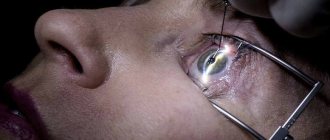
Among ophthalmological pathologies, a disease is distinguished when a child’s eyelid of one eye droops (blepharoptosis) and twitches in time with the movements of the jaw. This condition was first seen and described by Marcus Gunn, after whom this syndrome was named.
Marcus-Gunn syndrome - description of the disease
Marcus-Hun syndrome, named after the scientist who first described the disease in 1883, is an ophthalmic pathology. Another name for it is palpebromandibular synkinesis. The disease develops predominantly on one side of the face. This form is diagnosed in 69% of patients. The bilateral type of syndrome is observed in 31% of patients.
Often, the disease occurs in people with congenital blepharoptosis - a pathological drooping of the eyelid, which leads to partial or complete closure of the pupil.
Marcus-Gunn syndrome is not just a cosmetic defect that makes the face look apathetic and causes raised eyebrows. This pathology leads to decreased vision.
The eye is almost constantly covered by the eyelid, which impairs visibility. For this reason, the organs of vision are formed incorrectly. Especially with the congenital type of the disease. This is fraught with serious visual impairment.
Blepharoptosis in the syndrome can be partial, when the eyelid covers only a third of the pupil, incomplete, accompanied by overlapping of the pupillary area by more than half, and complete, when the pupil is not visible at all. In addition, there are true and false blepharoptosis. The latter is diagnosed when there is a large accumulation of fatty tissue under the skin of the eyelid, as well as a decrease in the elasticity of the eye itself.
This is the general picture of Marcus-Gunn syndrome. The causes of its occurrence determine the form and symptoms of the disease. The nature of treatment depends on these factors.
Symptoms
The first signs of Marcus Hun syndrome can appear in infants, when babies open their mouths and move their eyes, for example, during feeding. There may be watery eyes and swelling of the affected eyelid.
In most cases, the pathology affects only one eye, and the manifestations decrease with age. Most likely, patients simply learn to control their eyelids and mask ptosis at the right moments.
There is another symptom, named after Hun, which manifests itself as dilation of the pupil on the side of the lesion of the optic nerve, when the light lantern is swung and moved from the normal eye to the patient.
Symptoms
If the disease is congenital, then Marcus Gunn syndrome is detected in early childhood. The child may notice drooping of the upper eyelid. However, when opening the mouth, moving the lower jaw to the side or down, or clenching the teeth, the affected eye opens. This process occurs reflexively and the person does not control it. In infants, this symptom can be noticed while the baby is suckling. Drooping of the eyelid or ptosis can be subtle or very noticeable, as well as the degree to which the affected eyelid is dependent on mouth movements.
In children, symptoms include lacrimation, swelling of the eyelid and general weakness. With age, clinical signs disappear due to the development of skills by sick people that help mask symptoms. Mostly, the pathology affects one eye, but there are also cases of bilateral damage.
According to the severity of Gunn's syndrome, there are:
- Full. The pupil is completely covered by the eyelid and is not visible.
- Incomplete. The pupil is 2/3 closed.
- Partial. The eyelid slightly covers the pupil.
Marcus-Gunn syndrome: causes of ophthalmopathology
Carrying out diagnostic measures, the doctor first of all establishes the nature of Marcus-Gunn syndrome. Its causes can be congenital or acquired. Moreover, when we talk about the congenital nature of the pathology, heredity is not implied. The disease is not genetically determined in any way. It develops sporadically, that is, by chance. This happens during the period of intrauterine development. The syndrome occurs when there is an abnormal relationship between the trigeminal nerve and the nerve that controls the movements of the eyeball. The factors causing the anomaly are not precisely known.
Sometimes palpebromandibular synkinesis is a consequence of birth trauma. However, this form of pathology is no longer congenital, but acquired. In addition to birth trauma, its causes can be:
- natural aging of the body, accompanied by weakening of the muscles that are responsible for raising the eyelids;
- diabetic neuropathy is a complication of diabetes mellitus characterized by damage to nerve fibers;
- multiple sclerosis;
- Horner's syndrome is a lesion of the sympathetic nervous system that manifests itself in the eyes;
- stroke;
- traumatic brain injury;
- ocular migraine;
- inflammatory diseases of the brain, including encephalitis;
- chronic circulatory failure - slowly progressive brain dysfunction;
- severe psychological shock;
- side effect, complication after the Botox procedure.
