To understand the difference between stye and conjunctivitis, you need to know the nature and course of both diseases. Thus, barley is an infectious pathology, accompanied by swelling of the eyelid and purulent discharge. Conjunctivitis is characterized by inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye.
Despite the similar symptoms, the treatment of the diseases is radically different. It is not recommended to use medications on your own to avoid deep eye damage. Only a specialist will be able to determine the severity of the disease and the causes of its occurrence and prescribe the recommended medications.
Share
Tweet
Share
Cool
Send
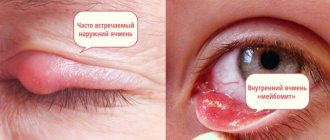
Sty
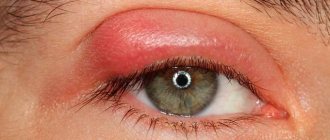
It is not difficult to recognize inflammation of the eyelid: it turns red and thickens, the eye itches, and after a few days a round-shaped swelling with purulent contents inside forms at the site of the itching. After the pus is released, the swelling decreases and after a few days the eyelid is restored. On average, the duration of ripening and rupture of barley is a week.
Attention! Self-squeezing barley is prohibited! This is fraught with serious complications, which may take several weeks to get rid of.
It is recommended not to take independent action, but to wait for seven days for the pus to drain naturally (after a week has passed and pain persists, you should consult a doctor).
Reasons for appearance
The main cause of styes is considered to be an infection of the eye, causing swelling of the eyelid. Staphylococcus, which causes the appearance of hordeolum, can enter the body for several reasons:
- in case of non-compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- when using low-quality or foreign cosmetics;
- during a period of weakened immunity (for example, after suffering a serious illness or a course of antibacterial therapy);
- for other reasons.
Symptoms
Symptoms of the disease manifest themselves as follows:
- there is pain in the eye, redness and swelling of the eyelid;
- swelling and purulent discharge from the corner of the eyelid appears;
- Internal inflammation contributes to the appearance of a macula.
Already in the first day after infection, barley appears and grows. The head, which secretes pus, appears after a couple of days. The recovery period begins in a week.
Forms of conjunctivitis
In addition to the described classification, there are also three forms of conjunctivitis:
- bacterial;
- viral;
- allergic.
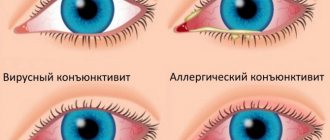
The first is characterized not only by redness of the eyes. There may also be pus and mucus discharge from one or both eyes. The viral form appears during a cold. The eyes turn red and tears flow. Conjunctivitis usually goes away along with the disease. You should be concerned if the inflammation does not go away after several weeks, but only gets worse. The latter, the allergic form, also includes redness, as well as swelling, tearing and itching.
Important! If you have additional symptoms, such as severe pain in the eyes, blurred vision during conjunctivitis, or photosensitivity, you should immediately consult an ophthalmologist.
Conjunctivitis
It is an inflammation of the conjunctiva (the transparent tissue covering the inner surface of the eyelid and the visible area of the sclera), often of an infectious nature.
The disease causes inflammation of the blood vessels of the conjunctiva, they become more visible and change their hue to pink or red (with an acute nature of the inflammatory process).
Some forms of conjunctivitis spread easily and can be dangerous to others. Despite the low severity of the disease, complications of conjunctivitis can have serious consequences for the eyes.
The eyes of newborns are very susceptible to this disease - bacteria may be present in the mother's birth canal, which does not bother the mother, but causes ophthalmia (a severe form of conjunctivitis) in infants.
What is the difference between the diseases?
Unlike conjunctivitis, which has various forms of manifestation, the course and treatment of hordeolum are always the same. So, with slight redness and timely treatment, conjunctivitis goes away quickly, and in the case of a film covering the eyelid and eye, the course of the disease is different, and so are the treatment methods.
There are the following forms of conjunctivitis:
- acute;
- adenoviral;
- chronic.
Attention! The duration of barley does not exceed 7 days, conjunctivitis in complex cases - up to 3 months.
Symptoms, causes and differences between stye and conjunctivitis:
| Disease | Symptoms | Causes of the disease | |
| Previous symptoms | Course of the disease | ||
| Barley (hordeolum) | Swelling and itching of the eyelid, pain, redness of the conjunctiva | Possible increase in temperature, formation of swelling of the eyelid and purulent nodule | Helminth infection, diabetes mellitus, weakened immunity, gastrointestinal problems |
| Conjunctivitis | Excessive lacrimation, photophobia, purulent discharge (more often after waking up) | Chlamydia, fungi, viruses, bacteria, cosmetics, contact lenses, allergens | |
The main differences between barley and conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis and stye are inflammatory diseases that affect the organs of vision. These two pathological conditions are manifested by hyperemia, lacrimation, swelling and some other unpleasant phenomena. How to understand which disease has developed - conjunctivitis or barley? At first glance, these diseases are similar. However, if you take a closer look at the etiology, pathogenesis and clinical picture of conjunctivitis and barley, you can see that these are two completely different diseases.
The main differences between pathologies include the following:
- With barley, a small tubercle forms in the area of the ciliary edge, which has a dense structure and gradually increases in size. With conjunctivitis, only slight swelling is visible.
- The clinical picture of conjunctivitis is more pronounced; in the bacterial form, pus may be discharged.
- With conjunctivitis, the white of the eye becomes inflamed, and with styes, the edge of the eyelid becomes inflamed.
- A pus on the eye is only infectious in origin; conjunctivitis can occur for various reasons.
- The duration of barley is about 7-10 days, therapy for conjunctivitis can last several weeks.
Treatment for stye and conjunctivitis is also different. In the second case, medications are selected taking into account the form of the disease, and in the first, the therapy is always the same.
