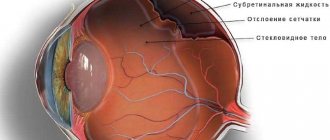
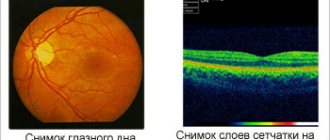
Our organ of vision has an inner layer called the retina. It is she who lines the inside of the eyeball. The retina is covered with a network of capillaries, tiny arteries, and veins. This entire blood flow has a name in Latin - “angio”. Well, pathology (“pathos”) is a disease. Retinal angiopathy in a child does not occur on its own. It is a complication of other diseases. But if you treat the underlying underlying disease and do not pay attention to the pathology that arises against its background, this can lead to a significant deterioration in vision and even its loss.
What is retinal angiodystonia?
This is a pathological process characterized by impaired vascular tone. Angiopathy is a consequence of various diseases accompanied by sharp transient changes in the tone of blood vessels. The functioning of the blood vessels of the eyes occurs under the influence of hormonal and nervous regulation.
In the event of a failure in these systems, the proper blood supply to the organs is disrupted, and pathological manifestations of various types occur.
Angiodystonia can develop at any age.
Lenticulostriate vasculopathy
Today, a huge number of children, including newborns, experience various neurological pathologies that are associated with diseases of one of the most important organs, the brain.
For these purposes, various research methods are used to make a timely and accurate diagnosis.
In the presence of cerebrovascular accidents, characteristic symptoms occur:
- Decreased concentration;
- Loss of consciousness;
- Memory and sleep disturbances;
- dizziness;
- frequent headaches.
Without a comprehensive neurological examination, it is impossible to determine the cause of the disease, which is why the help of not only qualified specialists, but also the parents themselves is important.
We also recommend that you read:
It is important! All parents should know that if any deviations or complaints occur in a child, they should immediately contact a qualified specialist. A special study and a correctly established diagnosis are the key to effective treatment of vascular pathologies in a child.
To prevent diseases and treat the manifestations of varicose veins on the legs, our readers recommend the NOVARIKOZ spray, which is filled with plant extracts and oils, therefore it cannot harm health and has virtually no contraindications
In what cases is brain diagnostics carried out?
Today, in pediatric medical practice, various studies of the brain in young children are widely used; these studies are carried out in cases where there is an assumption of the presence of such conditions:
- pathological deviation in brain development;
- focal lesions and tumor processes of the brain;
- intracranial hemorrhage; -
- occlusive hydrocephalus.
With the help of such diagnostics, it is possible to diagnose various brain pathologies at an early age.
Causes of cerebrovascular accidents
Against the background of pathology of cerebral circulation or hypoxia (oxygen deficiency), a condition such as lenticulostriate mineralizing angiopathy occurs. There are several reasons for the appearance of such pathological changes:
- congenital pathology of the walls of blood vessels (for example, telangiectasia). Small formations appear on the blood vessels of the brain, which increase in size when filled with blood. As a result of the rupture of such formations, blood penetrates into the brain tissue and hemorrhage occurs;
- calcification of the walls of striatal vessels - there is a process of gradual deposition of calcium salts, which lead to obliteration. Obliteration of the vessel is observed throughout its entire length. When the blood supply to adjacent tissues is disrupted and oxygen starvation occurs;
- intrauterine infection of the fetus - this condition poses a danger to the life and health of the child, as it often leads to disability or death;
- decreased tone of the vascular wall - a disorder of nervous regulation;
- traumatic damage to blood vessels - the presence of hemorrhages in the meninges and brain matter.
Oxygen starvation and intrauterine infections quite often lead to the development of a conditionally pathological condition in a child, which is called lenticulostriate mineralizing angiopathy. In this case, comprehensive monitoring over time is necessary.
Causes
The condition of the eye vessels depends on the blood tone of the whole body. Therefore, any disturbance in this area can cause retinal angiopathy. Most often, the pathological process occurs against the background of such diseases:
- blood pressure disorders;
- diabetes;
- atherosclerosis;
- autoimmune disorders;
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- pathologies of the nervous system that disrupt the regulation of vascular tone;
- autoimmune systemic vasculitis;
- congenital blood abnormalities;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- cardiovascular diseases.
