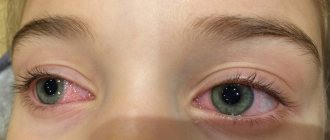
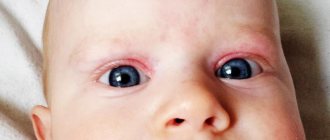
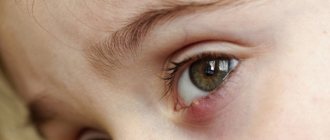
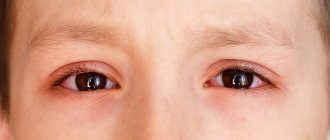
Ocular hypertelorism occurs due to abnormalities in intrauterine development due to exposure to toxins, infectious agents, or genetic failure. This causes an increase in the distance between the eye sockets. The palpebral fissures may become deformed, and sometimes visual impairment is observed. The severity of the defects depends on the degree of hypertelorism.
Often this pathology is combined with other manifestations, which indicate genetic abnormalities.
Definition of disease
According to statistics, orbital hypertelorism is the most common deformation of the skull, which affects not only bone, but also soft structures of the face. The disease began to be studied relatively recently; the first descriptions of such an anomaly appeared in the medical literature in 1924. Since that time, pathology began to be considered separately, differentiating it from a similar disease - telecanthus, which is characterized by similar symptoms, but there is no change in bone tissue. Today there are two types of hypertelorism:
The development of pathology is associated with excessive growth of the small wings of the sphenoid bone during the embryonic period. Because of this, a characteristic distance between the eyes arises, the bridge of the nose is much wider than normal, and the back of the nose has a flat shape.
Depending on the external features, two forms of such an anomaly are distinguished:
- Symmetrical . There are no other manifestations other than pathological distance between the eyes;
- Asymmetrical . The eyes are located at an excessive distance from each other, and there are also differences in their height, and squint may be pronounced.
Hypertelorism is not defined as a separate disease and is a characteristic feature of more than 130 diseases and syndromes.
Hypertelorism - what is it: the eye of the fetus on ultrasound, the nipple, the eye of the child
Hypertelorism, which is a symptom and not an independent pathology, most often manifests itself as an abnormal position of the eyes. Visually, the increased distance between their inner corners and the pupils is clearly noticeable.
Hypertelorism accompanies genetic diseases that affect the area of the skull and face, leading not only to cosmetic defects, but also to deterioration of vision, impaired sense of smell, and even problems in terms of mental development. The distances between the inner corners of the eye sockets widen when the wings of the sphenoid bone are too enlarged.
What is orbital hypertelorism?
The degree of the defect depends on the location of the visual organ, the distance between the eye sockets and the age of the person. With ocular hypertelorism, the oval of the face changes and the nasal fissures are deformed.
Scientists distinguish two types of this anomaly. With false epicanthus, the distance between the corners of the visual organ increases. True hypertelorism is characterized by expansion of bone formations. It begins when the front part of the skull is damaged, when a tumor appears in the nose.
A defect is considered a pathology if the value of the indicator in the form of the orbital-circumferential index exceeds 6.8. The angle at which the axes of the eye sockets diverge is sometimes 60 degrees, which is twice the norm.
How to treat viral conjunctivitis in children is described in detail in the article.
Deformation of the skull in the orbital form of the disease
Find out how to treat internal stye on the eye here.
Reasons for the appearance of a baby
The position of a child's eyes changes when the ethmoid bone, which is located at the base of the nose, widens and lowers. Problems in the development of the facial part of the skull, which lead to hypertelorism, arise from pathologies of a genetic nature, which are accompanied by a large number of defects:
- With Apert syndrome, the bones of the skull fuse much earlier, and the baby is severely retarded in mental development.
- With neurofibromatosis, a tumor forms in the brain, growths appear on the skin and various organs.
- For a chromosomal disorder, which is typical for Edwards syndrome, the child has deformed feet, low muscle tone, and a reduced size of the lower jaw. Small eye sockets are located at a great distance from each other.
