A family that is expecting a new addition is very happy about the birth of a baby. Most often, in euphoria, mothers do not understand that a child is not only a legacy, happiness, but also a huge responsibility for the life of a little person.
Young parents face problems such as crying at night, rashes, and colic. And this is not the whole list. Often a family is concerned that the baby has problems with his eyes and they begin to water.
Causes of severe lacrimation in infants
Excessive tear production in children 1–2 years of age and older can be a sign of many diseases. Let's look at some of them.
Viruses and colds:
- conjunctivitis (as a consequence of ARVI or influenza),
- dacryocystitis or blepharitis,
- keratitis or scleritis,
- inflammation of the paranasal sinuses or nasal cavity.
Allergy
If a baby who has just been born has watery eyes, red eyes and sneezes, then these are manifestations of an allergy. These are negative reactions to food or to external irritants, such as animal hair, etc. In the first days of life, a child’s body may react negatively to irritants, since the immune system is still very weak.
In case of allergies, due to swelling of the mucous membrane, the outflow of tears is significantly reduced. Fluid stagnation occurs, bacteria accumulate, the white membrane of the eye turns red, and all this is accompanied by severe itching.
To get rid of allergies and alleviate the child’s condition, you need to eliminate the sources of the disease or change the formula. It is better for a nursing mother not to consume allergens, such as strawberries, apricots, etc. The specialist prescribes special antihistamines.
Foreign body
The cause of tearing in a baby may be that an eyelash, dirt, a speck of dust, or a speck has gotten into the canal. To remove any foreign body from the eye, you need:
- wash your hands first, or better yet, disinfect them with an antiseptic,
- very carefully grasp the eyelashes and pull the upper eyelid forward so that the tears themselves wash away the dirt,
- A special rinsing solution will also help,
- carefully examine the eyelid; specks most often end up there.
If you cannot remove it on your own, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Conjunctivitis
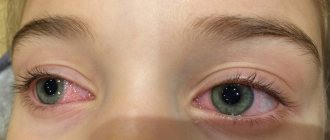
Tears can warn of the development of a disease such as conjunctivitis. In any form, the mucous membrane in children becomes inflamed, it becomes red and causes discomfort. Photophobia also appears and tears are produced. Sometimes a film or crust of pus may form on the eye. In this situation, the main thing is not to hesitate - as soon as you notice at least one symptom, immediately call your doctor.
Return to contents
Dacryocystitis
Young children often get sick, because in order for the immune system to resist infection, most of them need to be endured.
When babies have a cold, they often have dacryocystitis, which causes the eyes to fester and become watery. This happens because the infection gets to the mucous membranes of the mouth or eye, and not just into the respiratory tract. Then a defensive reaction of the body occurs, in which it seems to try to displace the virus through suppuration.
This inflammation of the tear ducts occurs in a very small percentage of babies at birth and also due to viral diseases. The doctor cleans the eye canal with dacryocystitis. According to parents' reviews, children show improvement immediately after the procedure.
Causes of increased tearfulness in childhood
If one eye is constantly watering in a baby, this happens for the following reasons:
- Blockage of the nasolacrimal duct;
- Pathological narrowness of the nasolacrimal duct;
- Pathologies of the structure and development of the organs of the visual and respiratory systems.
Tears are needed to moisturize and cleanse the eye. During intrauterine development, the lacrimal glands do not yet work, and the nasolacrimal duct is closed with a special film. After birth, this membrane must rupture to allow tear fluid to drain out. Sometimes this doesn't happen. Tears are released when blinking, but are not released into the nasal cavity. Some of the fluid accumulates under the lower eyelid, causing swelling. Some flows out, causing increased tearing.
This symptom should alert parents. They need to see an ophthalmologist to help them cope with the problem.
Sometimes there is no membrane in the nasolacrimal duct, but it is pathologically narrow. The liquid is only partially removed into the nasal passages, and its excess flows out again. The same thing happens with pathologies of the structure of the organs of the respiratory and visual systems. The earlier such deviations are identified, the easier it is to deal with them. In children of the first year of life, bone and cartilage tissue is still soft and pliable. If surgery on the nasolacrimal duct is required, it should be performed as early as possible. Minimally invasive probing usually helps solve the problem.
Why do the eyes of a baby fester?
