Blepharitis and chalazion are two fairly common eyelid diseases. Moreover, the second is often a consequence of the chronic course of the first. These diseases are accompanied by inflammation of the eyelids and have similar symptoms. Let's look at the features of these eye diseases and find out how they are treated.
In this article
- What is blepharitis and why does it occur?
- Symptoms of blepharitis
- Types of blepharitis
- How is blepharitis treated?
- Complications of blepharitis
- What is a chalazion?
- Symptoms
- How is chalazion treated?
What is blepharitis and why does it occur?
Blepharitis refers to various ophthalmological pathologies in which the edges of the eyelids become inflamed. In most cases, such inflammations take a chronic form and periodically worsen. An inflammatory process occurs after microbes, viruses, fungi or mites enter the meibomian glands. In some cases, blepharitis develops due to allergies. Pathogenic microorganisms are the direct causative agents of a disease. There are also internal reasons that can be called disposing factors:
- avitaminosis;
- mechanical injuries to the eyes and eyelids;
- infectious and viral systemic diseases;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- refractive errors;
- dry eye syndrome;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- weak immunity.
Most often people suffer from blepharitis:
- children;
- women who use cosmetics;
- allergy sufferers;
- patients with serious illnesses, such as diabetes;
- people with poor vision.
Often, inflammation of the eyelids is detected in users of scheduled replacement contact optics who do not care for them well. In principle, anyone can get blepharitis. A person is more vulnerable during a period of weakened immunity.
Symptoms of blepharitis
The symptoms of the disease depend on its type. First, let's list the general symptoms:
- itching and burning;
- redness and swelling of the eyelids;
- photophobia;
- lacrimation;
- mucous and purulent discharge from the eyelids;
- heaviness in the eyes.
These are typical symptoms not only for blepharitis, but also for many other eye diseases. You cannot self-medicate. An incorrectly selected drug can cause complications.
Types of blepharitis
Depending on the causes and symptoms of inflammation, several types of the pathology in question are distinguished:
- Scaly, or seborrheic. A characteristic feature is scales on the eyelashes, which are desquamated particles of the epidermis. Symptoms such as very severe itching, redness of the conjunctiva, and hardening of the edges of the eyelid are also observed. When the disease is severe, the eyelashes turn gray and fall out.
- Ulcerative. The disease is characterized by inflammation of the follicles of the cilia. Pus flows in large quantities from the excretory ducts of the meibomian glands. Crusts form on the eyelids, which subsequently cause scars. There is a disturbance in the growth of eyelashes and their loss.
- Demodectic. This blepharitis is caused by Demodex mites. It is almost always found on the skin of the face, but does not pose a danger if a person maintains hygiene, his immune system is strengthened and he monitors his health. Ticks that have entered the meibomian glands can begin to multiply due to hypothermia, a cold or a viral disease. Reproducing parasites feed on the secretions of the sebaceous glands. Mite waste products cause inflammation.
- Meibomian. This type of disease is accompanied by severe thickening and redness. When bacteria enter the excretory ducts of the eyelids, increased secretion production begins, but due to blockage of the glands, it does not come out. This leads to the development of inflammation.
- Acne. This disease is also called ophthalmic rosacea. It is characterized by the presence of rashes on the skin of the face and eyelids. Pink acne spreads quickly and causes discomfort in the form of burning and itching.
- Allergic blepharitis is the only type of pathology that is not caused by microbes and viruses, and therefore is not contagious. The allergy manifests itself in severe itching, profuse lacrimation, increased photosensitivity, and swelling.
It is possible to accurately determine the cause and type of blepharitis only after an examination, during which allergy tests are taken, laboratory tests of discharge and other procedures are performed.
Possible reasons
The following will list the pathologies that most often cause growths to appear in dogs of different ages:
- Eosinophilic granuloma. A common problem among decorative breeds prone to allergic reactions. Often found on the eyelids of dogs in the form of a small pea. May be single or multiple. The reason may lie in poor diet, insect bites or taking antibiotics. Single nodules tend to resolve on their own without any treatment. For multiple granulomas, glucocorticosteroid therapy may be prescribed. In all cases, the prognosis is favorable.
- Warts. There are breeds that have a tendency to develop warts all over their body. They are often found in pugs, mastiffs, bulldogs and terriers. They do not pose any danger, but if they are localized in problem areas, they will require removal using coagulation or cryodestruction. If a dog has a small formation on his eyelid that looks like a wart, then under no circumstances should you try to remove it yourself, as there is a risk of infection and the onset of an inflammatory process, which can seriously harm the eye.