- Hypertelorism occurs with craniostenosis, when bone sutures heal prematurely. It accompanies hernias of the skull and brain, congenital defects of the structure of the facial area.
Negative effects lead to disruption of intrauterine development of the fetus:
- prenatal infection;
- gene mutations at conception;
- hereditary predisposition;
- medications taken by a pregnant woman.
Hypertelorism occurs in Down syndrome, manifests itself in Crouzon and Toast syndromes, and develops when the facial bone is damaged due to trauma. It usually does not begin independently, but is combined with other pathologies.
A proven antiglaucoma agent - instructions for Ganfort eye drops.
A genetic test will help reduce the risk of developing such problems
Weakness of the blood vessels in the eyes is the cause of hemophthalmos.
Forms and symptoms
Features of the disorder in orbital hypertelorism are determined by the distance between the internal angles of the visual organ. In the first degree it is less than 34 mm, in the second – 39, in the third it exceeds 40. The norm for this indicator is 3 cm.
It happens that a child has very small eye sockets and slits. Sometimes a baby is born without them at all. This type of pathology, called microorbitism, affects the bones of the skull. They thicken and become deformed.
Rare congenital pathology
With a symmetrical appearance of the anomaly, the distance between the eyes widens. With asymmetric hypertelorism, they are located at unequal heights. The pupils look in different directions. Over time, heterotropia occurs.
Because the structure of the bones in the facial area changes, a person may have a bridge of the nose that is too wide or flat.
Hypertelorism accompanies many genetic pathologies and manifests itself in the form of:
- underdeveloped jaw;
- deformed feet and eyebrows;
- optic nerve atrophy;
- fusion of fingers and toes;
- cheekbone displacement;
- abnormal joint mobility.
Children who have this syndrome are usually severely retarded in mental development; adults have problems with intelligence.
If hypertelorism occurs together with Toast's disease, eyelash dysplasia is present, the child suffers from chronic conjunctivitis. With Greig's syndrome, paralysis of the abducens nerves of the eyes and astigmatism may occur.
Antimicrobial therapy – Gentamicin sulfate eye drops.
Diagnostic methods
To determine the type of lesion, they begin with an external examination. The doctor will find out what the person is complaining about, whether he has relatives with an abnormal face shape or wide-set eyes. The neurologist evaluates the patient's intellectual abilities and checks the condition of the muscles.
Using MRI and fluoroscopy, defects are found in the skull and brain. This method helps to find out why the facial bones are deformed. The distance between the eye sockets must be measured, which makes it possible to determine the degree of hypertelorism. To confirm the presence of pathology, a computed tomography is performed.
Farsightedness is not a death sentence – mild hyperopia is what it is.
Use of the medicine for other than its intended purpose - heparin ointment against bruises under the eyes.
Features of treatment
The article is for informational purposes only; a doctor who specializes in such syndromes must establish a diagnosis and prescribe a method of therapy. A consultation with an otolaryngologist is required.
Hypertelorism cannot be cured with medications and physiotherapeutic procedures. The only way to get rid of cosmetic defects and unpleasant symptoms is through surgery.
Before the operation, the type of which depends on the severity of the symptoms, the patient is examined by an ophthalmologist. The most favorable time for its implementation is no older than 8 years. Young children need intervention if heterotropia develops and the lacrimal canal narrows.
It is advisable to perform the operation on preschoolers, since then teeth will begin to form in the upper jaw, which will interfere with the procedure. If intervention is started at an earlier age, there is a risk that the baby’s cheekbones will shift.
If the problem is just beginning to appear, the shape of the skull is corrected by inserting special staples. In the first degree of violation, the wall of the orbits is cut, moved to the required distance, and cartilaginous tissue is restored.
When hypertelorism enters the second stage, they resort to rhinoplasty using part of the parietal bone. With the third degree of damage, it is necessary to change the shape of the forehead and model the base of the skull.
If microorbitism or false hypertelorism is diagnosed, bone tissue is dissected, nasal deformities are eliminated, and the appearance of the visual organ is restored.