Sometimes a pathology such as acidification of the organs of vision is observed. Factors for this phenomenon are usually:
- Dacryocystitis is an ophthalmological disease caused by blockage of the lacrimal canal and the formation of an infectious focus at the site of blockage. Symptoms: redness of the membrane, swelling of the eyelids, discharge of tears mixed with pus. If treatment is delayed, the disease affects the nerve endings and leads to vision pathologies.
- Congenital anomalies in the structure of the lacrimal canal. There are several types of pathology, but it is impossible to determine which one on your own. A pediatric ophthalmologist most often diagnoses: aplasia (no canal at all), diverticulum (protruding position of the lacrimal canal), fistula (external purulent fistula).
- Conjunctivitis. The disease can lead not only to increased tearfulness. If proper attention was not given to the eyes at an early stage, actively developing bacteria lead to decay in the area of the lacrimal canal. Grayish-yellow discharge appears from the eyes, especially abundant after sleep, purulent crusts form on the eyelids, the eyes stick together and are difficult to open. Sometimes photophobia develops.
- feeling of a foreign body in the eye;
- redness of the sclera;
- swelling;
- painful sensations;
- fear of bright light;
- increased lacrimation.
If a baby has watery eyes in one eye, then this phenomenon can be caused by any type of conjunctivitis. Often the following types of disease are diagnosed in babies 6 months and younger:
- autoimmune;
- allergic;
- viral;
- bacterial, provoked by gonococci, staphylococci and enterobacteria.
It happens that babies under one year old without crying, one or both eyes begin to water. This situation occurs when:
- colds;
- allergies;
- exposure to external factors (wind, sun, frost, etc.);
- dacryocystitis;
- conjunctivitis;
- eczema;
- pathologies of the lacrimal canals;
- pathology of lacrimal openings.
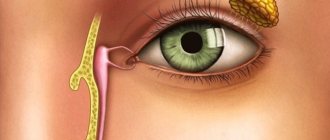
Reference. Through the nasolacrimal ducts, tears are delivered to the eyeball. The lacrimal sac is a structure that is covered by a muscle loop and serves to store tears.
Tearfulness occurs when pathogenic microorganisms and viruses enter the eyes. After their penetration, conjunctivitis develops.
Symptoms:
- swelling of the eyelid;
- swelling of the mucous membrane of the eye;
- redness of the conjunctiva and eyelids;
- photophobia;
- lacrimation;
- departments of mucous, purulent or mucopurulent nature.
Photo 1. Conjunctivitis in a newborn baby. A large amount of pus is released from the eyes, which prevents the visual organ from functioning normally.
Rinse the eyes with furatsilin solution for 10 days 2-3 times a day. To prepare the solution, take 100 ml of warm boiled water, crush the tablet, pour the powder into the water, and dissolve. Set aside for 1 hour. The solution can be used for 14 days. Before use, warm the liquid to 36-37 °C.
Important! Rub the eyes from the outer corner to the inner (towards the nose). This allows you to avoid transfer of infection to healthy areas of the organ of vision.
Infants under 12 months of age are instilled with a 10% solution of albucid. Treat both eyes with Tobrex ointment or erythromycin.
Attention! Inflammation quickly passes from the patient to the healthy visual organ. Both organs of vision should be treated to be on the safe side.
Allergy
Tearfulness can be the result of an allergic reaction to food, dust, fluff, wool, or synthetic clothing.
Symptoms:
- tearfulness;
- nasal congestion;
- itching in the organs of vision.
Treatment:
- Contact with the allergen must be avoided. Sometimes that's enough.
- If the allergy does not go away, the doctor prescribes antihistamines.
- To relieve symptoms, you can wipe your eyes with tampons soaked in chamomile infusion.
In this case, lacrimation causes inflammation of the lacrimal sac. The disease affects babies under 1 month of age.
Causes:
- Congenital anomalies in the development of the nasolacrimal duct: narrowing, elongation, tortuosity, closure of the canal with an embryonic film.
- Damage to the canal during medical procedures.
Symptoms:
- Tearing.
- Swelling in the area of the lacrimal sac.
- When you press on the area of swelling, a mucopurulent or purulent secretion is released.
- Redness of the conjunctiva, semilunar fold, skin over the lacrimal sac.