Also, pathological changes in the arteries of the fundus may appear under the influence of the following factors:
- presence of bad habits;
- spinal injuries;
- damage to the eyes, brain;
- intoxication of the body;
- menopause;
- radioactive radiation;
- unfavorable living conditions;
- avitaminosis.
Angiodystonia of the retina often develops during pregnancy due to increased load on the vessels.
In children, the disease can be triggered by severe toxicosis in the mother during pregnancy, previous infectious diseases, or a long process of childbirth.
What kind of illness is this?
What is lenticulostriate angiopathy and how to deal with it? This question interests many parents who care about the health of their baby. This pathological condition is nothing more than the formation in the nervous tissue (mainly in the area of the thalamic nuclei) along the vessels of specific mineral deposits - small-sized calcifications, which can provoke the development of blood microcirculation disorders in the brain and its ischemia. In most clinical cases, the formed deposits of calcium salts do not in any way affect the health and well-being of the baby. Such children do not have characteristic clinical symptoms, and the infant appears to be an absolutely healthy child. In this scenario, the newborn is registered with a pediatric neurologist and periodically observed by other specialists. If calcifications reach large sizes, this naturally affects the child and he begins to develop various neurological disorders that require therapeutic correction.
Symptoms
Retinal angiodystonia can manifest itself in different ways. Initially, there are usually no symptoms, which makes it difficult to diagnose the problem in a timely manner. Gradually, the patient begins to notice the following symptoms:
- pulsation in the injured eye;
- deterioration in the quality of vision;
- narrowing the field of view;
- myopia;
- fogginess, blurred vision;
- light flashes.
With retinal angiodystonia, the conjunctiva becomes covered with yellow spots, and burst capillaries are visible. In addition to the main clinical manifestations, additional signs may be observed:
- dizziness, headaches;
- nose bleed;
- numbness, pain in the limbs;
- abnormal heart rhythm;
- memory problems.
Depending on the type of disease, some secondary symptoms may also be observed.
Hello, my baby is 6 months old. Based on the results of the ultrasound, he was diagnosed
Hello, my baby is 6 months old. Based on the results of the ultrasound, he was diagnosed with striatal vasculopathy due to cerebral ischemia. Please explain what this means? Does this need to be treated? How? Thank you very much.
As a rule, if striatal vasculopathy does not manifest itself in any way, it is discovered by chance and is regarded as a finding caused by an unfavorable process suffered in utero. Brain cysts are often treated in a similar way. Often they turn out to be completely harmless and even resolve on their own. Western scientists, during a mass survey, discovered that brain cysts are more common in those people who do not complain of headaches than in the group of sufferers. It’s just that before, without having the necessary equipment, doctors could not detect foreign formations in the brain. Now they have this opportunity, but it is not always decisive.
So, in the case of striatal vasculopathy, its detection gives us the opportunity to say that the child suffered an unfavorable condition in utero associated with infection or hypoxia, but coped with it, and it will not have any special consequences.
It is necessary to understand that vasculopathy is the body’s reaction to some unfavorable process, therefore there is no specific treatment for striatal vasculopathy. If the problem that caused the vasculopathy led to the emergence of other problems, treatment will be prescribed aimed at eliminating the underlying problem, alleviating symptoms, and means that promote the resorption of hemorrhages.
Stages of development
Pathological processes in the ocular vessels develop in several stages:
- Angiopathy – small blood vessels are affected, the pathological process is reversible.
- Angiosclerosis - the functioning of the entire vascular system of the eyes is disrupted; the progression of the pathological process can be stopped, but it is impossible to restore lost vision.
- Angioretinopathy – pathological processes in the visual organs are destructive and irreversible. At this stage, vision loss occurs.
To prevent irreversible complications, treatment must begin as early as possible.
Features of the disease
Retinal vascular angiopathy, what is it? This is a pathological change in capillaries and blood vessels, which occurs due to a violation of nervous coagulation. It can be caused by obstructed outflow or inflow of blood in the lumen, a circulation disorder of vascular tone (nervous type). As a result, the tissue that the affected vessel supplied with blood dies.
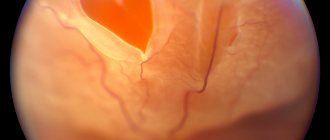
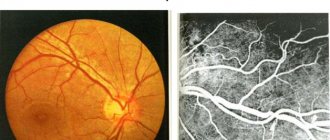
In the photo: Ophthalmoscopic picture of the fundus and retinal vessels is normal
Angiopathy - this disease can develop in both children and adults, but most often occurs after the age of 30 years or during pregnancy (after 6 months).
