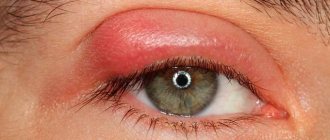
Cold stye refers to an eye disease such as chalazion. Externally, the disease looks like barley and is a chronic form of inflammation of the eyelids. A neoplasm appears on the affected eyelid, which is painful. A stye may go away on its own, while a chalazion requires therapy. More often the disease affects children than adults. Chalazion therapy in children is carried out using medications and folk remedies.
Reasons for the development of chalazion
As a rule, cold barley affects children 5-10 years old. The disease can occur either as an independent pathology or accompany other diseases.
The main reasons for the appearance of chalazion are considered to be:
- Colds, acute respiratory diseases, flu.
- Reduced immunity.
- Failure to comply with basic hygiene rules. The infection can get into the eyes through unwashed hands.
- Ophthalmological, dermatological diseases.
- Diseases of the digestive system.
- Avitaminosis.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Metabolic disorders, for example, diabetes.
- Blockage of the outlet openings of the ducts with secretions produced in excess.
Causes
The mechanical reason for the development of cold barley is the blockage of the meibomian gland duct. The fatty secretion does not have the opportunity to come out, and stretches the lumen of the gland duct. As a result, the surrounding tissues become inflamed, and a nodular compaction is formed at the site of inflammation.
Factors predisposing to the development of barley:
- inflammation of the ciliary edge;
- Rosacea is a skin disease characterized by multiple pustular rashes;
- seborrhea - intense sebum production.
The risk group includes people suffering from diabetes or chronic diseases of the digestive tract.
The impetus for the development of cold barley can be: vitamin deficiency, hypothermia, prolonged colds, infectious ophthalmological diseases.
Chalazion symptoms
Cold stye on the upper eyelid can develop in adults and children simultaneously in both eyes or only in one. The pathology is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Increased lacrimation develops.
- Vision deteriorates.
- Swelling develops on the eyelid.
- Swelling occurs on the affected eyelid.
- Palpation of the tumor causes pain.
- The tumor contains purulent exudate.
- There is a sting and pain in the affected eye.
- The skin around the eye itches and turns red.
A photo of cold barley is presented in the article.
It is quite problematic to distinguish chalazion from ordinary infectious barley in the early stages of development. The chalazion does not open on its own; over time, the tumor begins to increase in size and harden, interfering with the movement of the eyelids.
Prevention and prognosis
Cold barley, if left untreated, can be complicated by phlegmon of the eyelid. This is the process of formation of pus in fatty tissue, most often it develops when Staphylococcus aureus is introduced. Cellulitis is accompanied by pain in the affected area and increased body temperature. Surgical treatment is required. If the removal of the formation capsule was performed poorly, relapse is possible.
To prevent cold barley, you must follow the rules of personal hygiene:
- It is advisable to have your own face towel;
- When wearing contact lenses, put them on and remove them only with clean hands.
For dry mucous membranes of the eyes, it is recommended to use moisturizing drops. It is also necessary to always complete the prescribed course of treatment for blepharitis - inflammation of the eyelids.
Author of the article: Elizaveta Viktorovna Klokova, specialist for the website glazalik.ru Share your experience and opinion in the comments.
Degrees of pathology
Cold stye is classified by ophthalmologists into 4 stages depending on the severity.
- In the first degree of chalazion, redness of the skin on the eyelid is observed. The person feels slight discomfort.
- At the second stage, noticeable swelling develops, and discomfort becomes more pronounced. At this stage of chalazion development, therapy using traditional medicine methods is allowed. However, you should still consult your doctor first.
- At the third stage of development, the tumor grows and painful sensations appear. In this case, the pathology can be eliminated with the help of medications recommended by a specialist.
- At the fourth stage, the size of the tumor increases to critical size. Pus accumulates in the tumor cavity. Such a tumor can be eliminated only through surgery.
