In everyday life, few people think about the functions of their body, but simply take its coordinated work for granted. For a healthy person, it is quite natural to hear, see, smell and taste well. But as soon as you lose one of these opportunities, you begin to think about how important it is for the body to work without failures. Unfortunately, not everything always depends on our desires and efforts.
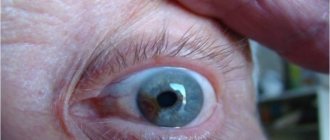
Eye injury always occurs suddenly and unexpectedly. A bruise can be caused by a blow from a hand, a branch, a ball, a stone, or from a fall. The degree of damage is directly related to the force of the impact. Some injuries are not serious, while others can cause vision loss. The main thing is not to panic, provide first aid and prevent the occurrence of complications.
The organs of vision are a rather sensitive area. They can perceive even minor violations acutely. Eye injuries cause severe pain, blurred vision, as well as swelling and hematoma. The most common cause of eye socket injuries is carelessness. This usually happens at home. Children are at risk because they are the most mobile.
An eye contusion, or bruise, is the most common type of injury to the visual organs. Damage occurs due to direct impact or explosion. In most cases, the eye that was contused returns to normal operation and continues to function normally. But sometimes a bruise can turn into serious problems.
The mechanism for causing contusion of the eyeball is quite simple. After the blow is struck, there is a sharp jump in intraocular pressure. Hypertension affects normal blood circulation, leading to rupture of blood vessels and tissues. The changes also affect the biochemical parameters of the ocular fluid. The development of a stress reaction is observed.
CAREFULLY! In more than thirty percent of cases, eye contusion ends in complete loss of vision.
The danger of a bruise is that internal hemorrhage can open. Despite the prevalence of this problem, not everyone knows how to properly treat a bruise. In this article we will talk in detail about what an eye contusion is, as well as how to properly provide first aid.
Classification
Depending on the severity, an eye injury can be:
- light;
- moderate;
- heavy;
- especially heavy.
The mild form is characterized by the appearance of hemorrhage under the skin and conjunctiva. With grade 1 eye contusion, slight swelling and erosion of the cornea, spasm of the lens muscles, as well as retinal clouding, which is reversible, are observed. Pathological changes are fully restored. There are no residual effects.
Moderate severity is characterized by a non-penetrating corneal wound and swelling. Temporary cataracts may occur. There is also paresis of the muscles of accommodation. At this stage, pain, burning and other unpleasant symptoms appear. There may be consequences affecting the health of the visual system.
Treatment of eye hyphema
With severe concussion, vision deteriorates by fifty percent. Grade 3 is characterized by rupture or even separation of the eyelids, sclera and iris. There is clouding or luxation of the lens. Severe cases may also result in retinal detachment and optic nerve damage. In especially severe cases, vision is completely absent. Complete destruction of the eyeball occurs, as well as rupture of the optic nerve.
In addition, experts distinguish between direct and indirect contusion. In the first case, the damaging factor acts directly on the visual apparatus. This could be a blow with a fist or a heavy object, the impact of a falling object, a strong gas or water jet, or a foreign body. With an indirect contusion, the blow is applied to the bone structures, most often the blow is directed to the head. In this case, there is no damage to the skin and mucous membrane of the eyeball.
Most often, the cause of eye injury is small debris, small insects, household chemicals, and fragments. When working in harmful and dangerous working conditions, it is necessary to use protective equipment.
Depending on the cause of the eye injury, there are:
- household. They usually arise against the background of family conflicts and fights. Most often, concussion occurs during alcohol intoxication;
- industrial. A person may be injured due to hazardous production units;
- military. They are the most dangerous. Injuries can occur during exercises or directly during combat operations;
- sports. Occurs during martial arts;
- agricultural. You can get hurt when harvesting.
IMPORTANT! In the first degree of severity, the functions of the visual apparatus are preserved. After treatment, vision will be completely restored without any consequences.
