What to do if there is swelling of the eyelids in an infant?
Everything that happens to the health of the baby causes concern among young parents. They do not know how dangerous certain changes in the child’s behavior and appearance are. Particular concern arises if a baby has swelling in one or two eyelids at once - what to do in this case? Find out why babies' eyes may swell.
In this article
Internal pathologies
Swelling is not always associated with physiological disorders or eye infections. The problem may indicate diseases of the endocrine, cardiovascular, digestive, and urinary systems.
If the red swelling and swelling is not inflammatory in nature, then both eyelids always become inflamed at once. The skin is not hyperthermic, there is no pain on palpation. Often the problem affects more than just the eyelids. The limbs also swell, and ascites forms.
Symptoms depend on the disease that caused the swelling. For example, if not only the eyelids swell, but also the fontanel of the infant, this is intracranial pressure.
Does your child often run to the toilet and complain of lower back pain? It is necessary to check the condition of the urinary system. When swelling of the eyelids is accompanied by rapid pulse and shortness of breath, this may indicate rheumatic inflammation of the myocardium.
Non-inflammatory edema requires special attention from parents. Timely examination allows you to make a correct diagnosis and solve the baby’s health problems in the shortest possible time.
Eyelids swell in infants: symptoms
Have you noticed that the child’s eye is swollen and the upper eyelid is red, and the baby himself is restless: does he cry a lot and does not sleep? In such a situation, consultation with a specialist is necessary. You should not try to relieve swelling on your own and wait for improvement within a few days. After all, a symptom such as swelling of the eyelids is a clear signal from the body about the presence of allergies, the development of an infection or serious systemic pathologies, or kidney problems. An experienced diagnostician, after a visual examination of a child whose eyelid is swollen, will prescribe an additional consultation with an ophthalmologist, allergist, etc. Only if the diagnosis is correct can the disease be dealt with quickly and its recurrence prevented.
Baby's eyelids swell - symptoms:
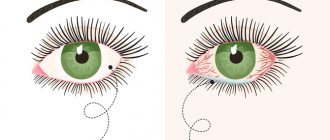
- the baby's eyelids are swollen - if the baby's two eyelids are swollen at once, and the eyes are red and itchy, it is possible that the baby is developing an allergy;
- swollen lower eyelids - the lower eyelids in children often swell due to prolonged crying, poor sleep, such swelling can be physiological and is present in many infants, but it is also observed with an allergic reaction, kidney disease, etc.;
- the newborn’s eyes are red, swollen and watery - if the swelling of the eyelids is bilateral and is accompanied by lacrimation and redness, this indicates the development of viral or bacterial conjunctivitis;
- only one eyelid swells, the lower one - severe swelling under one eye may indicate a problem such as dacryocystitis, obstruction of the tear duct;
- a child's eyelid is swollen and painful - this can be a symptom of stye, which causes itching and pain during the ripening period.
In many cases, swollen upper and lower eyelids in infants are the result of prolonged crying and an uncomfortable position during sleep. Such conditions are not dangerous and pass quickly. If you have been observing swelling in your child for several days, be sure to visit a doctor, since frequent swelling is not the norm.
Causes of the symptom
Inflammatory and non-inflammatory pathologies can cause the baby's upper eyelids to swell. Both upper eyelids or just one may become swollen. Sometimes nearby tissues swell: the bridge of the nose, cheeks. What are the reasons?
- Prolonged crying of a child. Typical for the younger age group.
- Sleep disorders: insufficient night sleep, uncomfortable pillow.
- Eyelids can become swollen due to eye strain from excessive use of gadgets, computer games, and watching TV.
- Diet violations: a large amount of salt in the child’s diet, excessive fluid intake.
- Foreign body, mechanical damage to the eyes (trauma, burns).
- Eyelids can become swollen due to allergies to medications, insect bites, food allergens, bacterial and worm toxins, or pollen (hay fever).
- Diseases of the organ of vision of an infectious nature: conjunctivitis, keratitis, blepharitis, dacryocystitis, barley, severe purulent diseases.
- Diseases of internal organs: kidneys, cardiovascular system, cancer. In somatic diseases, the eyelids will swell as a secondary symptom.
- Colds are a viral or bacterial infection (ARI, ARVI).
- Increased intraocular pressure.
- Violation of the rules for using contact lenses.
The eyelids will only become swollen and red due to crying, insufficient sleep, excess salt in food, or eye strain. There will be no other symptoms. If the upper eyelid is swollen, red, the baby’s eyes hurt, itch, and watery eyes appear, then the inflammation may be caused by infectious eye diseases or mechanical stress.
In case of an allergic reaction after contact with an allergen, parents see not only swollen red eyes, but also other manifestations of the body's hyperreactive response: itching, sneezing, hives.
With high IOP, the child complains of blurred vision, headache, a feeling of dilation of the eye, flashes before the eyes, and swollen eyes.
With acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections, swelling of the nasal mucosa, runny nose, sneezing, increased body temperature of the child are additionally noted; externally, the eyelids are swollen, the eyes are watery, and the sclera is reddened. Somatic diseases manifest themselves as symptoms of the underlying pathology.
Additionally, we invite you to read the article: swelling under the eye in a child.
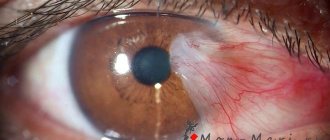
Conjunctivitis
Infection. Expressed in purulent discharge, profuse lacrimation, fever, redness.
Conjunctivitis is easy to treat , but if the process is started, the consequences can be serious, including blindness. Most likely, the doctor will advise regularly washing the child’s eye with a weak solution of furatsilin or potassium permanganate, as well as instilling sulfonamides and using antibiotic ointments.
If the films from the eyes are not removed, it may be diphtheria conjunctivitis - a serious disease. A child diagnosed with it is usually hospitalized urgently.
Conjunctivitis, accompanied by bloody discharge, is the result of infection with gonococcus in the birth canal. It can be treated effectively and quickly if measures are taken on time.
Why the lower or upper eyelid may swell in a baby - possible causes
A doctor must determine the exact cause of any ailment or unstable condition in an infant. If your baby's eyelids are swollen, you should first visit a pediatrician. If necessary, he will either prescribe an additional examination by a specialist - an ophthalmologist, an allergist, a cardiologist, or propose a correct treatment plan.
Why do the upper or lower eyelids of a baby swell - possible reasons:
- physiological swelling of the lower and upper eyelids - observed in newborns in the first weeks of life, if the swelling persists longer, consultation with a pediatrician and additional diagnostics are necessary;
- trauma, foreign body - the upper or lower eyelid may swell, since the child’s eyes are very sensitive, and even a small speck or eyelash that gets into the eye can cause swelling of the eyelids, in this case the process will be one-sided;
- conjunctivitis - newborn children are prone to conjunctivitis, since in the first months of life their eyes do not produce enough tears, and are therefore vulnerable to bacterial and viral infections;
- allergies - at risk are children with weak immunity, those on artificial nutrition, as well as those whose parents are allergic (with allergies, two eyes usually swell);
- dacryocystitis - if a baby’s lower eyelid is swollen and does not go away, it may be a blockage of the lacrimal canals, which leads to the appearance of edema; the disease can be congenital or acquired (often a one-sided process);
- barley - with barley, usually one eyelid swells - the upper or lower one, turns red and localized inflammation is visible on it; after the barley ripens, with adequate treatment, the swelling of the eyelids goes away.
If a child has a cold that lasts a long time and the eyelid is swollen, this may mean that the disease is complicated by inflammation of the paranasal sinuses. If your baby has been sick for several days and his upper or lower eyelids begin to swell, contact your pediatrician. It is possible that the child develops sinusitis, which, in the absence of adequate treatment, can become chronic and complicated by inflammation of the jaw, lower and upper eyelids, and orbit.