Diagnosis of pathology
In medicine, there are two types of this disease: upper and lower eyelids. Basically, the diagnosis is made by visual examination, which does not require additional tests. But in cases of relapse of the disease or the formation of a large number of tumors on the eyelids, additional tests may be prescribed. This is carried out in order to identify the cause of a significant decrease in immunity and detect the disease leading to the recurrence of chalazion.
Additional examinations
- An immunogram is performed to determine the state of the body’s immune system in order to normalize its functioning.
- Skin scraping and examination of eyelashes for the presence of mites, this requires 4 eyelashes from each eye, scraping from the eyelid and analysis of the contents of various types of pimples.
- A culture is carried out to detect staphylococcus, since it is often the main cause of a purulent infection.
- A general blood test to identify other inflammatory processes in the body that contribute to the recurrence of frozen barley.
- An analysis to determine the level of sugar in the blood, the increased content of which can cause dysfunction of peripheral vessels, which further disrupts the normal process of blood circulation and leads to an increase in foci of inflammation.
Important! The chronic nature of the pathology requires immediate consultation with a dermatologist, immunologist, infectious disease specialist in order to determine how to treat the pathology correctly.
If the underlying disease that causes the formation of repeated manifestations of chalazion is identified, the problem with relapses will disappear by itself and the inflammation will go away naturally.
Drug treatment
To treat cold barley in children and adult patients, medications intended for topical use are used. The pathology can be eliminated by:
- Yellow mercury ointment. This drug is an antiseptic and can quickly relieve symptoms of the disease. It is necessary to treat the lump with the specified drug three times a day.
- "Torbex" in the form of an ointment. The drug effectively fights swelling, inflammation, and itching. Use this medication three times a day.
- "Torbex" in the form of ophthalmic drops. Instillations of the drug are carried out three times a day, with a single dose of up to 2 drops.
- Hydrocortisone-based ointments can quickly suppress the symptoms of chalazion. The medicinal ointment should be placed under the eyelid affected by the disease three times a day.
- Advanced forms of chalazion are subject to treatment with steroid drugs. The medicine is injected into the cavity of the abscess, which helps eliminate inflammation.
What other treatment for cold stye is possible?
Symptoms of the development of cold barley according to different scenarios
There are different options for the formation and consequences of cold barley:
- Initial degree - swelling of the skin of the eyelid, dense to the touch (up to or more than 5 mm). There is irritation, minor pain, itching. The doctor prescribes conservative treatment, and if the tumor does not go away for more than a month, he recommends removing the chalazion.
- The middle phase is the occurrence of swelling of the eye, lacrimation, redness, an increase in the volume of the capsule, and painful sensations during pressure. From the inside of the eyelid, cold stye has a red tint with a gray center. As the tumor grows, discomfort increases as it puts pressure on the eyeball. If a rupture of the mucous membrane of the eyelid appears, or a strong proliferation of granulation, the cold barley must be urgently removed.
- When an infection occurs, the inflammatory process begins. An urgent surgical opening is required, otherwise scars will form on the eyelid.
Quite often, cold stye resolves on its own, without progression, but there is no point in waiting for this to happen; it is better to immediately consult an ophthalmologist. Untimely treatment of stye is especially dangerous for children, as they constantly rub their eyes and can introduce pathogenic microorganisms to the mucous membranes of the eyelids. People over 45 also need to visit a doctor if any tumor appears on the eyelids, as the conjunctival tumor may be of low quality.
Radical methods of therapy
If the neoplasm has an excessively dense structure, it must be excised surgically. Children tolerate the operation, performed under local anesthesia, very easily.
The incision is made from the inside of the eyelid, and therefore the appearance of cosmetic defects and scars after surgery is excluded. Excision of the tumor is indicated only if its development is not accompanied by inflammation.
After completion of the operation, a sterile bandage should be applied to the eye, which can be removed after two days. To prevent infection, the eyelid should be treated with antibacterial ointments.
When removing cold styes from the eye, a minimally invasive method is used. The tumor is excised using a laser beam. This procedure is performed very quickly, thanks to it you can permanently remove the chalazion.
