Treatment of autism in children: how to adapt a child in society?
In stock
Autism is a disorder of mental and psychological development in which there is a deficit in emotional manifestations. Autism spectrum disorders are characterized by deficits in the sphere of communication and communication. In translation…
Autism is a disorder of mental and psychological development in which there is a deficit of emotional manifestations
Autism spectrum disorders are characterized by deficits in the areas of communication and communication. Translated, the word “autism” means a person directed inward, withdrawn into himself. Depending on the form and degree of autism, cognitive abilities may be reduced or preserved.
Autism or autism spectrum disorder is often replaced by the acronym (ASD). ASD belongs to a group of neurodevelopmental disorders.
In simple words: “ Autism
is a disorder of mental development that manifests itself as a deficit in social interactions. In autism spectrum disorders, there are repetitive behaviors and a limited range of interests.”
Types of autism spectrum disorders
Today there are several types of autism:
Early childhood autism
It is also called Kanner's syndrome. Most often, this type of autism can be observed in the first years of a child’s life, sometimes even in the first months of life.
In early childhood autism, the following behavioral features are observed:
- refusal to communicate with loved ones;
- total attachment or complete detachment from communication with mother;
- lack of interest in the outside world;
- refusal to eat;
- lack of eye contact;
- repetitive movements, attachment to rituals.
Atypical autism
This form of autism can be observed at a later age, closer to adolescence.
In atypical autism, the following behavioral features are observed:
- symptoms are superficial, less pronounced;
- average level of intelligence;
- the presence of various types of talent, giftedness for some activity;
- speech retardation.
Asperger's syndrome
This form of autism is more common in boys. This type of autism is considered a mild form and is quite easy to correct.
With Asperger's syndrome, the following behavioral features are observed:
- low level of empathy and ability to empathize;
- social activity is impaired, communication difficulties. Often the child does not understand and is not ready to accept rules and social norms;
- intelligence does not suffer, and often acquires a special character.
Rett syndrome
A fairly severe form of autism, found only among girls. The following behavioral features are observed in Rett syndrome:
- inactivity of the limbs and monotony of their movements;
- lack of focus;
- convulsive seizures are possible;
- lack of speech, or very small vocabulary.
Atypical autism in children: diagnosis, symptoms, treatment in Tsaritsyno
Atypical autism (pervasive developmental disorder (PDD)) is a pervasive developmental disorder that manifests itself before the age of three years with abnormal functioning in all types of social interaction, communication, and restricted, repetitive behavior.
Atypical autism is a pervasive developmental disorder characterized by impaired social interaction and communication, repetitive or stereotyped behavior, and uneven mental development, often with mental retardation.
Atypical autism is also considered atypical childhood psychosis, a retardation in brain function with certain signs of autism. Often, children suffering from atypical autism are given a completely different diagnosis, in particular, schizophrenia. Experts confirm that diagnosis is difficult and quite complex. In most cases, parents consult with many doctors of various specializations, including a psychiatrist, a neurologist, and an otolaryngologist. Diagnosis is based on developmental history and monitoring of the child's development. Treatment consists of behavioral therapy and sometimes medication.
Atypical autism manifests itself in the first years of life. In most children, the cause is unknown, although signs suggest a genetic component. In some children, autism may be caused by an organic disorder.
Classification of autistic disorders:
- General disorders of psychological development.
- Childhood autism (onset between 0 and 3 years).
- Processual autism (onset before 3 years of age)
Atypical autism:
- atypical childhood psychosis (onset at 3-5 years); - moderate mental retardation with autistic features.
- Rett syndrome.
- Other disintegrative disorder of childhood (disintegrative psychosis, Heller's syndrome, childhood dementia, symbiotic psychosis).
- Hyperactive disorder associated with mental retardation and stereotypic movements.
- Asperger's syndrome.
The main symptoms of atypical autism:
- Communication skills are impaired, which may include, for example, an inability to maintain eye contact.
- There is no desire or difficulty in forming friendships.