Causes of swelling under the eye in children
There are so many factors for the development of eyelid edema that we divided them into two conditional groups: physiological and pathological.
The first include:
- Swelling of the eyelids in newborns. During childbirth, the baby's head is subjected to enormous stress, which sometimes leads to temporary circulatory problems. This causes the development of swelling of the eyes, which usually goes away after a few months.
- Heredity. Find out if your child’s close relatives also had “puffy” eyelids in childhood. If this is the case, then it is a matter of genetic predisposition and there is nothing to worry about. If doubts do not leave parents alone, it is worth showing the child to a pediatrician and ophthalmologist.
- Eating over-salted food. Excess salt in a child’s diet leads to the development of edema, which indicates fluid retention in the body.
- Overwork. If a child sleeps too little or, on the contrary, too much, does homework in poor lighting, does not leave the computer and TV, does not spend enough time in the fresh air - all this will sooner or later affect his face. These are completely natural reasons that result in red circles and swelling under a child’s eye.
- Prolonged crying. If the child cried for a long time and hysterically, swelling under the eyes may be observed the next morning.
If the swelling goes away on its own on the same day or the next morning, then you can forget about the problem. But if such a story repeats itself every day, you should take care of the child’s proper nutrition and daily routine. If he sits for days on end, with his head buried in his phone or tablet, while crunching chips and washing it all down with sweet soda, then you have swollen eyes in the morning. No kidneys can cope with such loads.
If a child complains of pain in the eyes, swelling is accompanied by burning and redness, or has a fever, then it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor. Perhaps the swelling is caused by an inflammatory process, and delay can lead to serious complications with the child’s health.
Now let’s look at the most common pathological causes of swelling under a child’s eye on the website supermams.ru:
- Acute conjunctivitis. Often leads to redness and swelling of the lower and upper eyelids. Without treatment, the infection can spread to the healthy eye, which also becomes swollen. Swelling is most pronounced in the first days of the disease. If you move the edge of the eyelid, you will notice that the conjunctiva is hyperemic.
- Hay fever or hay fever. This is an allergic disease caused by plant pollen. One of the signs of a seasonal allergic reaction is conjunctivitis. The eyes become watery and swollen, the conjunctiva becomes bright red, and blood vessels are clearly visible. In this case, the child complains of a runny nose, itching and burning in the eye area.
- Allergy to insect bites. If the bite is on the cheek, forehead or nose, the swelling will quickly spread to nearby tissues, including the eyelids. More often, unilateral swelling is observed, but when bitten on the forehead, the swelling descends to both eyes. The bite site is noticeable, the skin in this area is hot to the touch and itchy.
- Quincke's edema. This is the most dangerous manifestation of an allergic reaction to any irritant. It develops rapidly, sometimes a few minutes are enough for the eyes to completely swell to such an extent that the child cannot open them. The skin color remains unchanged, fluid may involuntarily leak from the nose and eyes, and breathing is difficult.
- Barley (hordeolum). The process of accumulation of pus in the sebaceous gland or hair follicle can also cause swelling of the eyelids, this is especially noticeable in the internal form of the disease. Blepharitis and chalazion also begin with this symptom.
- Abscess of the century. When the inflammatory process is active in the tissues of the upper or lower eyelid, pus may accumulate. There is significant swelling and redness under the child’s eye or above it, depending on the location of the inflammation. The skin at the site of the abscess is hot and painful. Sometimes the eyes become so swollen that the child cannot open them.
- Phlegmon of the orbit. The inflammatory process in the retina of the eye with the accumulation of purulent masses is often a complication after other eye infections and wounds - conjunctivitis, stye, foreign body entry. Rhinosinusitis can also cause the development of this type of disease. One of the symptoms is swelling of the child's eyes.
- Adenoids. When the nasopharyngeal tonsils are enlarged, which is quite often observed in children, this leads to breathing problems. As a result, the face becomes swollen, and the child tries to compensate for the lack of oxygen by inhaling through the mouth.
- Kidney pathologies. Swelling in the morning without itching or burning, when the skin of the eyes remains unchanged, may indicate problems with the urinary system. Swelling is usually bilateral, but sometimes one eye may swell more on the side on which the child slept at night.
Among other things, swelling of the eyes in a child can be observed due to impaired metabolism and intracranial pressure. Stagnation of venous blood and lymph in the eye area becomes the culprit for the appearance of bags under them.
What to do
In most cases, an examination by a doctor is required. But parents cannot sit and do nothing while their child suffers. We will describe first aid for various causes of swelling.
For bites
Insect bites, in addition to swelling, cause increased blood pressure, heart rhythm disturbances and even suffocation. If the child is allergic, it is necessary to take an antihistamine. A special gel (“Fenistil”, “Psilo-balm”) can be applied to the site of swelling to relieve itching, swelling and redness.
Under no circumstances should you rub or scratch the bite area!
There are a lot of folk methods. We list the safe and effective ones.
- Apply half a cut potato to the area of swelling on your face.
- A compress of parsley, mint or bird cherry leaves will also help to quickly relieve swelling.
If a foreign body enters
Is your eye red, swollen and watery? First of all, try to provide first aid at home, before visiting a doctor. If the body is large and deep, then under no circumstances try to pull it out yourself.
Doctors recommend the following procedure:
- Make sure your child does not rub his eye.
- Keep your eye closed. Blinking will cause more severe injury.
- Apply an eye patch and see a doctor.
If the irritant is a small speck, you can try to get rid of it yourself.
- Sequentially move back the lower and upper eyelids and inspect the tissue underneath. Find the foreign object.
- Try to remove the visible foreign object with a clean cotton swab or a corner of a cotton handkerchief.
- Rinse your eye with clean cool water - the discomfort will go away.
- If after removal a pain appears and it does not go away, put moisturizing drops into the baby’s eye.
After all the procedures, the eye can begin to fester. This means that an infection has entered the eye and conjunctivitis has begun to develop.
Main causes of swelling and redness
Swollen eyes in a child? There can be many reasons for this phenomenon. An accurate diagnosis must be made by a doctor. But parents, knowing the source of the problem, are able to alleviate the baby’s condition, as well as provide first aid. In addition, the more you understand the essence of the problem, the easier it is to solve it.
All provoking factors are divided into several groups:
- Eye diseases (hordeolum, conjunctivitis, etc.)
- Injuries
- General malfunctions in the body (improper functioning of the kidneys, heart, etc.)
- Allergy
Below is a description of the most common problems that cause a swollen eye.
Swelling of the eyelid due to stye
Barley is an abscess and is always accompanied by pain. It can appear on both the upper and lower eyelids. In rare cases, two eyes are affected. The swelling can be so severe that the eye becomes completely swollen and difficult to open. All this is complemented by redness and lacrimation. The disease responds well to treatment, which should only be prescribed by an ophthalmologist.
If you don't seek help, complications arise. Barley can appear after a child is frozen or gets an infection with dirty hands. However, its presence always signals low immunity and a lack of vitamins.
And yet, barley cannot be infected. But the child should have a separate towel at this time.
Chalazion
When the eyelid is swollen and red, and a white dot appears on it, which over time develops into a capsule, the presence of a chalazion can be suspected. With this pathology, as a rule, there is no acute pain, but without treatment, the seal increases in size and has to be removed surgically. And inflammation appears due to blockage of the sebaceous glands.
Yes, they exist throughout the centuries too. Fat, designed to protect the eye and prevent drying, accumulates in the form of a bead-like growth. Under the influence of bacteria, inflammation begins, which gradually becomes chronic.
Treatment in this case should be comprehensive. These are anti-inflammatory drops and ointments, antihistamines and vitamins. The main way to help your baby is to take him to the doctor on time.
Return to contents
Conjunctivitis
Inflammation can occur in children and adults. In addition to the tumor, the following appear:
- Discharge from the eyes. Purulent, with a bacterial form. Whitish when viral. After sleep, it is impossible to open the eyelids without rinsing, because they seem to be glued together with secretions.
