient’s age, lifestyle, type of strabismus, its clinical picture, and the presence or absence of concomitant pathologies.
Strabismus in infants. Characteristics of the pathology
As we said above, strabismus is a childhood pathology, since babies are born with weak eye muscles. When is strabismus in newborns considered normal? Most often it occurs due to low visual acuity and the baby’s lack of ability to fix an object with both eyes (binocular vision). After about two to three months after birth, the baby begins to recognize the people, objects, and objects around him, but visual acuity still remains quite low. After another couple of months, the eye muscles become stronger, and if the baby had strabismus, it goes away. Oculists say that strabismus in infants should completely go away in about six months, but if this does not happen, then you need to talk about eye pathology and seek help from a specialist. To correct strabismus in a newborn who is not yet six months old, use bright, large toys and mobiles (toys suspended in the air that move). The parent should ensure that the child maintains focus on the objects for as long as possible. This will solve the problem.
Speaking about the types of strabismus in newborns, it is worth highlighting the following:
- imaginary;
- hidden;
- true.
We'll tell you more about each below.
Eye nystagmus in children: what it is, causes and treatment
Human eyeballs are always in motion. However, if their fluctuations occur involuntarily and uncontrollably, then nystagmus is diagnosed. This condition can be either physiological or pathological.
Nystagmus is quite common in children. This visual impairment is determined visually, but is often asymptomatic at the initial stage, which makes timely diagnosis of the problem difficult.
In the absence of therapy, visual acuity decreases.
Features of childhood nystagmus
Nystagmus - what is it? This is an ophthalmological disease characterized by involuntary oscillations of the eyeballs in different directions. This visual impairment can develop at any age.
Immediately after the birth of a child, he cannot focus his gaze on a specific object; his eyes are constantly moving. This physiological nystagmus usually disappears after one month.
But if this does not happen, then deviations in the functioning of the central nervous system are diagnosed.
Nystagmus in a child is most often detected at the age of 3 months and usually manifests itself in a horizontal form.
Causes of pathology
Nystagmus occurs as a result of increased tone on one side of the labyrinth of the inner ear.
With normal functioning of the central nervous system and visual system, the vestibular analyzer sends a signal to both eyes at the same speed.
And with nystagmus, hypertonicity of the labyrinth is formed, as a result of which the synchronization of signals occurs. This leads to the fact that the eyeballs begin to make involuntary movements in different directions.
In childhood, this ophthalmological disease is most often congenital in nature, arising for the following reasons:
- genetic predisposition;
- birth injuries;
- infection in the prenatal period;
- smoking and alcohol consumption by the mother during pregnancy.
Acquired nystagmus in a child can develop against the background of the following pathological conditions:
- infectious diseases;
- albinism;
- optic nerve atrophy;
- retinal dystrophy;
- oncological processes;
- traumatic brain injury;
- brain diseases;
- eye refractive error;
- damage to the vestibular apparatus.
Sometimes the cause of the pathological deviation cannot be detected.
Nystagmus in newborns
Nystagmus in a child usually occurs in the first 3 months of the baby’s life. If the visual deviation did not appear before this time, then in the future it can only have an acquired character. If signs of the disease appear in a newborn baby, treatment is not carried out. In this case, the child is registered with a pediatric ophthalmologist and remains there until he reaches 1 year of age.
All this time, the disorder is considered a temporary physiological phenomenon, the etiology of which is not possible to identify. And only if the symptoms of nystagmus do not go away by 12 months, a detailed examination is prescribed and therapy is carried out.
Types of disease
Depending on what period of life the problem arose, nystagmus in children is of 2 types:
- Congenital. Appears in the first 3 months after the birth of a child.
- Acquired. Develops under the influence of negative factors at any age.
By nature, the disease is divided into physiological and pathological. In the first case, visual impairment occurs when observing fast moving objects. A similar condition can be observed while riding on attractions, quickly moving the gaze from one point to another, as well as when water gets into the ear canal or an infection of the inner ear.
Sometimes involuntary eye movements occur due to severe fatigue, when the child tries to focus his gaze on one object. This phenomenon is temporary and does not require treatment.
Pathological nystagmus occurs against the background of various diseases of the central nervous system, vestibular apparatus or visual system.