With 2nd degree contusion, temporary loss of vision occurs
Content:
- 1 CONTUSION OF THE ORBALL
- 2 SYMPTOMATICS
Description
↑ CONTUSIONS OF THE ORBALL
Orbital contusions
are injuries to soft tissue or bone walls that occur as a result of a sharp impact on the orbit with a blunt object with a large contact surface (stone, fist, ball, etc.) or as a result of an impact with the orbital area on hard surfaces (during a fall, road accident). transport accidents, shock waves, compression). Rarely occurring mechanisms of orbital contusion may include contusions caused by a jet of air or liquid from pneumatic or hydraulic mechanisms.
Contusion fractures can occur from a direct blow to the edge of the orbit or its wall, as well as from the spread of a fracture from the area adjacent to the orbit. In addition, there is a mechanism of contusion, which consists of a sharp and significant increase in intraorbital pressure as a result of a blow to the eyeball, which causes a fracture of the thin walls of the orbit (inner and lower) (Fig. 52). Such fractures are called “blowout” fractures. There is no doubt that in these cases the eyeball itself suffers. However, if the area of the traumatic object exceeds the area of the entrance to the orbit, the eyeball often remains undamaged.
Contusions of the soft tissues of the orbit are accompanied by swelling, hematoma, damage to the muscles of the eyeball (hemorrhage, rupture) and the optic nerve (compression, hemorrhage into the membranes, separation).
Fractures of the walls of the orbit can be:
- with or without damage to the edge of the orbit;
- finely fragmented or coarsely fragmented.
As a result of fractures (usually small-fragmented ones), defects of various shapes (round, triangular, slit-like, irregular) and sizes are formed in the wall of the orbit. Depending on the size, the defects can be small (up to 1 cm2), medium (from 1 to 2 cm2) and large (over 2 cm2). If the fracture is coarsely fragmented, then 1-3 large fragments are formed, which are confused downwards and to the sides, dragging the are the tissues of the orbit fixed to them.
In this case, there may not be a defect, but a smooth, unnoticeable deformation of the wall is observed, increasing the volume of the orbit (Fig. 52). If the fracture is incomplete and only one edge of the large fragment is displaced, so-called leaflet fractures are formed, in which the muscles and tissue of the orbit can be pinched. Such fractures can be single- or double-leaf (Fig. 120, Fig. 51 and 52). Based on the depth of damage, orbital fractures are divided into:
- on the front - in the front half;
- rear - in the rear half;
- medium-deep - in the middle third.
Depending on the location, fractures of the walls of the orbit can be:
- bottom wall;
- inner wall;
- outer wall;
- top wall;
- inferior inner corner of the orbit;
- inferior outer corner of the orbit;
- several (two or more) walls.
In fact, fractures of the thinnest, inner wall of the orbit are more common. However, most of them occur without clinical manifestations and go unnoticed. In this regard, fractures of the lower wall come to the fore, the clinical picture of which is most pronounced, which is the reason for almost every patient with such a fracture to consult a doctor. Fractures of the external and internal walls often occur simultaneously, which made it possible to distinguish this combination into a separate nosological form. fractures of the inferior inner corner of the orbit. Diagnosis of fractures of the outer and upper walls of the orbit, as a rule, does not pose any special problems, but these fractures are less common than fractures of the outer and inner walls. If the outer fracture is accompanied by a fracture of the lower wall, then they speak of fractures of the lower outer corner of the orbit.
↑ SYMPTOMATICS
Symptoms of orbital contusion can be divided into two groups: symptoms of fractures of the walls of the orbit and symptoms of contusion of the soft tissues of the orbit.
Characteristic manifestations
The main symptoms of an eye injury include the following:
- pain that gets worse when blinking;
- photophobia;
- redness of the eyeball;
- profuse lacrimation;
- hemorrhage;
- partial loss of vision;
- blurred vision;
- edema;
- headache;
- increased body temperature;
- attack of nausea and vomiting;
- involuntary closing of the eyelids;
- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness.
After the pain disappears, especially in the absence of a penetrating wound or damage to the eyeball, the injury is usually not given much importance. The consequence of this may be a deterioration in visual acuity. This occurs as a result of hemorrhage, clot formation and the formation of connective tissue, which disrupts the functioning of the visual system.