Usually, cosmetic defects in children are corrected quite well. If the baby suffers from Down's disease, the corners of the eye sockets will be repeatedly adjusted and the skin on the bridge of the nose will be removed.
Hormonal therapy for the treatment of inflammation - hydrocartized eye ointment.
Will Gilan Comfort eye drops help you cope with dryness? Read here.
Preventive measures
Hypertelorism is often inherited by the baby from the mother or father. It is difficult to prevent its occurrence. If your relatives have experienced symptoms of this syndrome, you should consult a genetics specialist before having children.
Following simple rules helps prevent congenital pathology. Those who are planning to conceive a baby need to give up alcoholic beverages and forget about smoking. A pregnant woman should try not to be exposed to the aggressive influence of the external environment, not to become infected with infectious diseases, and to use medications only as a last resort.
You can get rid of hypertelorism, which manifests itself in the form of defects that disfigure the face, in the first years of the baby’s life. It is undesirable to postpone the operation, since with age the deformities will begin to increase, vision will deteriorate, speech will suffer, and this will affect the psycho-emotional state of both the baby and the parents. See also information about anisocoria.
Hypertelorism of the eye
The distance between the eye sockets largely determines a person’s external attractiveness. However, in some cases, a large distance between the eyes not only causes a cosmetic defect, but is also accompanied by a violation of the development of bone and soft tissues of the skull. This is how orbital (orbital) hypertelorism manifests itself.
Have you been trying to heal your JOINTS for many years?
Head of the Institute for Joint Treatment: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to heal your joints by taking every day...
Read more "
What kind of syndrome is this
A significant excess of the normal distance between the edges of the eye sockets, or eye hypertelorism, is a congenital anomaly of the skull, accompanied by its complex deformation. This condition is combined with cerebral hernias and changes in the structure of the bones of the forehead and nose. It is observed in 130 genetic diseases and is often accompanied by structural defects of other organs.
The basis of ocular hypertelorism is the expansion of the ethmoid bone, which lies at the base of the nose. At the same time, it is located lower than normal. As a result, the eye sockets move to the sides. If you draw a conventional horizontal line through the skull in the area of the bridge of the nose, then similar axes drawn through the center of the eye sockets usually deviate from it by no more than 30°. With hypertelorism, this value reaches 60°.
Forms
There are 2 classifications of pathology based on data on the distance between the edges of the orbits. The interorbital distance (IOD) is measured between the middle parts of the anterior lacrimal ridges. They are located on the paranasal surfaces of the orbit.
In a healthy person, the MOR is up to 3 cm. Degrees of hypertelorism:
- first: MOP from 30 to 34 mm;
- second: MOP from 35 to 39 mm;
- third: MOR 4 cm or more.
This classification does not take into account the severity of prolapse (subsidence) of the ethmoid bone plate, on the basis of which the decision on surgical intervention is made.
A more precise classification takes into account the MOR and the distance between the beginning of the upper third of the orbits, where the frontal, lacrimal and maxillary bones connect.
| Degree | Type | Interorbital distance, mm | Distance between the upper inner corners of the eye sockets, mm |
| I | 1 | 30 — 34 | up to 34 |
| 2 | 35 — 39 | ||
| II | 1 | 35 — 39 | up to 39 |
| 2 | 40 — 44 | ||
| III | 1 | 40 or more | exceeds the MOP by no more than 4 mm |
| 2 | exceeds the MOP by 5 mm or more |
There is another form of the disease - microorbitism. It is accompanied by a reduction in the orbits and a short palpebral fissure. The eyes are small or absent. The shape of the skull bones changes: they become smaller, flattened and deformed.
False orbital hypertelorism occurs after injuries to the anterior part of the skull or with tumors in the area of the ethmoid bone and base of the nose.
Any form of pathology can be symmetrical or asymmetrical.
Causes
Eye hypertelorism causes harmful effects on the fetus in the prenatal period:
- toxins;
- maternal infectious diseases;
- chromosomal abnormalities.