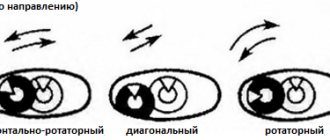
- Horizontal nystagmus. The eyeballs move left and right.
- Vertical. Oscillations occur from bottom to top and vice versa.
- Diagonal. The eyes move diagonally.
- Rotary. The eyeballs rotate in a circle.
Is it possible to cure nystagmus at home?
It is impossible to cope with nystagmus in children on your own; no traditional medicine recipes can help cope with such a problem.
Therefore, you should not search for such information on the Internet and try various untested remedies offered. Otherwise, the consequences can be extremely unpleasant.
At home, you can only perform various exercises prescribed by your doctor.
How to determine strabismus in newborns. What types are there?
The first type is imaginary strabismus in infants. This disease is considered normal and is associated with an asymmetrical arrangement of the eyeballs. The cause may also be the structural features of the skull, the visual axis of the eye, etc. Such strabismus is not diagnosed, does not affect vision in any way and does not require treatment. As for the latent type of disease, it is customary to call it a pathology in which a newborn’s eyeballs deviate from their normal position, that is, heterophoria. Usually, hidden strabismus is diagnosed in children who have just started school, so the eyes have a heavy daily load (reading, writing). Since it is quite difficult to determine this type of strabismus, a number of studies are being conducted that can show the functioning of binocular vision. With strabismus it is absent, but with heterophoria it is preserved. To treat hidden strabismus, you need to monitor visual hygiene and avoid overexertion. In this case, ophthalmologists prescribe contact lenses or glasses.
Often they resort to orthoptic programs using a synoptophore. If the measures were unsuccessful and the condition worsens, surgery is performed to correct strabismus.
True strabismus. Its types
As the name implies, true strabismus indicates that the child has vision problems. This form of pathology is immediately visible: the eyes begin to squint in different or one direction. Depending on where the eyes are “directed,” there is a concomitant or paralytic strabismus. The first is a hereditary form. More precisely, children do not inherit the disease itself, but the structural features of the eye structures that can lead to it. In this case, strabismus can be convergent (the eyes look at the bridge of the nose) and divergent (the eyeballs are directed in different directions from each other). It is also important to know that external and internal environmental factors can provoke the development of this type of disease in conditions of unstable binocular vision in children under one year of age. It is worth considering that the presence of other pathologies is one of the causes of strabismus. For example, farsightedness or myopia. Before starting therapy, it is necessary to find out the cause of strabismus, and if there are concomitant diseases, begin therapy with them. As for the methods, ophthalmologists advise treating the disease with the help of a device, including orthoptic and diploptic treatment.
Age plays a key role when choosing a method. Surgery to correct strabismus is indicated for children over three years of age if conservative therapy is insufficiently effective. The causes of the paralytic type of pathology in children can be various types of damage, diseases of the nervous system, and parasitic brain damage. That is, those reasons that can provoke paralysis, in which the eye begins to turn in the opposite direction. Double vision and dizziness are also present. Interestingly, this symptom goes away if one eye is closed.
After establishing the cause, they resort to electrical stimulation of the affected muscle with the help of exercises and prismatic glasses to eliminate the bifurcation. Correction of strabismus in children through surgery is possible only seven months after the main process has stabilized.
Possible causes of nystagmus in infants: types, diagnosis, prevention of the disease
A child's eyes begin to actively develop during the prenatal period. If a newborn's eyes move around, this may indicate a disruption in normal development. The earlier the pathology is diagnosed, the easier it is to treat.
A newborn's eyes are darting
Changes in vision in the first month
In the first weeks of his life, a child sees completely differently from an adult. The baby's eyeball has a flattened shape and grows quickly. His retina is not fully formed. There is no central vision due to the absence of the macula. The baby cannot see three-dimensional objects and estimate the distance to them.
Note! A child can sometimes develop what is called infantile strabismus. This occurs due to weakness of binocular vision or in cases where the woman led an unhealthy lifestyle during pregnancy.
Also, in the first months, children perceive the world around them in black and white and do not distinguish between colors. The first color that children begin to see is red.
Changes in vision up to one year
Why does a newborn roll his eyes when falling asleep or during sleep?