This eye disease is very dangerous because... can have quite serious consequences for the human body, including complete blindness. Most often both eyes are affected, i.e. retinal angiopathy develops in both eyes.
Classification of the disease
The prerequisites for the development of angiopathy are other pathologies that a person has, and it is they that characterize the types of the disease.
What is angiopathy and its types:
1. Diabetic – has two forms of development: macro- and microangiopathy. The first form is characterized by thin capillaries, which leads to circulation disturbances and hemorrhages. The second initiates damage (injury) to the large ophthalmic vessels.
In severe forms of the disease, hemorrhages and tissue hypoxia are observed, which leads to impaired visual function.
2. Hypertensive angiopathy of the retina - caused by arterial hypertension; in its presence, increased pressure on the walls of blood vessels leads to their damage. Hypertension in a progressive state is expressed by changes in the fundus: narrowing of the arteries (uneven), pinpoint hemorrhages, branching and dilation of veins.
To restore the retina, in the case of an unadvanced stage of the disease, the pressure should be normalized.
Hypertensive angiopathy of the retina of both eyes has the following symptoms: • blurred vision due to “jumps” in pressure; • decreased vision in stage 2 of the disease; • significant visual impairment at the 3rd stage of the disease (up to its complete loss); • yellowness or fatty deposits in the eye area.
In the photo: Hypertensive retinal angioscopy
3. Traumatic – caused by prolonged compression of blood vessels due to injury to the head, chest, spine (cervical spine).
When injured, pressure increases and hemorrhage occurs in the retina of the eye, which leads to deterioration of vision and it is not always recoverable.
4. Hypotonic angiopathy, what is it? The disease occurs when blood pressure is low, when blood flows rather slowly, and the blood vessels in the eyes become congested.
Symptoms: pulsation of veins, presence of tortuous vessels, dilatation of arteries.
5. Juvenile (Eales disease) retinal angiopathy - characteristic of childhood and adolescence. With inflammation of the blood vessels, hemorrhage often occurs in the retina of the eye. The reasons for the development of this disease have not yet been established, but the pathology can lead to the development of glaucoma, cataracts, and in the most serious cases, blindness.
Classification
Depending on the cause of origin, the following types of retinal angiodystonia are distinguished:
- Diabetic. It is a complication of diabetes mellitus, the treatment of which was not started in a timely manner. It can also occur due to improper diabetes therapy. As a result of serious disorders in the body, the vascular walls become thinner, lose tone and elasticity.
- Traumatic. The cause of the disorders is sudden strong compression of the chest or injury to the brain or cervical spine. This leads to hemorrhage in the eyes and increased intracranial pressure, causing a rapid decrease in vision.
- Hypertensive. Retinal angiodystonia develops against the background of increased blood pressure as a result of a malfunction in the process of narrowing of the ocular arteries. This pathological process is accompanied by arterial spasm, impaired blood circulation and stagnation of blood in the venous system. With prolonged absence of therapy, changes in retinal tissue occur.
- Hypotonic. It occurs against the background of low blood pressure due to slow venous blood flow caused by dilation of the arteries of the eyeball. As a result, hemorrhages and blood clots form. The pathology is manifested by dizziness, fainting, and severe weakness.
Read in a separate article: Eye retinitis: what it is, symptoms and treatment
Sometimes doctors diagnose mixed type angiodystonia. In this case, damage to both eyes is observed, which occurs against the background of general systemic diseases affecting the entire circulatory system. Develops mainly after 30 years of age and can cause complete loss of vision.
What is retinal angiopathy in a child?
Retinal angiopathy in newborns and small children appears due to cranial and ocular damage, increased cerebrospinal fluid pressure
Pathology is formed as a result of changes in blood vessels and capillaries, disruption of blood circulation in the retina. According to the disease that caused angiopathy, its types are distinguished:
- diabetic (caused by diabetes mellitus);
- hypertensive (manifests itself in conditions of persistent high blood pressure, while the veins are dilated and tortuous, the arteries are narrowed, less blood flows through the arteries, and less outflow occurs through the veins);
- traumatic (formed as a result of damage to the upper part of the body: eye, head, spinal bruises. They cause poor circulation in the head. The functioning of cells is disrupted, bleeding occurs, the supply of oxygen to the eyes is aggravated, vision deteriorates, and pain appears);
- hypotonic (caused by stable low blood pressure when the retina is not fully saturated with oxygen);
- juvenile (inflammation occurs, which is accompanied by hemorrhages in the vessels of the retina. The veins are damaged, there is a possibility of degeneration of the vitreous body and the inner membrane into connective tissue, and there is a threat of separation of the retinal tissue of the eye from the vascular tissue).