- Difficulty increasing vocabulary or loss of previously acquired language skills.
- Difficulty communicating with others.
- Weak speech skills
- Inability to engage in role-playing games, lack of imagination.
- Literal perception of speech and misunderstanding of the various semantic shades of words.
- Difficulty understanding non-verbal language.
- Not understanding other people's emotions, reacting inappropriately, or appearing unemotional.
- Commitment to strict adherence to routine and routine lifestyle.
- Self-stimulating behavior such as flapping your arms or rocking back and forth.
- Strange games, for example, they can spend hours tossing an object or fixing something, such as a floor tile.
- Difficulty processing sensory information and reacting abnormally to unusual smells, sounds, tastes, sights, textures, or colors.
Children with atypical autism are characterized by increased sensitivity of the organs of vision, hearing, smell, and touch.
Autistic children may use sign language instead of verbal communication. Children with atypical autism have difficulty learning and understanding sign language.
The severity of symptoms of this form of mental disorder can vary greatly. One child has a fairly high level of development, the other has difficulty explaining himself in words and does not find a relationship with the people around him. If the pathology occurs in a mild form, then not only parents, but also experienced specialists may not notice deviations in children.
Atypical autism is a disease for which no effective means or methods have yet been invented. Today, there is only the possibility of symptomatic therapy aimed at eliminating one symptom after another. Some children respond best to individual therapy, while others benefit from group therapy.
Therapy should be used over a long period, even in cases where atypical autism is mild.
At the Tsaritsyno clinic, an experienced neurologist will select an individual treatment method for each child, depending on his needs.
| № | Service | Price |
| 1 | Initial consultation with a pediatric neurologist with examination | 1000 rub. |
| 2 | Repeated consultation with a pediatric neurologist | 800 rub. |
| 3 | Drawing up a treatment plan | from 500 rub. |
| 4 | Issuing certificates for swimming pools (camps, kindergartens, etc.) | from 600 rub. |
Medical center in Maryino: Perervinsky blvd., 21.korp.1, telephones, (495) 658-99-08
Clinic in Tsaritsyno (Maryino branch) : Biryulevskaya st. 56, building 2. telephones; (499) 218-24-98
The causes of autism are considered through the prism of different theories
Biological theory
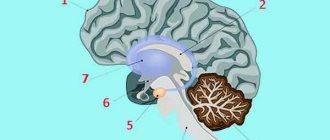
In this theory, the cause of autism is brain damage. A number of studies have shown that the brain of children with ASD has a number of structural and functional features.
Genetic theory of autism
This theory suggests that autism can occur with a fragile X chromosome, as well as with a high degree of gene mutation or gene polymorphism.
The theory of post-vaccination emergence of autism
This theory does not have much scientific evidence. Presumably, the development of autism is preceded by mercury intoxication. This hypothesis is confirmed only by the observations of parents, who trace a connection between vaccination and the manifestation of autistic characteristics of the child’s behavior.
Theory of metabolic disorders
The appearance of active behavioral traits is observed with phenylketonuria, mucopolysaccharidosis, and histedemia.
Opioid theory of autism
In this case, the appearance of autism is preceded by the ingestion of opioids, which place a huge burden on the human nervous system.
Autistic manifestations
As a rule, autism begins at a very early age. In this case, the child experiences:
- detachment from the outside world;
- desire for frequent self-isolation;
- decreased or increased response to sensory stimuli;
- difficulties in interpersonal relationships;
- difficult communication;
- monotony of actions.
In addition, an inability to think abstractly, an inability to concentrate, and problems with executive functions are recorded. But the same thing is inherent in some forms of schizophrenia, that is, these signs are not what distinguishes autism from schizophrenic disorder.
The symptoms of this disease may have different combinations in different cases. According to this, different types of autism are classified. The classification is rather vague, and its boundaries are very arbitrary. Autism was identified as a separate disease relatively recently. Many issues of diagnosis and treatment of this disease are still under discussion.
