Where does it hurt with cystitis in women?
Pain is one of the constant companions of the inflammatory process.
Therefore, many diseases that affect the bladder are accompanied by pain in the suprapubic area and the depth of the small pelvis. Aching pain occurs against the background of inflammation, leading to destruction of the mucous membrane of the bladder and irritation of pain receptors.58, 62 Against the background of progressive inflammation, the intercellular substance in the area of tissues affected by inflammation is filled with mediators of alteration and exudation (pro-inflammatory mediators). Increased sensitivity of pain receptors leads to the development of nagging pain in the lower abdomen with cystitis. With the appearance of generators of increased excitation in the affected structures, peripheral pain becomes chronic58, 59
Chronication of the pain syndrome is facilitated by processes that occur in tissues, blood vessels, and internal organs. Chronic urological pain usually appears against the background of pathologies of physiological processes occurring at the level of the humoral-endocrine and nervous systems59
With cystitis, the lower abdomen feels tight and the temperature rises: what to do?
With inflammation of the bladder, a low-grade fever (37-38°C) usually persists [7]. A slight increase in temperature has an adaptive significance and helps to increase cellular immunity, suppress the proliferation of uropathogens, and enhance cellular metabolism.60
If your body temperature rises above 38°C, chills, or pain in the side or lower back, you should immediately consult a doctor. Such symptoms may indicate that the infection has spread beyond the bladder and the development of pyelonephritis. Self-medication in this case is not advisable, since this can lead to the progression of inflammation.16
Diagnostics
If these symptoms are detected, a woman should seek advice from a gynecologist or urologist. After examining the complaints, they prescribe a set of additional studies:
- general blood analysis;
- urine test;
- smears from the vagina and cervical canal;
- ultrasound diagnostics of the pelvic organs;
- bacteriological culture of urine.
If the presence of an STI is suspected, doctors prescribe additional blood tests or urogenital smears. When pathogenic microflora is detected, an antibiogram is performed to determine its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs.
Cystitis: pain and its nature
Inflammation of the bladder is characterized by pain in the lower abdomen, which intensifies at the end of urination. It can be permanent, manifesting itself in the form of mild discomfort, noticeable burning or stinging. As inflammation progresses, the pain syndrome can become acute or paroxysmal in nature.16
But not in all cases the lower abdomen hurts with cystitis. Sometimes pain in the pelvic area is a sign of other pathologies. For example, diseases of the rectum, urethra and other internal organs.62
Causes of nagging pain in the lower abdomen and frequent urination in women
Such problems are most often a sign of certain pathologies. But sometimes unpleasant sensations can also appear due to natural physiological reasons.
Gynecological diseases
If you feel discomfort in the lower abdomen and want to go to the toilet in a small way, the symptoms most often indicate pathologies of the reproductive system:
- Vaginitis. The disease is accompanied by inflammation of the vaginal mucosa, which leads to problems with urination and the development of pain.
- Endometritis. The pathology is characterized by inflammation of the uterine mucosa. Accompanied by intense pain in the lower abdomen and vaginal discharge.
- Salpingitis. In the presence of this disease, the source of inflammation is localized in the fallopian tubes. The main symptoms are abdominal pain radiating to the lower back, chills, vaginal discharge, and frequent urination.
Problems also arise with uterine fibroids. When the formation reaches a large size, it compresses the bladder tissue. As a result, there is a frequent urge to urinate and discomfort in the lower abdomen.
Pathologies of the urinary system
Diseases of the kidneys or bladder often lead to the fact that a woman cannot go to the toilet normally. The following pathologies are the causes:
- Cystitis. The lower abdomen may hurt if an inflammatory process develops in the bladder. There is a burning sensation when trying to go to the toilet.
- Urethritis. The disease is accompanied by inflammation of the tissues of the urethra.
- Pyelonephritis. Inflammation of the kidneys leads to a rapid deterioration in a woman’s well-being. She feels heaviness in the abdomen and lower back, problems with urination, and possibly blood in the urine.
- Polyps. The appearance of special growths occurs on the walls of the bladder. As a result, women have a constant tummy tug.
Problems with urination and pain occur in the presence of urolithiasis. They are explained by the movement of sand or stones along the urethra. A feature of the disease is the ability to be asymptomatic for a long time.