Photo 2. Dacryocystitis in an infant. There is swelling and redness in the area of the lacrimal canal, and there is purulent discharge.
Treatment:
- Massage.
- Treating the eyes with sterile cotton swabs soaked in chamomile infusion or strong tea.
- In severe cases, probing of the lacrimal canal is performed.
This dermatological disease is accompanied by skin inflammation and itching. Children most often have seborrheic or allergic eczema.
Symptoms:
- dry skin;
- peeling of the eyelids;
- “sourness” of the eyes;
- nervousness.
Treatment:
- eliminate allergens;
- use La-Cri and Elidel creams;
- if the eczema is microbial, a course of antibiotics is prescribed.
ARVI or acute respiratory infections in a child are often accompanied by lacrimation.
Symptoms:
- increased body temperature;
- headache;
- sneezing;
- runny nose;
- apathy;
- lacrimation.
The first thing you need to do is treat your cold. During illness, they take antipyretic, antiviral, and immunomodulatory drugs. To combat lacrimation, wash your eyes with a solution of strong tea or chamomile decoction.
It is characterized by dislocation (displacement), stenosis (narrowing) or fusion of the lacrimal openings. Types of pathologies of lacrimal openings:
- Eversion of the point. The point is not deepened into the lake of tears and does not come into contact with the tear. During surgical treatment, the lacrimal punctum is returned to its place. With a slight eversion of the inferior lacrimal punctum, operations used for its stenosis can give a positive result.
- Narrowing point. In some cases, lacrimation is a consequence of a narrowing of the point (its diameter is less than 0.1 mm). During surgery, the sphincter of the point or the point itself is dissected and a fragment of the inner wall of the tubule is removed.
- Clogged or absent lacrimal openings. Initially, the points are probed with a conical probe. If repeated probing does not help, they are dissected.
Anomalies in the development of the lacrimal ducts are treated only with the help of plastic surgery. But unfortunately, they do not always give a positive result.
A lacrimal sac fistula is a fistula (hole) through which tears and pus are constantly released. The tumor is cut off or burned out under local anesthesia.
Diverticulum is a pathology that causes souring of the eyes. Protrusion of the wall of the sac is most often observed in its lower part, at the junction with the nasolacrimal duct. Small protrusions of the lacrimal sac do not greatly impede tear flow. But mucous secretions can easily linger in them.
In the future, this leads to the development of dacryocystitis. Diverticula of the lacrimal sac are detected by radiography or dacryoscintigraphy. The operation is performed in the first year of life and no later than three years.
Reference. Before surgical intervention, the problem is solved mechanically: pressure is applied to the lacrimal sac to evacuate the contents of the sac from the diverticulum.
We invite you to read Chapter 15 Glaucoma - Clinical lectures on ophthalmology
Aplasia is the absence of the lacrimal gland. To eliminate the pathology, a conjunctival cavity taken directly from the salivary gland is transplanted. The secretion of the salivary gland is as close as possible in its physicochemical composition to the secretion of the lacrimal gland.
In fact, there are endless reasons for tearing eyes in newborns and infants. If you notice a similar manifestation in your child, be sure to pay attention to the presence of accompanying symptoms, which will greatly facilitate the diagnosis:
- If the baby's eyes are watery, and at the same time the temperature rises, a runny nose, difficulty breathing and a cough appears, then most likely it is a respiratory viral infection.
- If the eye not only waters, but also festeres, and also if the eyes turn sour after sleep, this may indicate conjunctivitis. It may also be accompanied by redness.
- Similar symptoms, by the way, are observed with dacryocystitis. But with this disease there is also the presence of swelling in the area of the inner corner of the eye - this is an inflamed lacrimal sac.
- If the eye is very red, watery, and the baby behaves capriciously and constantly screams, this may indicate the presence of a foreign body: an eyelash, lint, or soap getting into the eye leads to similar symptoms.
- Another cause of tearing and red eyes is allergies. Moreover, anything can be an allergen, from a product consumed by a nursing mother to household items.
Many other factors can provoke lacrimation in a baby, but in any case, parents should notice the violations in time and provide timely assistance.