The pathogenesis of the syndrome is quite difficult to establish. The mechanism of its development is still unclear to scientists, but the basis of the disease is the pathological connection between the mandibular and oculomotor nerves.
Causes of the syndrome
The pathological process can be congenital or acquired.
The first is often inherited due to a violation of the normal development of the muscle that regulates the rise of the upper eyelid. Synkinetic palpebromandibular syndrome can also result from birth trauma.
Acquired Gunn Syndrome also occurs when:
- weakening of the muscles that control eyelid elevation due to the natural aging process;
- diabetic neuropathy;
- as a complication after the Botox procedure;
- multiple sclerosis;
- Horner's syndrome;
- chronic cerebral circulatory failure;
- ophthalmoplegic migraine;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- stroke;
- encephalitis.
The pathogenesis of the syndrome has not been established, but some authors explain the development of the syndrome by a pathological relationship between the oculomotor and mandibular nerves or between their nuclei.
G (Part 15)
March 22, 2011
Hoover phenomenon
It is expressed in the fact that if the patient, lying on his back with straightened lower limbs, lifts his healthy limb, then at this moment the paretic one involuntarily presses on the bed. The phenomenon belongs to the group of coordinator synkinesis and is often observed in patients after a stroke.
Hun-Salus symptom Characterized by the presence of sclerosis of fiber vessels in the fundus and the “crossover phenomenon,” which occurs due to depression of the artery at the site of its intersection with the dilated vein. There are three degrees of symptoms:
- expansion of the vein on both sides of the intersection;
- formation of swelling in the area of the chiasm;
- the disappearance of the vein at the site of the cross due to the formation of an arcuate bend, plunging deep into the retinal tissue.
The symptom is observed in patients with hypertension.
Hun synkinetic syndrome (Hun phenomenon, eyelid-mandibular syndrome, Marcus-Hun symptom)
It occurs more often with familial ptosis and consists of a paradoxical raising of the drooping eyelid while lowering the lower jaw and moving it to the side opposite to the ptosis. V. Gunn believed that the eyelid rises in proportion to the width of the opening of the mouth, and according to Mayer, the eyelid rises higher when the jaw on the opposite side is lowered. The clinical manifestations of the syndrome are varied. A. Glaurov observed a synkinetic raising of the upper eyelid not during lowering, but during compression of the lower jaw, as well as during compression of the lips and swallowing, which indicates damage to the nuclei not only of the III and V, but also of the VII, IX and X cranial nerves.
Sometimes the syndrome is observed with loud talking, yawning, chewing, but never observed with whistling. The etiology and pathogenesis of this syndrome have not been established. Some authors explain the mechanism of its occurrence by a pathological relationship between the oculomotor and mandibular nerves or between their nuclei.
According to I. B. Vainshtok, there is no single mechanism for the occurrence of the syndrome, which is confirmed by the variety of its clinical forms. The syndrome was described by the English ophthalmologist R. Gunn in 1883 and I. Mayer in 1889 as a kind of synkinetic syndrome, as well as by I. B. Weinstock in 1961.
Gunta syndrome (cerebellar myoclonic dyssynergia)
Characterized by generalized and oppositional myoclonus and cerebellar symptoms with sudden static disorder (falling).
It is observed in organic diseases of the brain and cerebellum with localization of the pathological process in the area of the dentate nucleus and the superior cerebellar peduncles. Described by Hunt in 1921
Gurevich symptom (Gurevich-Mann symptom, oculostatic Gurevich phenomenon)
It consists of a violation of statics when moving the eyeballs - a tendency to fall back with convergence and look up and to fall forward with divergence and look down. When looking to the side, the patient deviates in the same direction. It is observed in patients with a concussion or stenosis of the vessels of the medulla oblongata.