The severity of clinical symptoms directly depends on the degree of mechanical impact. In mild cases, patients may have no complaints at all. If the injury is more complex and the impact of force is significant, the clinical symptoms of contusion are pronounced and easily diagnosed.
Contusion causes pain in the eye socket and head
Conjunctiva
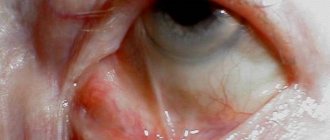
With minor injuries, minor hemorrhages under the conjunctiva may occur. They do not require special treatment. In severe cases, hemorrhages are significant and increase already in the first day.
Cornea
With a slight degree of damage to the cornea, continuous tearing, increased sensitivity to the light source, spasm of the eyelids, pain, and burning are observed. In severe cases, clouding of the cornea occurs.
Sclera
The following symptoms may indicate a rupture of the sclera, which leads to complete loss of vision:
- blurred vision;
- decrease in intraocular pressure;
- the appearance of blood in the vitreous body.
Iris
With minor injuries, a constriction of the pupil is observed, which disappears on its own after a few days. In severe cases, complete separation of the iris may occur.
Ciliary body
Most often, damage to the ciliary body is fraught with the development of iridocyclitis - inflammation of the choroid. The following signs may indicate a detachment of this part of the eye structure:
- intraocular hypotension;
- reduction of the anterior chamber;
- detachment of the choroid.
Lens
With contusion, dislocation, subluxation and even rupture of the lens are possible. Over time, cataracts may develop - clouding of the lens.
Vitreous body
The main manifestation of damage to the vitreous body is hemorrhage, which can impair vision. The accumulation of blood appears in the form of flakes, threads and dots.
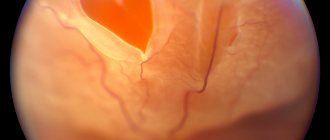
Ocular fundus
During the examination, the doctor may pay attention to the following pathological changes:
- retinal clouding and breaks;
- rupture of the choroid;
- optic nerve atrophy;
- retinal disinsertion.
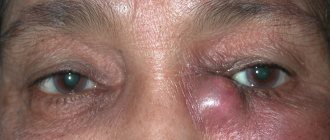
Damage to the periorbital structures is indicated by bruising around the eyes, pain, and swelling of the eyelids.
Complete rupture of the eyeball, penetrating wounds of the eye
Such injuries are usually accompanied by severe pain and a significant decrease in visual acuity. The main symptoms are:
- With a complete rupture of the eyeball, massive subconjunctival hemorrhage is possible (often under the entire area of the bulbar conjunctiva), the anterior chamber becomes deeper or shallower compared to the fellow eye, hyphema occurs (often with blood clots), eye movements are limited (especially in the direction of the rupture), from the eyeball may leak its internal contents.
- In the case of a penetrating injury to the eye, a rupture across the entire thickness of the sclera or cornea is observed, which is accompanied by the symptoms described above.
Common symptoms for the above conditions are low IOP (in some cases normal or elevated), pupil deformation, periorbital ecchymosis, iridodialysis, cyclodialysis, retinal concussion, subluxation or luxation of the lens, vitreous hemorrhages, tears in the choroid and retina caused by trauma optic neuropathy.
Diagnosis of complete rupture of the eyeball, as well as penetrating eye trauma, is performed using a slit lamp or flashlight. This condition is easily visualized by simple inspection. Further examination, however, must be postponed until after surgery to avoid any pressure on the injured eyeball, which could lead to the displacement of ocular contents.
As a primary action, patients with such injuries are put on a protective shield over the eye and are prohibited from eating or drinking. Bed rest is required in a specialized eye hospital. Then, systemic antibiotics are prescribed (for example, intravenous Cefazolin and Gentamicin every 8 hours). A prophylactic tetanus vaccination is performed. To prevent vomiting, which can worsen the condition of the eye, intramuscular antiemetic drugs (for example, Compazin) are prescribed every 8 hours. They immediately begin to collect detailed analysis necessary for urgent surgical intervention. Computed tomography of the eye orbit and brain area is performed in axial and coronal projections. It is possible to prescribe a two-dimensional ultrasound examination, which is often required during surgery to determine the exact location of the rupture site, as well as to exclude the presence of intraocular or intraorbital foreign bodies.
