Using a fistula for hemodialysis: care and useful tips
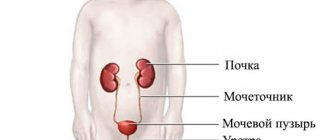
The kidneys are one of the most important organs of the entire excretory system.
If their work is disrupted, a person develops serious pathologies. If deficiency develops, the patient is prescribed a hemodialysis procedure.
During this procedure, a special fistula is used. This article will discuss this design, the features of its installation and application.
general information
Hemodialysis (“artificial kidney machine”) is a procedure performed to restore kidney function in cases of acute or chronic failure. With this disease, the organ cannot cope with its functions and toxins accumulate in the body along with urine.
Let's consider the essence of the hemodialysis procedure: with the help of a special drug, the patient's blood is cleared of toxic substances, and the water-electrolyte balance is adjusted.
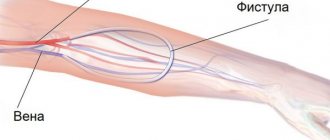
If the patient is on constant dialysis, then a special fistula is installed. This is a kind of “vascular place” from which contaminated blood is removed and returned back in a purified form.
Thanks to this device, the walls of the venous vessels expand significantly and blood circulation through them accelerates.
This is what causes difficulties when taking a puncture. Doctors have found a unique method of installing a fistula, which simplifies the process of blood purification. It is worth noting that suturing of blood vessels is carried out only on one arm.
Indications for use
Hemodialysis fistula is necessary to improve the hemodialysis process. The main indications for use are:
- acute or chronic kidney failure;
- imbalance of electrolytes in the body;
- swelling;
- severe poisoning with toxic substances or food products;
- low glomerular filtration;
- uremia;
- urinary problems.
Arteriovenous fistula and its features
This is a special shunt that is installed between an artery and a vein. Thus, the walls of blood vessels are sealed and the process of cleansing the blood of toxins is accelerated.
It is located under the skin, is not subject to the formation of blood clots, and a puncture needle is easily inserted into it.
There are several types of arteriovenous fistula: radiocephalic, brachiocephalic, brachiobasilar. Depending on the diameter of the vessel used, radial and brachial fistula are distinguished.
However, even this procedure has its advantages and disadvantages. Among the advantages are:
- the device is created exclusively from human vessels, no foreign materials are used;
- is located clearly under the skin;
- infection and blood clot formation are excluded;
- with proper care can be used for up to 10 years;
- Scientists are constantly improving this device.
Disadvantages include:
- the maturation of the fistula lasts up to 60 days;
- there is a risk that the device will not mature due to a number of negative factors: poor circulatory pressure, a small area of the operated vessels, etc.
In addition to this type of device, a hemodialysis patient can have an artificial prosthesis or catheter installed. They are much inferior in functionality to AVFs, so they are not used often.
Preparation for the procedure
The fistula is installed surgically. Before this, it is imperative to undergo diagnostics of the cardiovascular system and establish the usefulness of the kidneys.
Examination and tests
Diagnostic procedures include:
- Ultrasound of the cardiovascular system and kidneys;
- assessment of heart function;
- complex of liver-renal tests;
- angiographic examination of the circulatory system;
- fluorography;
- blood and urine tests (general, biochemical parameters, hepatitis, HIV).
Be sure to tell your doctor if you are taking anti-inflammatory or blood thinning medications, as they may affect the progress of the surgical procedure.
Stages of passage
The installation procedure is simple and, if the doctor is sufficiently experienced, takes no more than an hour. Local anesthesia is used, and the shunt is installed mainly on one arm.
In rare cases, when there are not enough human vessels, the doctor may use special medical catheters or tubes, they replace certain sections of the vein. It takes an average of 30 to 60 days for the fistula to swell; during this period it is strictly forbidden to puncture or injure it.