Features of the treatment of pathologies
How to treat conjunctivitis
To get rid of conjunctivitis, you must follow the general principles of treatment:
- Contacting a specialist is strictly necessary, especially if symptoms last more than three days.
- If one eye is affected, drops are used for both eyes (the healthy one is instilled first, then the patient).
- It is prohibited to use common family belongings during illness.
- You should not use an eye patch, which will promote the growth of bacteria underneath and further aggravate the disease affecting the cornea of the eye.
- Before instilling eye drops, it is necessary to remove accumulated plaque from mucus and pus using furatsilin.
In children, treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis is carried out with local antibacterial drugs in ointments and drops. For purulent conjunctivitis, the use of antibacterial drugs should be agreed with a doctor.
Important! Viral conjunctivitis often goes away on its own without treatment within 7 days (provided there is no purulent discharge from the eyes).
Within a week, immunity is developed and the disease recedes. Viral conjunctivitis does not require the use of antibacterial drugs. Inflamed eyes are washed with saline solution, antiseptic or chamomile decoction. The eye is washed in the direction from the outer corner to the inner (from the temporal part to the nose).
Allergic conjunctivitis requires limiting contact with the allergen. If restrictions are not possible, the doctor selects antiallergic drops and antihistamines.
Mandatory consultation with a doctor requires:
- the occurrence of conjunctivitis in infants (up to 1 year);
- no improvement on the third day of treatment;
- the occurrence of photophobia against the background of redness of the eyes;
- burning sensation and pain in the eyes;
- blurred vision;
- the appearance of blisters on the upper eyelid.
The doctor may prescribe the following therapeutic procedures:
- Ultraviolet irradiation for acute viral damage to the eyelids (has an anti-edematous and restorative effect, improves metabolism in the tissues of the eye, and triggers restoration processes in them).
- Electrophoresis using a bath technique or nasal administration of turundum in solution.
Any of the methods requires a doctor’s prescription and depends on the stage of the disease and the severity of the disease.
Causes and symptoms of conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the conjunctiva, the mucous membrane that covers the outside of the eye. Taking into account the etiology of occurrence, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- Bacterial. It occurs as a result of exposure to a purulent infection, most often by coccus bacteria. The pathological process first affects one organ of vision, and then the second. The prognosis is mostly favorable.
- Viral. It is most often diagnosed as developing as a result of a viral infection entering the body. Often the disease goes away on its own within 1-2 weeks after infection.
- Fungal. The pathological process occurs due to increased activity of the fungal flora. With this form of conjunctivitis, purulent blisters can form, in place of which fistulas remain.
- Allergic. One of the most frequently diagnosed forms of disease caused by contact with allergens, which can be wool, pollen, food, and so on. Accompanied by other manifestations of an allergic reaction - coughing, sneezing, runny nose.
Conjunctivitis can occur if the following predisposing factors are present:
- hypothermia;
- eye injuries;
- improper use of contact lenses;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- use of low-quality or expired cosmetics;
- increased sensitivity to medications.
The likelihood of developing inflammation of the conjunctiva increases significantly if a person frequently comes into contact with various physical and chemical irritants (dust, radiation, smoke). Regardless of the form of the pathology, the patient experiences the following main manifestations of conjunctivitis:
- tearfulness;
- hyperemia;
- swelling;
- itching, burning;
- increased sensitivity to light;
- sensation of a foreign body in the eye;
- soreness, discomfort.
With bacterial conjunctivitis, in addition to the main manifestations, the discharge of purulent contents, sticking of the eyelids immediately after sleep and the formation of yellow scabs on the edges of the eyelids are observed. The fungal form of the pathology is accompanied by the release of clear liquid from the sclera.
Read in a separate article: Is sick leave given for conjunctivitis in adults and children?
How to treat stye
Despite the painlessness of the disease, its treatment is required, depending on the duration of the inflammation. The doctor prescribes drops and ointments; in some cases (usually at the initial stage), warming is recommended.
The use of ointments is required in the early stages of maturation of the tubercle (this method is especially effective when pus comes out inside and not outside).
Prevention of infectious eye diseases
Prevention of stye
To prevent the occurrence of barley, you must adhere to some simple rules of prevention:
- Take care of personal hygiene: wash your hands and face often.
- Do not touch your eyes with dirty hands.
- Use an adequate amount of cosmetics and wash off makeup before going to bed.
- Only individual towels!
- Regular strengthening of the immune system.
- The diet should contain more fruits and vegetables.
Prevention of conjunctivitis
Since the disease is contagious, the following rules must be followed:
- Use only your own face towel.
- Do not use cosmetic samples (also do not share your cosmetics with other people).
- When using contact lenses (especially extended wear), strictly follow the rules for storing and washing them.
Expert opinion
Danilova Elena Fedorovna
Ophthalmologist of the highest qualification category, Doctor of Medical Sciences. Has extensive experience in diagnosing and treating eye diseases in adults and children.
American scientists in their studies revealed the possibility of infection from cosmetics samples by 67%. It is the probes that are considered the main carriers of eye viruses and bacteria.
Following simple rules of prevention will help prevent infection with eye diseases.
The main differences in the treatment of conjunctivitis and stye
So, to get rid of barley, it is enough to wait the time necessary for the purulent contents of the tubercle to mature. The main thing is not to try to remove the rod yourself. You should not use decorative cosmetics during this period. To relieve inflammation in the eye, you can use special eye drops.
In the case of conjunctivitis, you will have to visit an ophthalmologist. If this is not done, extremely serious consequences may develop, including loss of vision. The doctor prescribes treatment only after he has established the exact cause of the pathology. If the route of infection is bacterial, then antibiotics are used to eliminate the disease. If inflammation develops due to allergies, antihistamines are prescribed.