- Redness. Not only the eyelids are inflamed, but also the eyeballs.
- Fear of light and lacrimation.
- Cutting and burning.
This pathology can be caused by bacteria, viruses or an allergic reaction. Therapy includes rinses, eye ointments and drops. Also, depending on the form, it is advisable to include antiviral drugs and allergy medications. Of course, a doctor should prescribe medications, because treatment depends on the age of the child and the characteristics of the course of the disease.
Before going to a specialist, you can wipe your baby’s eyelids with furatsilin solution. Two tablets need to be crushed and diluted in 250 ml. warm water, soak a cotton pad in the solution and squeeze lightly, carefully remove the plaque. During the procedure, movements should go from the edge of the eye to the conjunctival sac.
After cleansing, drip your eyes with chloramphenicol. Conjunctivitis can be infected. After procedures, wash your hands with soap. It is also important to ensure that your child does not rub his eyes.
Allergic edema
Does your child have a swollen upper eyelid? The problem may be allergies. The eyes become watery and itchy, and the skin often peels off. One of the signs is the absence of pain. This condition is often accompanied by sneezing, coughing, itching and rashes all over the body.
Eyelids are swollen - what examinations are needed?
Despite the similarity of the symptoms of diseases in which the lower or upper eyelids swell, there are still significant differences that can be used to preliminarily assume the presence of one or another disease. During a visual examination of the child, doctors take into account how often the eyelids swell, whether the process affects both eyes or only one, whether the baby is breastfed or on artificial nutrition, and also examines the medical history, including that of the parents.
Swelling of the lower or upper eyelids - diagnosis:
- visual inspection;
- allergy tests;
- scraping from the eyelids for microbiological examination;
- blood and urine tests;
- consultation with an ophthalmologist, allergist.
What to do if a baby's upper eyelid is swollen? What is the reason for this condition? Among the unobvious reasons why a newborn's eyelids may swell are diseases of the stomach and intestines, diabetes mellitus, and weakened immunity. Therefore, parents should react as quickly as possible to any changes in the child’s health and seek help from specialized specialists. Remember that you cannot ignore a painful condition for a long time if a child’s eyes are swollen, trying to cure, for example, compresses, allergic swelling. Without specific treatment for allergies, there is a high threat to the child’s life.
Why do my eyes swell in the morning?
Puffiness of the eyes in the morning can cause:
- overwork of the child;
- sleep disturbance ;
- too much fluid intake;
- a large amount of salt in the diet;
- psycho-emotional stress ;
- prolonged interaction with gadgets (phone, tablet, computer) or watching TV;
- vitamin deficiency ( vitaminosis );
- decreased hemoglobin levels ( anemia ).
Morning swelling goes away on its own during the day , it does not cause any discomfort, therefore it does not require drug treatment; it is enough to eliminate its cause.
Allergic eye swelling in infants: symptoms and treatment
Allergies in newborns can manifest themselves in the form of swelling of the eyelids, rashes, and redness on the skin. Since the child is still too young, parents do not have information about intolerance to certain substances, nutritional components, or medications that can cause unwanted symptoms. Those at risk of having swollen eyes due to allergies include not only formula-fed children, but also those who are breastfed. Allergies to breast milk are not uncommon. Also among allergic agents: pollen, dust, washing powder, pet hair, creams, shampoos, soaps and other hygiene products.
Causes of symptoms
There are a number of reasons that cause swelling and redness of the eyelids in children of different ages. The most common are infectious diseases and mechanical damage.
Infectious diseases are one of the main and common causes of swelling of the eyelids in a child.
Experts identify several of the most likely causes of the disease.
- Conjunctivitis. The disease is caused by infection or mechanical damage, which results in an inflammatory process. Occurs at any age. Affects only the upper or lower eyelid. Children often develop reactive conjunctivitis. It is characterized by a rapid course, the formation of purulent contents that envelop the eyelid.
- Barley. The disease is associated with inflammation of the ciliary bulb. Characterized by slight swelling. A red spot appears at the site of the tumor, in which a purulent core gradually forms.
- Cellulitis is an inflammatory process affecting the eyelids. Accompanied by fever, pain in the inflamed area, redness of the sclera of the eyes.
- Insects. A mosquito or other insect bite on the eyebrow or eyelid leads to redness and swelling of the tissue. Most often the bite hits the corner of the eyebrow. Swelling from the tissues of the eyelid gradually spreads to the entire eye. A red lump forms at the site of the bite. The eye begins to itch, the mucous membrane turns red, and watery eyes appear.
- Mechanical damage. A strong blow to the eye area, dust and dirt entering the mucous membranes lead to profuse lacrimation and redness. In some cases, the eye may become swollen and inflamed.
- Allergic reaction. The allergy manifests itself in the form of redness of the eyes and itching. There is also swelling of the nasal mucosa, runny nose, and rash all over the body.
- Difficult birth. Newborns may experience swelling of the eyelids and eyes as a result of prolonged labor, accompanied by a long anhydrous period and hypoxia.
Swollen eyelids in a child may be the result of an acute allergic reaction.
In addition to the main causes, diseases of the internal organs can provoke redness and swelling of the eyes. These include:
- infectious diseases;
- high intracranial pressure;
- swelling of internal organs;
- heart disease;
- period of teething;
- prolonged crying.
Depending on the root cause, more or less pronounced symptoms of the disease are observed. A one-month-old baby reacts to inflammatory processes more acutely. His discomfort is expressed in the form of crying, refusal to eat, and short sleep.
Dermatitis
Such a common disease as eyelid dermatitis leads to very severe swelling in the visual area.
Causes of dermatitis:
- allergic reaction;
- fungus and virus;
- disruptions in bowel function;
- decreased immunity.
Atopic
Occurs against the background of an allergic reaction, helminthic infestations or metabolic disorders.
Symptoms:
- Exhausting itching .
- The skin has a pronounced red color.
- Numerous small bubbles with liquid appear on the affected area then they become covered with a crust; when it comes off, weeping wounds remain.
Allergic
Occurs when an allergen gets on the skin, mucous membranes or inside the body (pollen, animal hair, household chemicals, cosmetics), and can occur after an insect bite.
Symptoms:
- Unbearable severe itching .
- Redness and swelling appear instantly .
- No pain on palpation.
Seborrheic
Occurs when there is excessive colonization of a certain type of fungus that lives on human skin. It provokes disruptions in the functioning of the body of various types.
Symptoms:
- Yellow crusts and a lot of small white scales appear between the eyelashes .
- The edge of the eyelid becomes red.
- There is a feeling of dry eyes and “sand” in them.
- is observed .
- In severe cases , vision is impaired, the picture is perceived blurry, sometimes double.
Due to medications
Severe swelling of the eyelids due to an allergic reaction can be caused by medications :
- tablets, syrups, tinctures and so on;
- vaccinations, Mantoux test.
Symptoms:
- a sharp jump in body temperature;
- drop in blood pressure;
- severe redness of the area around the eyes;
- profuse lacrimation ;
- partial or complete closure of the organ of vision;
- swelling of the entire area around the eyes (both eyelids, puffiness of the cheeks and neck).
The main reason for an allergic reaction to vaccination is the increased sensitivity of the child’s body to the components of the vaccine.
Symptoms
In addition to swelling in one eye, a child may also experience additional symptoms:
- slight or excessive increase in body temperature;
- unpleasant sensation in the eye area: pain, itching, burning;
- suppuration on the skin or in the eye area;
- severe redness of the conjunctiva and cornea;
- increased production of tear fluid;
- severe crying;
- symptoms of illness: weakness, fatigue, lethargy, drowsiness, poor appetite;
- headache, dizziness;
- damage to the skin with the possibility of minor or significant bleeding;
- runny nose with clear or purulent discharge;
- mark on the skin from an insect bite;
- increased reaction of the eyes to bright light (photophobia);
- bruises around the eyes.