The essence of the operation is to carry out the following manipulations:
- injecting local anesthesia into the patient's arm;
- treatment of the incision site;
- then the doctor makes an incision in the skin and ligates the necessary artery, then crosses it;
- at the next stage, the lateral venous vessel is removed and a clamp is applied to it;
- then these two vessels are dissected and stitched together;
- At the last stage, the doctor heals the incision on the arm and applies a sterile surgical dressing.
During the operation, the patient does not feel pain; in the future, proper care of this device is very important.
How to care for a fistula
To get an ideal fistula, you need to take care of the venous vessels and not subject them to frequent punctures. There are certain requirements for caring for this device.
If the patient wants to keep it in a functional state for as long as possible, then it is necessary to strictly adhere to all recommendations. Let's consider this issue in more detail.
Checking status
During the postoperative period, it is necessary to keep the operated arm strictly at rest; it is forbidden to lift heavy things or sleep on this side.
To check the operation of the device, it is recommended to carefully monitor the noise that comes from it: it should be the same, continuous and distinct. In case of any violations, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor.
Maintaining personal hygiene
An important condition is compliance with the rules of personal hygiene.
It is necessary to ensure the cleanliness of the hand on which the fistula is installed and periodically treat it with disinfectant solutions.
It is recommended to wash with soap that has a neutral pH.
The use of creams, lotions or other perfumes is strictly prohibited. The surface of the skin should be dry.
Protection from injury
It is necessary to protect this device from injuries, as they will provoke severe subcutaneous bleeding. Under no circumstances should blood pressure be measured or given injections on the operated arm.
Free blood flow
When squeezing a hand with an installed fistula, the risk of developing blood clots increases, so you need to wear loose clothing and avoid wearing bracelets, watches or other similar jewelry. It is not recommended to bend your arm too much at the elbow.
Maintaining normal temperature
Severe changes in temperature increase the risk of blood clots, especially for patients with arterial hypertension. Do not overuse baths, saunas or hot baths. These procedures lead to the dilation of blood vessels, as a result of which the pressure drops sharply and the outflow of blood decreases.
During the cold season, the walls of blood vessels narrow and the outflow of blood becomes weaker. In winter, it is recommended to wear warm clothes to avoid hypothermia.
Complications and prognosis
If used incorrectly, the patient may encounter the following complications:
- infection;
- poor blood flow;
- development of chronic heart failure;
- blood clot formation;
- strokes of ischemic nature;
- aneurysm at the site of the fistula.
When the first unpleasant signs appear, you should immediately contact the institution where the operation was performed.
In the absence of associated complications, the installation of an AVF is positive. This also applies to its timely removal.
Conclusion and useful information
For hypertensive patients, it is recommended to maintain constant monitoring of blood pressure to reduce the risk of thrombosis. It is recommended to take stabilizing drugs, which are selected by the doctor.
To extend its service life, you need to properly care for this structure, carefully treat it after each dialysis session, and consult a doctor for the slightest irregularities.
It is imperative to avoid the development of an infectious process. The first alarming symptoms are: purulent discharge, redness of the skin, external defects. In this case, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor who will correct the fistula.
It is very important to do this procedure only in a good medical center with experienced specialists; this will significantly reduce the risk of complications.
If you follow all the necessary recommendations and monitor the condition of the fistula, you can guarantee the effectiveness of its use, and this in turn helps the patient with renal failure to live a full life.
Fistula for hemodialysis: features of use and care
A hemodialysis fistula is a device for repeated hemodialysis. As a result of impaired renal function, renal failure develops, accompanied by the removal of nitrogen metabolism products and toxins from the blood, an imbalance of electrolytes and acid-base balance. Patients who develop acute or chronic kidney failure are prescribed hemodialysis.
What is and features of a fistula
Dialysis purifies blood outside the body by filtering it through a semi-permeable membrane based on the difference in concentrations of substances in the bloodstream and the dialysate. The hemodialysis machine is called an “artificial kidney.” In the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), the method received code Z49 - care including dialysis.