Retinal angiopathy in newborns and small children appears as a result of cranial and ocular damage, an increase in cerebrospinal fluid pressure. If such a diagnosis is made, the baby must be urgently shown to a specialist to conduct a more thorough examination and choose the right treatment.
If timely assistance is not provided, rapid damage by angiopathy can cause:
- retinal dissection. A stable increase in intraocular pressure provokes detachment of the internal tissue to the attachment site;
- hemorrhages caused by rupture of the sides of the vessels. There is a possibility of bleeding in the ocular vitreous body or in the retinal area;
- modification of the inner membrane of the eye in the direction of reducing its shape due to a small influx of nutrients.
The disastrous outcome of these conditions can be absolute or partial loss of vision. Timely initiation of therapy will help prevent dangerous symptoms.
Angiodystonia during pregnancy
Angiodystonia of the retinal vessels often occurs in pregnant women. The reason for this is the changes occurring in the body of the expectant mother. As a result of a significant increase in blood volume, all blood vessels expand, which subsequently leads to the development of problems in the visual apparatus. This happens especially often in the third trimester under the influence of factors such as surges in blood pressure and gestosis.
In mild cases, retinal angiodystonia goes away on its own within 3-4 months after delivery. With a more complex course of the pathology, there is a risk of rupture of retinal vessels during childbirth, which can lead to complete loss of vision. Therefore, if a woman’s condition has worsened significantly during gestation and there is a threat to life, it is necessary to urgently terminate the pregnancy.
Lenticulostriate mineralizing angiopathy
Comments:
: 49
Lenticulostriate mineralizing angiopathy - this diagnosis can often be seen in the results of a neurosonographic study in young children from three months of age.
The disease is diagnosed in almost every fifth child who underwent this study, as a result of which his parents begin to panic: what kind of pathology is this, what can it lead to and how to cure it.
Features of the disease
This term appeared around the 60-70s, when child neurology was just beginning to develop.
However, due to the imperfection of diagnostic procedures and the paucity of equipment, it did not receive specifically substantiated signs and was practically not mentioned in textbooks on pediatrics and neurology.
It was given to all children, without exception, in whom, during a neurosonographic study, the smallest changes were identified in the area of the subcortical nuclei, more precisely, the thalamus.
- V.Rohto eye drops will help restore vision after intense or prolonged work in front of the computer;
- Eliminate itchy eyes and restore clarity of vision;
- Relieve signs of fatigue;
- Moisturize your eyes if they are excessively dry, including those caused by wearing contact lenses.
If you look at it literally, the term “mineralizing” means that as a result of a pathological process, organized calcifications (deposits of salt ions, mainly calcium) can form in the nervous tissue or in the thalamus itself.
Such formations usually indicate previous cerebral ischemia in these areas. One of the options for the appearance of foci of calcification may be the development of Farah disease (however, this disease is extremely rare).
Angiopathy of cerebral vessels is a prerequisite for the development of this pathology. A feature of the disease is that microcalcifications are formed along these vessels and are localized mainly in the thalamus.
On the one hand, any changes visualized in such small patients must be eliminated.
On the other hand, if there are no clinical manifestations in the child (development of sensory disorders or other pathology), then no treatment may be required.
But you should definitely schedule a consultation with a pediatric neurologist and conduct a control ultrasound examination of the brain.
Normally, while the baby is in the womb, he receives the necessary nutrients and oxygen from the mother's blood and does not lack them.
But during childbirth, the following violations may occur:
- Long stay of the child in the maternal birth canal. In this case, the child experiences significant oxygen starvation, which primarily affects the brain, the main oxygen-dependent organ. This leads to the development of ischemic foci in the blood supply zone of the middle cerebral artery and, as a consequence, to calcification of blood vessels and nervous tissue adjacent to the thalamus.
- Birth injury. It is the second most common cause of intracerebral ischemia. Leads to the formation of intracerebral cysts, which, located in the thalamus, can be perceived as calcifications.