Hereditary syndromes that are accompanied by this disorder:
- Edwards;
- Apert;
- Down;
- Crouzon;
- Greig;
- Toast;
- neurofibromatosis.
Orbital hypertelorism often accompanies other cranial developmental disorders:
- premature closure of the sutures between the bones of the skull (craniostosis);
- hernia of the skull and meninges, accompanied by protrusion of brain tissue in the anterior or lower sections;
- cleft palate, upper lip.
Manifestations
Orbital hypertelorism, in addition to divergence of the inner edges of the orbits, is characterized by a wide bridge of the nose and a flat nose. There are widely spaced eyebrows, slanted eyes, folds at the inner corner of the eye (epicanthus), displacement of the cheekbones down and to the sides, a cleft in the upper lip, and increased joint mobility. With an asymmetrical anomaly, strabismus and different heights of the eye sockets may occur.
This pathology is part of complex congenital anomalies. It may be accompanied by mental retardation, deformation of the feet, hands, blindness and other disorders.
The same banned issue for which Ernst fired Malakhov!
Joints and cartilage will be cured in 14 days with the help of ordinary...
Treatment
The type of operation depends on the severity of the pathology. Before surgery, the patient is examined by a neurologist, ophthalmologist, and neurosurgeon. A computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging scan is performed. Treatment is performed at the age of 5 - 8 years. Surgery at an earlier age is necessary for pathology of the lacrimal canal or strabismus.
The choice of intervention period is determined by the psychosocial aspects of child development at primary school age. In addition, before the age of 6 years, there are rudiments of teeth in the upper jaw, which may interfere with intervention on the lower edge of the orbit. The disadvantage of treatment at a young age is that the cheekbones are too thin, which can move as the child continues to grow. If the operation is performed on an adult, such consequences do not occur.
In the mildest cases, extracranial correction can be used using special staples that correct the shape of the skull.
In case of eye hypertelorism of the first degree, the bone wall of the eye sockets is dissected, they are brought closer to a normal distance, and the bone and cartilaginous tissues of the nose are restored.
In case of grade II pathology, nasal plastic surgery with a graft from the patient’s own parietal bone can be additionally used.
If there is a III degree of ocular hypertelorism, surgical treatment includes dissection of the frontal and other bones, modeling of the orbits, vault and base of the skull, and reconstruction of the nose.
With microorbitism, the bony walls of the eye sockets are cut, they are pulled apart, while simultaneously modeling the shape of the forehead. The resulting defect is closed with a graft from the own bone of the cranial vault.
Treatment of false hypertelorism is carried out according to the same principles: dissection of bone tissue, elimination of deformation of the forehead and nose, restoration of the shape of the eye sockets.
Typically, facial deformities can be easily corrected. The state of his health is determined by the underlying disease (Down syndrome, etc.). As the child grows, additional interventions may be needed, for example, correction of the corners of the eyes, removal of excess skin in the bridge of the nose. Such cosmetic surgeries can be performed throughout the patient's life.
Hypertelorism of the eye is a congenital malformation of the skull, accompanied by an increase in the distance between the orbits. It is often accompanied by other developmental defects and leads to a pronounced cosmetic defect. Surgical treatment is carried out in childhood.
Causes
The reason for stooping is lifestyle. If a person leads an inactive lifestyle and does not devote at least 10 minutes a day to physical activity, then slouching cannot be avoided. The reason may also be psychological. Most often, spinal curvature occurs in insecure people.
Symptoms
Slouching has its own specific symptoms that are immediately noticeable, so they are easy to recognize.
- Rounded back.
- Overhanging belly.
- The head is pushed forward.
- The chest is tilted forward.
- Dropped shoulders.
- Protruding shoulder blades.
In addition, the back gets very tired, and you only want to be in a horizontal position all the time.
Features of stoop in adults and children
Nowadays, stooping is observed more and more often in children. It should be noted that children are born with a straight spine, which has no bends at all. In the second month, the first curve appears - cervical lordosis. And six months later, the baby develops a second curve - thoracic kyphosis. By the age of one year, the child develops lumbar lordosis. The entire spine is formed by the age of seven.