An arteriovenous fistula simplifies the procedure. Access to the circulatory system becomes better. A subcutaneous anastomosis (connection) of the radial artery with the lateral vein of the arm is created. Microsurgery allows you to create an anastomosis in the wrist area on your non-dominant hand. Arteriovenous access is created in advance, 2-6 months before the start of hemodialysis; 3-4 weeks are needed to form a tight and high-quality access. During the procedure, the anastomosis will experience pressure created by the blood during perfusion.
Fistula installation for hemodialysis is possible on the upper and lower extremities. If the vascular network is developed in the arm, there are 5 places to create access.
Rules of use
Before starting to create access, it is necessary to calculate the risks of the operation and diagnose organs and systems:
- instrumental examination (ultrasound diagnostics) of the cardiovascular and urinary systems,
- general blood and urine analysis,
- testing for the presence of HIV and hepatitis virus,
- angiography,
- X-ray examination of the chest organs.
The doctor will determine the presence of contraindications and the possibility of correcting the condition of organs and systems in accordance with the concomitant pathology. He will explain the essence and possibility of performing the operation, and give recommendations for caring for an arteriovenous fistula.
- damage to veins of various etiologies,
- previously performed operations on blood vessels at the site of the upcoming operation,
- diabetes mellitus, characterized by the development of angiopathy,
- atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels in an advanced stage.
A fistula is formed during hemodialysis as follows:
- The branching of the lateral saphenous vein of the arm is identified.
- The distal branches are ligated.
- The bifurcation of the vein is dissected.
- The bifurcation of the vein is adjusted to the radial artery to create a connection.
- The end of the vein is connected to the lateral surface of the radial artery.
- What types of catheters are there for hemodialysis?
- Plasmapheresis techniques for multiple sclerosis
- Why clean blood?
After applying a fistula, the following is recommended:
- lie on your back, the arm on which the operation was performed should be at a height exceeding the level of the heart, straightened,
- dressing covering the surgical site, dried and clean,
- prevent the possibility of squeezing the hand and keep movements to a minimum. Will help avoid blood clots,
- to develop a vessel, exercise with a rubber ball or expander.
- Before dialysis, wash the hand on which the anastomosis is located,
- application of an aseptic dressing is carried out after bleeding has stopped at the end of the procedure,
- needles are inserted along the entire length of the fistula,
- Vibration of the vessel walls should be periodically checked. Lack of vibration is a sign of a blood clot.
During the procedure, follow the rules:
- Thoroughly disinfect the puncture area.
- The area should not be touched until the end of the procedure.
- After the procedure, the patient can stop the bleeding with a napkin; the pressure should not include pinching of the vessels.
- If you are not sure that the needle did not enter the vessel during puncture, first inject 10 ml of sodium chloride solution. If the needle is not in the vessel, the solution will get under the skin - the ball under the skin will begin to swell.
- Remember the location of each puncture, next time make it 1 cm further from the previous one.
It takes 2 weeks for the puncture hole to heal completely.
Fistula Care
During non-dialysis times, follow these rules:
- do not wear clothes, watches and other accessories that may compress the blood vessels of the operated arm,
- you cannot measure blood pressure on a limb with a fistula,
- do not carry heavy objects (bags) on the fistula limb,
- try not to crush your hand in your sleep,
- do not use vascular access for hemodialysis as a place for blood collection or intravenous infusions,
- avoid damage to the operated limb.
Check the condition of the fistula at home daily. Pay attention to the presence or absence of swelling, hyperemia, pain, vibration over the anastomosis. Inspecting your hand should become a habit. If pain, severe swelling, or inflammation occurs, seek help from a doctor.
How many years is it designed for?
Fistula is a long-term solution; with proper care, it can last for several decades. The service life depends on how the operation was performed, whether complications arose after the operation or during hemodialysis. In case of poor-quality anastomosis formation, ineffectiveness is possible due to insufficient blood flow velocity.
The service life may be shortened due to the development of complications of aneurysm, thrombosis of the fistula for hemodialysis.