In addition to the birth process, the fetus may experience hypoxia during its development.
The main reasons for this are:
- Hypertonicity of the uterus. Contraction of the uterus leads to spasm of the vessels feeding the fetus (extending from the placenta), which causes intrauterine fetal hypoxia to develop, which can lead to premature birth or miscarriage.
- Encircling the fetus with the placenta. The development mechanism is the same, only its cause is a long placenta, which, as a result of fetal movements, can wrap around parts of its body or neck, leading to hypoxia. May be fatal to the fetus.
- Lack of iodine. This microelement is essential for the development of the fetal nervous system. With its deficiency, the neural tube is poorly differentiated, and existing foci of hypoxia are transformed into microcalcifications.
All these conditions are fundamental in the development of lenticulostriate angiopathy.
The main instrumental method for studying this pathology is ultrasound of the brain, as well as neurosonography.
Brain ultrasound is indicated for children under 14 years of age. It is the main diagnostic method of research, since it does not cause any harm to the child’s body, and in especially young children (up to one year), due to the inferiority of the head bone structures, it allows you to see the nervous tissue of the brain and determine the presence of foci of calcification in it.
Neurosonography is a type of ultrasound examination. The technique for carrying it out is the same, but for the study a special sensor is used, which is installed on the area of the large fontanel.
These diagnostic procedures are carried out in children aged one, three and six months. With such a schedule of procedures, it is possible to observe the dynamics of processes identified in the brain.
During the study, it is possible to either identify compaction of the walls of the striatal arteries, or detect hyperechoic inclusions in the area of the subcortical nuclei. These facts may indicate that the child’s mother had some problems during pregnancy, which similarly affected the child’s body.
What should be done if a similar diagnosis was made after an ultrasound examination?
If the presence of calcifications is confirmed by the second ultrasound, medications such as Pantogam, Cortexin or Emoxipin are started. These drugs have an antioxidant effect and help restore cerebral blood flow in ischemic areas. Medicines are taken for up to six months, and if positive dynamics of the process are observed, they are canceled.
If these medications are ineffective, observation is continued by pediatric neurologists, and if necessary, the question of using early neurosurgical surgery is raised.
If we take into account the structural features of the thalamus, we can talk about the clinic of its damage due to insufficient blood supply.
The thalamus is the center for processing almost all information coming from the senses (the only exception is the perception of smells). With a lack of blood supply, one or another sense may be impaired, and with significant oxygen starvation, atrophy of the thalamus can occur.
More severe consequences of the development of lenticulostriate vasopathy may be a delay in mental and mental development.
In this case, there is a lag of several months, and later even years, in addition, the appearance of symptoms of damage to the pyramidal and extrapyramidal systems, and sensory organs.
This will be accompanied by the appearance of pathological reflexes in childhood, as well as clinical manifestations of cerebral ischemia.
What can be done to prevent the development of ischemia of the thalamus and adjacent region?
You should completely abandon all bad habits, in addition, special attention should be paid to timely diagnosis and treatment of all emerging symptoms.
Particular emphasis should be placed on proper nutrition; foods containing iodine or its salts in large quantities should be mandatory in the daily diet. If during childbirth there were predisposing factors for the development of hypoxia, you should definitely consult with a pediatric neurologist in order to determine the risk of developing pathology of the thalamus or other lesions of the central nervous system.
- Momordica oil in Vien Dau Gac PV capsules is indicated for people with vision problems, as well as those whose activities are associated with constant eye strain;
- Restores damaged tissue;
- Accelerates recovery from inflammation
Source: https://zdorovyeglaza.ru/raznoe/lentikulostriarnaya-mineralizuyushhaya-angiopatiya.html
Diagnostic methods
Often, to identify pathological changes in the vessels of the fundus, it is enough to perform an ophthalmoscopy, with the help of which the doctor assesses vascular tone, determines areas of dilation and narrowing of arteries and venules. To identify the nature of angiodystonia and the stage of its development, the following diagnostic measures can be additionally carried out:
- rheoencephalography – studies the blood vessels of the brain;
- electrocardiogram - allows you to identify heart diseases that cause retinal angiodystonia;
- electroencephalography, ultrasound of the eyes - determines the condition of all tissues of the visual apparatus.
The ophthalmologist may also prescribe a variety of laboratory tests.
Blood pressure measurement is required.