Emergency surgery is performed to preserve the eyeball and further restore vision. In case of severe eye injuries, with the impossibility of restoring vision in the future, the question of enucleation (removal of the eyeball) is raised immediately or within one to two weeks after the injury.
In the medical department, everyone can undergo examination using the most modern diagnostic equipment, and based on the results, receive advice from a highly qualified specialist. The clinic is open seven days a week and operates daily from 9 a.m. to 9 p.m. Our specialists will help identify the cause of vision loss and provide competent treatment for identified pathologies.
In our clinic, appointments are carried out by the best ophthalmologists with extensive professional experience, the highest qualifications, and a huge amount of knowledge. The cost of treatment at MGK is calculated individually and will depend on the volume of treatment and diagnostic procedures performed.
First aid
Before we talk about what to do if you bruise your eye, let's look at some things to avoid:
- rub the injured eye;
- touch the injured eye with dirty hands;
- press on the eyelids;
- use cotton wool for penetrating wounds, as small fibers can get into the eye;
- wash the eye if there is a penetrating wound;
- neutralize the effect of one chemical substance by another;
- use alcohol-containing solutions;
- independently remove foreign objects;
- wash the eyelids with a deep wound.
Providing timely first aid for eye injuries plays a decisive role. Everyone needs to become familiar with a set of simple actions that will help minimize the possible consequences of an eye contusion.
IMPORTANT! For minor injuries, the victim can provide first aid to himself.
For minor bruises, apply a compressive bandage and place ice between the layers of fabric. You should go to the emergency room as soon as possible. If significant damage is present, a cold soak should be applied to the eye. To do this, you can use ice or a handkerchief soaked in cold water. It is best to apply the compress to the temporal area next to the affected eye or eyelid area.
The complex of treatment measures for traumatic eye injuries may include the following:
- applying a bandage to protect from light;
- exclusion of physical activity, body shaking, jumping and pushing;
- instillation of Albucid eye drops for preventive purposes;
- stopping bleeding;
- use of analgesics to relieve pain;
- the use of sedatives in the development of anxiety.
In case of contusion, a bandage is applied to protect from light
In case of injuries, it is necessary to carefully clean the damaged area from contamination with water or antiseptic solutions. The wound should be covered with a clean bandage. If there is heavy bleeding, it is best to place a hemostatic sponge on the wound and apply a bandage on top.
ATTENTION! When you apply cold, do not put pressure on the eyeball.
If you feel a speck in your eye, carefully examine your eye in good light. Gently pull the lower eyelid down. Most often, small specks are found in this area.
If you find a small foreign object, rinse your eye with water. Do not attempt to remove a foreign body with a handkerchief, cotton wool or tweezers. Even after removing the speck, you may still have an unpleasant scratching sensation. They will go away on their own within a few days.
If there is a large object sticking into the eyeball, create a protective frame over the eye to prevent it from moving, and then secure it. This can be done using a disposable paper cup. The healthy eye should be covered with a tissue. Simultaneous vibrations of the eyeballs can lead to the displacement of a foreign body and additional damage. Place Albucid in the eye and immediately go to a specialized emergency room.
If a chemical gets into your eye, rinse it with plenty of running water for twenty minutes. In this case, the eyelids should be open. If the substance gets into both eyes, rinse them at the same time, do not waste precious time.
Traumatic conjunctivitis
One of the types of eye inflammation is traumatic conjunctivitis. It is an infectious complication of eye damage. The disease, as you might guess, occurs as a result of mechanical damage to the membrane of the eye. If you behave carelessly, a branch, a small pebble thrown from under the wheels of a passing car, and much more can get into your eye. Unfortunately, it is impossible to foresee everything. Therefore, no one is immune from one type of injury or another.