The symptom is very persistent and is often observed for a long time (years) after the injury, often being the only objective sign of a former concussion. It was described in detail by the Soviet neurologist M. O. Gurevich in 1938 for post-traumatic conditions of the brain. In 1940, M. S. Margulis described it in the vestibular form of encephalitis.
“Handbook of Neurological Semiology”, G.P. Lip
Read further:
← B (Part 1) →
Ш (Part 1)
Sharapova's symptom is characterized by a peculiar “buzzing” noise in the head, which intensifies in a lying position and in a state of complete rest. Described by the Soviet neurologist B.I. Sharapov in 1936 for thrombosis of the dural sinuses. Charcot's triad Includes nystagmus, scanned speech, and intentional tremor. In multiple sclerosis, it is less constant than the Marburg triad. Described by a French neurologist...
Ш (Part 2)
Schwabach test It is carried out using a sounding tuning fork, which is placed on the mastoid process on the side of the vestibulocochlear organ being studied and the duration of bone conduction of sound is determined. The resulting value in seconds is compared with the bone conductivity of the unaffected vestibulocochlear organ of the patient or with the conductivity of a healthy person. When the sound-conducting apparatus is damaged, bone conduction is lengthened; when the sound-receiving apparatus is damaged, it is shortened. Shvetsova...
Ш (Part 3)
Schilder test During the test, the examiner, standing with his eyes closed, stretches his upper limbs forward. When the head is sharply turned to the side, the lower limb on the same side is slightly raised and both upper limbs are slightly deviated in the same direction. The change in the position of the upper limbs is especially pronounced during cerebellar processes. Described by the German psychiatrist P. Schilder in 1912...
Ш (Part 4)
Barbell test (test for the duration of breath holding) Determined by the following method: after two deep inhalations and exhalations, a calmly lying patient is asked to take a deep breath and hold his breath for as long as possible, holding his nose with his fingers. The duration of holding your breath is determined using a stopwatch. Similarly, the time of holding the breath during exhalation is noted. Between determining the duration of the delay on inhalation and exhalation...
Shcherbak (thermoregulatory) reflex Method of inducing a reflex: the patient’s rectal temperature is determined, after which his upper limb is immersed for 20 minutes in water at a temperature of 32°C. Then, over 10 minutes, the water is gradually heated to 42°C and the rectal temperature is re-measured immediately after heating and after 30 minutes. With the thermoregulation function preserved, immediately after warming the limb...
Symptoms of Marcus-Gunn syndrome and treatment of pathology
This ophthalmological disease manifests itself primarily in drooping eyelids (ptosis). In this case, involuntary contractions of the levator of the upper eyelid, the muscle responsible for raising it, are observed. This happens when a person makes chewing movements. The patient is unable to lift the upper eyelid with conscious effort.
The syndrome, which has a congenital etiology, is detected during the first examination of the baby. Sometimes symptoms are noticed when the mother is feeding the baby. The newborn opens his mouth and his eyelids lift.
As the child grows, the signs of the disease become more pronounced. Even slight movements of the jaws cause contractions of the levator of the upper eyelid. In some cases, strabismus develops with Marx-Hun syndrome.
Also, when pathology develops, the following symptoms may be observed:
- swelling of the eyelids;
- excessive uncontrollable lacrimation;
- impaired binocular vision, which is associated with strabismus and lazy eye syndrome;
- lack of eye reaction to light;
- decreased visual acuity.
Characteristic symptoms
In a calm state, one or both eyes do not open completely due to blepharoptosis. Synkinesia is observed - a reflex lifting of the eyelid during jaw movements (during talking, chewing food).
The severity of drooping of the ptotic eyelid, as well as the degree of dependence of its rise on mouth movements, may vary.
It takes some effort to close your eyes. As a result, they quickly get tired and there is increased tearfulness.
Massage
Physical pressure on the eyelids can also help. First you need to clean the surface of makeup (if any) and treat your hands with an antibacterial agent. Then apply a little massage oil and begin the procedure. The steps are as simple as possible:
- The upper eyelid should be stroked from the inner corner to the outer.
- The bottom one is in the opposite direction.