Causes of discharge
White plaque on a person’s eyes is most often non-infectious in nature and has a liquid structure - it does not dry out into crusts, like purulent deposits. It is usually not accompanied by such unpleasant symptoms as redness of the conjunctiva, itching, burning, or swelling of the eyelids. But if such symptoms have been established, then it is necessary to seek advice from an ophthalmologist.
The following ailments lead to the accumulation of discharge from the eyes of an adult:
| Cause | Symptoms |
| Blepharitis | Leads to the appearance of foamy discharge with the formation of crusts and scales. Accompanied by itching, burning, swelling |
| Bacterial infection | This could be conjunctivitis, which produces thick, sticky mucus. Symptoms such as headache, cough, fever, body aches appear |
| Cold | Appears due to viruses and is accompanied by redness of the organ of vision, lacrimation and tear discharge |
| Dacryocystitis | This is an inflammation of the lacrimal sac, which is caused by congestion in the eye area. When pressed, a white or yellow substance flows out of them |
| Recurrent stye | This is an inflammation of the eyelid, which is accompanied by redness, swelling and purulent discharge. |
| Chalazion | It is an inflammation of the eyelid around its cartilage and meibomian gland. The reason is blockage of the gland exit channel and accumulation of secretory fluid |
| Sinusitis, sinusitis, otitis media | Such otolaryngological diseases affect the walls of the orbit, which become inflamed |
| Diabetes | With this disease, there is a high risk of developing glaucoma, barley, conjunctivitis, and blepharitis. These ailments are accompanied by white discharge |
| Allergy | Provokes the appearance of clear liquid discharge |
Discharge in a child
Even at 2 years old, a child cannot describe his complaints, so parents need to closely monitor his health. If he starts actively rubbing his eyes, this should alert you. There is usually swelling and redness before the discharge appears. The accumulation of formations with a yellow crust and inflamed eyelids indicates the addition of an infectious process.
Discharge from the eyes of a child may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- stretching mucus from the organs of vision,
- burning, stinging and pain in the eyes,
- swelling in the area of the bridge of the nose,
- blurred vision,
- lacrimation, eyelid hyperemia,
- increased sensitivity to bright light,
- irritability,
- frequent blinking,
- restless sleep,
- lack of appetite.
If yellow discharge accumulates in the corners of the child’s eyes, the eyelids are swollen and red, crusts have formed, and the pain does not stop, then he should be seen urgently by a doctor.
Mucus from the eyes of a newborn
In newborns, discharge from the eyes occurs due to improper development of the eyeball and tear ducts. Underdevelopment of the lacrimal sacs leads to stagnation of tear fluid. As a result, tears thicken and turn into mucus, which flows out in the form of a string.
Since the lacrimal canals and nasal ducts are interconnected, the infant should be treated by an ophthalmologist and otolaryngologist.
Therapy includes:
- light massage of the lacrimal sac,
- washing the eyes with furatsilin solution,
- the use of antibacterial drugs in the form of ointments or drops,
- in severe cases - rinsing the lacrimal canal using a special probe.
Diagnostics
In order to determine the disease that causes lacrimation, it is necessary to distinguish between the symptoms that appear. If a baby goes from warm to cold, for example, this can cause a defensive reaction in the form of tears. This fact is not a disease and does not require any treatment.
There are congenital abnormalities in the development of the baby’s nervous system, and this can cause tearing. If a newborn’s eyes are very watery, there are a variety of reasons:
- Lacrimal duct injuries
- Generic pathologies of the mucous membranes
- Abnormalities in the structure of the nose or simple runny nose
- Deviations in the development of lacrimal sacs
- Closing the nasolacrimal duct with embryonic films
| If your eyes are watery, you need to be examined by an ophthalmologist. The specialist immediately begins diagnosing the little patient’s eyes. |
Held:
- Examination of the external and internal eyelids, the condition of the lacrimal openings using biomicroscopy.
- A nasal and tubular sample is taken.
- Endoscopic examination of the nasal cavity.
- The lacrimal ducts are probed and washed.
- X-ray of lacrimal canals.
If there are complications, do a CT scan of the head. With its help, it is possible to identify malignant formations of the paranasal sinuses, pituitary gland, basal cell carcinoma or polyps that can provoke lacrimation.
There are also congenital pathologies of the lacrimal ducts. If signs of abnormalities are detected, it is better to correct them using surgical methods. The doctor will prescribe treatment and give certain recommendations.