Traumatic conjunctivitis includes conjunctivitis caused by the following types of injuries:
- mechanical;
- chemical;
- thermal.
Eye injury can occur not only as a result of a foreign object entering it. It also results from a bruise of the eyeball with hemorrhages in the conjunctiva as a result of a strong blow or fall. Thermal burns can be caused by intense steam exposure. It is accompanied by the formation of crusts on the mucous membrane. In this case, copious discharge occurs from the eyes. Mucus sticks together eyelashes and eyelids.
Similar symptoms occur with a chemical burn. It occurs when toxic substances get into the eyes. Conjunctivitis is the body's reaction to exposure to chemicals. These are varnishes, paints, chemical compounds, industrial vapors, alkalis and acids.
Microtrauma can be caused by tiny specks and even animal hair. When a grain gets on the mucous membrane, it causes discomfort; a person begins to rub his eyes, thereby increasing the pressure of the foreign object on the membrane of the eye.
This type of injury often occurs in children. Children rub their eyes with unwashed hands, thereby introducing germs and small particles onto the mucous membrane.
In all cases, the cause of traumatic conjunctivitis is an external influence.
Diagnosis and treatment
The examination of the patient begins with collecting an anamnesis, that is, a medical history. The specialist needs information about how the injury was sustained. An ophthalmologist will necessarily examine the cornea, retina, lens, and eyelid. The patient will undergo initial measures to treat the injury site and, if necessary, remove the foreign body.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the following diagnostic procedures may be required:
- radiography;
- Ultrasound;
- checking visual acuity and visual fields;
- ophthalmochromoscopy;
- tonography;
- rheography.
ATTENTION! The goal of the treatment process for eye contusion is to prevent dangerous complications.
Treatment is carried out selectively, taking into account the mechanism of damage. The therapy is aimed at eliminating deformation of the eyelids, blood vessels, eye tissues and membranes, as well as stopping inflammatory and hydrodynamic processes.
Minor eye injury does not require special treatment. The wound will heal quickly. The patient may be prescribed maintenance drops with an antimicrobial effect, for example, Albucid. He is advised to monitor the condition of the visual apparatus and, if any negative changes occur, contact an ophthalmologist.
For more serious injuries, specialists prescribe antibiotic drops, as well as ointments for bruises and bruises. In some cases, hospitalization in the ophthalmology department and surgical intervention are indicated.
Treatment of eye injury begins with a comprehensive examination
Drops
For various injuries, the following eye drops are most often used:
- Vitasik. The drug has the ability to restore damaged mucous membrane of the organ of vision. Thanks to the action of Vitasik, mechanical injuries heal in the shortest possible time;
- Balarpan. This is a natural remedy that contains components found in the cornea. Balarpan accelerates regeneration processes and eliminates dryness;
- Hyphenation. The drug protects, nourishes and moisturizes the mucous membrane of the eye. Hyphenes cope with pain and accelerate tissue healing;
- Solcoseryl. Available in gel form. It is a source of nutrients and vitamins. Solcoseryl even copes with the consequences of a burn;
- Kornegel. The gel contains components that regenerate damage to visual structures. The drug effectively eliminates dryness, burning, and also destroys infectious agents;
- Albucid. An affordable product with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
Folk recipes
At home, you can use traditional medicine as an auxiliary treatment. The following recipes give good results:
- A compress of calendula infusion helps relieve swelling and inflammation. To prepare it, you need to take a tablespoon of calendula and one hundred milliliters of boiling water;
- Burdock leaves will help cope with pain. It should be washed and dried, and then applied with the back of it to the eye. Place a plastic bag and a warm cloth on top of the sheet;
- Ginger and turmeric paste will improve blood circulation. This remedy can be used if there is no bleeding. Take half a teaspoon each of turmeric and ginger and mix with a spoon of water. Place the paste on a cloth and then apply it to your closed eyelids. Place polyethylene and a scarf on top;
- A compress of cabbage leaves will help get rid of the hematoma. Mash the leaves until the juice releases and apply to the damaged area for two hours;
- apply ten percent salt in the form of lotions, this will help relieve bruising and inflammation;
- An iodine mesh applied to closed eyelids will normalize blood circulation and speed up the healing process. During the procedure, you should be extremely careful not to get the solution into the eye;
- Onion gruel with sugar will work as an analgesic.