Based on the above symptoms, the doctor can offer a specific diagnosis, but it must be confirmed using laboratory and instrumental examination methods.
The baby's eyes are watery and the eyelids are swollen - what to do?
Young children often have swollen and watery eyes when conjunctivitis develops, and purulent discharge may also be present. This happens if a bacterial infection occurs due to infection or improper care of the newborn. What should you do if your baby’s eyelids are swollen and conjunctivitis begins? It is necessary to follow all stages of treatment prescribed by the doctor.
Treatment of conjunctivitis in newborns:
- cleansing the eyes of pus - if the eyes are swollen and there is pus, you need to use a warm antiseptic solution based on boiled water;
- antibacterial therapy - for microbial infections, eye drops with an antibiotic are prescribed; for infants, drugs with the least degree of toxicity are selected;
- antiviral and antimicrobial ointments - depending on the type of infectious agent, the drug is prescribed in the form of an ointment, which must be carefully placed behind the newborn’s eyelid.
To wash the eyes, you can also use decoctions of herbs that have an antiseptic effect, but first you need to make sure that the child is not allergic to one of the components of the herbal collection. Decoctions of herbs such as chamomile, calendula, and sage are best suited for cleansing the eyelids of pus.
Acute purulent conjunctivitis in children. Child's vision
This disease is very common among children. I can safely say that there is no child who has not suffered from conjunctivitis at least once, even with the most careful care.
Acute purulent conjunctivitis develops when a pyogenic infection enters the conjunctival cavity - most often with unwashed hands, less often with foreign bodies (specks, dust in windy weather, etc.). As a rule, both eyes are involved in the process, sometimes there may be a lag of 1-3 days.
The clinic is typical: lacrimation, suppuration, in the morning the eyelashes are stuck together with dried pus, the eyes are difficult to open after washing. The eyeballs turn red, and the color intensifies towards the fornix of the conjunctiva. Swelling and redness of the edges of the eyelids may occur. Complaints of a feeling of sand behind the eyelids (this is a very characteristic complaint for conjunctivitis), burning (“eyes are burning”), and sometimes itching.
In young children, the clinical picture is more dramatic: swelling may spread to the cheeks, body temperature may rise, and general lethargy, drowsiness, and moodiness may appear.
Acute purulent conjunctivitis can be cured in one or two days if everything is done correctly.
For treatment, the simplest means are enough: a weak pink solution of potassium permanganate (very light so that the color is barely noticeable), a 0.25% solution of chloramphenicol (ready-made drops are sold at any pharmacy) and tetracycline eye ointment (not to be confused with ointment for external use!) . You just need to know a few secrets:
- in the morning, clean your eyes with a swab soaked in a weak solution of manganese, then open your eyelids and rinse the conjunctival cavity generously with a stream of the same solution; it is convenient to do this using a rubber balloon (“bulb”) or a syringe without a needle;
- drip one drop of chloramphenicol;
- repeat instillation every hour.
If purulent discharge appears during the day, then...
- repeat washing with manganese solution;
- Before going to bed, put tetracycline ointment behind your eyelids.
I will explain the principles of treatment of acute purulent conjunctivitis:
- There is no point in instilling drops if there is purulent or mucous discharge in the conjunctival cavity. There are so many microbes in it that no drops are enough for treatment. Therefore, after waking up and during the day, as necessary, the conjunctival cavity should be washed. In addition to the manganese solution, you can use tea leaves, chamomile infusion, or simply boiled water for rinsing.
- There is no point in instilling two or more drops, since the capacity of the conjunctival sac is one drop. The rest goes to the cheek.
- With profuse lacrimation, and even more so suppuration, the medicine is washed away by discharge from the conjunctival cavity, and literally after 20 minutes it is no longer there. If drops are instilled 6-8 times a day (as doctors usually advise), then a selection of microbes resistant to chloramphenicol occurs, and conjunctivitis becomes chronic. Therefore, you need to drip every hour, and if you have the patience, then every half hour. Do not be afraid of an overdose, chloramphenicol is practically not absorbed from the conjunctival cavity and has only a local effect.
- When we sleep, thermostatic conditions are created behind closed eyelids, and bacteria “not killed” during the day begin to multiply. That is why, with chronic conjunctivitis, the only sign may be eyelashes sticking together in the morning. Of course, one could continue to instill frequent drops - this is a very effective measure, but both the patient and the caregiver need to get enough sleep. Therefore, before going to bed, you need to put tetracycline ointment behind your eyelids; its antibacterial effect will last until the morning. If the child is put to bed during the day, then apply the ointment during the day before bedtime. I don’t like to prescribe ointment while I’m awake: it blurs my vision, makes my eyelids sticky, and creates a feeling of discomfort. It is better to instill drops during the day.
After 1-2 days, when the symptoms of conjunctivitis subside, you can switch to instilling drops 6 times a day and be sure to apply ointment before bed. It is necessary to treat until the symptoms disappear and for another three days - otherwise the single surviving bacteria begin to multiply, and we get chronic conjunctivitis with bacteria that are particularly resistant to antibiotics.
And yet, I do not recommend using sodium sulfacyl (another name for albucid) in children, which is primarily recommended in pharmacies. And our doctors really like to prescribe it. It causes a very strong burning sensation when instilled. After the first drop, you will lose the child’s trust, and the treatment will turn into torture.
There is a 15% solution of albucid for children (30% for adults); it burns the same as a 30% solution, but its benefits are half as great. The solution of chloramphenicol is indifferent, that is, no solution. If the drops are heated to body temperature, children do not feel it at all. You don’t even need to wake up the children, but lift the sleeping child’s eyelid and drip a warm drop. The child won't wake up.
Treat it like this all day, and put ointment on it at night so you can get some sleep.
By the way, the temperature of the drops is checked this way: drop a drop on the back surface of the brush. If you feel neither heat nor cold (that is, you don’t feel a drop at all), then you can give it to your child.
In case of acute purulent conjunctivitis, you should never cover your eye with a bandage, otherwise pus will accumulate behind the eyelids, and this can damage the cornea of the eye.
Allow the discharge to flow out freely.
Finally, the most important thing: the patient must have a separate towel, a separate pillow, a separate handkerchief, etc., so as not to infect others.
In my opinion, Albucid is already a thing of the past, I don’t even know why it is prescribed now, you can’t give it to yourself, much less to a child. The doctor prescribed me good drops, I think they are called floxal, on the second day there was less pus in the eyes, and it is allowed for my children from birth. But it’s better, of course, to consult a doctor.
2015-07-0303.07.2015 06:25:21, Tatyana Pravikova
Tobrex helps well. The last time they didn’t help us, the ophthalmologist prescribed Signicef. The child was 10 months old... Levomycytin doesn’t help us at all... and tetracycline for the eyes at night... everything is written correctly. But it’s such a war with the eyes every day...
2019-04-0505.04.2019 15:49:04, Mother of three
It’s better if the doctor prescribes it anyway, it will be more reliable. I dripped okomistine, antiseptic drops. The inflammation is quickly relieved and there is no burning sensation when you drip)))
2015-03-1414.03.2015 13:37:59, MilenaR
Thank you very much for the advice, useful information! But as for the drops, it seems to me that there are more effective ones than chloramphenicol...
2015-03-1212.03.2015 23:26:59, MilenaR
Instead of Levomycitin, I drip Okomistin, it is not so hot and helps faster, but otherwise I treat it the same way)
2015-12-2424.12.2015 17:22:09, Akigis
Which ones specifically? Otherwise, the pharmacy only advised me to use Albucid, but I know how they burn and didn’t take it...
2015-03-1313.03.2015 20:12:05, Kopina Valentina
There are 6 reviews in total Read all reviews.