Watery eyes in the morning: general symptoms
Note! If your eyes water in the morning, this is considered normal in the absence of the following additional symptoms:
- itching, burning and irritation;
- severe persistent redness of the conjunctiva;
- painful sensations.
This tearing is explained by the fact that at night the glands responsible for the production of tear fluid work poorly and the mucous membranes of the eyes lose a large amount of moisture during the night.
In the morning, when the glands are activated, there is an accelerated restoration of the balance of tear fluid on the surface of the eyeball , and its small excesses are released out in the form of tears.
Additionally, yawning stimulates morning tear production - during this process, the infraorbital muscles tense and change position, which compress the lacrimal sacs and tears are released.
Obviously, short-term morning tearing is normal and does not require intervention.
But if such a disorder does not go away for a long time and causes discomfort or pain, it may be due to pathological conditions.
But they already require accurate diagnosis and proper treatment.
Treatment methods
Careful hygiene of mother and child is imperative. You need to wash your baby's eyes several times a day with warm chamomile infusion and use antimicrobial drops.
A massage that should be shown to parents by a specialist helps a lot. It is needed for dacryocystitis to open and clean the tear duct.
Return to contents
Treatment of conjunctivitis
After the doctor confirms the diagnosis, he will prescribe the necessary medications or procedures. It could be:
- massage of the nasolacrimal duct area,
- treatment with chloramphenicol,
- washing the eyes with furatsilin, herbal decoctions.
Traditional Treatments
To alleviate the baby’s condition, you can use drops such as “Albucid”, “Sulfacyl-sodium”, “Ophthalmoferon”. They should be applied under the lower eyelid, after cleansing the eye of pus.
Some people prefer ointments such as tetracycline. Simple furatsilin also helps well. To do this, you need to dilute one tablet in a small amount of water and wipe your eyes with this solution.
| Before starting treatment, you should definitely consult a specialist. |
Folk remedies
Herbal formulations do an excellent job of relieving the symptoms of tearing in children. These are different decoctions that need to be used to wash the eyes, ointments and lotions. Chamomile or sage helps a lot. Calendula has long been used by our ancestors to wash the eyes of babies.
Decoction recipes
- Parsley should be wrapped in cheesecloth and placed in hot water for a few minutes. After cooling the broth, you need to blot sterile gauze and apply it to the baby’s eyes for 3-5 minutes.
- Having brewed strong tea, cool it and leave for 30 minutes. The compress is applied to the eyes for half an hour.
- Fresh rose hips, jasmine and clover need to be chopped and poured with boiling water for 20–30 minutes. The cake is lightly wrung out, wrapped in gauze and applied to the eye area.
- Chop burdock and calendula leaves, wrap in cloth and dip in boiling milk. After leaving for 10–15 minutes, squeeze out the compress and apply it to the baby’s eyes.
By washing with herbal decoctions several times a day, you can avoid viral infections and inflammation. It must be remembered that the decoctions must be sterile and carefully strained from suspensions and microscopic particles.
Nursing mothers can wipe their eyes with breast milk. But this method is only suitable for newborns; for three-month-old babies it is better to use other methods.
Return to contents
Massage of the lacrimal sac of the eye
Before the procedure, you need to prepare the child. Carefully remove all pus from the eyes. To do this, you need to wipe the eyes with a well-moistened disk in liquid (so that it drips) from the outer corner to the inner one.
During massage procedures, the child should lie on his back:
- gently squeeze the liquid out of the lacrimal sac,
- drip the furatsilin solution and remove the pus with a sterile swab,
- carry out massage movements.
To do this, you need to make jerking or vibrating movements with your fingers (from top to bottom), lightly pressing on the skin. You need to start from the inner corner of the eye. The massage procedure should consist of 10 pushing movements and one vibrating in the opposite direction (from bottom to top). Sliding movements should be performed quickly enough, 2 seconds each. for every pressure.
| Massage is done 5 to 10 times a day. If the ophthalmologist, after a re-examination, determines that the canal has opened, then the massage course can be gradually stopped. |
Probing
Due to poor-quality washing during treatment procedures, traumatic damage to the canals can occur, which often leads to their narrowing, change and subsequent overgrowth. If treatment does not produce results within several weeks, then you need to contact your doctor again, who may prescribe probing.