ATTENTION! It is wrong to treat an eye injury only with folk remedies.
Symptoms of damage
Blunt eye injuries are often the result of a fight.
Blunt eye injuries are not always pronounced. Surprisingly, a blow to the visual organ can be quite strong and cause significant problems with vision, but there will be no swelling or tissue rupture.
Given this, there are a large number of factors to consider when assessing injury symptoms. Most often, blunt eye injury is accompanied by several or a complete “bouquet” of the following signs:
- hyperemia;
- edema;
- hemorrhages;
- violation of tissue integrity;
- pain discomfort;
- anatomical abnormality of the position of the injured organ (problems with mobility, displacement, etc.);
- decreased visual acuity;
- headaches and dizziness.
Naturally, almost all the signs will appear in the injured area and it will not be difficult to notice them. If the symptoms are particularly severe, it is unacceptable to hesitate - the injured person should be promptly taken to professionals to provide proper assistance. Otherwise, the risk of developing irreversible consequences, including loss of visual function, is quite high.
Possible complications
An eye injury can lead to the following consequences:
- purulent inflammation followed by removal of the eyeball. This usually occurs when the injuries received are not treated in a timely manner;
- penetration of staphylococcal infection threatens vision loss and even death;
- keratitis - inflammation of the cornea - significantly impairs visual acuity;
- ophthalmia - an inflammatory process without suppuration - occurs some time after injury;
- optic nerve displacement;
- infection with subsequent blood poisoning;
- ptosis – drooping of the upper eyelid;
- brain abscess.
So, an eye contusion is a serious mechanical damage that can lead to complete loss of vision. Timely first aid will allow you to avoid dangerous complications and restore full functioning of the visual system.
Prevention of conjunctivitis
As noted at the very beginning of the article, it is impossible to completely foresee everything; in everyday life it is very difficult to avoid injuries, especially for mobile children. Meanwhile, when wearing lenses, you can protect your eyes from bacteria and small dust particles that can cause irritation of the mucous membrane. To do this, it is enough to follow basic hygiene rules.
- If you constantly use contact lenses, their hygiene deserves special attention.
- Contact lenses should only be removed and put on with clean hands.
- It is advisable that you have special tweezers with soft ends on hand for removing lenses from the container and disinfecting them.
- When it is not possible to wash your hands to remove or put on contact vision correction devices, use a special stick with a suction cup.
- During wearing, small dust particles and particles may fall on optical products. Once under the lens, they injure the mucous membrane. Therefore, contact optics need to be washed and disinfected constantly.
Conjunctivitis often occurs in children due to poor personal hygiene. In addition, conjunctivitis is a contagious disease that is transmitted from child to child. Therefore, children need to be provided with personal hygiene items in kindergarten and school. In conclusion, we would like to add that conjunctivitis can cause serious complications if treatment is neglected. Therefore, at the first symptoms of conjunctivitis, you need to make an appointment with an ophthalmologist.
Features of treatment of eyelid damage
Even a minor scratch can cause a cosmetic defect, discomfort and complications. Therefore, it is necessary to treat all eyelid injuries, but treatment should be carried out only after consulting an ophthalmologist.
The injured eyelid must be examined by an ophthalmologist, which will allow timely detection of complex injuries to the components of the eye. In addition, trauma to the lower eyelid (less often the upper) provokes rupture of the lacrimal ducts, which is outwardly invisible, but will become a significant obstacle to recovery.
Bruises will require urgent application of cold in the first 24 hours, and treatment with heat the next day. Warm compresses and lotions promote blood flow and faster resorption of hematomas. Special ointments are also used to relieve swelling and blue discoloration.
If erosion occurs, surgical debridement of the affected area with the application of an antiseptic will be required, but such a procedure should be carried out by an ophthalmologist.
Treatment of erosions and wounds is always carried out taking into account possible cosmetic defects and expected dysfunction.