Interestingly, autism is 5 times more common in boys than in girls. The exact reasons for this have not been established, but there are certain theories. According to one of them, the female body contains a protective genome, which in most cases prevents the development of this pathology. According to another hypothesis, girls simply have better developed communication skills, so mild forms of autism often go unnoticed in them.
Symptoms of autism can be divided into three groups
Violation in the sphere of social interaction:
- lack of interest in other people
- lack of desire to participate in any activity
- low level of interest
- lack of copying skill as a way to inherit the behavior of significant adults
- the child may not notice the absence or presence of parents
- lack of response when addressed by name
- lack of desire and interest in any games based on interaction
- showing resistance when hugging
- communication disorders
- avoiding eye-to-eye contact
- echolalia - automatic repetition of any words without addressing anyone
- may have a rich vocabulary, but do not use it when communicating and communicating
Communication impairment:
- autism is characterized by stereotypical and limited behavior and reactions
- monotony of games and interests
- the presence of obsessive movements
“The only predictable feature of autism is unpredictability; the only consistent feature is inconsistency.”
Manifestation of violations of actions:
- prolonged viewing of an object in space
- swaying in place, running in a circle, spinning around its axis
- lack of plot in interaction games
- desire to eat inedible
- tiptoeing
- impaired fine motor skills, difficulty holding objects
- increased salivation due to severe muscle hypertonicity
- rejection of the new and unfamiliar
- aversion to touching, hugging
- self-harm
- no sense of danger
- sleep disturbance
- peculiarities of eating behavior, strong attachment to a certain set of foods
Autism
The concept of “autism,” according to many psychiatrists, despite repeated attempts to define the “autistic spectrum of symptoms,” remains quite vague.
It appears that autism is a complex syndrome, possibly integrating a number of manifestations of schizophrenia, including cognitive and emotional impairments, as well as behavioral changes.
According to E. Bleuler (1911), autistic thinking is divorced from reality, judgments are formed in accordance not with logic and real facts, but with the affective needs of the patient.
According to G. Benedetti (1983), autism and the primary symptoms of splitting are two sides of the same disease process. In this case, autism is interpreted by the author as a protective-compensatory reaction to splitting.
Many researchers have emphasized that autism to some extent excludes empathy.
Patients become less accessible to natural external stimuli. The surrounding world, physical reality, attracts them to a much lesser extent than their own inner world, which, according to patients, is more interesting and deep.
Autism intensifies with delirium and oneiric clouding of consciousness.
Patients strive for isolation, become withdrawn, silent, have formal contact with others, showing an indifferent attitude even towards close people. “They... go into the quiet, undisturbed world of their ghosts” (Schüle G., 1988).
Passivity is a fairly common companion to autism. The patient may not leave the house for a long time and lie in bed for a long time. Here there is a violation of social communications, a narrowing of the circle of communication and, most importantly, the need for it.
Differential diagnosis of autism symptoms in schizotypal, schizoaffective disorders and paranoid schizophrenia is presented in Table 13.
Autism syndrome includes signs of altered thinking: increased passive imagination and impaired logical reasoning. It is difficult for a patient with schizophrenia with distinct symptoms of autism to put himself in the shoes of another person, to recognize his feelings, to understand what the latter means, what meaning he puts into his words and what his intentions are.
Studies have shown that a person with schizophrenia, no matter how developed his intelligence, has difficulty understanding incorrect statements and deception.
In autism, certain intersections can be traced with the difficulty of understanding oneself, insufficient autobiographical memory, and impaired reasoning ability.
