Description
Angiopathy is a group of diseases characterized by damage to the vascular wall. This pathology is characterized by a violation of the tone of the vascular wall due to a violation of neurohumoral regulation. With angiopathy, temporary spasms and vascular paresis develop. As a result, the permeability of the vascular wall increases, and hemorrhages often occur. In diabetic angiopathy, damage to the vascular wall is caused by metabolic disorders. There is a thickening of the basal membranes of the vascular walls and proliferation of their endothelium. The lumen of the artery narrows. Microcirculation in the blood-supplied tissues is disrupted and ischemia (lack of oxygen) develops. Against the background of such pathological processes, favorable conditions are created for the development of the atherosclerotic process.
Retinal angiopathy
Vasodilators include
Xanthinol nicotinate and Pentoxifylline (drugs Trental , Agapurin , Pentoxifylline-Teva , Pentilin , Arbiflex , Pentoksifillin-Acri , Vazonit ).
Pentoxifylline can be called a complex drug that combines the effects of a vasodilator, angioprotector and antiplatelet agent. These drugs are widely used for angiopathy of various origins. They start taking pentoxifylline with 100-200 mg three times a day for the first two to three weeks, and then switch to taking 100 mg twice a day for a month. Locally acting drugs (eye drops) that improve metabolism are prescribed Taufon , Emoxy-optik (active ingredient emoxypine , which, along with an antioxidant effect, has angioprotective and anticoagulant effects).
Vasospasm and ischemic processes, venous stagnation or atherosclerotic changes can be detected in the fundus. Depending on this, the treatment is adjusted. When ischemic processes predominate in the vessels of the retina, Sermion (has a vasodilating effect mainly on the vessels of the brain), Emoxy-Optic . A vitamin-mineral complex is also introduced into the treatment in a monthly course. In case of impaired venous outflow and venous stagnation, venotonic drugs ( Phlebodia , Venolek , Vasoket ) are prescribed. In addition to their venotonic effect, they also have an angioprotective effect and improve lymphatic drainage. It is very important to treat the underlying disease against which angiopathy developed.
Treatment of diabetic angio- and retinopathy includes:
- First of all, it is important to constantly monitor blood sugar levels - patients should take a glucose-lowering drug recommended by a doctor and adhere to a low-carbohydrate diet. Patients are shown moderate physical activity, which promotes more rational consumption of glucose by muscles.
- Key aspects of control of diabetic retinal angiopathy are control of blood pressure and lipids (statins and fibrates).
- For antihypertensive purposes in diabetes mellitus, it is best to use drugs from the group of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors ( Enalapril , Lisinopril , Perindopril Teva , Prineva , Ramipril ), which not only control blood pressure, but also slow down the onset and progression of renal failure - also an important complication of diabetes mellitus along with angiopathy. These drugs prevent the appearance of proteinuria in diabetes mellitus, and when it occurs, they prevent the development of chronic renal failure.
- The use of antioxidants - high doses of tocopherol (1200 mg per day), vitamins C , Probucol, α-lipoic acid ( Alfa Lipon , Berlition , Espa-lipon ), Emoxipin , Mexidol , lutein-zeaxanthin complex and the food supplement Eikonol , containing polyunsaturated fatty acids . Alpha-lipoic acid preparations are important for diabetes mellitus because they have a complex effect - anti-sclerotic, antioxidant, regulates blood sugar. Ocuwait-Reti-Nat forte , which contains fish oil and vitamin E, is also recommended.
- Diabetes mellitus increases the fragility of blood vessels and a frequent complication of the fundus is the appearance of hemorrhages . With long-term use of Doxium (calcium dobesilate), hemorrhages resolve within 4-8 months, and new ones do not appear.
All patients, regardless of the degree of diabetes compensation, are recommended to undergo such courses of treatment twice a year.