Cut and lacerated wounds will require more complex treatment: with horizontal and especially vertical wounds, sutures will be required.
Treatment of penetrating wounds will be even more difficult: it will require complex treatment of all affected structures.
Oral administration is always indicated: Ascorutin, Etamzilate, Calcium dobesilate.
In difficult cases, infusions of a 10% calcium chloride solution may also be prescribed.
How can minor eyelid injuries be dangerous?
With minor erosions, bruises, and wounds, as a rule, damage occurs that does not affect other structures of the eye or parts of the face (superficial). They are quite painful and create significant discomfort, as a cosmetic defect occurs: swelling, redness, lacrimation. After 4–24 hours, a hematoma will form at the site of the blow or bruise, which will change color as it resolves: from purple and blue-black to pale green. It will take up to two weeks for the cosmetic defect to completely disappear.
In addition to these complications, such seemingly insignificant injuries as cuts and scratches can provoke more complex consequences:
- Infection of other structures, which leads to purulent sinusitis, conjunctivitis; in the most severe cases, pus can enter the brain. This will require complex and lengthy treatment.
- When muscle tissue is damaged, adhesions occur, which lead to incomplete closure of the eyelids (ptosis); only surgery can restore normal mobility.
- If an infection gets into the wound, a scar may appear in its place, which will disrupt the correct position of the eyelid, and it will turn outward. Treatment will take up to 1 month, and this defect can only be completely eliminated through surgery.
First aid
Only a specialist can provide qualified assistance for eye injuries. However, first aid can and should be provided immediately after the injury occurs. So, a number of actions should be taken:
If the eyelid is damaged, cold must be applied, but one should not forget about the rules of sanitation. The skin of the eyelids stretches well and this leads to faster formation of hematomas; cold will help stop the bleeding and thereby reduce the hematoma.
The injured eye should be covered with a sterile bandage and consulted with an ophthalmologist as soon as possible.
If there is severe pain in the eye or headache, the victim is given painkillers and an ambulance is called.
It is not recommended to treat wounds yourself.
If an eyelid injury is detected in a child, it must be shown to an ophthalmologist. Only he can competently conduct an examination and prescribe competent treatment.
Symptom of glasses
Sometimes blue-black circles appear on the eyelids and around the eyes, very reminiscent of glasses applied to the eyes (reminiscent of glasses). This manifestation occurs as a result of a fracture of the base of the skull or facial bones, approximately every fifth person with this diagnosis.
Most often, the “glasses symptom” appears immediately after injury, but it can also occur a day after the incident.
This pathology requires immediate treatment at the hospital.
Useful video
First aid for a blow to the eye and relief of the consequences of injury.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2031
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 2 ratings, average: 4.00 out of 5)
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.
Bleeding in the eye
A person receives up to 90% of information about the world around him through the organ of vision. The eye is a very sensitive organ; the eyes need to be protected and treated with attention to injuries and damage. Bleeding in the eye can occur at any age and for a variety of reasons. When is this a sign of pathology, and when can you do without a doctor? Why do complications develop, and can this be avoided?
First of all, hemorrhage is not a separate disease, but a symptom, sometimes indicating the presence of vascular or visual analyzer disease.
If the pathology occurs against the background of injury or physical activity and is not accompanied by severe pain or visual impairment, then this situation is usually not dangerous.
If additional symptoms are observed and the hemorrhage does not go away, you cannot do without the help of an ophthalmologist. Treatment depends solely on the cause of the problem and is prescribed only after examination.
What to do?
If you think you have an eye contusion
and symptoms characteristic of this disease, then an ophthalmologist can help you.
We wish everyone good health!
Diseases with similar symptoms
Migraine with aura (overlapping symptoms: 8 out of 20)
Migraine with aura (decapitated migraine) is a neurological disease that is characterized by the spread of severe pain of a pressing, pulsating nature to one half of the head. In this case, pain is accompanied by visual and auditory disturbances. The patient may also have impaired coordination of movements and problems with speech. Such symptoms can last from 5 minutes to an hour.
Did you like the article? Share with friends on social networks: