Causes
Predisposing factors to the development of pathology are:
- scleritis;
- genetic abnormalities;
- destructive processes in the eyeball area;
- parasitic diseases;
- uncontrolled use of medications;
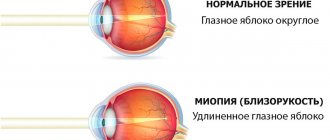
- prolonged rubbing due to incorrectly selected corrective optics;
- pathological lesions of the eyelids;
- allergic reactions;
- entry of foreign particles into the organs of vision;
- due to surgery, namely complications after it;
- parasites entering the eye chamber.
Causes of chalazion, Moll cyst and dermoid cyst
The production of thick secretion by the gland occurs due to various pathologies that are not fully understood. There is an opinion that most often this condition is caused by gastrointestinal diseases - gastritis, pancreatitis, enterocolitis, etc.
The thick secretion cannot be removed from the gland in a timely manner, resulting in its blockage and the formation of a cyst. If such a capsule begins to collapse or an infection penetrates into it, an inflammatory process will develop, which often leads to an abscess of the eyelid.
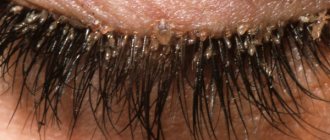
Frequent inflammation of the eyelid margins. These include: blepharitis, stye, demodicosis of the eyelid, injury to the eyelid when using contact lenses, cosmetics or false eyelashes, getting foreign objects, debris, etc. into the eyes. Allergies in the eyelid area are manifested by seborrheic blepharitis, hay fever, allergic conjunctivitis.
Chalazion
A Moll cyst can develop for the following reasons:
- herpes;
- allergy;
- papillomavirus;
- cosmetical tools.
A dermoid cyst on the eyelid appears due to hormonal imbalances in the body. Therefore, it is most often diagnosed during puberty, in pregnant women or during menopause. Another reason is the presence of trauma in this area.
Neoplasm of the eyelids
Classification
Depending on the root causes that provoked the development of the disease, several forms of cysts are distinguished:
- Implantation. Develops as a result of trauma to the organs of vision and penetration of the integumentary epithelium into the eye cavity. Occurs as a result of surgical intervention.
- Congenital. Pathology develops against the background of abnormalities during intrauterine development. It is possible to diagnose the pathology after the birth of the child.
- Stromal. The cyst is characterized by spontaneous appearance and resorption. The disease is reborn in a new zone. Education is characterized by rapid growth.
- Exudative. It is a consequence of glaucoma. Develops as a result of prolonged use of anticholinesterase medications.
- Spontaneous. Develops without taking into account predisposing factors. It is divided into 2 subspecies: pearl and serous forms.
- A dermoid cyst is a benign formation in the area of the visual apparatus. Pathology develops against the background of disturbances in the intrauterine development of the fetus. Externally it is characterized by round or oval shapes. The growth of dermoid formation is slow.
- Post-inflammatory. The cyst progresses during the rehabilitation period or due to stagnation of the lymph process. An additional provoking factor is the inflammatory process in the area of the eye apparatus.
- Retention. Progresses at the sites of damage. The provoking factor is trauma. Externally, the formation resembles a ball filled with mucus. In this pathological condition, there is no pain syndrome.
Depending on the number of neoplasms they are divided into:
- single;
- multiple.
Neoplasms develop in various areas of the visual apparatus:
- subepithelial;
- intraepithelial.
Depending on the type of formation, the following types of cysts are distinguished:
- pearl;
- conjunctival cyst;
- serous;
- iris pigment cyst;
- exudative;
- degenerative corneal cyst.
What it is
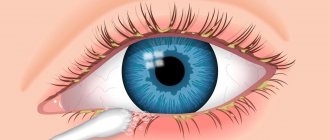
A conjunctival cyst is a formation on the mucous membrane in the eye that looks like a small bubble filled with mucus or clear liquid. There are four types:
- Congenital. The defect occurs due to delamination of the iris, when one of the upper layers extends beyond the mucous membrane.
- Traumatic. It is formed when the eye is damaged, even through a closed eyelid, and often appears after surgery on the cornea or elimination of strabismus in a child.
- Spontaneous. In this case, doctors cannot detect the reasons why the tumor appeared in the eye. Visually, it differs from other types of cysts; the bubble has a neat shape and is barely noticeable on the white.
- Exudative. This type is usually a complication of glaucoma.
Cysts are also single-chamber and multi-chamber; they can be localized both on the white of the eye and on its iris. The photo shows what a cyst looks like in a child.
Neoplasms on the mucous membrane of the eye can develop at any age, including in young children after injuries or surgery on the visual organs
For reference: in approximately 22% of cases, a dermoid cyst of the eye is diagnosed. Postoperative formations are usually detected at a young age, and men are more susceptible to such tumors than women. By themselves, they do not pose a major health threat. But they cause varying degrees of discomfort and are a favorable factor for the development of more serious ophthalmological pathologies.