Treatment of hypertensive retinal vascular angiopathy is based on the treatment of hypertension. Various groups of drugs are used, which a cardiologist can recommend. It is important to monitor blood lipid levels. Among the drugs from the statin group, Rosuvastatin is contraindicated in severe renal impairment, and with a moderate decrease in renal function, the dose of Rosuvastatin should not exceed 40 mg. Atorvastatin does not have such restrictions , so its use is safe in patients with kidney pathology. This is especially important for patients with diabetes, who often have kidney damage due to the underlying disease.
For rheumatic retinal lesions, attention is paid to treating the underlying disease. In case of pronounced changes in the fundus, in addition to the treatment prescribed by the rheumatologist, a course of para- or retrobulbar injections of glucocorticoids is carried out. To resolve exudates and hemorrhages, tissue therapy is prescribed (aloe extract, Biosed, FIBS, Peat, Bumisol, vitreous), injections of Lidase or Chymotrypsin , lidase electrophoresis.
Traumatic angiopathy develops after severe general injuries accompanied by shock: compression, reproduction, fractures of the limbs and base of the skull, brain injury. Timely provision of assistance and treatment of shock reduces the risk of severe angiopathy.
Another mechanism of traumatic angiopathy is associated with compression of the chest, tissues of the neck and head, which is accompanied by an increase in intracranial pressure and serious changes in the tone of the retinal vessels. Treatment is aimed at reducing intracranial pressure and improving blood circulation in the vessels of the brain and retina.
Classification
Depending on the diameter of the capillaries affected by the pathological process, the following types of angiopathy are distinguished: Macroangiopathy - develops with atherosclerotic vascular damage. Has a severe course. Macroangiopathies usually develop in the vessels of the heart and lower extremities. Microangiopathy means damage to small vessels by a pathological process, developing as a result of necrosis, thrombosis, hyalinosis, fibrinoid swelling. Microangiopathies include damage to the vessels of the retina of the eyeball, as well as damage to the capillaries of the kidneys. The most common diabetic angiopathy occurs in patients with diabetes mellitus. Vascular lesions can have different localizations. Most often affected: Renal vessels (diabetic nephropathy); Retinal vessels (diabetic retinopathy); Vessels of the lower extremities. Hypertensive angiopathy is also distinguished. This disease develops during the progression of hypertension and is most clearly manifested in the fundus. In the opposite condition (hypotension), hypotonic retinal angiopathy develops. Morel's dysoric angiopathy develops in Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia. This disease is characterized by a combination of amyloidosis of the walls of arteries and arterioles, and the formation of senile plaques. There are two forms of the disease: drusen and congophilic. Mostly young men develop Ila disease or proliferating retinitis. This disease is characterized by the development of cataracts, multiple hemorrhages in the retina and vitreous body. As juvenile angiopathy progresses, glaucoma appears and the retina of the eyeball becomes detached.
Diabetic angiopathy
Eye health. Symptoms, treatment and prevention of herpetic keratitis
Depending on the severity of the disease, complex treatment or one of the following types of therapy is used:
Drug treatment
Drug therapy is carried out comprehensively using:
- antiviral drugs (Acilovir, Zovirax, Virolex, Nucleovir, Interferon, Poludan, Pirogeshal) suppress viral activity in the body;
- topical agents (ointments Kerecid, Tebrofen, Florenal) act specifically on the lesion;
- immunostimulants (Levamisole) increase the body’s natural ability to fight infection;
- drugs aimed at relieving symptomatic manifestations (Dexamethasone, Succinic acid).
Drug treatment of keratitis is best carried out in a hospital setting under the constant supervision of specialists.
Symptoms
The manifestation of angiopathy primarily depends on the location of the pathological process. May be observed: Decreased visual acuity; Loss of vision; Pain in the legs with the development of “intermittent claudication,” when pain occurs when walking and subsides after a short rest; Feeling of burning, itching in the legs; The appearance of petechiae, telangiectasia on the skin; Frequent and persistent nosebleeds; Hemoptysis; Gastrointestinal bleeding; Hematuria (the appearance of blood in the urine); Trophic disorders in the periphery from dryness and flaking of the skin on the extremities to the development of gangrene of the foot.