Source: https://www.7ya.ru/article/Ostryj-gnojnyj-konjyunktivit/
Causes of swelling in one eye
If only one eye is swollen, this may cause the following reasons:
- insect bite followed by an allergic reaction in a child;
- seasonal and periodic allergies to plant blooms, animal hair, bird feathers, house dust, food;
- bruises, cuts, abrasions on the skin around the eyes;
- development of an infectious inflammatory process on the eyelids, including blepharoconjunctivitis;
- viral diseases in which the organ of vision is involved in the pathological process, for example, influenza, parainfluenza, adenovirus, herpes;
- the formation of a wound on the skin around the eyes, followed by infection and suppuration;
- colds;
- entry of a foreign body under the eyelids with subsequent tissue infection;
- increased pressure inside the skull;
- pathologies of the renal system with the formation of edema;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- prolonged crying until hysteria occurs;
- state of teething.
Some of these causes can be determined visually by your doctor; others will require diagnostic tests.
Other reasons
Itching, redness and peeling of the skin around the eyes can be caused by somatic diseases, both congenital and acquired. The main reason for their occurrence is nervous shock, against which serious illnesses develop, for example, glaucoma, cataracts, diabetes, hormonal imbalance, and pathologies affecting internal organs.
Genetic individual trait
Congenital skin pathologies (for example, pigment spots) can be localized in close proximity to the organs of vision, causing the visual sensation that the eyelids are red and constantly swollen.
Worm infections
Redness and peeling of the skin around the eyes provoke helminthic infestations. They suppress the body's immune system, which leads to inflammation of the skin of the eyelids and the development of blepharitis.
Age characteristics of children 1-3 years old
Redness and swelling around the eyes in newborns and children under 3 years of age indicates that an inflammatory process of an infectious nature is developing in the body. It may be accompanied by intoxication of internal organs and systems.
In addition, redness can be caused by:
- changes in the circulatory and lymphatic system;
- tendency to colds;
- illnesses and teething;
- genetic predisposition;
- ailments affecting the liver, kidneys, heart;
- anemia.
Since the cause of alarming symptoms can be hidden in any factor, only a doctor can tell you what to do to eliminate it.
The lower eyelids of a newborn baby are swollen due to dacryocystitis - what to do?
Is your baby's lower eyelid swollen? This could be dacryocystitis. Blockage of the tear duct in infants can be congenital or acquired. In the fetus in the womb, the tear ducts are closed and protect the respiratory system from the ingress of amniotic fluid. Normally, at the birth of a child, the tear duct should open - the baby cries, and under pressure the film breaks and the ducts open. If this does not happen, the newborn may develop dacryocystitis due to tear stagnation - the lower eyelid will swell. Secondary dacryocystitis, in which the lower eyelid swells, develops in older children against the background of prolonged illness or injury.
If you notice that your child’s lower eyelid or eyelid above the eye is very red and swollen, contact your pediatrician - the doctor will prescribe a course of specialized treatment. Without treatment, swelling does not go away; the disease is complicated by purulent infectious conjunctivitis, which can affect the baby’s visual acuity. Often with dacryocystitis, a fistula of the lacrimal sac appears. Dacryocystitis is diagnosed by an ophthalmologist by performing a tear duct patency test.
How to treat dacryocystitis, in which the eyelid swells:
- regular hygiene of the eyelids, cleansing the eyes of pus and discharge - if the eyelid swells severely and there is discharge, antiseptic solutions are used;
- antibacterial drops and ointments - drugs are prescribed by a doctor based on the results of cultures and the sown microflora;
- massage - using movements with light pressure, it is necessary to massage the area from the corner of the eye and along the nasal septum, repeating the exercise up to 10 times, two to three times a day.
Parents of children whose lower or upper eyelids swell should be extremely careful and responsible, since the symptoms of this disease are often confused with conjunctivitis and they try to treat it with compresses, eye drops, etc. In the case of dacryocystitis, even after antibacterial therapy, the improvement will be insignificant, since, in addition to medications, massages are also necessary to free the lacrimal canal. If conservative methods are ineffective and the eyes are still swollen, surgery is prescribed - puncture of the lacrimal canal.
Conjunctivitis in children
Conjunctivitis in a child can occur in isolation; in some cases the ocular symptoms are preceded by catarrhal symptoms. With conjunctivitis of any etiology, children develop a symptom complex, including swelling of the eyelids, conjunctival hyperemia, increased lacrimation, fear of light, foreign body sensation or pain in the eyes, blepharospasm.
In children, an eye infection can be suspected even before clinically significant manifestations appear due to restless behavior, frequent crying, and constant attempts to rub their eyes with their fists. With isolated conjunctivitis in children, the body temperature is usually normal or subfebrile; in case of general infection it can rise to high values.
Due to the thickening of the conjunctiva and its injection by blood vessels during the disease, visual function is slightly reduced. This deterioration is temporary and reversible: with adequate treatment of conjunctivitis, vision is restored immediately after the children recover.
Bacterial conjunctivitis in children
With conjunctivitis of bacterial etiology, eye damage is bilateral, often sequential - first the infection manifests itself in one eye, and after 1-3 days the other eye is affected. A typical sign of bacterial conjunctivitis in children is mucopurulent or viscous purulent discharge from the conjunctival cavity, sticking of the eyelids, and drying of crusts on the eyelashes. The color of the conjunctival discharge can vary from light yellow to yellow-green.
The course of bacterial conjunctivitis in children can be complicated by blepharitis and keratoconjunctivitis. Deep keratitis and corneal ulcers develop rarely, mainly against the background of a general weakening of the body - hypovitaminosis, anemia, malnutrition, bronchoadenitis, etc.
Gonoblenorrhea of newborns develops 2-3 days after birth. Symptoms of conjunctivitis of gonorrheal etiology are characterized by dense swelling of the eyelids, bluish-purple coloration of the skin, infiltration and hyperemia of the conjunctiva, serous-hemorrhagic, and then profuse purulent discharge. The danger of gonococcal conjunctivitis in children lies in the high likelihood of developing purulent infiltrates and corneal ulcers that are prone to perforation. This can lead to the formation of a cataract, a sharp decrease in vision or blindness; when infection penetrates into the internal parts of the eye - endophthalmitis or panophthalmitis occurs.
Chlamydial conjunctivitis in children develops 5-10 days after birth. At older ages, infection can occur in closed reservoirs, and therefore outbreaks of the disease in children are often referred to as basin conjunctivitis. The clinical picture is characterized by hyperemia and infiltration of the mucous membrane of the eyelids, ptosis of the eyelids, the presence of abundant liquid purulent secretion in the conjunctival cavity, and hypertrophy of the papillae. In children, extraocular manifestations of infection are often possible: pharyngitis, otitis, pneumonia, vulvovaginitis.
Diphtheria conjunctivitis usually develops against the background of diphtheria of the pharynx, mainly in children under 4 years of age. It should be noted that currently, thanks to mandatory vaccination of children against diphtheria, isolated cases of infection are observed. Eye damage is characterized by painful swelling and hardening of the eyelids, which, when opened, release a cloudy serous-hemorrhagic secretion. Gray, difficult to remove films are visible on the surface of the conjunctiva; after their removal, the bleeding surface is exposed. Complications of diphtheria conjunctivitis in children may include infiltrates and ulcerations of the cornea, clouding of the cornea, perforation of the ulcer and death of the eye.
Viral conjunctivitis in children
Viral conjunctivitis in children usually accompanies the course of ARVI, and is therefore characterized by a temperature reaction and catarrhal symptoms. In this case, the involvement of the eyes in inflammation occurs sequentially. Viral conjunctivitis in children is characterized by copious, liquid, watery discharge from the conjunctival sac, giving the impression of constant lacrimation.