Diagnostics
Retinal angiodystonia is diagnosed using a standard set of procedures
designed to detect vascular anomalies:
- rheoencephalography - study of cerebral vessels to determine the intensity of blood supply;
- Dopplerography of blood vessels - ultrasound examination of individual basins of the bloodstream, which reveals arterial and venous insufficiency;
- electrocardiography is a classic method for recognizing signs of systemic cardiovascular disorders;
- retinal angiography.
The most informative research method is ophthalmoscopy - examination of the fundus of the eye using a special lens. This method allows the doctor to visualize vascular changes in the retina, establish their location and determine the degree of complexity. To find out the causes of the disease, laboratory blood tests are carried out (for sugar, hormones, etc.).
Treatment
Treatment of retinal vascular angiodystonia is primarily aimed at eliminating the root cause. Since angiodystonia most often occurs due to surges in blood pressure, the treatment regimen may be as follows.
Treatment of hypertensive angiodystonia
Medications that lower blood pressure (Captopril, Tenoric) must be prescribed, and the following medications are also recommended:
- diuretics – Hypothiazide, Enalapril;
- sedatives – Corvalol, Seduxen;
- antiarrhythmic drugs - Verapamil;
- painkillers (for headaches) - Pentalgin, Ketonal.
Treatment of hypotonic angiodystonia
Herbal medicines and natural adaptogens aimed at increasing blood pressure and strengthening the immune system are recommended. These include echinacea and lemongrass.
Your doctor may also prescribe the following medications:
- means for improving blood supply to the brain - Piracetam;
- ophthalmic drops that activate metabolism - Taufon, Emoxylin;
- vitamin drops for eyes – Aevit, Lutein Complex.
All medications must be selected by a doctor on an individual basis.
For better results, it is recommended to undergo physical therapy (magnetic therapy, acupuncture).
Is it necessary to treat lenticulostriate angiopathy?
As is known, the thalamo-striatal region of the brain is responsible for a number of important functional aspects on which the normal functioning, growth and development of the child’s body depends. That is why, after discovering pathological inclusions of calcium salts in a given area, most neurologists suggest the baby’s parents undergo a course of treatment. The main goal of such therapy is to restore adequate blood circulation in the cerebral tissue and eliminate the consequences of ischemia.
What happens if, during the first neurosonographic study, calcifications were discovered in a child aged one month, which affected the striatal zone?
Such young patients are registered with a pediatric neurologist, and at three months of age they undergo a repeat ultrasound examination with monitoring of changes. Sometimes it happens that pathological inclusions resolve on their own; in other cases, calcifications increase in size and provoke an expansion of the ischemic zone.
In the latter case, the child is prescribed drug treatment aimed at correcting disorders, improving trophism and metabolism of cerebral structures.
If there are calcifications along the striatal vessels, the child is recommended to take daily medications to help restore normal blood flow in ischemic tissues. This treatment is carried out for three months, after which its results are assessed. As a rule, young patients take the drugs Cortexin and Pantogam, against which the inclusions either completely disappear or decrease in size.
In cases where the baby is resistant to the therapy and calcifications increase to large sizes, the child’s parents are recommended to consult a pediatric neurosurgeon, who will offer the option of the most correct surgical intervention to eliminate the pathological formations.
Prevention
The development of retinal angiodystonia can be prevented by leading a healthy lifestyle and adhering to the following recommendations:
- get rid of bad habits;
- avoid injury;
- consume more dairy products and fish;
- normalize weight;
- undergo regular medical examinations;
- avoid long and heavy diets;
- exercise;
- take sedatives.
People over 40 years of age are recommended to follow an anti-cholesterol diet. You also need to monitor your blood pressure and blood sugar levels.
If you suspect angiodystonia, you should consult an ophthalmologist as soon as possible.
Author of the article: Kvasha Anastasia Pavlovna, specialist for the website glazalik.ru Share your experience and opinion in the comments.
Traditional treatment
Due to the fact that angiopathy is just a symptom accompanying the course of various diseases, the fight against it should begin with the diagnosis and treatment of the underlying disease.
A comprehensive fight against vascular problems certainly includes drugs whose action is aimed at treating the underlying disease (the cause of angiopathy):
- sugar-lowering tablets or insulin injections for diabetics;
- for atherosclerosis or hypertension - not only means that normalize blood pressure, but also “normalize” cholesterol.