Retinal vascular angiosclerosis: what is it, ICD 10 code, causes, symptoms and treatment
Retinal angiosclerosis is a pathology in which the lumen of the vessels of the fundus of the eye narrows and their walls thicken. At the same time, their functional abilities deteriorate.
Its ICD 10 code is H35, which means other retinal diseases. The severity of the symptoms of such a disease depends on the degree of its neglect.
In the absence of competent and timely treatment, it can lead to complications and cause visual impairment.
- 1 The essence of the problem
- 2 Signs
- 3 Therapy
- 4 Prevention
- 5 Outcome of the disease
The essence of the problem
Angiosclerosis occurs against the background of hypertension, so it is necessary to look for the causes of vision pathology among the factors that provoke an increase in pressure.
At risk are patients who have bleeding disorders, diabetes, autoimmune diseases, traumatic brain injuries, and cervical osteochondrosis. The problem is often encountered by older people, as well as those who have bad habits.
Nicotine and ethyl alcohol negatively affect the circulatory system and provoke fluctuations in blood pressure.
Angiosclerosis does not occur suddenly. It goes through several successive stages. Each of them has special symptoms. It is important to consider that in the initial stages the disorder can be successfully corrected, so even with the most minor changes, therapy should be started immediately.
With angiosclerosis, the abnormal process affects the retina, the organ responsible for adequate perception of colors, as well as the formation of a three-dimensional image in the mind. It is the inner shell, which is penetrated by the smallest vessels. If the pressure in the latter increases, vision problems begin.
The situation is considered especially difficult if blood clots clog the retinal vessels.
Doctors distinguish two stages that the disease goes through in its development. The initial one is more mild and is regarded as angiopathy. Sharp jumps in blood pressure lead to negative changes in the blood vessels, but their structure is not yet damaged. At this stage, they can expand significantly, which will be noticeable to the ophthalmologist during the examination.
At this time, recovery occurs most often (regardless of whether the retina of one eye or both is affected).
The second stage is more severe. This is already hypertensive angiosclerosis itself. In this case, the vessels piercing the retina begin to intertwine. Their walls undergo spasm, due to which the lumen decreases and normal blood flow stops. Ophthalmologists divide the second stage of the disease into three substages:
- First. The lumen of the vein narrows. A nearby artery begins to put pressure on this vessel.
- Second. The vein becomes tortuous.
- Third. The bend is pronounced. Part of the affected vessel becomes invisible and is visualized as a rupture.
The later the problem is discovered, the worse it is for the patient. At later stages, abnormal processes become irreversible.
That is, vision loss occurs irrevocably and a person forever loses the ability to see. To prevent this, you need to consult an ophthalmologist.
To achieve good results, it is important not only to stop pathological changes, but also to eliminate the factors that provoked them.
Signs
Initially, the pathology does not manifest itself. The only thing that worries the patient is the periodic flashing of spots before the eyes and rapid overexertion, for example, when reading, watching TV or working at the computer. Most patients do not attach any importance to this and attribute everything to fatigue.
As the problem develops, the unpleasant manifestations of the disease intensify. Common symptoms of retinal vascular angiosclerosis include disorientation in space, migraine, loss of image fields and a decrease in its clarity, tension in the eyes (it does not go away even during rest).
Not so typical symptoms include tinnitus, sleep disturbances, memory problems, and regular nosebleeds.
Already based on the patient’s complaints, angioscoerosis can be suspected. However, to confirm these assumptions and identify the nature of the problem, a number of diagnostic procedures are prescribed.
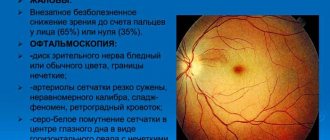
First, the specialist examines the fundus of the eye. To eliminate pupil accommodation, a special drug is instilled into the eyes beforehand.
During the procedure, the doctor evaluates the condition of the lens, eye chambers, retina and blood vessels.
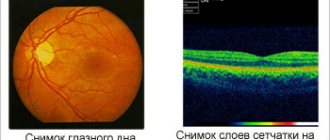
In addition, fluorescein angiography is prescribed. It is needed to find out what condition the eye vessels are in and how passable they are.