As a result of injuries in the postoperative period, there is a possibility of damage to the formation. You need to treat your fistula hand with care and avoid overexertion with physical activity. If you take care of the condition, this will allow the anastomosis to work for a long time.
What information is missing from the article?
- Detailed review of medications
- More practical treatments
- Innovative developments in this area
- Qualified expert opinion
How to properly prick a fistula on hemodialysis
Rules for puncture:
- The puncture is carried out at a distance of 3-4 cm from the anastomosis.
- Place the arterial needle antegrade; in case of retrograde placement, hematoma may develop at the puncture site.
- The venous needle is placed only along the bloodstream.
- In the case of using a single-needle dialysis scheme, the needle is positioned along the blood flow.
- Puncture the fistula in a new place (an aneurysm is likely to develop due to thinning of the vessel walls).
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
Whatever treatment method the doctor chooses, it has advantages and disadvantages. Favorable factors include:
- the use of patient tissue allows one to avoid allergic reactions and a number of complications, in contrast to the use of artificial materials,
- the risk of developing fistula thrombosis is lower than other approaches,
- low likelihood of developing infectious complications,
- duration of use (up to tens of years),
- the shortest access, the anastomosis is located under the skin,
- New surgical techniques are being developed.
The disadvantages of the procedure include:
- Possible hemodynamic disorder (increased venous pressure).
- To use access for dialysis, time for “maturation” is required.
- Unsuccessful formation of an anastomosis may reduce the speed of blood flow, making access irrational.
- Risk of developing aneurysms.
To reduce the likelihood of blood clots, heparin ointment is used. The dose of heparin administered is calculated based on the patient's weight based on the activated clotting time.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of large arteriovenous fistulas is not difficult. Small fistulas can only be detected with modern medical equipment. It is very important to carry out treatment when there are no complications yet. Doctors from Israeli clinics achieved this result in their practice. The latest highly specialized medical technology allows Israeli doctors to diagnose arteriovenous fistulas of any size and location.
To diagnose arterial venous light, use:
- Ultrasound – Dopplerography, ultrasound scanning;
- CT;
- MRI;
- Angiography.
Fistula for hemodialysis: features of use and care
A hemodialysis fistula is a device for repeated hemodialysis. As a result of impaired renal function, renal failure develops, accompanied by the removal of nitrogen metabolism products and toxins from the blood, an imbalance of electrolytes and acid-base balance. Patients who develop acute or chronic kidney failure are prescribed hemodialysis.
What is and features of a fistula
Dialysis purifies blood outside the body by filtering it through a semi-permeable membrane based on the difference in concentrations of substances in the bloodstream and the dialysate. The hemodialysis machine is called an “artificial kidney.” In the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), the method received code Z49 - care including dialysis.
An arteriovenous fistula simplifies the procedure. Access to the circulatory system becomes better. A subcutaneous anastomosis (connection) of the radial artery with the lateral vein of the arm is created. Microsurgery allows you to create an anastomosis in the wrist area on your non-dominant hand. Arteriovenous access is created in advance, 2-6 months before the start of hemodialysis; 3-4 weeks are needed to form a tight and high-quality access. During the procedure, the anastomosis will experience pressure created by the blood during perfusion.
Fistula installation for hemodialysis is possible on the upper and lower extremities. If the vascular network is developed in the arm, there are 5 places to create access.
Rules of use
Before starting to create access, it is necessary to calculate the risks of the operation and diagnose organs and systems:
- instrumental examination (ultrasound diagnostics) of the cardiovascular and urinary systems,
- general blood and urine analysis,
- testing for the presence of HIV and hepatitis virus,
- angiography,
- X-ray examination of the chest organs.
The doctor will determine the presence of contraindications and the possibility of correcting the condition of organs and systems in accordance with the concomitant pathology. He will explain the essence and possibility of performing the operation, and give recommendations for caring for an arteriovenous fistula.