Sexually transmitted infections
Diseases can be bacterial or fungal in origin. Infections are transmitted from a sick person during unprotected sexual contact. Characterized by general symptoms:
- unusual vaginal discharge that has an unpleasant odor;
- itching and burning of the genital mucosa;
- frequent and painful urination;
- the appearance of rashes or other formations on the surface of the genital organs;
- unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen during intimate relations.
If left untreated, the symptoms of STIs become more pronounced and cause a lot of suffering to the woman. Sometimes diseases occur in a latent form, which is characterized by the almost complete absence of a characteristic clinical picture.
Physiological factors
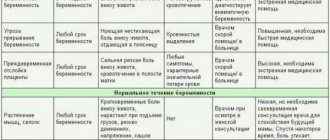
During pregnancy, the rapidly enlarged uterus puts pressure on the bladder, which leads to increased urination and discomfort in the lower abdomen. Normally, severe and acute pain should be absent. Otherwise, doctors suspect that the woman has diseases of the genitourinary system. In the absence of pathologies, the pregnant woman’s well-being is completely restored after childbirth.
Many women experience problems with urination and pain when menstruation occurs. This is explained by the hormonal changes in the body that occur during this period. If the pain intensity is mild and there are no other alarming symptoms, there is no cause for concern.
When menopause occurs, women face the problem of frequent urination or urinary incontinence. This is caused by the natural loss of tissue tone of the internal organs. A sharp decrease in the level of sex hormones leads to an increase in the sensitivity of bladder receptors.
Other reasons
Non-pathological factors that can cause the problem:
- Hypothermia. Leads to exacerbation of some chronic diseases - pyelonephritis, cystitis, inflammation of the ovaries.
- Eating foods with a diuretic effect: cucumbers, watermelon, pumpkin, cumin, garlic.
- Soul feelings. The release of stress hormones into the blood leads to frequent urination.
- Individual characteristics of the body. With a weak muscular corset of the bladder, frequent urination is natural.
Taking certain medications (diuretics, sedatives, calcium channel blockers, etc.) also provokes similar problems. At the end of the course of treatment, the woman’s condition returns to normal.
How to treat cystitis and pain?
Cystitis is an infectious and inflammatory disease, one of the complications of which is pain. Therefore, treatment requires not only adequate antimicrobial therapy, but also the use of painkillers.16, 59
As part of complex therapy, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as antispasmodics and painkillers are usually used. Their action is aimed at reducing the tone of the bladder, relieving the frequent urge to urinate, and eliminating inflammatory pain.16
Treatment
If the cause of the disease is an infection, treatment is conservative and is carried out in two directions:
- Symptomatic therapy (aimed at eliminating pain during urination and other accompanying symptoms of the underlying disease).
- Etiotropic therapy (complex treatment of the underlying disease).
As a medical treatment, antibacterial drugs are prescribed that neutralize pathogenic microorganisms and relieve focal inflammation. According to indications, the complex of therapeutic measures can be expanded with physiotherapy and diet.
For allergic diseases, the allergen is identified and eliminated, and treatment is carried out with antihistamines.
And only in rare cases, for diseases of an oncological nature or caused by mechanical damage, treatment can be surgical.
Many pains during urination can be prevented by observing the rules of personal hygiene, emptying the bladder on time, avoiding hypothermia, using contraceptives and following the principles of a healthy diet.
Fitolysin® paste for pain and stinging due to cystitis
Phytolysin® paste is a natural diuretic, which contains 4 essential oils and 9 types of plant materials. It has pronounced antispasmodic, anti-inflammatory, and diuretic effects. The drug relieves frequent urge to urinate, eliminates inflammation and reduces inflammatory pain.6
Herbal preparations, such as Fitolysin® paste, are used in conjunction with antibiotics. They help create favorable conditions for clinical as well as microbiological recovery.
Fitolysin® paste has a convenient release form, which greatly simplifies the dosage and use of the product. The course of treatment lasts on average 2-6 weeks, but can be longer if necessary.6
Methods of therapy and prevention
Treatment of frequent urination is carried out taking into account the reasons that caused it. A course of antibiotics and urological antiseptics (Canephron, Uronephron) are often prescribed. To eliminate pain, antispasmodics are used - No-Shpa, Spazmolgon. To restore the microflora of internal organs, probiotics are prescribed - Linex, Bifiform.
To prevent problems of this kind, a woman needs to visit a gynecologist 1-2 times a year for preventive examinations or more often if there are complaints. You must constantly adhere to the rules of personal hygiene, eat a balanced diet, and avoid hypothermia and stress. To generally strengthen the body, it is useful to engage in sports or physical exercise.