- Papilloma. Formations that are very similar in appearance to warts, but differ from them in that they are prone to a malignant course. First, a small growth the size of a grain appears on the eyelid, which in a few months can grow to the size of a large pea. Most oncologists are inclined to believe that all papillomas must be removed followed by histological examination. This can be done using electrocoagulation or laser. For calm pets, local anesthesia will be sufficient. Sedation is used in cases where there is a risk that the animal will behave aggressively, which may affect the quality of the operation, given that it is performed on the eye. There is one problem with papillomas - they often appear again in the same place. Most often, English and French bulldogs suffer from them, since their entire muzzle has been covered with them since childhood.
- Melanoma. Sounds like a death sentence for humans, but is not so dangerous for animals. It occurs very often, but does not have a tendency to relapse and metastasize, therefore it is considered a conditionally malignant type of cancer. It may appear as a small black growth on the eyelid, which does not bother the dog in any way until it begins to ulcerate. The diagnosis can only be confirmed using biopsy and histology. In all cases, it must be completely removed surgically within healthy tissue. The prognosis is favorable provided that it is removed in a timely manner.
- Demodecosis. If localized in the muzzle area, it can cause small growths to appear on the dog’s eyelids. Hair loss and flaking are also observed in this area. In puppies, this phenomenon is called juvenile demodicosis. Everything goes away within 2-3 weeks. In adult dogs, the activity of this type of mite can provoke a sharp decrease in immunity or cancer, so it is recommended not to delay identifying the cause. Scraping or plucking the affected area will confirm the presence of a mite.
- Sebaceous gland cyst of the eyelid. Hard lumps the size of a grain of rice. May appear in both eyes. They do not bother the dog at all (no itching or pain). There is a tendency towards inflammation. Without cytology it is impossible to confirm the diagnosis. Large cysts must be surgically excised.
- Barley. A common occurrence among all breeds. The appearance can be triggered by hypothermia, a bacterial infection or severe stress. A round pink growth appears on the eyelid. As the process progresses, purulent contents begin to be released from it. Barley can be internal or external. May affect the lower or upper eyelid. In severe cases, the eye may even become swollen. For treatment, eye anti-inflammatory drugs (tetracycline and erythromycin ointments) are used.
- Sebaceous gland carcinoma. A malignant formation on the eyelid that must be immediately removed. Such tumors can ulcerate, grow to large sizes and metastasize. An effective method of removal is to influence the formation with liquid nitrogen, which leads to the destruction of cells and the disintegration of the tumor itself. There is a chance of relapse (in 10-15% of cases during the first year after surgery), so the dog is advised to regularly examine the eyelid area.
How is blepharitis treated?
Treatment of this disease is carried out with the help of medications - eye drops, ointments, gels. The type of medicine is determined by the causes of inflammation. The general principles of therapy are:
- maintaining hygiene;
- performing rinses;
- eyelid massage;
- instillation of solutions based on natural tears;
- diet.
As for drugs, antihistamines, antimicrobials, antiseptics, glucocorticosteroids, and sulfonamides can be prescribed.
It is possible to eliminate inflammation and improve blood circulation in the eyelids and eyeballs during physiotherapy. If medications do not help, the patient is sent to:
- UHF therapy - treatment with a high-frequency electromagnetic field;
- magnetic therapy;
- ultraviolet irradiation therapy;
- darsonvalization - exposure of the affected tissues of the eyelids to high-frequency pulsed current;
- irradiation with Bucca rays - ultra-soft x-rays.
What to do if the chalazion ruptures?
A rupture of a chalazion of the upper or lower eyelid requires taking immediate measures to sanitize the damaged part of the eye.
In such a situation, it is recommended to do the following:
- Take a piece of sterile cotton wool and then soak it in 3% hydrogen peroxide.
- Close the eye tightly, then carefully, avoiding contact of the antiseptic solution with the mucous membrane of the eye, treat the wound surface.
- Using leisurely movements, remove any remaining purulent contents from the rupture site.
- Place a piece of sterile bandage on the surface of the eye, securing it with a medical adhesive plaster.
- Go to the hospital to see an ophthalmologist or surgeon.
If your home medicine cabinet does not contain all of the above first aid supplies, or if a person does not have special skills in treating wounds on the surface of the eyelid, then it is better to immediately seek help from a specialist.
To minimize the likelihood of a bacterial infection entering the wound, you should cover your eye with a sterile bandage on the way to the doctor.