- damage to veins of various etiologies,
- previously performed operations on blood vessels at the site of the upcoming operation,
- diabetes mellitus, characterized by the development of angiopathy,
- atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels in an advanced stage.
A fistula is formed during hemodialysis as follows:
- The branching of the lateral saphenous vein of the arm is identified.
- The distal branches are ligated.
- The bifurcation of the vein is dissected.
- The bifurcation of the vein is adjusted to the radial artery to create a connection.
- The end of the vein is connected to the lateral surface of the radial artery.
- What types of catheters are there for hemodialysis?
- Plasmapheresis techniques for multiple sclerosis
- Why clean blood?
After applying a fistula, the following is recommended:
- lie on your back, the arm on which the operation was performed should be at a height exceeding the level of the heart, straightened,
- dressing covering the surgical site, dried and clean,
- prevent the possibility of squeezing the hand and keep movements to a minimum. Will help avoid blood clots,
- to develop a vessel, exercise with a rubber ball or expander.
- Before dialysis, wash the hand on which the anastomosis is located,
- application of an aseptic dressing is carried out after bleeding has stopped at the end of the procedure,
- needles are inserted along the entire length of the fistula,
- Vibration of the vessel walls should be periodically checked. Lack of vibration is a sign of a blood clot.
During the procedure, follow the rules:
- Thoroughly disinfect the puncture area.
- The area should not be touched until the end of the procedure.
- After the procedure, the patient can stop the bleeding with a napkin; the pressure should not include pinching of the vessels.
- If you are not sure that the needle did not enter the vessel during puncture, first inject 10 ml of sodium chloride solution. If the needle is not in the vessel, the solution will get under the skin - the ball under the skin will begin to swell.
- Remember the location of each puncture, next time make it 1 cm further from the previous one.
It takes 2 weeks for the puncture hole to heal completely.
Fistula Care
During non-dialysis times, follow these rules:
- do not wear clothes, watches and other accessories that may compress the blood vessels of the operated arm,
- you cannot measure blood pressure on a limb with a fistula,
- do not carry heavy objects (bags) on the fistula limb,
- try not to crush your hand in your sleep,
- do not use vascular access for hemodialysis as a place for blood collection or intravenous infusions,
- avoid damage to the operated limb.
Check the condition of the fistula at home daily. Pay attention to the presence or absence of swelling, hyperemia, pain, vibration over the anastomosis. Inspecting your hand should become a habit. If pain, severe swelling, or inflammation occurs, seek help from a doctor.
How many years is it designed for?
Fistula is a long-term solution; with proper care, it can last for several decades. The service life depends on how the operation was performed, whether complications arose after the operation or during hemodialysis. In case of poor-quality anastomosis formation, ineffectiveness is possible due to insufficient blood flow velocity.
The service life may be shortened due to the development of complications of aneurysm, thrombosis of the fistula for hemodialysis.
As a result of injuries in the postoperative period, there is a possibility of damage to the formation. You need to treat your fistula hand with care and avoid overexertion with physical activity. If you take care of the condition, this will allow the anastomosis to work for a long time.
What information is missing from the article?
- Detailed review of medications
- More practical treatments
- Innovative developments in this area
- Qualified expert opinion
How to properly prick a fistula on hemodialysis
Rules for puncture:
- The puncture is carried out at a distance of 3-4 cm from the anastomosis.
- Place the arterial needle antegrade; in case of retrograde placement, hematoma may develop at the puncture site.
- The venous needle is placed only along the bloodstream.
- In the case of using a single-needle dialysis scheme, the needle is positioned along the blood flow.
- Puncture the fistula in a new place (an aneurysm is likely to develop due to thinning of the vessel walls).
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
Whatever treatment method the doctor chooses, it has advantages and disadvantages. Favorable factors include:
- the use of patient tissue allows one to avoid allergic reactions and a number of complications, in contrast to the use of artificial materials,
- the risk of developing fistula thrombosis is lower than other approaches,
- low likelihood of developing infectious complications,
- duration of use (up to tens of years),
- the shortest access, the anastomosis is located under the skin,
- New surgical techniques are being developed.