Probing is an operation that is performed under local anesthesia and almost always ends successfully.
Eye wash
Using cotton pads or gauze swabs, the child needs to apply lotions or rinses if the eye is watery and red, approximately every 2-3 hours on the first day of illness and three times a day in the subsequent week. You cannot rub; first, you should carefully remove the crust from the eyelid, and then moisten the eye from the outside to the corner, gradually applying a disc or tampon for 1-2 minutes. It is necessary to treat both eyes, even if the second one is not susceptible to infection, and use clean material for treatment each time.
Furacilin , as well as herbal infusions are used as antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory agents , the most effective of which are considered:
- clover (1 tablespoon of dried flowers per glass of boiling water, leave for at least half an hour and filter thoroughly);
- from plantain leaves (1 tablespoon pour boiling water and cool);
- from calendula and chamomile (2 tsp and a glass of boiling water, wait until it cools);
- from oak and celandine (helps against dacryocystitis in infants, a handful of mixed leaves in a glass of boiling water, let it brew for an hour and a half, filter and use).
Parents are usually cautioned against treating with tea leaves if the child has a watery eye, since it is difficult to correctly determine its concentration. In order not to harm the inflamed eye, it must be weakly concentrated, otherwise suppuration, itching and tearing will only intensify.
Dacryocystitis
In the inner corners of the eyes there are openings of the tear ducts, closed with a protective membrane until the baby is born. During childbirth, it breaks, opening the way for tears. If the openings in the baby are blocked, stagnation of tears occurs, which leads to dacryocystitis.
When infections of various etiologies occur, mucus forms in the eyes, and the newborn’s eye waters. The disease is accompanied by purulent discharge and redness of the white of the eye. The symptoms are similar to conjunctivitis, but a distinctive feature is the location of the lesion: with dacryocystitis, only one eye waters.
Treatment
The doctor will definitely prescribe treatment. As a rule, it consists of a massage of the lacrimal sac. The doctor himself will show you how to do it. The massage is performed with cleanly washed hands, and the nails should be cut short. Also, in addition to this, the specialist will note the importance of maintaining hygiene. At home, you can wipe your baby’s eyes with sterile cotton swabs moistened with clean boiled water or tea.
A newborn's eye is watery - how to treat it
Important! If you have dacryocystitis, you cannot use eye ointments on your own without an ophthalmologist’s prescription. Drops for dacryocystitis are useless.
Video: What to do if babies' eyes turn sour
If massage and hygiene do not help, the child may be prescribed canal probing. The procedure is not dangerous and is performed on an outpatient basis.
Decay of the eye in a child
Tips for caring for the eyes of young children
In the first days of life, the baby's eyes are more vulnerable than ever. Improper care of them can provoke changes in the structure of the eye or lead to disease. Therefore, for proper washing you will need cotton pads, boiled water at room temperature, paper or gauze handkerchiefs.
- Soak a cotton swab in water and squeeze out.
- Wipe your baby's eyes from the edge of the eye to the nose.
- Taking a new disk, repeat the procedure on the other eye.
- Remove any remaining water with a napkin.
It is recommended to carry out this procedure every morning, but if there is a need for this, then several times a day, after sleep.
We provide assistance if a newborn has a watery eye
How can a mother help her baby in this case? Alternatively, you can try massaging the tear ducts - they are located just below the protrusion in the inner corner of the eye . The massage puts pressure on the stagnant fluid and, as a result, this pressure should open the tubule and the tears can calmly come out. Actions must be performed regularly and very carefully, since a newborn baby is still very fragile and weak.
If massage of the tubules does not help, you should consult a doctor who will prescribe antibiotic drops or ointment.
During the first 6 months, tubular blockage may appear and go away again and again. As a last resort, if the opening of the lacrimal canaliculi does not occur due to massaging and local treatment, you should consult an ophthalmologist who will perform probing. The procedure does not take much time, can be performed under general anesthesia and involves the insertion of a thin wire probe into the tear ducts, which will open the ducts for the passage of tears.
In general, blockage of the tubules should not cause panic and fear, but if any alarming symptoms appear, it is best to consult a specialist , since the health of a recently born baby requires increased attention and it is better to play it safe and be fully confident that there is nothing wrong with the baby’s condition threatens.