Conservative treatment of cold stye
In the initial stages of the disease, drug treatment is used. It could be:
- use of antiseptic eye drops. They suppress the development of pathogens, be they bacteria, viruses or fungi (Okomistin, Albucid, Ofloxacin, Vitabact);
- use of mercury ointment. Mercury ointment has high biological activity and is widely used in the treatment of ophthalmological diseases;
- physiotherapeutic procedures, for example, UHF therapy. This is a high frequency electric field treatment. The procedure has a good anti-inflammatory effect, the maximum session duration is 15 minutes. If prescribed by a doctor, electrophoresis or laser heating may be prescribed.
Read in a separate article: Tobrex for barley on the eye: application features
Dry heat compresses are also used for treatment.
Dry heat can only be used if there is no inflammation. Otherwise, this may contribute to the development of an abscess and phlegmon.
Kalanchoe and aloe
- You will need aloe or Kalanchoe juice. It is necessary to squeeze the juice out of the leaves. A cotton pad is moistened in it and the chalazion is treated up to 5 times a day. The application should take up to 15 minutes. Apply a tampon soaked in the medicine to the affected eyelid. It is recommended to perform such procedures three times a day.
- Drops based on aloe, Kalanchoe. For chalazion of early development, juice obtained from aloe and Kalanchoe leaves is effective. The concentrate should be diluted with water 1 to 10. It is recommended to instill the product five times a day. A single dose is up to 4 drops.
Removing stye from the eye surgically and without surgery
A chalazion is a dense encapsulated accumulation of sebaceous secretion from the meibomian gland inside the lower or upper eyelid.
Translated from Greek, the word “chalazion” roughly corresponds to the Russian “gradinka” or “pea”; This means something hard, round and small in size.
Outwardly, this pathology resembles the well-known barley, but there is a difference between them, and a very significant one.
First of all, barley (hordeolum) is an acute purulent infectious-inflammatory process caused in most cases by bacterial pathogens (usually Staphylococcus aureus); In this case, it is not the meibomian gland that becomes inflamed, but another sebaceous gland (Zeiss) or an eyelash follicle.
With adequate treatment - or even without it, if the immune response is strong enough - the stye disappears after 5-7 days.
Chalazion occurs due to other, non-infectious reasons (although a previous inflammatory process is a direct risk factor), proceeds differently and requires a different approach to treatment.
The meibomian glands, of which there are about seventy on one pair of eyelids (on the upper one a little more than on the lower one), produce a special sebaceous-mucosal secretion designed to lubricate and reduce friction during blinking, on the one hand, and on the other hand, for hydroregulation and prevent too much abundant wetting of the eyelid with tear fluid. The exit tubules are located along the ciliary border of the eyelid, closer to the surface of the eye.
If the exit channel of the gland is blocked, and the secretion continues to be produced, its accumulation in the blocked mouth leads to swelling and inflammation of the meibomian gland, then to the breakthrough of the secretion into the surrounding cartilaginous tissue and encapsulation there in the form of an internal “sac”, which, gradually thickening and hardening, forms characteristic “pellet in the eyelid”.
Chalazion occurs in any age category, starting from early childhood, however, some sources indicate that, due to certain age-related characteristics, this disease is somewhat more often diagnosed in patients 30-40 years of age and older.
In this same (older) age group, differential diagnosis with other neoplasms is especially important - in particular, with the very dangerous adenocarcinoma of the sebaceous gland.
In itself, a “classic” uncomplicated chalazion does not pose any threat to life and health, does not affect visual acuity, but creates a noticeable cosmetic defect, which sometimes persists for up to a year or more, and tends to recur. Therefore, reasonable measures are necessary for its timely treatment and prevention, as well as to eliminate the most common causes and risk factors (if they are avoidable in a particular case).
Causes
As mentioned above, a previous infectious and inflammatory process (conjunctivitis, blepharitis, hordeolum, etc.) can lead to the development of chalazion.