The disadvantages of the procedure include:
- Possible hemodynamic disorder (increased venous pressure).
- To use access for dialysis, time for “maturation” is required.
- Unsuccessful formation of an anastomosis may reduce the speed of blood flow, making access irrational.
- Risk of developing aneurysms.
To reduce the likelihood of blood clots, heparin ointment is used. The dose of heparin administered is calculated based on the patient's weight based on the activated clotting time.
Symptoms of arteriovenous fistulas
As a rule, a small arteriovenous fistula appears at first, but it quickly enlarges. Only a large fistula can cause complications. The main symptoms are:
- Poor circulation in organs and tissues;
- Decreased blood pressure, increased venous pressure;
- Disruption of the cardiovascular system;
- If the fistula occurs in the vessels of the extremities, then sometimes you can see an enlarged pulsating vein. A local increase in temperature and hyperemia is observed above such a vein;
- A murmur can be heard on auscultation above the dilated vein.
There are two types of arteriovenous fistulas.
Creation of a fistula for dialysis
Congenital
Fistulas formed in the intrauterine development of the embryo. Already in the first weeks of a child’s life, venous hypertension and pathological ischemia of the limbs are provoked. Typically, there is enlargement of the limbs, pigmentation of the skin, hyperhidrosis (increased sweating), as well as swelling of the saphenous veins.
Purchased
Arteriovenous fistulas are the result of wounds, trauma, or the cause of previous medical procedures.
It is worth emphasizing that for a positive effect during hemodialysis, arteriovenous fistulas are created deliberately during surgery.
Arteriovenous fistula for hemodialysis
Hemodialysis is a procedure for purifying the blood in patients whose kidneys cannot cope with this function. A fistula is a natural or artificially created fistula, that is, a channel that connects any body cavities or a cavity with the external environment. An arteriovenous fistula for hemodialysis is an artificial fistula necessary for access to the blood system. The essence of the operation is that the artery is connected directly to the vein, due to which the vessel thickens, and it becomes easier to connect it to a blood purification device (“artificial kidney”).
Indications for surgery
The most common indication for hemodialysis is chronic renal failure. It is also necessary for poisoning by toxins or poisons. In a healthy person, the kidneys act as a kind of filter, controlling the amount of water in the body and purifying the blood of toxins. In 5 minutes, absolutely all the blood passes through the kidneys and circulates through the vascular bed. In one day, the kidneys manage to filter more than 180 liters of blood, while toxins are excreted in the urine.
In case of chronic renal failure, the blood must be filtered artificially, since the patient’s body cannot cope with this task. For these purposes, special devices were developed. With chronic dialysis, that is, the patient is regularly connected to the device, it is necessary to have constant access to the vascular bed. To do this, simple operations are performed to create a fistula, which will allow obtaining the maximum amount of blood for purification.
Method of operation
Before surgery, the patient must undergo a complete medical examination. Doctors pay attention not only to the condition of the kidneys and urinary system, but also take blood for analysis, examine the heart and blood vessels. The fistula for hemodialysis is located on the forearm, and the operation itself takes place in several stages.
- The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. After this, the surgical access site is disinfected.
- Next, a skin incision is made on the forearm, the artery is exposed, it is ligated and all its lateral branches are blocked.
- Then the surgeon works with the vein at a distance of 4-5 cm from the artery. You need to do the same manipulations with it as with the artery.
- Next, these two vessels need to be sewn together. To do this, a small longitudinal incision (2─2.5 cm) is made so that a suture can be placed on the edges of the vessels.
- At the end of the operation, the wound is sutured layer by layer and covered with a bandage.
After the procedure, time must pass until the fistula forms. During the first week, the patient must be in the hospital so that doctors can constantly monitor him. Discharge usually occurs on days 7-10, but even after that the patient comes to the hospital for examination. Hemodialysis using a fistula can be performed no earlier than a month after surgery.