With herpetic conjunctivitis in children, rashes in the form of blisters may be found on the skin of the eyelids and conjunctiva; with measles conjunctivitis - a measles-like rash; with chickenpox - smallpox pustules, which, after opening, turn into scars. Sometimes viral conjunctivitis in children is complicated by the addition of a secondary bacterial infection, which is accompanied by the appearance of purulent discharge from the eyes.
Effective treatments
Treatment for puffy eyes should begin with eliminating the root cause.
Conservative
Conservative therapy is the use of medications that are prescribed for a particular disease. Treatment is often required with several groups of drugs aimed at eliminating swelling, relieving inflammation and strengthening the immune system.
IMPORTANT! The use of any medications must be agreed with a doctor.
- For infections, broad-spectrum antibiotics or antiviral drugs are prescribed in the form of tablets, drops or ointments. These can be Erythromycin and Tetracycline ointments, Sulfacyl sodium, Tobrex, Floxal.
- Adenoviral infection is treated in stages. First you need to get rid of the inflammation, then restore nasal breathing and start taking antiviral drugs. In this case, the child must stay at home and remain in bed. To rinse the nasal passage, Aquamaris, Saline solution and other saline compositions are prescribed. Popular drops include Isofra, Polydexa, Dioxidin, and Protargol. Sulfacyl sodium drops are instilled into the eyes.
- Allergic edema is treated with antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs for topical use (usually gels, ointments and creams with a soothing effect or hormonal ointments). The most well-known remedies for allergies are Zodak, Fenistil, Suprastin.
- Non-inflammatory edema is eliminated by normalizing sleep and rest patterns.
- In some cases (allergies, inflammation, ARVI), special nasal drops are prescribed: Isofra, Polydexa, Dioxidin. They relieve congestion, eliminate itching, discomfort, rhinitis, sneezing and inflammation.
- Eye injury involves careful cleansing of the eye (if a speck or eyelash has appeared in it) and the use of drops that restore the mucous membrane (Vitasik, Balarpan, Hyphenosis).
Cosmetic
Cosmetic methods for eliminating edema are most often used to treat adults. This includes various injections, cosmetic procedures and even plastic surgery - blepharoplasty.
Children are prescribed physiotherapeutic treatment methods:
- electrical stimulation;
- mesotherapy;
- massage (manual, roller, vacuum).
Massage to relieve swelling of the eyelids can also be done at home. To do this, parents need to use clean hands to massage the inflamed tissue around the eyes using low-intensity circular movements, followed by several tapping movements. For massage or after its completion, you can use decongestant masks, creams and ointments, taking into account the specifics of their use in childhood.
Folk remedies
After diagnosis, folk remedies are allowed to eliminate swelling, but only after consultation with a doctor. But it is important to understand that, firstly, alternative medicine eliminates the symptom itself - swelling, but does not act on the cause. Secondly, the use of folk recipes is advisable only in complex therapy with physiotherapy or drug therapy.
The most popular non-traditional remedies are:
- A mixture of parsley and milk (sour cream). To do this, you need to take a bunch of fresh parsley, chop it (preferably in a wooden mortar so that the greens release juice), mix with a small amount of milk or sour cream. The resulting mixture must be wrapped in a clean cloth or gauze and applied to the eyelids for 15-20 minutes.
- Parsley decoction . Parsley is famous for its decongestant properties, so a healthy decoction is prepared from it. A bunch of greens is chopped, poured with a liter of water and simmered over low heat for half an hour. The decoction is taken three times a day, 100 ml.
- Flaxseed . Flaxseed and its oil are famous for their antibacterial and diuretic effect. Taking it orally helps remove excess fluid and eliminate swelling. A decoction is prepared from flaxseed: 4 tablespoons of the raw material are poured into a liter of water, boiled for 15 minutes, filtered and taken half a glass three times a day. Flaxseed oil is taken ready-made, 1 tablespoon on an empty stomach, half an hour before breakfast.
- Chamomile. Chamomile is known for its anti-inflammatory properties, so an infusion is made from it and used for washing or lotions. A tablespoon of flowers is poured into 200 ml of boiling water, cooled, after which the infusion is used daily for evening washing or lotions are made: moisten a clean cloth, squeeze and apply to the eyelids for 15-20 minutes.
- Tea bags . The easiest and fastest way to relieve swelling. For the procedure, you need to use two tea bags, cool them, squeeze them lightly and apply to your eyes for 10-15 minutes.
- Cucumbers . If you have a fresh cucumber in the house, you need to cut off a couple of thin rounds and apply to your eyelids for 15-20 minutes.
After using folk remedies, you can use a soothing cream or ointment. Regular baby cream works well.
To achieve a lasting positive result, each folk remedy must be used for at least 20 days.
Treatment of pathology
Therapeutic measures depend on the identified pathological process. The specialist, based on the individual characteristics of the patient (weight, age) and the severity of the disease, can prescribe the following medications:
Antiallergic drugs
The following drugs are used:
- Visine (cost 370 rubles);
- Allergodil (costs 450 rubles)
- Ketotifen (cost from 80 rubles).
Visin Allergodil Ketotifen
In advanced cases, drugs containing hormones are prescribed:
- Dexapos (cost 70 rubles);
- Dexamethasone (costs 120 rubles);
- Maxitrol (price 560 rubles).
Dexapos Dexamethasone Maxitrol
Antiviral drugs
They strengthen the immune system, eliminate infection, reduce the risk of complications and exacerbations, relieve pain, and speed up the healing process:
- Oftalmoferon (cost 270 rubles);
- Oftan Idu (cost from 90 rubles);
- Poludan (costs from 95 rubles);
- Aktipol (costs from 270 rubles);
- Adgelon (cost from 650 rubles);
- Tobradex (price 446 rubles);
- Futsitalmic (costs 266 rubles);
- Okomistin (cost 170 rubles).
Antimicrobials
For infectious diseases, the use of antibacterial eye drops is indicated, among which the following are considered the most popular and effective:
- Tobrex (cost from 170 rubles);
- Tsifran (costs 187 rubles);
- Gentamicin (costs 95 rubles);
- Levomycetin . Can relieve red eyes in infants and adults. Inexpensive, accessible drug. Costs 60 rubles.
Torbex Cifran Gentamicin Levomycetin
Remedies against demodicosis
Dermatologists prescribe antibiotics for dermodicosis:
- Trichopolum (cost 83 rubles);
- Ornidazole (cost 94 rubles);
- Metronidazole (costs 160 rubles).
Ornidazole Trichopolum Metronidazole
Additionally, immunomodulators and sedatives are used.
Treatment for eye irritation
Treatment for redness caused by eye irritation is based on:
- using cold compresses and tea bags. They remove swelling, redness, and discomfort;
- washing eyes with rose water. 5 drops of the product are dissolved in a glass of warm water and the procedure is carried out in the morning and evening hours. Rinsing is done by instilling the prepared solution with a pipette, 3-5 drops each;
- using herbal infusions as compresses. They help remove dryness and redness if you steam a large spoonful of herbal raw materials in a glass of boiling water, leave for half an hour, strain, soak pieces of cloth in the prepared solution and apply to the eyelids for 5-7 minutes.
Traditional methods of treatment
When deciding how to remove painful redness and burning in the eyelid area using folk methods, it is necessary to exclude ophthalmological diseases, photos of which can be viewed on the Internet.
They help a lot:
- Parsley or dill lotions. Fresh herbs are finely chopped and wrapped in clean gauze pieces, and then applied to the eyes for 10 minutes.
- Chamomile decoction. Gauze is soaked in it and also applied to the eyelids.
- Baking soda can remove redness if you soak gauze in a weak soda solution and apply it to your eyelids.
- Fresh brewed black tea. A proven method that can help relieve redness, swelling and flaking around the eye area. To do this, pour boiling water over the tea leaves, soak cotton swabs in it and apply to problem areas for 10-15 minutes.