Normal vision changes in babies are:
- At one month of age, a child is able to see shadows and light and the outlines of large objects at close range. He sees his mother's face more clearly.
Important! At this time, it is important to check the pupil's reaction to light.
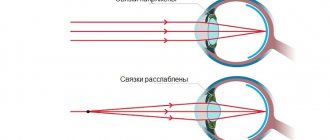
- In the first 3 months, the sensitivity of the retina increases sharply and the ciliary muscles become stronger. The child can steadily fix his gaze on moving objects and distinguish between red and green colors.
- At the age of 4-6 months, active development of vision occurs. A macular spot forms and the eyes' sensitivity to light increases.
- Before the child reaches one year of age, the final formation of binocular vision occurs.
Children under one year old cannot have 100% vision. Their eyes get tired even after a slight load. Visual acuity finally returns to normal by the age of one year.
The eye of a premature baby is immature and has an incomplete anatomical structure. Premature babies are at risk for developing retinopathy and visual impairment. All premature babies should be examined by an ophthalmologist no later than the fourth week of life.
Why does a child's eyes shift?
Discharge from the eyes of a newborn - causes of mucus
Nystagmus is involuntary eye movements. They cause the cerebral cortex to receive incorrect and unclear information.
Reasons why a child's eyes dart:
- birth injury;
- a brain tumor;
- damage to the vestibular apparatus;
- albinism (a genetically determined disease in which there is no melanin pigment in the iris, skin and hair);
- refractive error of the eye (myopia or farsightedness);
- strabismus (it is noticeable how the newborn’s eyes are directed in different directions);
Strabismus in a baby
- pathology of the optic nerve;
- destructive processes with the retina in the eye shell;
- infectious diseases, including in the inner ear.
How to check your baby's vision
Simple procedures are used to test your vision at home.
In the first 2 months, the newborn’s reaction to its own appearance should be observed. You need to approach the baby at a distance of about 20 cm. The child must react (for example, smile). This can also be done after sleep.
After a month, you should offer your baby bright yellow or red toys. If his vision is formed correctly, then he will certainly pay attention to them. After another month, the baby should be interested in toys of cool colors: blue or green.
From the age of five months, you need to show the child objects alternately: at close or far distances. If vision develops normally, the baby will fix his gaze on the toy. You should also show bright circles.
Toy for child
Dr. Komarovsky recommends checking by observation:
- does the baby concentrate his gaze on the toy at the age of 1 month;
- does he close his eyes from a bright light source;
- whether he recognizes his parents by the age of three months.
Important! During the vision test, there should be sufficient lighting in the room.
Before one year of age, it is impossible to determine visual acuity using the Sivtsev and Orlova tables.
When to visit an ophthalmologist
Parents should urgently contact a pediatric ophthalmologist if they have the following symptoms:
- pupils of different diameters;
- in bright light they do not narrow;
- the eyes began to turn red;
- after 2 months of age, the child does not fix his gaze on any object;
- physiological infant strabismus does not go away by 4 months of age;
- a cloudy pupil is detected;
Baby's cloudy pupils
- the child does not show interest in objects of yellow, red, blue and green colors;
- The toddler does not try to grab the object he is looking at, does not react to it (including does not grunt).
Prevention of visual ailments
In order to prevent the development of nystagmus, vision training plays an important role. The main stimulus is the abundance of sunlight. The children's room should have a window facing the sunny side. It is important to have toys that the child can easily reach.
Until the age of three months, it is important to conduct training sessions. You should purchase cards with large black and white images of objects. It is recommended to fix some of them above the crib. It is useful to hang a baby mobile above the crib. The child will be able to look at it while feeding or when falling asleep.
Mobile for baby
From three months, pictures should be in color. They contribute to the development of correct color perception.
It is recommended to listen to the following advice:
- In addition to sufficient sunlight, the room should have good electric lighting.
- Until the age of three months, toys should be placed above the crib (or stroller) at a height of 40-50 cm;
- From two months onwards, it is recommended to place the baby on his stomach. This will promote vision development.
- When falling asleep, the light should be dimmed.
Nystagmus in newborns develops for natural or pathological reasons. Parents should closely monitor vision development. If even the slightest deviations appear, for example, abnormal movement of the eyes, the baby should be shown to a doctor. Eye diseases need to be treated as early as possible.