Postoperative care
A mature arteriovenous fistula looks like an abscess on the forearm. If treated properly, it can last for many years and even decades without complications. To do this, the patient needs to get used to it and follow some instructions:
- do not put pressure on the arm on which the fistula is located (do not sleep on it, do not wear jewelry or clothes with tight sleeves);
- exclude physical activity (you can use your hand in everyday life, but sports will be contraindicated);
- do not measure pressure on this arm;
- listen to the noise ─ it should be the same all the time;
- if possible, do not provoke surges in blood pressure.
You need to understand that with any pathologies you need to consult a doctor. If the nature of the blood noise in the fistula has changed or bleeding does not stop for a long time after dialysis, the patient needs to be examined. An increase in local temperature should also be a cause for concern - this fact indicates the presence of inflammation. This situation can happen if hygiene is not maintained, especially after dialysis.
The patient must constantly raise his hand to his ear and listen to the noise. It should be drawn out, constant and rhythmic. This sound resembles the operation of mechanisms and is formed when blood moves through the veins. Any disturbance of this sound is a reason to consult a doctor. Decreased audibility or complete absence of sounds indicates the formation of blood clots, which must be removed surgically.
At first, many patients are afraid to touch the fistula and use their hand, but then they get used to the new way of life. You can and should touch it - this is the only way to feel the movement of blood through the connected vessels and control the local temperature.
There is no need to worry that light household loads will be harmful. On the contrary, moderate movements will prevent blood stagnation and keep the fistula in working condition for a long time.
Advantages of arteriovenous fistula over other methods
An arteriovenous fistula is not the only way to gain access to the vascular bed for hemodialysis. Artificial fistulas, subclavian or femoral catheters are also used. There is also a method of peritoneal dialysis, which does not require vascular access. Sterile liquid is poured through a special catheter tube directly into the abdominal cavity, and the filter in this case is the peritoneum. Then the solution is drained.
However, an arteriovenous fistula is considered the best option for the patient and, if there are several options, it is chosen. There are several reasons for this:
- To create a fistula, the patient’s own tissue is taken, which cannot cause rejection or allergies, unlike artificial materials.
- The fistula is located just under the skin and is easy to use to gain access to blood.
- The risk of infection, as well as the formation of blood clots, is minimal with this method.
- The same fistula can last for many years if properly cared for.
The result of treatment depends not only on hemodialysis, but also on the responsibility of the patient himself. Arteriovenous fistula is one of the most gentle and affordable options for chronic renal failure. Compared to other methods of blood purification and kidney transplant surgery, this procedure is the safest.
Disadvantages and possible complications
Unfortunately, this method is not suitable for all patients. If the patient has low blood pressure or anemia, after suturing the vessels, a fistula may not form. In this case, it will be impossible to access the vessel through a non-working fistula. Among the disadvantages, one can also highlight the duration of fistula maturation. The first hemodialysis can be performed only a month after the operation.
Complications occur in rare cases. Among them are possible:
- formation of an aneurysm (expansion of the walls of blood vessels with the danger of their rupture);
- decreased or loss of sensitivity in the hand;
- insufficient oxygen supply to the myocardium;
- compression of the carpal (wrist) nerve, which can cause the hand to function less well.
Complications appear in isolated cases. You need to understand that chronic renal failure is a disease that the patient will have to fight all his life. In this case, a person needs to get used to a new lifestyle, constant procedures, prohibitions and diet. A hemodialysis fistula allows for regular blood purification without any particular danger to the body.
Sources: https://fok-zdorovie.ru/ochishhenie-organizma/fistula-dlya-gemodializa-osobennosti-ispolzovaniya-i-uhod https://fok-zdorovie.ru/ochishhenie-organizma/fistula-dlya-gemodializa-osobennosti -ispolzovaniya-i-uhod https://pochkizdrav.ru/pochechnaya-nedostatochnost/fistula-dlya-gemodializa.html https://toxikos.ru/otravleniya/forsirovanniy-diurez