During the examination, a specialist can identify a violation of capillary tortuosity, swelling of nerve fibers, and disruption of the choroid plexuses. The essence of the procedure is the introduction into the body of a drug that has fluorescence (glow).
As it moves along the capillary, the specialist can see the areas of narrowing and widening of the walls.
In confusing situations, MRI and CT may be prescribed. These procedures allow you to see the choroid plexuses not only in the eyes, but also in other organs. Often the examination also includes laboratory tests.
To confirm or refute the presence of diabetes, a blood sugar test is performed.
Therapy
Treatment methods for hypertensive retinal angiosclerosis are chosen by the doctor. At the same time, he takes into account the degree of neglect of the problem and the reasons that provoked its development.
The purpose of the conservative effect is to enhance metabolic processes, normalize blood circulation in the structures of the visual organ, and also improve the nutrition of the retina. For angiosclerosis of any nature, specialists prescribe agents to dilate blood vessels (for example, Vazonit).
This helps prevent pathological changes in the walls of blood vessels and the formation of blood clots.
In addition, products from the following groups may be recommended:
- Microcirculation stimulants (“Actovegin”). They are used for ischemic and congestive processes, retinal dystrophy. A specialist can also prescribe medications that reduce the permeability of the walls of arteries and veins (“Dicynon”).
- Anticoagulants (“Aspirin Cardio”, “Trombonet”). They are needed for patients who have an increased risk of blood clots or who have already had a blockage in their blood vessels.
- Venotics (“Phlebodia”, “Normoven”). The drugs are indicated for venous stagnation. They are used as aids for angiosclerosis in diabetics.
- Metabolism stimulants. They may be intended for oral administration or injection. Usually this is “Cocarboxylase” or “Neurorubin”. Additionally, a specialist may prescribe medicine in the form of drops for local use (“Taufon”).
Attention!
To speed up recovery, experts advise taking 1 tsp of pollen. three times a day.
During treatment, it is important to follow the recommendations given by your doctor. Hypertensive patients need to take statins, antihypertensives and sedatives.
Patients who have suffered serious injuries or suffer from autoimmune diseases are prescribed glucocorticoids, Lidase and Chymotrypsin. They are introduced into the body by injection.
Patients with diabetes are given a diet and prescribed antioxidants and drugs that lower blood glucose levels. They are also recommended to exercise lightly.
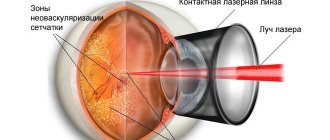
In the most advanced cases, laser treatment is used. Depending on the nature and spread of the abnormal process, two types of coagulation are performed:
- Panretinal. Laser "strokes" are applied to the retina in a grating pattern of more than 1,000 dots (usually up to 2,000). The macula area, which is responsible for visual acuity, is not affected. Laser “puncture” affects only the superficial zones of the retina. It does not enter the photoreceptor layer. Therefore, visual function is not impaired after exposure. At the same time, the retinal points exposed to the laser begin to change their physiological properties. Their need for oxygen decreases. The retina's dependence on angiopathic vessels that cannot cope with their task is reduced. As a result, more oxygen reaches the macula and its condition improves, and visual function is restored.
- Focal. This method of therapy is especially effective for macular swelling. A specialist uses a laser to seal the permeable walls of blood vessels, which are causing the accumulation of excess fluid. Then the swelling subsides and vision improves.
To restore trophism faster, the patient is recommended to undergo a course of physiotherapy. This can be acupuncture, pneumomassage, pulse and color exposure, magnetic therapy. Good results are obtained by using the Sidorenko Glasses simulator. To tone the blood vessels, you can do yoga and swimming, and go to massage sessions for the collar area.
Prevention
Proper nutrition helps not only prevent the development of the disease, but also alleviate its course, as well as speed up recovery if it has already developed. Abuse of sugar and carbohydrates leads to metabolic disorders. The body has no need to burn fat, but there are enough reasons for its accumulation.