Treatment of diabetic retinopathy
If angiopathy is diagnosed in patients with diabetes, diet comes to the fore - patients should completely eliminate fatty, spicy, excessively salty and sugar-containing foods from their diet, saturate the daily menu with vegetables, fruits, cereals, herbal teas and natural juices
For diabetics with the second type of disease (non-insulin-dependent), it is very important to monitor their body weight and prevent obesity
Patients with diabetes without manifestations of retinopathy should be observed by a retinologist and ensure that blood glucose levels (up to 6.7 mmol/l), blood pressure and glycated hemoglobin (up to 7%) are always normal.
Important: methods to preserve vision in diabetic retinopathy include:
- drug therapy;
- surgery;
- laser coagulation of the retina.
Drug treatment of diabetic retinopathy involves the injection directly into the vitreous of drugs that block vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF therapy). Their main task is to strengthen the vascular walls and prevent further hemorrhages in the retina. The most popular drugs are Ranibizumab, Bevacizumab, Aflibibercept.
Laser therapy is designed to cope with retinal swelling and eliminate hemorrhages. For some patients, 1 procedure is enough to cope with the manifestations of diabetic retinopathy, while others require a whole course (or even several).
Injections of corticosteroids into the retina (Dexamethasone is most often used) complement both anti-VEGF drugs and laser surgery. True, hormonal treatment for diabetic retinopathy has several significant side effects - injections can provoke the development of glaucoma and cataracts.
As for surgery for DR, in most cases we are talking about vitrectomy (excision and subsequent replacement of the vitreous gel in the central part of the eye). The procedure can be performed under either local or general anesthesia. The direct indication for surgery is severe hemorrhage into the vitreous, which can subsequently lead to blindness.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely cure DR, but timely treatment measures will help stop the further development of pathological processes in the vessels and prevent their complications.
Treatment of angiopathy caused by arterial hypertension
Hypertensive retinopathy can only be combated by monitoring blood pressure levels (taking antihypertensive drugs). For rapid vision loss and retinal edema, laser therapy, injections of corticosteroids or anti-VEGF drugs (Pegaptanib, Ranibizumab) are used.
Treatment options
Complete treatment of angiopathy is possible only with the combined use of symptomatic and etiotropic therapy. For such a disease, which is not burdened by additional complications, children are prescribed medications. This takes into account the age and characteristics of the child’s body, as well as the general clinical picture. In addition, traditional medicine methods are often used to relieve symptoms.
If this disease was diagnosed in a newborn, expectant management is used in treatment. In pediatrics, there are many cases where the symptoms of the disease disappeared without a trace as the baby grew older.
Medication approach
Elimination of the causes of the development of the disease in a child is exclusively individual. This disease is a serious and dangerous disorder, so it is strictly forbidden to self-medicate - this can only aggravate the problem. Prescription of drugs should only be carried out by a doctor. Information on medications prescribed to children is presented in the table.
| Group of drugs | Drug names | Purpose of application |
| Normalizing general and local blood flow | Solcoseryl, Arbiflex, Emoxipin, Pentilin, Trental | Improving blood circulation in the retina |
| Eye drops | Anthocyanin Forte, Taufon, Lutein Complex | Improving the functional state of the ocular vessels |
| Multivitamin complexes | Lutein Forte, vitamins A, B, C, E, P | Strengthening the walls of blood vessels |
| Antiplatelet agents | Curantil, Dipyridamole, Ticlopidine | Decreased platelet aggregation |
| Angioprotectors | Pyricarbate, Calcium Dobesylate, Detralex | Reducing the permeability of blood vessel walls |
Surgical intervention
In severe forms of the disease, when conservative treatment does not bring the expected result, surgical intervention is used to treat children in pediatrics. The following procedures help preserve visual function:
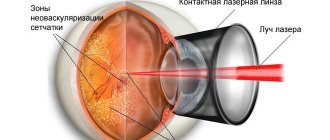
- Laser coagulation of the retina. The operation takes no more than 20 minutes and is performed under local anesthesia. The procedure is aimed at attaching the retina to the tissue using a laser, which prevents its further detachment.
- Vitrectomy. The procedure involves removing the vitreous humor of the eye, allowing you to preserve and restore vision.