When the massage is finished, it is recommended to cover your eyes for 10 minutes with cotton pads previously soaked in fresh chamomile infusion.
Diagnostic methods used for suspected Marcus-Gunn syndrome
The symptoms of the syndrome are so obvious that identifying it is not difficult. However, the doctor needs to identify the causes of the pathology, especially if it is acquired. First, the ophthalmologist checks the patient's visual acuity. After this, an examination of the eye is performed using a slit lamp. This method allows you to assess the condition of the conjunctiva, eyelids, and cornea. X-rays are prescribed for injuries. If there is a suspicion that the syndrome is a consequence of damage to the central nervous system, the patient is sent for magnetic resonance imaging. You may need help from a neurologist.
Diagnostic measures
The ophthalmologist performs a visual examination during which he examines the mobility of the eye and eyebrows, the placement of the upper eyelid, and the width of the eye opening. It also collects the patient’s medical history, clarifying the possibility of inheriting the disease, getting it as a result of trauma or concomitant pathologies. Additionally, a consultation is taken with a neurologist to identify concomitant neurological abnormalities.
Usually diagnosis does not cause difficulties, since the symptoms are too characteristic. However, to confirm the syndrome and accurately determine its cause, the doctor prescribes a variety of procedures. First, visual acuity is assessed, then biomicroscopy is performed - an examination of the eye using a slit lamp. In this way, the condition of the eyelids, conjunctival cavity and cornea is checked.
If the cause of the syndrome is the result of trauma, then radiography is prescribed. Magnetic resonance imaging is performed if the disease is a consequence of damage to the central nervous system. In this case, consultation with a neurologist is also recommended.
Photos and videos to understand what blepharoptosis looks like in life:
Hun syndrome: causes, symptoms and treatment of the syndrome
Marcus Gunn syndrome is a rare ophthalmological pathology that is characterized by reflexive conjugal movements of the eyelid and lower jaw. The drooping eyelid rises after the patient moves the lower jaw. This occurs due to an abnormal connection between the 5th cranial and oculomotor nerves.
The disease is often combined with strabismus, amblyopia and other eye pathologies.
Diagnostic measures
To accurately establish the diagnosis, the doctor performs a variety of procedures. First of all, the ophthalmologist talks with the patient to exclude or confirm the hereditary factor of the disease. Then a visual examination of the patient is carried out, during which the doctor evaluates the mobility of the eye and eyebrows, the placement of the movable eyelid, and the width of the eye opening.
Then visual acuity is examined and biomicroscopy is performed using a slit lamp, which allows you to evaluate the structure of the eye. Thus, the doctor checks the condition of the upper and lower eyelids, the conjunctival cavity and the cornea.
If the pathology appears as a result of injury, then an x-ray is taken. Magnetic resonance imaging is needed if the disease arises as a result of damage to the central nervous system. In addition, it is necessary to consult a neurologist.
Treatment methods
The main treatment for congenital Marcus Gunn syndrome is surgery. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia, which is why doctors do not recommend it for patients in the younger age category (under 5 years). But, if the visual axis is completely covered by the eyelid, then the operation must be performed.
From the age of 5, surgical intervention is indicated to treat strabismus and lazy eye syndrome, as they reduce visual acuity. The doctor also removes the upper part of the tarsal cartilage and the lower edge of the Müller muscle, since when their functionality is inflamed or impaired, the eyelid droops.
There is also a non-drug treatment method. The palpebral fissure is formed before the age of 10. If the eyelid gap is no more than 3 cm, then the patient must learn to regulate the lowering of the eyelid using the masticatory muscles. To make the task a little easier, the eyelid is fixed with a medical plaster, but it must be removed at night.
Possible outcome of the disease
In most cases, the prognosis is favorable. In adults and elderly patients, the severity of synkinesis of the upper eyelid and lower jaw decreases over time, but these data do not prove any facts. Perhaps patients get used to these symptoms over time and stop paying attention to them. With severe synkenesis of the eyelid and jaw, surgery is indicated.