For those who care about their health, it is recommended to eat white meat and foods that contain Omega-3 and Omega-6. At the same time, the consumption of carbohydrates (porridge, baked goods), starch and sugar should be limited.
With increased stress on the eyes, special gymnastics will help. It will prevent the development of vascular disorders and decreased visual acuity. The main thing is to do it regularly. There are different sets of exercises. An ophthalmologist can tell which one is suitable for a particular patient after examination and questioning.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GYLO-dCuUP0
You need to make it a habit to take daily walks in the fresh air and play sports (physical activity should be moderate). This will keep the body in good condition, which will naturally reduce the risk of developing vascular pathologies. At the end of the day, it is important to remember to remove your makeup and wash your face. Those who use contact lenses need to be especially careful about their eye hygiene.
Outcome of the disease
The prognosis depends on how timely and correctly the treatment was performed. If the pathology is identified at the initial stage and treated immediately, the patient can expect a favorable outcome. That’s why it’s so important to go for preventive examinations to an ophthalmologist at least once a year, even if nothing worries you. Without treatment, the following complications are possible:
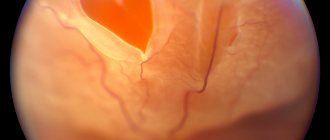
- Retinal disinsertion. Due to impaired microcirculation, the tissue loses its functions. There is a gradual decrease in vision until it is completely lost. The retina is separated from the membrane of the eye.
- Tissue necrosis. If blood circulation is impaired, the eyeball cannot receive enough nutrients and oxygen. As a result, cells begin to die.
- Optic nerve atrophy. This occurs due to insufficient blood supply to these tissues. The signal received by the organs of vision ceases to be transmitted to the central nervous system. This is how complete loss of vision develops.
Angioscoerosis is a serious disease, the progression of which ends in disability. There are various factors that can trigger its occurrence. They need to be eliminated in time. Ophthalmologists treat pathology. They individually select medications and calculate their dosages. In the most severe cases, patients are prescribed surgery.
Source: https://sosud-ok.ru/sosudi/angioskleroz-sosudov-setchatki.html
Diagnostics
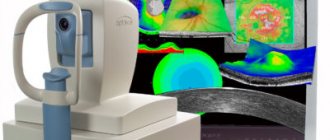
When a patient is suspected of having angiopathy, a physical examination, palpation, percussion, auscultation, and collection of patient complaints and medical history are performed. Then, to clarify the diagnosis, several studies are prescribed: Ultrasound examination of blood vessels - Doppler examination and duplex scanning are performed, providing information about the condition of the vascular wall and the speed of blood flow. Fundus graphy is used to study the fundus of the eye. The resulting computer image visualizes the vessels of the retina of the eyeball. Angiography is an X-ray examination that begins with the introduction of a radiopaque contrast agent into the lumen of the vessel. Then a series of images is taken, with which you can evaluate the patency of the vessel and the speed of contrast advancement. Magnetic resonance imaging - this research method, which does not carry a dose load of radiation, allows you to visualize the structure of the soft tissues of the body on the monitor screen. Computed tomography is aimed at obtaining layer-by-layer images from the area of the pathological process.
Causes
An example of diagnosing myopia using a special table from an ophthalmologist. Good vision will be if rays of light passing through the lens and cornea are normally focused on the retina of the eye. In myopic people, the focus location is changed and is in front of the retina. The eyeball grows, and accordingly, vision decreases.
There are several reasons for this:
- Violation of occupational and study hygiene, causing high visual stress and overwork of the eye muscles.
- A hereditary factor manifested in weak connective tissue, predisposed to an enlargement of the eyeball.
- High ocular pressure, that is, a change in ophthalmic tone, leads to deformation of the eyeball.
Physiological factors of impaired accommodation of the eye muscles tend to progress. This is why it is so important to diagnose myopia, identify its cause and begin treatment.