Table 13. Differential diagnosis of autism symptoms in schizotypal, schizoaffective disorders and paranoid schizophrenia
| Schizophrenia spectrum disorders | Schizotypal disorders | Schizoaffective disorders | Schizophrenia |
| Behavior | Changes in external behavior, its stereotyping | Passive submission | Ambivalent behavior |
| Social communications | Changes in social communications, isolation, unsociability, loss of interest in public life | Narrowing the circle of interests | Social isolation, isolation |
| Thinking | Violation of the adequacy of the goals set, due to switching to the world of the desired imaginary reality | Decline in creativity | Reasoning, amorphous thinking. Various forms of autistic thinking: overvalued and delusional variants, delusional fantasizing |
| Personality Features | Introversion, decreased mental flexibility and personality plasticity, rigidity | Leveling individual properties of temperament | Apathy, abulia |
| Attitude to illness | Total anosognosia | Nosognosia (shift of the disease into the past, psychologization and somatization, recognition of individual signs of the disease | Partial anosognosia |
Supporters of Z. Freud interpreted autism and decreased activity as an unsuccessful attempt at pathological compensation, “a separation from the orientation to reality.” Thus, the biological genesis of a number of manifestations of schizophrenia was denied.
According to the information theory, especially popular in the 60-70s of the twentieth century, blocking information when the brain is unable to adequately process it contributes to the emergence of autism in schizophrenia (Nuller Yu.L., 2000).
In childhood, the first descriptions of autism belong to H. Asperger (“Autistic psychopathy in childhood,” 1944) and L. Kanner (“Nervous Child,” 1943). Interest in childhood autism increased significantly after the work of L. Wing (1981). The incidence of autism is 10 per 10,000 population, Asperger's syndrome - 2 per 10,000 population. Boys get sick more often than girls, in an approximate ratio, according to ICD-10 8:1. Differential diagnosis of autism and Asperger's syndrome due to some social neglect, communication impairment, limited interests, stereotypical behavior is usually carried out with such mental disorders as obsessive-compulsive, schizoid/schizotypal personality changes, social phobia and schizophrenia.
Treatment of autism in a child
Autism cannot be completely cured. But by selecting suitable psychological and pedagogical methods and appropriate drug treatment, we can achieve maximum socialization and rehabilitation of a child who has autistic behavioral traits. To improve the quality of life of a child with ASD and give him a chance for a full life in the future, an integrated approach to rehabilitation and socialization is needed, combining drug and non-drug therapy.
Therapy for children with ASD consists of two main components:
Non-medical psychotherapy
- Behavioral therapy is the basis for the socialization of a child with ASD. This type of therapy helps to correct behavioral characteristics, which subsequently leads to the development of communication skills.
- Training under the TEACCH program. The method consists of visually presenting everything that the child needs to master. Visual aids and pictures arouse persistent interest in a child with ASD, thereby promoting the development of cognitive activity.
- Speech therapy, speech classes, improve speech and communication skills. Often sessions with a speech therapist help improve verbal communication.
- Behavioral therapy helps to acquire self-care skills, social skills and help reduce symptoms of maladaptive behavior.
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is a wide range of techniques used to treat autism and many other behaviors. The method focuses on teaching individual tasks using the principle: stimulus, response and reward.
- The SCERTS model is an educational model for working with children with autism spectrum disorders. The abbreviation means emphasis on: SC, ER and TS. SC - social communication, development of functional communication and emotional expression. ER - Emotional Regulation - the development of well-regulated emotions and the ability to cope with stress. TS - Transactional Support - Implementing supports to help families, educators, and therapists respond to children's needs, adapt environments, and provide tools to enhance learning.
- Animal-assisted therapy. The use of animal therapy, especially canistherapy, provides positive dynamics in socialization and communication in ASD. By gaining knowledge about natural processes in the animal world in an accessible playful form, a child with ASD learns to independently observe, analyze, and generalize. Classes with a therapy dog help increase sociability and communication in children with autistic traits.
Thanks to the dog, the child begins to be interested in what is happening around him, he develops attention, memory and speech.
It is also noted that our little brothers force sedentary or simply inactive children to move. After a short interaction with a child with autism, you may notice that he first notices the dog and then his parents. Before this, he could not react at all to others. You can attend classes with professional therapy dogs by signing up for a canister therapy class at our center.
Drug therapy
This is a complex of drugs to improve brain function. Previously, we described in detail this type of treatment for autism spectrum disorders.
A secondary role in the treatment and rehabilitation of autism is given to drug therapy. This type of treatment is effective when used in combination with methods of pedagogical and psychological correction.
