Make an appointment with a venereologist by phone or by filling out the online form
| Select a clinic | Circumcision | Sexual infections | Urethral swab |
Strangury
is a condition in which there is difficulty in passing urine. This does not mean that urination is completely restricted. It still happens, but not completely and the bladder is not completely emptied.
The presence of such a condition is clear evidence that there is some kind of urological disease in the body that requires timely treatment.
Symptoms of strangury
- Sluggish, vertically directed urination.
- Urine is released not as a stream, but as a drip.
- Urinary flow turbulence.
- With a clear urge to urinate, urine is not released.
- Strong straining is required to start urination.
If you notice this, you should make an appointment with a urologist as soon as possible. After all, lost time in this case is not just unnecessary suffering, but also the likelihood of developing serious pathological processes.
Types of disease
The success and correctness of therapy depends on the form of manifestation of difficulty urinating in women. Pathology is divided into the following types:
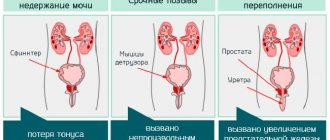
- strangury. Accompanied by painful sensations during miction, a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder after it. Complaints of constant pressure in the lower abdomen and the desire to urinate;
- pollakiuria. Manifested by frequent trips to the toilet without an increase in the daily volume of urine excreted;
- incontinence. Urine is excreted involuntarily, there is no urge to perform urine;
- urinary retention. Develops after constant incomplete emptying of the bladder. Miction is unstable, accompanied by frequent stops and restarts.
The disease is divided into several types
Problems with urination in women provoke hypertrophy of the bladder muscles, so one trip to the toilet cannot completely empty it. This causes the process of urination to be made with effort. Urine comes out completely after several visits to the toilet. Over time, voiding becomes more intermittent, which causes stagnation of urine and chronic urinary retention (ischuria).
Treatment of stranguria
There is no classical treatment plan for this pathology, and it is also difficult to find two identical cases of strangury. Each clinical picture has individual prerequisites for the development of the disease, and the complex treatment prescribed by the urologist will be aimed at the root cause.
- Available: doctor’s appointment from 1500 rubles
- Convenient: open daily from 8:00 to 21:00
- Quickly: we will carry out all the diagnostics at the first appointment
- Complete: has all the necessary equipment
Diagnostics
In case of ischuria, the patient first needs to undergo a urological examination. During the appointment, the doctor will ask the patient about complaints and carefully study the anamnestic data to detect risk factors for diseases. The initial examination sometimes reveals additional symptoms that indicate a preliminary diagnosis. To clarify the cause of the disease, instrumental and laboratory tests are prescribed.
Required tests:
- Ultrasound visualization of organs. Ultrasound allows you to obtain images of anatomical structures in real time without harm to the patient, so this method is often used to diagnose acute pathologies. In case of urinary retention, the doctor may perform an ultrasound of the bladder, kidneys and prostate gland.
- Cystoscopy is a visual examination of the bladder. The doctor inserts a flexible tube equipped with a camera into the urethra to examine the lining of the organ.
- Neurological examination if a disorder of the central or peripheral nervous system is suspected.
- Ascending ureteropyelography is an x-ray examination of the urinary tract that allows one to assess the volume of residual urine.
The prescribed diagnostic procedures depend on the patient’s condition and his individual medical history.
Urology department of “CLINIC No. 1”
Any urological disorders, including strangury, will be treated by experienced urologists at the multidisciplinary center in Khimki. We invite you for diagnosis and treatment. Do not delay visiting a doctor, because the possibilities of modern medicine will allow you to effectively get rid of a problem that is unpleasant from a physical and emotional point of view. Make an appointment and regain your self-confidence and health.
Prices for services
| Name | Time | Price | |
| Bougienage of the urethra | 1430 | ||
| Intracavernous injection (with Caverject) | 4180 | ||
| Reduction of paraphimosis | 2145 | ||
| Collection of material for microbiological examination | 275 | ||
| Urine collection with a catheter in women | 610 | ||
| Replacing the Pezzer catheter | 1210 | ||
| Instillation into the urethra | 825 | ||
| Instillation of the bladder (with the cost of the drug) | 1210 | ||
| Bladder catheterization in men | 990 | ||
| LOD therapy (1 session) | 1100 | ||
| Prostate massage (1 procedure) | 1100 | ||
| Operation - plastic surgery of the frenulum of the penis | 8470 | ||
| Surgery for hydrocele of the testicular membranes (according to Bergman and others) | 18150 | ||
| Operation Circumcisio | 18150 | ||
| Digital rectal examination | 850 | ||
| Dissection of the frenulum (frenulotomy) | 6050 | ||
| Sanitation of the urethra (1 instillation) | 500 | ||
| Removal of epididymal cyst | 14520 | ||
| Removal of genital warts (more than 10 units) | 4250 | ||
| Removal of genital warts (from 3 to 5 units) | 2450 | ||
| Removal of genital warts (5 to 10 units) | 3630 | ||
| Replacement of epicystostomy | 950 | ||
| Appointment with a urologist, treatment and diagnostic, primary, outpatient | 1500 | ||
| Appointment with a urologist, therapeutic and diagnostic, repeated, outpatient | 1000 | ||
| Extended consultation with a urologist with drawing up a treatment plan | 1650 | ||
| dilatation of the glans penis with separation of synechiae with cathegel anesthesia | 3300 | ||
| dilation of the glans penis with separation of synechiae without anesthesia | 2750 | ||
| Marmar operation (microsurgical) for varicocele on one side | 55000 | ||
| Injection of the drug "caverject" | 1650 | ||
| Urofluometry | 990 | ||
| Expand all prices | |||
Causes
- BPH (benign prostatic hyperplasia) or prostate adenoma. The disease is most common in people over 45 years of age. It is characterized by an increase in the volume of the prostate gland (an organ located under the bladder and surrounding the upper part of the urethra), as a result of which the overgrown tissue of the organ compresses the lumen of the urethra. This symptom has a gradual onset and may be accompanied by increased urgency, urine leakage, and frequent urination at night (nocturia).