Other reasons include general oily skin (hyperfunction of the sebaceous glands), injuries and burns of the eye, chronic endocrine, gastroenterological, hematological (presumably) disorders - in short, any pathology that can disrupt the functioning of the glands and the composition of their secretion - as well as helminthiasis, immune system weakness, vitamin deficiency.
Sometimes chalazions appear almost simultaneously in two eyes or on different eyelids of the same eye. Recurrence in the same place can be caused by undertreatment or incomplete removal of the previous chalazion.
Symptoms
In the initial phase, the eyelid turns red, itches and most often causes “bursting” pain; many patients note a painfully aggravated reaction to bright light, increased lacrimation, and a sensation of a foreign body.
Then the pain subsides; a characteristic round compaction forms inside the eyelid, rolling freely under slightly hyperemic skin (on the side of the conjunctiva, hyperemia is more pronounced). The swollen area may have a grayish-white center.
In this state, the chalazion, if it does not resolve (spontaneously or as a result of treatment) in 2-4 weeks, can remain for months. It is very likely that it will become secondary to infection and purulent inflammation of the internal capsule; sometimes such a purulent sac opens and the contents leak out.
In certain localizations (closer to the inner, mucous surface of the eyelid), mechanical irritation and inflammation of the conjunctiva by friction is also possible.
How does the pathology manifest itself?
At the initial stage of the disease, it becomes painful for a person to blink.
Unlike ordinary barley, in which suppuration and breakthrough occur, cold barley hardens and takes on the appearance of a soft, round tumor. The disease has 3 stages of development. How the signs differ is shown in the table:
| Stage | Symptoms |
| Initial | Mild pain when blinking or touching the eyes |
| Slight local redness at the site of future formation | |
| Average | Increased pain |
| The appearance of a small formation | |
| Redness of the eyelid skin | |
| Feeling of a foreign body inside under the eyelid | |
| Yellowish contents are visible on the vesicle under the skin | |
| Heavy | Barley breakthrough occurs |
| Seal of the formation, if it has not ruptured | |
| Significant increase in size | |
| Eyelid deformity | |
| Increased pressure on the eyeballs |
Treatment without surgery
Since chalazion seems to be an “understandable” and relatively harmless disease, attempts to self-treat it with folk remedies are widespread.
These methods are so numerous and varied that, even if they were effective, humanity should have long ago forgotten about chalazions. However, most patients (at least 75%) sooner or later consult an ophthalmologist.
In the early stages of formation, a chalazion should be treated with anti-inflammatory, absorbable and, if indicated, antibiotic ointments, drops, gels, etc.
, as well as 1% mercury yellow ointment and physiotherapeutic procedures (ultraviolet or ultra-high-frequency heating). At later stages, with a significant volume of chalazion, injections of corticosteroid hormones into the capsule are sometimes successfully practiced.
If all other procedures are ineffective, as well as if the patient is unwilling to put up with a cosmetic defect and/or be subjected to bizarre experiments within the framework of traditional medicine for a long time, surgical removal of the chalazion is prescribed.
Stye in a child
In children, with barley, a swelling first appears in the area of the edge of the eyelid, then, over time, it turns red and increases in size. A completely infectious process occurs directly around the eyelash.
The child's eyelid swells, which leads to a significant narrowing of the palpebral fissure. If a stye is left untreated for a long enough time, the child's eye may stop opening altogether.
As a rule, the presence of barley is accompanied by pain in the head. In addition, the child may experience eyelid twitching.
Barley is often found in children who go to kindergarten or primary school. If it does not disappear after eye drops and ointments are applied, surgical treatment is resorted to. Before the intervention, the baby is prescribed a blood test for clotting, their sugar level is determined, and their stool is analyzed for the presence of worms.
The procedure itself includes the same steps as in adults, but instead of local anesthesia, general anesthesia is used. The laser beam is not used if the child is under 14 years old.