A child may experience slouching in the following cases:
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Fast growth.
- Psychological factor.
- Scoliosis.
Unfortunately, modern children are inactive. Constantly spending time at the computer weakens the back muscles, and the child develops a stoop.
With rapid growth, the spine becomes elongated and the muscles do not have time to quickly develop along with the spine. Because of this, the back muscles are unable to support the back and the baby begins to slouch.
Lack of self-confidence and complexities are psychological problems that can cause slouching. In this case, the child begins to slouch unconsciously.
In addition to all this, children may also experience rare cases of stooping: anomalies during intrauterine development, rachitic kyphosis. spinal injuries in infancy. cerebral palsy.
If slouching is not treated promptly, it can lead to structural changes in the spine. There may be a hump that will be difficult to get rid of.
Spinal disorders can also occur in older age. The reasons for this are: sedentary work, underdeveloped back muscles, psychological factors, diseases of the back and spine.
When a person sits for a long time, the back quickly gets tired. And if this is repeated for years, then the muscles gradually lose their tone and simply become weak, which contributes to the development of stoop.
Frequent stress on the back can also lead to curvature of the spine. In older age, diseases such as osteochondrosis and osteoporosis can cause stooping.
Diagnostics
The degree of stooping is difficult to determine by eye. Therefore, the following methods for diagnosing stoop are used.
- X-ray of the spine. In this case, a picture is taken where three points are marked - the top of the bend, the points of the outer vertebrae of the bend. Next, the three points are connected to form a triangle. This triangle is used to determine the angle of inclination and the stoop coefficient.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. This procedure helps to identify structural changes in the intervertebral discs.
Slouches of the first, second and third degrees are distinguished.
How to get rid of stoop and fix it at home
You can get rid of stooping at any age, if it is not advanced to the third degree. There are various exercises, gymnastics and stretches that help get rid of slouching. All exercises can be performed at home.
Stretching
Stretching exercises are very easy to do and quite effective. Each stretch is performed for 30 seconds several times a day.
- Exercise lock behind your back. Stand straight with your feet shoulder-width apart. Take your hands back and join them in a lock behind your back. Slowly roll your shoulders back, opening your chest as much as possible and squeezing the front of your shoulders. Keep your head and neck straight while performing the exercise.
- Exercise to relax the spine. So, stand up straight. Raise your hands up, connecting your fingers. And strive upward as high as possible, then slowly lower your arms, hold them in a horizontal position at shoulder level and sway like a spring. You will immediately feel a slight relaxation and tension in your spine.
- Plank. This exercise is very easy to do. Position yourself in a push-up position with your arms straight under your shoulders. The whole body forms a continuous straight line. You need to hold this position for at least a minute.
- Bridge exercise. Lie in a horizontal position on the floor. Then move your arms back, bending your elbows so that your palms completely touch the floor. Then begin to lift your body. Do not make sudden movements under any circumstances. Having reached the maximum point, stay in this position for a few seconds.
- The bridge exercise is the opposite. Lie on the floor on your stomach. Raise your body slightly, then grab your feet with your hands. Only your stomach should touch the floor. Hold this position for a few seconds; if you do not feel any discomfort during the exercise, you can pump back and forth.
- Yoga. An excellent option for treating slouching is yoga. Various yoga poses relax and strengthen the back muscles.
If you feel pain when doing exercises, you should seek help from a specialist who will help you choose the right course of treatment for stooping.
Causes
Hypertelorism is a congenital pathology. The pathology is formed during the rapprochement of the orbits during the embryonic development of the fetus. It is believed that the disorder is triggered due to the influence of pathogenic factors on the mother’s body, for example, excessive consumption of alcohol, toxic substances, certain hormonal drugs, as well as due to previous infectious diseases. All this can lead to the following congenital problems, in which there is a likelihood of developing orbital hypertelorism:
- Craniostenosis or previous fusion of the sutures of the cranial bone;
- Cranial hernia and cleft;
- Various craniofacial vascular malformations;
- Other conditions in which normal formation of the skull does not occur - tumors, bone changes after injury.