Hun syndrome is more common than doctors diagnose it during examination. Therefore, neurologists and ophthalmologists should be more careful in order to promptly diagnose the disease and determine the right direction of treatment for patients in the younger age category.
To learn more about eye diseases and their treatment, use the convenient site search or ask a specialist a question.
Source: https://ofthalm.ru/sindrom-gunna.html
Marcus-Gunn syndrome: treatment
Today, this pathology is successfully treated surgically. However, surgery is not always prescribed. If the syndrome is caused by an unsuccessful operation or Botox injection procedure, the patient is first prescribed drugs that restore neuromuscular conduction, for example, Proserin, as well as vitamins B1 and B6. They are administered by injection. Physiotherapeutic procedures and facial massage are also prescribed. If the signs of the disease have not disappeared within 2-3 months, surgery is performed.
A non-surgical method of treating the syndrome is also possible with a false form of blepharospasm.
Elimination of its symptoms is carried out through physiotherapy. The patient undergoes electrophoresis with Proserin solution, galvanotherapy, microcurrents, and massage. There are also special gymnastics to increase the tone of the facial muscles. Lifting cream and traditional medicine can be beneficial for false blepharoptosis.
Exercises for the eye and facial muscles are performed as follows:
- make circular movements with your eyes clockwise and counterclockwise;
- open your eyes as much as possible, holding your eyelids in this position for 10 seconds;
- blink quickly for 30 seconds;
- lower your eyes down, holding your gaze on the tip of your nose for 15 seconds.
The eyelids may be taped to hold them in place. This method is used to treat children under 10 years of age. It is before this age that the palpebral fissures are formed.
Providing medical care
When blepharoptosis develops as a result of unsuccessful botulinum therapy, Proserin, injections of vitamins B1 and B6, physiotherapeutic procedures, and facial massage are prescribed. However, all these measures contribute only to a small extent to the restoration of muscle function. Usually the pathology disappears on its own within 1-2 months.
Non-surgical treatment of Marcus Gunn syndrome is also possible in case of a false form of the disease or a neurogenic cause of the syndrome.
Correction is carried out by prescribing physiotherapy (electrophoresis with Proserin solution, Darsonval, microcurrents, galvanotherapy) and massage.
At home, special gymnastics that increase the tone of the muscles of the upper part of the face and strengthen them, the use of lifting cream, wiping the face with tincture of birch leaves, potato juice, parsley root decoction, and treatment with ice cubes are beneficial.
Gymnastic exercises for blepharoptosis include:
- circular movement of the eyes (the head is securely fixed);
- maximum opening of the eyes and holding them in this position for about 10 seconds, followed by closing and tensing the muscles for the same time (the procedure is repeated up to 6 times);
- rapid blinking for about 30 s, with the head thrown back (repeat up to 7 times);
- lowering the eyes while holding the gaze on the nose for about 15 s and followed by relaxation (up to 6 times).
Since the formation of the palpebral fissure occurs before the age of 10, children are prescribed fixation of the eyelid with a medical plaster. This method is also used as short-term relief after botulinum therapy or inflammation of the conjunctiva. If blepharoptosis is up to 3 cm, then it is possible to independently learn to control the lowering of the eyelid using the masticatory muscles.
Emergency help
It may be required if the syndrome occurs due to unsuccessful botulinum therapy. In such situations, the patient is prescribed special treatment for Marcus-Gunn syndrome:
- Taking the drug "Proserin".
- Administration of vitamins B6 and B1 by injection.
- Face massage.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
All of the above is aimed at restoring muscle functions. The pathology itself disappears in 1-2 months. Sometimes it may take longer.
The same treatment is indicated in cases where the syndrome occurs due to a neurogenic cause. Or with a false form.
Diagnostics
When diagnosing children, the doctor will primarily rely on the patient's anamnesis and complete history. A full inspection will be carried out.
Diagnostic measures also include:
- radiography;
- MRI;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- visual acuity analysis;
- examination of the lacrimal gland;
- biomicroscopy.
It is important to differentiate Marcus Gunn syndrome from other diseases (particularly ptosis) in order to prescribe the correct treatment. Sometimes visiting an ophthalmologist is not enough and you need to visit a neurologist.