Chalazion removal surgery
First of all, it should be noted that there are no special reasons for preoperative anxiety or, especially, fear in this case: the procedure is quite simple, has been worked out a long time ago, is performed on an outpatient basis and usually lasts about 20 minutes “from entering the manipulation room to leaving the room” (as was said a hundred years ago). At the same time, the professional level of the clinic and the qualifications of the doctor certainly matter, so the choice of an ophthalmic center should be meaningful and justified.
Local, subcutaneous anesthesia: after mandatory antiseptic treatment, an anesthetic is injected with a thin needle (usually a solution of lidocaine or novocaine), which ensures reliable insensitivity of the surgical field.
The problem area is fixed using a window clamp; the chalazion capsule is opened (along the suppurating fistula canal, if there is one) and exhumed along with all the contents. Depending on the location, the incision is made either from the outside of the eyelid or from the conjunctival side.
Then the surgical field is once again treated with antibacterial agents, drained if necessary and closed with suture material. A relatively tight bandage is applied.
How to remove stye with surgery?
Before performing the procedure, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination by the attending physician, who will determine the time for the operation. The surgical intervention is carried out in several stages.
- Treatment of the area near the eye. The patient's head is covered with a sterile napkin. Only the operated eye remains open. After which the area around the barley is treated with alcohol or other disinfectant. This is necessary to disinfect the site where surgery will be performed.
- Fixation of the century . During the procedure, the eyelid is secured with clamps, which prevents the risk of bleeding and damage to nearby tissues. If the tumor is located on the inside of the eyelid, the surgeon turns it out a little for better visibility.
- Incision. The incision is made in the traditional way using a scalpel or laser beam. If the stye is located internally, the incision is best made with a laser, since this is a difficult place for traditional surgery to reach.
Photo 1. The operation to remove barley at the stage of an incision, which is made using a laser beam.
- Delete. Removal of stye is performed using a scalpel - the doctor opens the formation, removes the purulent contents, then carefully removes the capsule with a special spatula.
- Processing of purified barley. After the eye is completely cleared of pus, an antibiotic ointment ( Tetracycline ) is placed under the eyelid. This remedy prevents the development of inflammatory processes in the operated eyelid.
- Stitching. When an incision is made from the inside, a healing ointment is sufficient. If surgery was performed with an incision in the skin of the upper or lower eyelid, sutures are placed on the wound.
- Applying a bandage. After surgery, a sterile pressure bandage is applied to the eye. Having received the necessary recommendations from the doctor, the patient can go home. He will have to wear a bandage for several days, removing it only to apply eye drops or ointment.
Reference. If barley removal is performed in childhood, the procedure is performed under general anesthesia.
Postoperative period
After surgery, it is important to carefully follow all the doctor’s recommendations, since the duration of wound healing depends on this. It is necessary not only to wear a tight bandage, but also to regularly use regenerating drugs. The recovery period lasts about 7-10 days. To avoid infection after surgery, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- protect the eye from water to prevent bacteria or infection from entering the wound;
- do not touch the crusts on the wounds - they should fall off on their own;
- do not touch the operation site, do not rub or scratch it;
- limit long-term visual activity ;
- Do not wear a contact lens for ;
- Avoid getting dust in the eyes;
- avoid direct sunlight , use sunglasses;
- Do not visit the sauna until the wound is completely healed .
for 3-4 days after surgery, but this will go away over time. At the end of the recovery period, the functions of the eye fully return.
Attention! It is strictly forbidden to open or squeeze out the stye yourself, as this can significantly worsen the situation.
Laser removal methods
Modern medical technologies, primarily using a laser scalpel, in this case have clear advantages over traditional ophthalmic surgery. Laser surgery is much less invasive and virtually bloodless; results are more predictable and accurate. The risk of complications and the duration of postoperative rehabilitation are significantly reduced.
By contacting our ophthalmological center for chalazion removal, you receive an individual approach (the exact method and surgical approach is selected), which guarantees the highest treatment result.