What to do if redness is caused by eye fatigue? Traditional healers and ophthalmologists recommend blinking more often when working at the computer, monitoring the air humidity in the room, doing eye exercises, enriching your diet with vitamins, and spending time in the fresh air more often.
The eyes are swollen, a child has stye - what to do?
The appearance of a small reddened bump on a child’s eyelid may indicate the development of a stye. Usually, the eyes swell and a boil appears in a child when his immunity is weakened, and also if the baby is overheated or frozen. Staphylococcal infection can also provoke the development of barley. If you notice that your child's upper or lower eyelid begins to swell and a stye appears, consult a doctor so that he can prescribe a suitable ointment that will soften the skin and speed up the ripening of the stye.
How to treat stye in a newborn:
- cleansing the surface of the eyelids from secretions - if the eyes are swollen and there is mucus and secretions, use a warm solution of furatsilin; cool liquids can be harmful, since cold provokes stagnation;
- warm compresses based on herbs with an anti-inflammatory effect (provided the child has no allergies) - for barley, decoctions of chamomile and dill seeds help well;
- antibacterial ointments are placed behind the lower eyelid - this way they are evenly distributed on both the upper and lower eyelids; the ointment is necessary to prevent bacterial infection;
- eye drops are prescribed if the eyes are swollen and conjunctivitis develops with stye.
What to do if the upper or lower eyelid swells and hurts? In the case of a child, visiting a doctor is mandatory, and adults should not ignore such dangerous conditions. It is better to seek advice in a timely manner. The choice of drugs for the treatment of barley in infants is small, so their selection should be carried out by a specialized specialist who will take into account the child’s age, his tendency to allergies and select the optimally suitable medications.
Eye swelling due to conjunctivitis in children
Swelling of the organ is a symptom of an inflammatory process of various etiologies and is an accumulation of fluid in the tissues of the eye. Manifests itself as an increase in size and change in the shape of the affected organ.
With conjunctivitis, as the name implies, the main place of localization of inflammation , and therefore the development of edema, will be a thin membrane covering the inner surface of the eyelids and the anterior surface of the sclera of the eyeball - the conjunctiva. Symptoms of inflammation can also affect the eyelids.
Signs of edema with conjunctivitis
Because the conjunctiva of the eye is a thin layer of tissue, the increase in size of the organ that is typical for edema is difficult to track.
A sign of impaired circulation of fluid in it will be a feeling of discomfort, interference in the eye , itching and dryness of its surface.
Swollen eyes can be identified by the fact that the upper or lower eyelid is swollen and pasty, but touching them remains painless .
The appearance of the eye will differ somewhat in allergic and bacterial conjunctivitis. In the first case, the surface of the mucous membrane will be dry and itchy; in the second, it may be covered with discharge, as if clouded with pus. If conjunctivitis is of allergic origin, the inflammation will be more pronounced, and if it is viral, it will be more painful.
Treatment methods for the upper eyelid if it is swollen
Methods of combating the manifestation of conjunctivitis largely depend on its nature : whether it is caused by pathogenic microorganisms, viruses, protozoa, foreign body entry, or is part of an allergic reaction of the body.
How to relieve swelling? The main methods for damage to the conjunctiva of the eye include: instillation of medications into the conjunctival sac, compresses and lotions, and rinsing.
Reference! Each of these methods has its own advantages and disadvantages, but relief, as a rule, comes with their combined use.
Instillation of medicines
The choice of medications in this case belongs to the doctor, being dependent on the etiology of conjunctivitis.
The general algorithm for administering medications by eye drops is as follows:
- Prepare cotton pads, drops prescribed by the doctor, warm boiled water, a mirror (if you plan to carry out the procedure yourself).
- Using a cotton pad moistened with water, remove discharge, if any, and clean the outer edge of the eyelids.
- Using your thumb and forefinger, pull back the edge of the lower eyelid and, using a pipette or dispenser, inject the required amount of medicine into the space between the lower eyelid and the front surface of the eyeball - the lower conjunctival sac.
- Release the eyelid and blink the treated eye several times , distributing the drops over the surface of the conjunctiva.
Gel introduction
The algorithm for introducing the gel into the conjunctival sac of the eye generally coincides with the procedure for instilling medications. The required amount of gel is applied to the mucous membrane of the lower eyelid using a dispenser on a tube. Then make circular eye movements several times for optimal distribution of the drug.
Compresses
Compresses increase local blood circulation and lymph outflow , which contributes to the resorption of swelling. When treating conjunctivitis, cold or warm compresses are used.
For allergic conjunctivitis, a cold compress . For this you need to prepare boiled water at room temperature.
It can be replaced by either strongly brewed black or green tea, or a decoction of medicinal herbs - chamomile, sage, calendula, but they can only be used knowing that there is no allergic reaction to these plants, otherwise the situation can greatly worsen.
Photo 1. Compresses on the eyes made from cotton pads soaked in tea or a decoction of medicinal herbs relieve swelling.
You will also need a clean cloth or gauze pad. Moisten the fabric folded several times with water or the prepared solution and squeeze lightly. Then apply it to the sore eye. Hold for about 4-5 minutes , then you can repeat the procedure, but not earlier than after a quarter of an hour.
Instead of a cold compress, you can successfully use ice cubes ; they are applied from the outer corner of the eye to the temple, from the lower eyelid down and to the side.
A warm compress involves using a heated solution to wet the tissue. Suitable for relieving swelling in bacterial conjunctivitis, increases blood circulation, thereby helping to relieve inflammation. The algorithm for using it in the main points coincides with the previous version, but keep it until it cools down .
Washing
Warm solutions are used to wash the eyes . To heat the liquid to the desired temperature, it is better to use the “water bath” principle, lowering the container with the medicinal solution into a larger vessel with hot water.
Before use, you should once again make sure that the liquid is not overheated .
For rinsing to relieve swelling of the eye, we recommend furatsilin solution, saline solution, strong brewed black tea and herbal decoctions with anti-inflammatory effects - chamomile, sage, calendula (previously carefully strained).
To carry out the procedure, you will need a small rubber bulb or a syringe without a needle or a pipette, and cotton pads . Before use, instruments must be treated with boiling water for disinfection (it is best to boil them), except for syringes from sterile packaging.
Tilt your head to the side so that the outer corner of the eye being washed is higher than the nose, pull back the lower eyelid and pour in the solution, making one or two passes . A cotton pad is needed to collect fluid flowing from the inner corner of the eye.
Medicines
Medicines used to relieve swelling in conjunctivitis are selected depending on the causes of inflammation.
Drops and gels containing interferon are suitable for anti-inflammatory therapy for the viral form. An example is Oftalferon . This drug contains, in addition to interferon, diphenhydramine and boric acid, due to which it has a calming and anti-inflammatory effect.
Photo 2. Oftalmoferon eye drops, 10 ml from.
It should be instilled in small portions ( 1-2 drops ) up to 8 times a day in the acute phase of the disease and up to 3 times to consolidate the effect. It has no other contraindications other than individual intolerance to the components.
Important! Application is possible for patients of any age. Like other drugs in this series, it is demanding on external conditions; the temperature should be 2-8°C .
Allergoferon is a gel with a main antihistamine and antiviral effect and an additional anti-edematous effect. In addition to interferon, it contains loratadine. Contraindicated for children , it has possible side effects, manifested as an allergic reaction - itching, sneezing, impaired sense of smell.
Drops with an antibacterial effect are effective in combating pathogenic microorganisms and also have an anti-edematous effect, relieving inflammation.
Albucid belongs to the group of sulfonamides and is a 20 or 30% solution . It has a main bacteriostatic effect. Can be used by both adults and children. This remedy is used up to 6 times a day, 1-2 drops in each eye.
Antihistamines can have local and systemic effects. They quickly and effectively relieve swelling due to allergic conjunctivitis.
Allergodil is suitable for patients over 4 years with an allergic origin of the disease. It is required to instill one drop into the eyes twice a day. Not recommended during breastfeeding and the first trimester of pregnancy.