In recent years, cases of ocular hypertelorism due to genetic pathology, which can occur even if all instructions are followed during pregnancy, have become more frequent. For example, an increased distance between the eyes is almost always diagnosed with Down syndrome.
How to prevent and prognosis?
Ocular hypertelorism can be prevented by avoiding exposure to toxic and other negative factors on the body during pregnancy. It is important that a pregnant woman gives up bad habits, eats right and does not overwork. It is necessary to avoid infection with infectious diseases, which can subsequently lead to abnormalities in intrauterine development. If an operation is performed to eliminate a cosmetic defect in hypertelorism, the prognosis for the child’s life is favorable and there is no cosmetic defect.
Risk group
The risk group includes the following categories of patients:
- children whose mother suffers from alcoholism or drug addiction or was irradiated during pregnancy;
- patients who have a history of serious mechanical damage to the brain or facial part of the skull;
- persons who have undergone implantation of metal prostheses in the facial area.
If a person is at risk, he needs to consult with doctors, especially a plastic surgeon, who can help correct cosmetic defects.
Symptoms
Hypertelorism is easy to identify by visual inspection. Symptoms characteristic of the disease are always observed, the severity of which may differ depending on the degree of development of the pathology.
- Excessively large distance between the medial ocular fissures;
- Deformation of the palpebral fissures is possible - they may have an irregular shape, be too wide or narrow;
- Abnormal structure of the nose - the bridge of the nose is too wide and the back is flat;
- Multidirectional movements of the eyeballs;
- Congenital strabismus, deformation of the optic nerve and other ophthalmological diseases are observed.
In most cases, hypertelorism is accompanied by intellectual impairment, underdevelopment of the jaw apparatus, and abnormal development of the feet.
How is the disease diagnosed?
Despite the obvious visual severity of the disease, a number of diagnostic measures are required to make a more accurate diagnosis.
The main actions of a specialist are:
- collecting basic information about the presence of a diagnosis of hypertelorism in parents or close relatives;
- visual examination of the patient . Carrying out the necessary measurements of head circumference and calculating deviations from the norm;
- performing brain tomography .
After an external examination and history taking, the patient requires consultation with an ophthalmologist, surgeon or psychiatrist, depending on the presence of additional problems.
An examination by specialists reveals a number of serious pathologies and allows the patient to be assigned a disability.
For your information! After carrying out a number of mandatory measures, the specialist compares the data obtained with generally accepted ones and makes a diagnosis. The patient can be diagnosed with three degrees of hypertelorism.
Diagnostic methods
Concomitant organ pathologies can be detected in a baby using MRI. A pathological sign can be identified during an external examination of the child immediately after birth. To confirm hypertelorism, it is necessary to calculate the interorbital circumference index. It is also important to take a history from parents to check for genetic abnormalities among close relatives. It is possible to carry out karyotyping of the genome to identify violations of the genetic structure. A neuropsychiatric examination and identification of maxillofacial anomalies is recommended. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging help to detect structural abnormalities of the bones of the skull and other organs, which are often combined with such pathology.
Hypertelorism is the wide-set eyes that can be seen during an external examination of a child.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, it is necessary to calculate the interorbital-circumferential index (IOCI). The head circumference should be divided by the distance between the medial canthus and the resulting index multiplied by 100. Orbital hypertelorism is characterized by an index value of 6.8 or more. When measuring the distance between tear ridges, use a table of age parameters. It is also necessary to measure the angle of divergence of the sagittal axes of the orbits from the midline. In individuals with hypertelorism, this angle varies from 30 to 60°. During an objective examination, attention is paid to the shape of the eyelids, the location of the external canthal ligaments and the slope of the forehead. Additionally, the following is shown:
- Visometry.
There is an asymmetric decrease in visual acuity. In severe cases, high-grade unilateral amblyopia is diagnosed. When performing computer refractometry, it is more often possible to identify the hypermetropic type of clinical refraction. - X-ray examination.