Features of the operation in children
Surgical intervention to remove the cyst is prescribed only for the most advanced form of the disease. Basically, the pathology can be dealt with using a conservative method of treatment by taking medications or warming up during physiotherapy.
Chalazion (“hailstone”) is an ophthalmological disease characterized by a benign tumor-like compaction located in the thickness of the eyelid. The disease develops against the background of blockage of the meibomian gland and chronic inflammation in it.
There are two main methods that are successfully used by doctors in the treatment of this disease: surgical (surgical) and non-surgical (conservative). The latter includes the use of various kinds of ointments, drops and injections, mainly antibacterial and corticosteroid drugs, as well as physiotherapy.
Source: https://PrimaMed-kzn.ru/bolezni/hirurgicheskoe-udalenie-yachmenya-na-glazu.html
Compresses
- Applications of cabbage leaves. You need to mix the white of one raw egg and cabbage pulp. The resulting product should be distributed on a napkin and applied to the affected eyelid. Remove this compress after 15 minutes. The cabbage-egg mixture can draw out purulent contents from swelling and eliminate the process of inflammation.
- If the tumor has appeared recently, warming it up is acceptable. To do this, you need to heat the salt over a fire, put it in a canvas bag and apply it to the damaged eyelid. Do this procedure at night. After the salt has cooled, it is necessary to remove the dry compress. This manipulation can be carried out using heated cereal.
- Application using dill seeds is the most effective method of combating chalazion. To prepare, you will need to boil 100 ml of water and add 2 tablespoons of dill seeds. Simmer the mixture for 10 minutes. The boiled seeds are cooled to a warm state, distributed over a cloth or napkin, and applied to the affected eyelid. The compress must be removed after 15 minutes.
- Flaxseeds. Flax seeds need to be calcined in a frying pan and poured into a linen bag. The resulting product is applied to the inflammation and kept until it cools.
Treatment of cold stye on the eye should be comprehensive.
How and why does stye occur?
The main cause of the disease is lack of personal hygiene.
A chalazion occurs when a regular stye hardens and is characterized by an inflammatory formation at the edge of the cartilaginous tissue of the eyelid, followed by hardening. The pathological process occurs due to blockage of the sebaceous (meibomian) gland and accumulation of secretions. A stye on a child’s eye is formed due to infection with dirty hands. In adults, the disease is provoked by the following factors:
- oily skin type;
- prolonged exposure to the cold;
- incorrect use of contact lenses and improper care of them;
- endocrine disorders;
- decreased immunity;
- use of low-quality or expired cosmetics;
- frequent ARVI;
- lack of vitamins and microelements;
- eating a lot of sweets, which increases the oiliness of the skin;
- disruption of the digestive system;
- Carrying out cosmetic procedures with contaminated instruments.
Washing
For chalazion, rinsing with products based on various medicinal herbs is effective.
- Marshmallow infusion. In a quarter liter of cold boiled water you need to put 6 grams of marshmallow rhizomes and leave for 8 hours. The product is then filtered. The affected eye is washed with the infusion obtained in this way.
- Infusion of chamomile and eyebright. It is necessary to mix the same amount of the indicated herbs and steam a teaspoon of the mixture using 200 ml of boiling water. Medicinal herbs are infused for 15 minutes, then filtered and used to wash the eyes.
- Fennel infusion. It is necessary to pour a teaspoon of fennel seeds with a quarter liter of boiling water and leave the mixture for 20 minutes, after which the mixture can be filtered and used for rinsing.
- Camomile tea. To prepare it you will need a teaspoon of dried plant flowers and a glass of boiling water. The ingredients are mixed and left for 5 minutes. After which the infusion must be filtered, after which it will be completely ready for use.
Prevention
To avoid frozen stye, it is recommended to carefully monitor the hygiene of your hands and face. When purchasing cosmetics and skin care products, you should check expiration dates, storage conditions and product documents. It is better to avoid dubious purchases. You also need to eat right, strengthen your immune system, and avoid hypothermia. It is strictly forbidden to touch or rub your eyes with contaminated hands. When using contact lenses, you should strictly adhere to the rules for storing and installing them.