Complications of blepharitis
This disease is rarely accompanied by complications; it often develops into a chronic form, which, as a rule, occurs due to incorrect, untimely started therapy or its complete absence. Blepharitis can cause conjunctivitis, blepharoconjunctivitis, keratitis and other ophthalmic pathologies. In other words, the inflammation spreads to the eyeball - the conjunctiva, cornea, etc. Chronic blepharitis can lead to the formation of a chalazion, which sometimes has to be treated surgically. Let's take a closer look at this disease.
What is a chalazion?
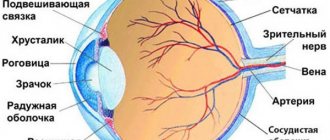
A chalazion, or hailstone, is a benign compaction in the thickness of the cartilage of the eyelid. Its formation occurs as a result of blockage of the excretory ducts of the meibomian glands. This disease is quite common. It is diagnosed in 7% of patients with inflammation of the eyelids. People of all ages suffer from it, but it is more often detected in people over 30 years of age. This is due to a decrease in the production of secretions responsible for lubrication of the conjunctiva.
The main cause of chalazion is blockage of the excretory ducts of the glands. Because of this, the lipid contents do not flow out, but accumulate in the lumen of the duct, which leads to tissue inflammation and the formation of a nodular seal. It often occurs against the background or as a result of the following diseases:
- barley;
- chronic blepharitis;
- rosacea;
- seborrhea.
Factors also predisposing to chalazion are:
- hypovitaminosis;
- hypothermia;
- viral diseases;
- gastrointestinal pathologies;
- diabetes;
- poor hygiene, including when using contact lenses.
Symptoms
When a chalazion develops, a round-shaped compaction forms under the skin of the eyelid. It is located in the thickness of the cartilage. This does not cause pain. The seal slowly enlarges and can grow up to 5-6 mm in diameter. The swelling becomes pronounced.
A visible cosmetic defect occurs. In some cases, a patient develops several chalazions on the upper and lower eyelids.
This pathology may also be accompanied by:
- lacrimation;
- itching;
- redness of the conjunctiva.
As the hailstone increases in size, it begins to affect the quality of vision, causing diplopia and image distortion. Often the chalazion opens spontaneously. Its contents flow out and the swelling immediately subsides. If this does not happen, the lump turns into a cyst with mucus inside.
Chalazion can also occur in a more severe form, with suppuration. In such cases, the following symptoms appear:
- throbbing pain;
- redness of the eyelids and skin around the eyes;
- swelling;
- increased body temperature;
- softening of hailstones.
Stye on a dog's eye: causes, symptoms and treatment
A pet very often resembles its owner in its character and behavior. They often have common diseases.
One of these ailments is considered to be the appearance of animal barley on the eye, which in turn is a rather painful pathology.
Modern veterinary medicine has not yet developed a drug that would rid a dog of this disease forever, nor has therapy been developed.
Etymology of the disease
Barley is considered to be inflammation of the sebaceous gland or hair follicle of the eyelash. This disease is also a type of pathology such as blepharitis.
Types of barley
According to the location of this disease, barley is divided into:
- External (located on the upper or lower eyelid, resulting in swelling).
- Internal (located on the inside of the eyelid, a small tubercle appears on the skin).
The size of the stye is determined, as a rule, by the level of the dog's immunity and the degree of infection. The process begins with the formation of a tubercle the size of a grain of millet on the skin surface; it can increase significantly in size.
Causes
When a fungus, microscopic mites, or microbes enter the area of the sebaceous gland or hair follicle, the skin becomes infected. The pathogen, multiplying exponentially, begins to actively move to tissues adjacent to the source of inflammation.
Styes are mainly formed in small, weak puppies due to:
- Hypothermia,
- The presence of a stressful situation for the animal,
- Lack of essential vitamins in the body,
- Unbalanced nutrition,
- Lack of proper eye care for children,
- Conjunctivitis.
Symptoms of the disease
Barley can be found not only outside the eyelid of a pet, but also inside it. This disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- The appearance of an inflamed tumor on the dog's eye.
- Itching.
- Anxiety on the part of the pet associated with pain.
If a dog has stye on its eye, it begins to experience pain in the area of the inflammatory tumor, which also itches. If a dog starts scratching an eye already affected by the disease with its paws, it can introduce an infection into it, so the owner will have to stop such actions.
After some time, a purulent head forms at the site of the swelling, which subsequently opens.
Treatment
Barley can be cured at home using hydrocartisone and tetracycline ointments. Hydrocortisone should be applied to the site of inflammation, while tetracycline, on the contrary, is usually applied to the lower eyelid.