An X-ray of the facial skeleton in a direct projection shows an excessive interorbital distance in combination with asymmetry of the orbits. The study makes it possible to detect gross deformations of the bones of the facial skull. - Computed tomography.
A detailed analysis of axial and frontal sections is carried out. The advantage of the study is the ability to study the anatomical features of the structure of the medial walls of the orbit. A CT scan of the facial skeleton is performed immediately before surgery for detailed planning of the operation.
Possible complications
In rare cases, orbital hypertelorism can lead to serious complications. Usually this is the formation of a cranial hernia, the development of any forms of cranial dysplasia. If surgery is not performed on time, then ophthalmological diseases may develop over time - acquired strabismus, optic nerve atrophy, increased intraocular pressure. Ocular hypertelorism is also a risk factor for decreased visual acuity and the development of glaucoma.
Hyperteloriz provokes the occurrence of glaucoma
Forecast
Orbital hypertelorism develops due to a congenital malformation of the skull. It is possible to restore the structure of the face only in early childhood.
The pathological syndrome is not life-threatening, does not result in severe complications, and does not lead to deterioration in physical health. However, this cosmetic defect provokes problems when the baby adapts to the environment and negatively affects the psychological state.
How serious is the diagnosis of hypermetropic astigmatism in children and what to do is described in the article.
Treatment
To date, the only treatment method is surgical plastic surgery. Surgical intervention is possible starting from two years of age. Moreover, the methods and technology of the procedure completely depend on the severity of the pathology and the degree of development of ophthalmological and neurological symptoms. In general, early surgery can prevent complications from developing and reduce the risk of social pressure.
Conservative treatment is necessary only in cases where orbital hypertelorism is accompanied by various complications.
Usually, drugs are prescribed to reduce intraocular pressure, moisturizing drops, and antispasmodics to prevent pain caused by a violation of the location of the eyeball.
Treatment of hypertelorism
Partial treatment of the disease can be carried out exclusively by surgery. During the operation, plastic surgery of the facial bones of the skull and eye sockets is performed.
In more complex situations, reconstruction of almost the entire anterior part of the skull is required. This is a rather complex operation that requires a long period of rehabilitation.
Typically, experts do not recommend surgery unless the patient has specific indications.
In this case, the decision regarding plastic surgery is made either by the patient himself or his relatives.
Since treatment of hypertelorism is completely impossible, the main task of parents who have a child with a similar problem is to create optimal conditions for its development .
If you have mental disorders, it is important to start working with psychiatrists and psychologists as early as possible.
Classification
According to its form, hypertelorism is divided into:
- Symmetric. The eyes are at an abnormally wide distance from each other. No pathologies of vision or orbits are detected. The form is considered favorable for prognosis, but requires surgical intervention.
- Asymmetric. The eyes are set wide apart and at different heights. You may have strabismus (squint) due to weakness of the eye muscles. Lack of muscle strength leads to the fact that the eyeballs cannot make synchronous movements. The pupils look in different directions. The form is unfavorable and requires long-term treatment.
Depending on the degree of defect, there are three types:
- I degree – MOR 30-34 mm,
- II degree – MOP 35-39 mm,
- III degree – MOR 40 mm or more,
where MOR is the interorbital distance, which is measured between the middle of the anterior lacrimal crests. Normally it does not exceed 30 mm.
Prevention
There are no effective ways to prevent the development of this serious pathology. To prevent fetal developmental disorders, it is necessary to adhere to all recommendations and instructions during the entire period of pregnancy. Of great importance is adherence to sleep and rest patterns, avoidance of toxic, narcotic and hormonal substances, as well as a balanced diet. Starting from the first trimester, it is necessary to undergo regular medical examinations in order to promptly notice the presence of abnormal development of the craniofacial apparatus.
Example of manifestation of orbital hypertelorism
Spasm of eye accommodation or false myopia
The causes and treatment of eyesores (leukomas or corneal opacities) are described in this article.
Find the reasons for the appearance of yellow circles under the eyes at the link.
What is orbital hypertelorism?