Removing a stye from the eye surgically
If conservative methods do not produce results, surgical removal of barley is prescribed. The operation is performed on an outpatient basis using local anesthetics.
The operation can be performed in the classical way, but laser surgery is more effective and painless. After the procedure, an additional course of medication is prescribed for better recovery.
If the operation is not performed on time, there is a risk of complications in the form of an extensive inflammatory process.
Surgical removal is prescribed only in 10% of cases, when symptoms increase and the formation causes significant pain and discomfort.
Indications and contraindications
Barley is an inflammatory process that develops in the hair follicle of the eye. As a result, a tubercle forms on the eyelid, on the inside or outside. A related anamnesis is a chalazion - a lump under the eye at the site of blockage of the meibolian gland.
Ophthalmologists are of the opinion that chalazion is formed as a result of chronically untreated stye. Both diseases can be treated with medication; in 30% of cases, symptoms disappear on their own without the use of medication. But the most severe forms of pathologies require surgical intervention.
Removal of chalazion and stye on the eye is prescribed in the following cases:
- unsuccessful conservative therapy for 2 weeks;
- tubercle dimensions are more than 5 mm in diameter;
- compaction of the neoplasm;
- the presence of a cyst or abscess on the eyelid;
- severe discomfort;
- painful sensations on palpation.
It is not advisable to resort to surgery if the patient has poor blood clotting.
The need for surgery is determined by an ophthalmologist. He must study the medical history and the full course of treatment. The operation to remove barley has a number of contraindications. The procedure is not performed for existing acute infectious diseases or during exacerbation of chronic pathologies. Relative contraindications include poor blood clotting.
How to prepare?
The operation does not require hospitalization and is performed on an outpatient basis. To begin with, the patient must undergo a series of laboratory tests, primarily a blood test.
The ophthalmologist immediately before the procedure performs an examination to determine the exact location. Women should not paint their eyes; cosmetics will only activate the inflammatory process.
The duration of the entire procedure does not exceed 30 minutes. For an anesthetic effect, local anesthesia is used.
Removal methods
If removal is indicated, the patient can choose how to get rid of the stye. This procedure is not considered urgent; you can choose a day. Two methods are considered popular: classical surgery and laser. Both operations involve local anesthesia and then removal of the purulent capsule from the eyelid. The surgical operation takes place in stages:
Before the actual manipulation begins, the problem area is numbed.
- The patient lies down on the table, the head is secured with special belts.
- The surgical field is treated with an antiseptic.
- Anesthesia is administered and the patient waits 3-5 minutes for it to take effect.
- The eyelid is fixed with a clamp.
This gives the surgeon direct access to the stye and reduces the risk of bleeding. - The tubercle is opened and the entire capsule is removed.
- Treated with an antiseptic.
- Stitch the wound.
- Apply a sterile dressing.
The laser method is simpler and painless.
During the operation, an incision and excision of the capsule are also made, but with the help of equipment. Thus, the procedure is carried out without contact, eliminating the possibility of bleeding. Disinfection is also carried out using the laser method. Ophthalmologists recommend using this method to remove internal stye.
The duration of the operation is shorter than surgery, maximum 20 minutes. The risk of relapse is reduced to zero. The main disadvantage of laser surgery is its price, which significantly exceeds the cost of the traditional method.
Possible complications and risks
In 95% of cases, operations go without problems, but there is a possibility of relapse. This is possible as a result of incomplete removal of the capsule, in which case additional cleaning is required.
The process of suppuration is also possible if you do not follow the doctor’s recommendations for taking medications in the postoperative period.
But more negative consequences are observed if the stye is not removed in time; a cyst forms in its place, which can develop into a malignant formation.
Source: https://EtoGlaza.ru/bolezni/gnoynik/udalenie-yachmenya-hirurgicheskim-putem.html