- Urethral stricture is a narrowing of the urethra, which can be caused by trauma, previous therapeutic and diagnostic procedures (bougienage, cystoscopy, etc.), or previous infections. In this case, the length of the stricture can be from minimal (up to 0.5 cm) to significant (more than 2-3 cm).
- Phimosis is a narrowing of the foreskin, which makes it impossible or difficult to open the head of the penis. It is most typical for young people, as well as for patients suffering from diabetes.
Other reasons may be: sclerosis of the bladder neck (most typical for men who have previously undergone transurethral manipulation), prostate cancer, urethral stones, etc.
However, do not think that this symptom can only occur in men.
For women, the main reasons for difficulty urinating are:
- Neurogenic bladder is a disease of neurological origin (consequence of strokes, spinal cord injuries, Parkinson's disease; due to intervertebral hernias; can also develop with diabetes), in which proper innervation of the bladder is disrupted, which reduces its contractility
- Prolapse of the pelvic organs (cystocele, rectocele, hysteroptosis) is a pathology that occurs in women when the muscles and ligaments of the pelvic floor are weakened and is characterized by prolapse of the pelvic organs, leading to disruption of the outflow of urine through the urethra due to its bending. The reasons for this weakening may be previous births of large fetuses, hysterectomy, genetic factors, as well as hormonal changes in postmenopause.
- Formations of the urethra and surrounding tissues are a pathology characterized by compression of the lumen of the urethra by additional volumetric growths (paraurethral cyst, Gratner's cyst or vaginal cyst, urethral polyp, etc.), often accompanied by splitting of the urine stream.
Prevention
To prevent problems with urination, you need to be careful about your health, avoid heavy physical activity, strengthen the muscles of the perineum and control your weight. In addition, you need to follow simple recommendations:
- avoid casual sex;
- avoid hypothermia;
- wear underwear made from natural fabrics;
- adjust your diet by removing salty, spicy and fried foods from the menu;
- undergo regular examinations and treat any illnesses;
- give up bad habits.
If any alarming signs appear, you should seek help from a doctor. In the first stages, you can quickly cure the disease and avoid serious complications. You cannot ignore the problem that has arisen, otherwise the pathology will become chronic. In this case, general health worsens, skin irritation appears in the groin area, and infectious diseases are possible. Sometimes even death occurs. Therefore, you should not wait until your bladder empties on its own. It is better to immediately contact a specialist. Difficulty urinating in women is a serious disease that requires urgent treatment. It causes poisoning of the body, distension of the bladder and other serious complications. In the absence of therapy, the prognosis is extremely unfavorable and the consequences are very severe.
Symptoms
When experts talk about difficulty in the urinary process, they mean a general set of symptoms that may be present in one or several signs at the same time.
The following violations can be considered alarm signals:
- inability to form a full-fledged stream or remove physiological fluid in droplet volumes;
- the stream is too thin, without pressure, directed straight down;
- very prolonged act of urination while maintaining the same volume;
- strong pushing and straining, which must be resorted to in order for urine to begin to be excreted;
- significant splashing of urine that accompanies the process, or splitting of the stream;
- pain, burning and other severe discomfort.
All these symptoms, as a rule, affect the duration of the process, sometimes they are accompanied by hematuria - the presence of blood clots, mucus, or simply the red color of the urine due to the ingress of blood into it.
If the outflow disorders are very severe and there is a high level of pain, a woman may need to have a medical catheter installed to facilitate the drainage of urine.
Any of these symptoms is a sufficient reason to contact a specialist who can determine the cause of the problem. Sometimes symptoms occur against the background of a deterioration in general health, which indicates an aggravated process.
How to treat difficulty urinating
The therapeutic course is prescribed according to the established cause of the pathology. It is aimed at mitigating the symptoms, eliminating the causes of the disease, and destroying the viruses and pathogenic microorganisms present.
Treatment of the pathology begins with the prescription of anticholinergic medications. They are designed to reduce tension in the smooth muscles of the urinary tract and normalize the act of urination.
If the disease is caused by harmful bacteria that have entered the organ, antibiotics are used: Clarithromycin, Trimethoprim, Amoxicillin, Ciprofloxacin, Amoxiclav. Cyston, Monurel, Canephron are used to relieve the pain of micturition. For thrush caused by a fungus, Fluconazole can be used. If difficulty urinating is due to the presence of a tumor, surgery is used to remove it.
Urinary incontinence requires special treatment. It is often called stress. Urine secretion occurs during coughing, laughter, and lifting heavy objects. Pathology is provoked by intra-abdominal pressure, compression of the pelvic muscles and bladder.
Treatment of the problem requires contacting a neurologist or psychotherapist. After normalization of the patient’s psychological state, the pathology will disappear. Pregnant women can cope with the problem of difficult miction by performing special therapeutic exercises.
It should be remembered that even if the symptoms are absolutely similar to someone you know, you cannot repeat their treatment regimen, since the course of therapy is always selected individually, taking into account the physiological characteristics and pathologies present.