Veterinarians recommend treating both eyes, even if the inflammatory process affects only one of them. You should smear your eyes about 5-6 times a day .
The owner must certainly remember the fact that before using ointments during treatment, the eyes should be rinsed very thoroughly . This is done using boiled water or decoctions of chamomile and calendula. These herbs are renowned for their famous antiseptic properties, which in turn can prevent further spread of inflammation.
Some dog owners advise burning stye on the pet's eye with alcohol. Place a few drops of alcoholic liquid on a cotton pad and apply it to the affected eye for just a couple of minutes. This procedure is carried out 2-3 times a day.
One of the most common means of treatment is considered to be dry heat.
For this method, boil one chicken egg, peel it, and then turn it into a clean handkerchief or napkin and apply it to the sore eye.
This method is used after opening the abscess, otherwise the pus will break into the dog’s eye and not out. The owner can warm up the sore spot with a used warm tea bag .
You can apply lotions to the stye; to do this, soak a cotton pad in a soda solution (a teaspoon of baking soda per glass of water).
It is not recommended to open the abscess on your own , nor is it recommended to squeeze pus out of the stye with your hands. These actions can become a source of infection in the depths of the orbit, for example, sepsis or meningitis.
If a dog constantly has styes appearing in front of his eyes, then the owner will definitely need to contact a veterinarian, who will offer a solution to the problem using antibiotic therapy, a course of immunostimulants, or opening the abscess through surgery, which is carried out in extremely severe cases.
Host safety
Dogs clearly react when any irritant is brought to their eyes. If the owner is going to carry out procedures to treat barley, he needs to purchase a muzzle, since the pet can simply bite its owner.
To avoid contact with bacteria, which can easily pass from dog to person, it is best to use clean latex gloves, and you should also wash your hands thoroughly with soap and rinse.
Source: https://sobakainfo.ru/yachmen-na-glazu-u-sobaki-prichiny-simptomy-i-lechenie/
How is chalazion treated?
At an early stage, drug therapy is used. The patient is prescribed eye drops and ointments. Eyelid massage, heat compresses, and UHF therapy can also be used in treatment. In case of severe inflammation, injections with corticosteroids are given. The drugs are injected into the compaction cavity, which leads to rapid resorption of the contents of the chalazion.
Surgery is prescribed in extreme cases when the disease does not go away and begins to affect vision. Hailstone removal surgery is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthetic. After excision of the formation, sutures are placed on the eyelid, and a tight pressure bandage is placed on the eye. For 5-7 days, the patient instills drops and applies ointments with an anti-inflammatory effect.
Today, laser methods for chalazion removal are also used. First, the hailstone capsule is dissected, after which its contents are evaporated by a laser. This treatment is less traumatic. No stitches are needed.
So, blepharitis and chalazion are common diseases with similar symptoms. In this case, sometimes inflammation of the edges of the eyelids leads to the formation of hailstones. These ailments can be treated quickly. It is important not to neglect them and start treating them when the first signs appear.
Chalazion treatment
Throughout the treatment, the doctor monitors the patient’s well-being. The pattern that will lead to recovery depends on the stage of development of the chalazion. In this case, the doctor’s recommendations correspond to this list:
- When the seal has just begun to form, warm compresses are applied to it. The number of procedures is 4 per day. If the encapsulation process has not begun in the neoplasm, then in order to quickly release the accumulated fluid, you can perform a light massage with your fingertips.
- An overgrown chalazion is treated with medications. Most often, mercury ointment and drops are prescribed. Sometimes corticosteroid-based drugs are injected into the lump itself. With their help, swelling is relieved and the inflammatory process stops. Physiotherapy helps to consolidate the effect of conservative treatment - procedures using polarized light, helium-neon laser and UHF.
- If a chalazion cannot be cured with medication, it must be removed. The operation is performed under local anesthesia and most often lasts about half an hour. After surgery, swelling forms at the site of exposure, which disappears after a few days.
- An alternative to removing cholazion with a scalpel is laser surgery. In this case, special eye drops are used as anesthesia. The seal on the eyelid is completely removed. After the procedure, you need to ensure that there is no eye contact with water for some time. There are no scars after such an operation.
A possible treatment regimen for chalazion looks like this:
Or:
It is worth noting that after removing the contents of the capsule through an incision with a scalpel, recurrent appearance of the chalazion is possible. With laser removal of the capsule itself along with its contents, no cases of relapse were observed.