The degree of the defect depends on the location of the visual organ, the distance between the eye sockets and the age of the person. With ocular hypertelorism, the oval of the face changes and the nasal fissures are deformed.
Scientists distinguish two types of this anomaly. With false epicanthus, the distance between the corners of the visual organ increases. True hypertelorism is characterized by expansion of bone formations. It begins when the front part of the skull is damaged, when a tumor appears in the nose.
A defect is considered a pathology if the value of the indicator in the form of the orbital-circumferential index exceeds 6.8. The angle at which the axes of the eye sockets diverge is sometimes 60 degrees, which is twice the norm.
How to treat viral conjunctivitis in children is described in detail in the article.
Deformation of the skull in the orbital form of the disease
Find out how to treat internal stye on the eye here.
Forms and symptoms
Features of the disorder in orbital hypertelorism are determined by the distance between the internal angles of the visual organ. In the first degree it is less than 34 mm, in the second – 39, in the third it exceeds 40. The norm for this indicator is 3 cm.
It happens that a child has very small eye sockets and slits. Sometimes a baby is born without them at all. This type of pathology, called microorbitism, affects the bones of the skull. They thicken and become deformed.
Rare congenital pathology
With a symmetrical appearance of the anomaly, the distance between the eyes widens. With asymmetric hypertelorism, they are located at unequal heights. The pupils look in different directions. Over time, heterotropia occurs.
conclusions
Ocular hypertelorism is a common symptom that is characteristic of many genetic diseases. Due to the fact that there are no effective ways to treat and prevent the disease, you should approach pregnancy responsibly, starting from the planning stage. And if pathology still cannot be avoided, it is necessary to raise the question of surgical correction as early as possible, which will reduce the risk of complications and facilitate the child’s social adaptation.
Also read about what aphakia of the eye is (congenital or acquired absence of the lens) and whether color blindness can be cured.
What are the causes of the pathology
Eye hypertelorism is a congenital pathology, which is usually associated with various genetic diseases. For example, too widely spaced eye sockets are observed in children with nephrofibromatosis, Apert, Down, Toast, Edwards syndromes and other ailments that are accompanied by multiple fetal malformations. The immediate causes include various anomalies in the structure of the brain or skull - the presence of tumors, too rapid fusion of parts of the skull, cranial hernias and clefts.
Of course, it is possible to identify some risk factors that can disrupt normal intrauterine development or provoke a genetic pathology in the fetus. Thus, infections suffered by the mother during pregnancy, as well as the ingestion of toxins, including heavy drugs, large doses of alcohol, narcotic substances, etc., have a negative impact on the child’s condition.
Sources
- https://ProZrenie.online/zabolevaniya/redkie/prichiny-gipertelorizma-i-metody-lecheniya.html
- https://fb.ru/article/292251/gipertelorizm—eto-chto-takoe-prichinyi-i-simptomyi
- https://okulist.pro/bolezni-glaz/gipertelorizm.html
- https://EyesDocs.ru/zabolevaniya/redkie-bolezni/gipertelorizm.html
- https://o-glazah.ru/drugie/chto-takoe-gipertelorizm.html
Pathogenesis
In the mechanism of development of hypertelorism, the leading role is played by disruption of the formation of skull bones. There are three main stages of morphogenesis: membranous, cartilaginous and bone. Exposure to triggers at the membranous stage is associated with the most unfavorable prognosis; the occurrence of the first changes at the stage of bone tissue formation is less significant. The influence of trigger factors on the fetus in the first trimester of pregnancy can cause severe deformations of the skull bones. Such changes are phylogenetically the youngest and are difficult to correct surgically.
Visual changes do not always reflect the depth of the lesion. The size of the distance between the orbits is significantly influenced by the degree of prolapse and the width of the horizontal plate of the ethmoid bone. The more the perforated plate protrudes outward, the more pronounced the pathological changes are. In this case, the number of cells of the ethmoid labyrinth in the anterior sections significantly exceeds the norm. The posterior segment topographically corresponds to the reference values. Clinical symptoms largely depend on the anatomical parameters of the lesser wings of the sphenoid bone.