Surgical treatment for Marcus-Gunn syndrome
If drug and procedural treatment are ineffective, surgery is prescribed. Usually it is not performed if the patient is less than 5 years old, however, in severe forms of the pathology, surgical intervention cannot be avoided even at a very early age. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia. There are three types of surgeries that are used for Marcus-Gunn syndrome:
- The Hess technique is a method of tightening the eyelid using the frontalis muscle. Surgery is prescribed if the superior rectus muscle or levator muscle does not work.
- The Mote method is the treatment of blepharoptosis using the superior rectus muscle in levator palsy.
- Blashkovich's operation is the formation of a fold of the muscle of the upper eyelid.
The type of procedure that is suitable for the patient is determined by the surgeon.
After the operation, stitches are placed and removed after two weeks. Absolute contraindications to surgical treatment are paralysis of the 3rd pair of cranial nerves and a complete lack of sensitivity of the cornea.
Treatment
Typically, doctors do not offer specific approaches to treatment if the disease is at a mild stage and causes more external discomfort. The choice of a specific treatment method for Marcus Gunn syndrome depends directly on the severity of the ptosis itself. It is worth noting that surgical intervention is used more often in patients with late stages of the disease, when severe ptosis interferes with normal human activities. The operation is also indicated for patients with complications such as strabismus (strabismus) or amblyopia. Amblyopia is a form of decreased vision that varies in origin.
Patients with mild forms of the disease usually undergo the process of tarzomyectomy, which is the removal of part of the eyelid muscle of the diseased eye, after which it is strengthened with a special graft.
Treatment of Marcus Gunn syndrome in children begins after 4 years of age, which should reduce the risk of developing these complications in the form of strabismus or a significant deterioration in vision clarity with further aggravation of pathological processes. If there are minor external manifestations of the syndrome, surgical treatment is recommended to begin much later. Advances in optical surgery technologies make it possible to restore the function of the eyelids and visual abilities, but the treatment of facial synkinesis may not be completely completed due to the lack of an absolute solution.
Therefore, doctors often focus on eliminating existing symptoms and stopping new ones.
The postoperative period must be monitored by a specialist, the patient is prescribed a course of antibiotics and other medications for eye rinsing, various drops and ointments.
Gymnastics
Unfortunately, treatment for Marcus-Gunn eyelid syndrome (with mandibular synkinesis or any other associated symptom) is not possible. Because the pathology is congenital. But it is possible to reduce its manifestation. Here are some exercises you can do at home:
- The gaze is directed forward. Make circular movements with your eyes 5 times at a slow clockwise pace.
- Look, open your mouth, start blinking frequently and quickly. Do this for 30 seconds. In the following days, gradually increase the time.
- Close your eyelids, count to 5, then sharply open your eyes, looking forward. Do 6 reps.
- Close your eyes. Slightly pull the skin of the outer corners of the eyes, and in this position, raise the eyelids as much as possible.
Train every day. They say this is an effective set of exercises that helps fight Marcus-Gunn syndrome.
Possible outcome of the disease
The prognosis is generally favorable. Even in older patients, the severity of symptoms of the pathology decreases. Sometimes a person simply gets used to this disease and tries not to notice it. However, almost everyone wants to eliminate the cosmetic defect, even if the syndrome does not affect vision.
In case of a congenital type of the disease, it is necessary to be examined by an ophthalmologist more often - at least 2 times a year. Before surgery, the doctor must monitor the development of the syndrome. After surgical treatment, it is important to prevent recurrence of the disease.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis for Gunn syndrome is quite favorable if the disease is detected and treated in time.
No special measures have been developed to prevent the disease. Preventive measures include ensuring safety at work (eye protection with a mask or goggles). All people with Marcus Gunn syndrome should undergo preventive examinations by an ophthalmologist twice a year.
Hun syndrome causes not only aesthetic discomfort, but can provoke the development of strabismus and “lazy eye” syndrome. Therefore, ophthalmological pathology must be treated for further normal human life.
Author of the article: Bakhareva Elena Sergeevna, specialist for the website glazalik.ru Share your experience and opinion in the comments.