Symptoms
The main symptomatic manifestations of the formation of a corneal cyst are:
- narrowing and blurred vision;
- the appearance of translucent dots before the eyes;
- dull bursting pain;
- eyelid deformation;
- reduction in picture quality;
- narrowing of the field of view;
- blurry outlines of objects when looking at them;
- formation of floating flies;
- conjunctival hyperemia;
- increased intraocular pressure;
- the appearance of a yellowish area.
Diagnostics
An experienced ophthalmologist can suggest a diagnosis even during an external examination of the patient.
And to clarify you need to do:
- examination using a slit lamp. If the cyst is located in the eye and not on the eyelids;
- visual acuity test;
- visual field check;
- eye pressure measurement;
- X-ray, tomography;
- histological examination (if there is a suspicion of malignancy).
Treatment
Removal of the cyst takes place according to several methods of therapy:
Surgical intervention
If there is a small-scale formation, it is eliminated using laser equipment. This technique allows not only to eliminate the cyst, but also to destroy the pathological cells next to it. Due to the manipulation, there is no need for a long rehabilitation period. Large formations are eliminated by surgery. Anesthesia is used for the procedure to reduce pain.
Drug therapy
To eliminate the pathology, drops with a corticosteroid composition are prescribed. Additionally, antibiotics and desensitizing drugs are used. Therapy can stop the progression of the pathology, but does not completely cure. To treat cysts, medications are prescribed:
- Oftalmoferon;
- Albucid;
- Aktipol;
- Oftan.
To eliminate swelling and lacrimation, antiallergic drugs are prescribed.
Traditional herbal medicine
It is treated using traditional medicine recipes, permissible only after consultation with an ophthalmologist, which is necessary to prevent the development of complications. Several ways to treat education:
- wash the area of formation with morning dew;
- treatment of the affected area with algae infusion;
- bury the organs of vision with a solution of cornflowers.
Complications
If you have a genetic predisposition to congenital formations, you must visit an ophthalmologist at least 2 times a year. After removal of the tumor, it is advisable to avoid visual stress. Complications of the disease develop due to a large formation. There may be an increase in the level of pressure inside the eye cavity and a decrease in image quality. After the manipulation, to prevent complications, it is advisable to:
- limit physical stress;
- It is forbidden to self-prescribe medications;
- reduce the load on the visual apparatus.
How does pathology manifest itself?
The tumor is localized on both the lower and upper eyelids. Sometimes this process occurs simultaneously on two eyelids. When palpated, a dense nodule is felt. Outwardly it looks like a slight protrusion of the upper or lower eyelid.
At the onset of the disease, many patients confuse chalazion with stye. But after 2 days, significant differences appear: the tumor becomes larger and painful.
The cyst of the lower eyelid or upper eyelid is not fused to the skin. Therefore, when pressed, it moves freely. The eyelid at the site of the tumor turns red. The size of the cyst ranges from several mm to 1 cm. The color of the chalazion is white or grayish.
If timely therapy is not carried out, then suppuration begins, which clinically manifests itself as follows:
- development of edema in the mucosal area;
- increased body temperature;
- itching in the area of formation;
- lacrimation;
- pain.
As the chalazion grows, pressure occurs on the cornea of the eye, which can lead to astigmatism and decreased visual acuity. A large cyst develops if the chalazion is not opened in time.
Moll cyst
With this disease, lacrimation and photophobia develop. Most often, the skin is hyperemic and swollen. Bubbling transparent rashes filled with liquid form inside the eyelid. They can merge together and fester.
Moll cyst
If left untreated, a person will begin to experience the following symptoms:
- general malaise;
- increased body temperature;
- neurological pain;
- hyperesthesia or paresthesia in the affected area.
Dermoid cyst
You can detect such a cyst by looking closely at the eyelid, and a small compaction first appears under the skin. As the inflammatory process progresses, this formation increases and begins to put pressure on adjacent tissues. Here are the main characteristics of a dermoid cyst:
- most often rounded in shape;
- elastic and dense to the touch;
- there is no pain when pressing;
- not fused to the skin;
- the skin does not change color, there are no rashes;
- remains unchanged for a long time.
At the initial stage, such a cyst does not bother a person in any way, but as it grows, vision may decrease, and there is also a risk of it degenerating into a cancerous tumor. Therefore, dermoid formations must be removed.
Prevention
The main preventive recommendation against the development of pathology in the area of the visual apparatus is compliance with hygiene rules. Prevention can reduce the likelihood of a neoplasm:
- Before going to bed, be sure to wash off cosmetics from the organs of vision;
- follow the rules for wearing devices to correct picture quality;
- carry out preventive exercises at least 2 or 3 times a week;
- carry out daily hygiene of the sebaceous glands;
- balance your diet by filling it with fresh vegetables and fruits.
Useful video
The appearance of a cyst is provoked by many factors, not only external influences, but also internal causes. The most common form of formation is a dermoid cyst. Due to removal of the formation, short-term rehabilitation is observed. If small cysts are eliminated, recovery is possible the next day.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2031
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.