The main goal of drug treatment
– this is the elimination and neutralization of symptoms that reduce the effectiveness of pedagogical and psychological correction, such as aggression, stereotypes, motor disinhibition, self-aggression, negativism.
Also, some medications stimulate brain activity, thereby activating memory and thinking processes.
Groups of drugs used in the complex treatment of autism:
- Nootropic drugs. Medicines in this group are aimed at stimulating brain activity, activating memory and thinking processes, and increasing the resistance of the central nervous system to mental stress.
- Antidepressants. It is believed that sedative antidepressants may help improve contact with the child.
- Tranquilizers. Their use is indicated for severe fears and high levels of anxiety.
- Neuroleptics. This group of medications is used to correct such manifestations as aggression, auto-aggression, motor disinhibition, fears, anxiety, stereotypic motor agitation. Some help increase speech activity, improve the ability to communicate, and improve intellectual productivity.
IMPORTANT! The need for drug treatment and prescription of drugs is made strictly by the doctor after diagnosis. Remember that self-medication is dangerous!
Atypical autism with mental retardation
For people with autism spectrum disorder, assessing their mental development is difficult. Mental retardation is diagnosed by testing skills, knowledge, and skills by passing tests. A child with atypical autism is not always able to demonstrate his knowledge because he experiences difficulties with speech and communication.
An example of an error in diagnosing mental retardation in autism is Sonya Shatalova. The girl, who was considered a child with severe mental retardation, who still does not speak, has been writing wonderful poems since the age of 8, analyzing events, and is the author of deep aphorisms.
It often happens that the diagnosis of “mental retardation” is made earlier than autism spectrum disorders are identified. An interesting theory is that the number of autistic people in the modern world and in the last century is approximately equal. The difference lies in the principles of diagnosis. Previously, before the concept of “autism” appeared, patients were given schizophrenia, mental retardation, debility and other diagnoses associated with mental disorders, development and organic brain damage. The diagnosis of “childhood autism” 30 years ago sounded like “early childhood schizophrenia.”
DON'T BELIEVE MYTHS ABOUT AUTISM: BASIC MISCONCEPTIONS AND THEIR EXPOSURE
THIS IS NOT TRUE: AUTISM IS A DISEASE, AUTISTS SHOULD BE TREATED
Autism is not a disease in the conventional sense. Yes, this is a disorder, but it is based on an innate hypersensitivity to external stimuli, because of which a person experiences severe overload. It is more correct to say that an autistic person is NOT TREATED, but is corrected and taught to control overloads, cope with increased anxiety, and communicate to the people around him about his feelings and needs in an acceptable form; learn to cope with situations that are uncomfortable for them.
THIS IS NOT TRUE: ALL AUTISTS ARE ILLNESSED AND NOTHING CAN BE DONE ABOUT IT
Many autistics are very well-mannered and tactful, others are rude and straightforward - this may not be the fault of autism itself, but the lack of timely help (the child did not participate in special developmental programs). All people “suffer” from this. Autistic people's frequent mood swings and irritability are caused by sensory overload. This is why an autistic child must be taught to cope with these overloads.
THIS IS NOT TRUE: AUTISTIC CHILDREN ALWAYS HAVE DELAYS IN DEVELOPMENT
Autistic people, like all other people, can be geniuses or have a low level of intelligence. Certainly autism and mental retardation are not synonymous. The learning difficulties of autistic children are mistaken for developmental disabilities due to ignorance. The traditional curriculum is not suitable for them. Often, studying a subject on your own can be much more effective.
THIS IS NOT TRUE: AUTISTS DO NOT NEED COMMUNICATION WITH OTHER PEOPLE
They don't tend to be friendly with every passerby, that's true. Moreover, it is difficult for them to make contact with a person they do not like. In fact, everyone has the same attitude towards strangers and unlikable people, it’s just that autistic people don’t know how to put on “artificial masks” (smile when you don’t want to, give compliments just to gain trust, etc.).