Traditional medicine
To treat angiopathy in children, parents often resort to alternative medicine. When using folk remedies, you need to take into account that they can only be used as an addition to drug therapy. In addition, you must always coordinate your actions with your doctor. The most effective folk methods of treating the disease are presented in the table.
| Recipe | Cooking method | Method of use |
| Infusion of dill seeds | 1 tsp. grated dry raw materials, pour 200 ml of boiling water. Strain the solution infused for 1 hour. | Take the medicine 1 tbsp. l. 4 times a day. |
| Decoction of grape leaves | Pour 2 handfuls of grape leaves into 500 ml of water, cook the mixture over low heat for about 20 minutes, then cool and strain. | Drink 100 ml of the product on an empty stomach 3-4 times a day. |
| Cumin drops | Pour 1 handful of cumin seeds into a glass of water and boil the mixture for 5 minutes. Add 1 tsp to the hot solution. crushed cornflower flowers. Strain the cooled broth. | Place 1-2 drops into eyes 2 times a day. |
Do you need a diet?
The requirements for nutritional correction during the treatment of disorders in children depend on the underlying disease. If a child is diagnosed with signs of hypertension, it is recommended to reduce salt intake to a minimum. If angiopathy occurs against the background of diabetes, the baby’s nutrition should be based on recommendations for diabetics. Along with this, it is imperative to limit the amount of calories and cholesterol in the food your child eats.
Clinical picture of the disease
During the development of the disease, one eye is almost completely excluded from the visual process, and the second takes on the entire visual load. The disease may be asymptomatic or have the following clinical manifestations:
- Decreased vision that cannot be corrected optically. Deterioration can occur in one eye or in both eyes at once.
- Impaired color perception.
- Dark adaptation disorders.
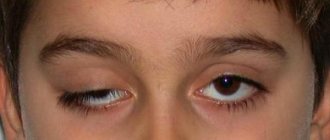
- Convergent or divergent strabismus.
- Difficulty perceiving volume, double vision.
- Children experience learning difficulties, headaches and increased fatigue.
Decreased vision quality ranges from slight to complete loss of vision.
With monolateral amblyopia, acuity is practically not affected due to the fact that the healthy eye takes over the functions of the patient. Therefore, not all patients realize that not everything is fine with their vision. The detection of pathology very often occurs by chance.
This disease occurs mainly in children; it is very rare in adults. Adults experience double vision or a feeling of blurred vision. It develops in patients with severe strabismus due to the inability to combine two different images in the brain.
Another symptom of lazy eye in adults can be a sharp and prolonged decrease in vision. With hysterical amblyopia, vision is restored some time after the end of the nervous breakdown.
The prognosis of the disease in adults is much less favorable compared to children.
Children may also experience the following characteristic symptoms:
- Drooping of the upper eyelid.
- Involuntary movement of one eyeball and asynchrony of eye movements.
- When trying to look at any object, the child begins to squint or try to tilt his head.
- There are complaints of fatigue, headaches while reading or other work that requires visual strain.
Possible complications
Impaired functioning of blood vessels can lead to various types of dystrophic changes in the retina. In addition to deterioration of vision or myopia, such a pathology can lead to its complete loss. If treatment is not carried out in a timely manner, this can cause complications such as:
- rapid deterioration of vision;
- glaucoma;
- retinal hemorrhages;
- progression of myopia;
- cataract;
- decreased functioning of the optic nerve;
- retinal disinsertion;
- complete blindness.
In advanced stages of the disease, treatment may not be effective enough
It is important to recognize the course of the pathology in time, before irreparable dangerous changes in the retina begin to occur.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Varicose veins and foot massage
But often this symptom is a sign of pathological conditions and ophthalmological diseases:
- eyeball injuries;
- hypothermia of the visual organs;
- any ophthalmological diseases of an infectious nature;
- reaction to certain medications;
- allergic reactions;
- foreign bodies entering the eyeball;
- overwork;
- hemorrhages in the vascular system due to high blood pressure due to diabetes or hypertension.
In the absence of the necessary treatment, there is a high probability of developing complications that negatively affect vision. The most common complications include:
- deterioration of vision, which with further inattention to the condition of the eyes can develop into complete blindness;
- hemorrhages in the retina - this consequence can occur with improperly selected treatment, significant strain on the eyes, as well as with the development of hypertension, which is expressed in increased blood pressure;
- damage to the cornea, which can provoke the formation of cataracts. These conditions, in turn, can lead to gradual loss of vision and headaches, which significantly reduce the patient’s quality of life.