Treatment
The treatment of angiopathy in Israel is approached strictly individually, taking into account the nature of the disease in each patient and the severity of the process: Drug therapy is aimed at improving microcirculation in tissues. Angioprotectors, anticoagulants, antispasmodics, antiplatelet agents, and drugs that normalize blood clotting and improve blood circulation in the cerebral vessels are used. Insulin therapy is used to correct blood glucose levels. Physiotherapy – to correct the condition of angiopathy, the use of plasmapheresis, electrotherapy, and mud therapy is indicated. Surgical treatment has several directions. In the early stages of the disease, lumbar sympathectomy is effective, with preference given to the endoscopic surgical technique. Weakening the sympathetic influence on the artery wall leads to the elimination of the spastic component of pathogenesis. Various reconstructive operations are performed on blood vessels, restoring their lumen and improving microcirculation in tissues. In advanced cases of diabetic angiopathy of the vessels of the lower extremities with the development of wet gangrene and symptoms of intoxication, amputation of the extremities is performed at various levels. After such a traumatic but necessary operation, a prosthesis is selected or made individually for the patient, allowing him to perform a sufficient amount of active movements. For retinopathy, cryosurgical or laser electrocoagulation is used. For atherosclerosis, endarterectomy, percutaneous endovascular balloon angioplasty, and stenting are used.
Features and treatment of eye injuries in children
Most eye injuries in children are of a domestic nature and relate to blunt injuries and microtraumas. Burns and penetrating wounds account for no more than 8 and 2% , respectively. The main reasons are insufficient childcare and poor organization of games. Boys susceptible to eye injuries than girls ( 85% vs. 15% ).
Symptoms of damage to the visual organs in children do not differ from those in adults. Treatment has its own nuances, which should always be accompanied by good pain relief , especially with penetrating trauma.
in childhood . If surgery was performed and non-absorbable sutures were placed on the cornea, they are removed as soon as possible.
The essence of the problem
Angiosclerosis occurs against the background of hypertension, so it is necessary to look for the causes of vision pathology among the factors that provoke an increase in pressure.
At risk are patients who have bleeding disorders, diabetes, autoimmune diseases, traumatic brain injuries, and cervical osteochondrosis. The problem is often encountered by older people, as well as those who have bad habits. Nicotine and ethyl alcohol negatively affect the circulatory system and provoke fluctuations in blood pressure. Attention!
Poisoning with toxic substances can lead to hypertension and problems with the visual organ. This often happens to those who work in hazardous industries and do not engage in intoxication prevention.
Angiosclerosis does not occur suddenly. It goes through several successive stages. Each of them has special symptoms. It is important to consider that in the initial stages the disorder can be successfully corrected, so even with the most minor changes, therapy should be started immediately. With angiosclerosis, the abnormal process affects the retina, the organ responsible for adequate perception of colors, as well as the formation of a three-dimensional image in the mind. It is the inner shell, which is penetrated by the smallest vessels. If the pressure in the latter increases, vision problems begin. The situation is considered especially difficult if blood clots clog the retinal vessels.
Doctors distinguish two stages that the disease goes through in its development. The initial one is more mild and is regarded as angiopathy. Sharp jumps in blood pressure lead to negative changes in the blood vessels, but their structure is not yet damaged. At this stage, they can expand significantly, which will be noticeable to the ophthalmologist during the examination. The specialist will immediately notice slight redness during the examination of the fundus. In addition to the retina, the abnormal process can affect the optic nerve. At this stage, the patient may not complain of unpleasant symptoms, but the specialist will still prescribe therapy. At this time, recovery occurs most often (regardless of whether the retina of one eye or both is affected).
The second stage is more severe. This is already hypertensive angiosclerosis itself. In this case, the vessels piercing the retina begin to intertwine. Their walls undergo spasm, due to which the lumen decreases and normal blood flow stops. Ophthalmologists divide the second stage of the disease into three substages:
- First. The lumen of the vein narrows. A nearby artery begins to put pressure on this vessel.
- Second. The vein becomes tortuous.
- Third. The bend is pronounced. Part of the affected vessel becomes invisible and is visualized as a rupture.