Erius (syrup) is approved for use in patients older than one year. It has a systemic long-term effect, so it is taken once a day. The dose ranges from 1.25 ml for children 1 – 5 years old to 5 ml for adults.
Attention! Like other products in this group, it is not suitable for pregnant and lactating women.
The video explains how to treat conjunctivitis depending on the cause of the eye disease.
How and with what to relieve swelling by eliminating the cause
The combination of drug therapy and traditional methods of relieving swelling in the eyes will quickly alleviate the condition and restore beauty to the eyes. But the main means of combating swelling of the conjunctiva and eyelids is treatment of the disease itself.
Puffiness of the eyes is a common symptom that occurs with various eye ailments. It is also characteristic of conjunctivitis. It is not always possible to immediately determine the cause of swelling. In this regard, there is no need to rush to stop this symptom. It is necessary to identify the factor that provokes it, and then begin full treatment.
How to relieve swelling from the eyes due to conjunctivitis?
Usually the answers to the questions “how quickly can you remove swelling from the eyes?”, “what to do if your right or left eye is swollen?” are of interest to people who have not yet been to the doctor and do not know the cause of the symptom. Otherwise, the patient would know how to eliminate it.
Self-treatment without an accurate diagnosis can be dangerous. To better understand this, you should take a closer look at the causes of such a symptom as eye swelling, in what diseases it is observed and why swelling occurs with conjunctivitis.
Source: https://www.vam3d.com/otek-glaz-pri-konjunktivite-u-detej/
Diagnostics
After visiting an ophthalmologist, a long diagnostic process begins. If the cause lies in ophthalmological diseases, after a series of diagnostic procedures it will be possible to make a diagnosis.
In other cases, it will be necessary to visit other specialists, in particular an otolaryngologist, pediatrician, allergist, cardiologist and others.
Analyzes
To make a diagnosis, you will need to undergo a number of standard tests - a general blood test, stool analysis (to detect helminthic infestations) and urine.
Allergy tests are performed to rule out allergies.
Cytological analysis of scrapings allows one to establish sensitivity to antibiotics and identify the pathogen.
When diagnosing barley, the following laboratory methods are used:
- bacteriological smear analysis;
- glucose tolerance test;
- blood culture for sterility;
- Demodex test.
Strokes
Determining the cause of swelling of the upper eyelids in a child often begins with a smear. To do this, the doctor, using a sterile swab-probe or a platinum loop, carefully removes the secreted material from under the eyelid.
The most accurate result will be obtained if a smear is taken in the morning immediately after waking up.
Next, the biomaterial is placed on a glass slide, after which one or more of the following analyzes are performed:
- cytological (infectious or allergic nature of the disease);
- bacteriological (determination of pathogens);
- bacterioscopic (detection of the microbial composition of the smear: the presence of streptococci, staphylococci, Escherichia coli and diphtheria coli, chlamydia, gonococci and some fungi).
A conjunctival smear allows you to make an accurate diagnosis with high accuracy.
Prevention of eyelid swelling in children
Hand hygiene by a mother who constantly interacts with her baby significantly reduces the likelihood of developing a bacterial infection, which is what causes the baby’s eyes to swell. The better the care of the baby is organized, the optimal microclimate in the house is constantly maintained, the less the risk that the eyes will swell due to conjunctivitis.
How to avoid recurrence of eyelid swelling in infants:
- gently washing the child with warm boiled water, caring for the surface of the newborn’s eyelids;
- scheduled dry and wet cleaning of the room where the child is located;
- regular ventilation of the room, timely hygiene procedures;
- balanced diet, healthy sleep, massages;
- air humidification during the period of central heating operation - due to dry air, the mucous membranes of the eyes are irritated, they become vulnerable to various infections, and may swell;
- Walking in the fresh air strengthens the child’s immunity, which helps prevent allergies.
A baby's eyelids may swell and hurt due to improper diet, unbalanced nutrition of the mother, etc. Remember that swelling of the upper or lower eyelid is not the norm; they are often a symptom of dangerous pathologies: anemia, thyroid diseases, problems with internal organs. Therefore, try to get advice from a qualified specialist as quickly as possible.
Swelling of the eyelids in a baby
As a rule, bags under the eyes in infants occur due to conjunctivitis or stye. First, a red dot and swelling appear on the eyelid, and then an abscess forms. Sometimes this abscess goes away on its own, and sometimes it becomes chronic. Therefore, it is necessary to cure it at the first appearance of signs of barley. Under no circumstances should the abscess be squeezed out. If you have conjunctivitis, you should also not apply compresses to your eyes.
Usually, with barley, the eye is instilled with albucid and heated. Fluid will ooze from the eye and will need to be removed regularly. The eyes should be washed with a solution of furatsilin or manganese. Treatment lasts about a week.
Newborns (2-3 days old) sometimes have conjunctivitis caused by gonococci in the birth canal. Because of this infection, the child experiences copious discharge from the eyes and severe swelling in the eyes. If treatment is not started promptly, blindness may occur.
Bags under the eyes in infants can be caused by the following diseases:
- incompatibility with the mother's Rh factor, which can lead to hemolytic disease, anemia or jaundice;
- severe anemia;
- mucous swelling due to hypothyroidism - disorders of the thyroid gland; dangerous because it interferes with the mental and mental development of the child;
- a simple allergy to some foods that the mother eats, or to what is given as complementary foods;
- hydrocephalus, in which the intracranial pressure of the baby increases - the baby’s fontanelles swell, the baby often cries and worries;
- liver diseases;
- kidney disease - the child often goes to the toilet, blood is mixed in the urine, pain in the lumbar region, fever;
- heart disease, myocardial inflammation;
- viral diseases;
- diabetes;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia.
But swelling under the eyes is not always the result of some disease. This may simply be caused by crying for a long time or lack of sleep.
Possible complications
Therapy for a baby is not an easy undertaking, so it is extremely important to follow all the instructions and recommendations of a specialist. To prevent a child from suffocating at night from lack of oxygen, it is worth constantly monitoring his well-being. Therefore, it is vitally important to begin prompt treatment of the pathology, otherwise the following may occur:
- Restless behavior of the baby.
- Drug-induced rhinitis.
- Partial atrophy of the nasal mucous membranes.
- Hypoxia.
- Fatal outcome.
If you are very concerned about your baby’s condition, even if there are minor deviations in his health, you should immediately go to a medical facility and consult a pediatrician.
It might be useful to read:
- Composition of perindopril, instructions for use, at what pressure it is prescribed, contraindications;
- Anti-hair loss drug “rinfoltil” - reviews, features and composition Rinfoltil series for hair;
- Shampoo for hair loss Rinfoltil Espresso Enhanced formula with caffeine: price, reviews, analysis of the composition of Rinfoltil ampoules;
- Rinfoltil ampoules for women (10 ampoules) Rinfoltil capsules instructions for use;
- Allokin-Alpha - instructions for use, indications, release form, side effects, analogues and price Allokin alpha, storage conditions;
- Allokin alpha: instructions for use, indications and analogues Allokin indications for use;
- Preductal - instructions for use Preductal and Preductal MV - instructions for use;
- What is the difference between Finlepsin and Finlepsin Retard? ;
Answers from experts
Dj: I was lying with gestosis for 9 months. The swelling started already on the 8th, and all at once, after a long trip. We were admitted to the day hospital, then to pathology. I agree with Larisa, this is not only unpleasant, but also not good for the baby. Due to edema, the baby lacks oxygen, and hypoxia may begin... Try to control the fluid. . You should consume approximately 1.5-2 liters of liquid (count drinks, soups, vegetables and fruits too) and excrete about the same amount, maybe a little less. Try to stay on your feet as little as possible when you lie down - make your legs higher. When sitting, put something under your feet... Breathe more fresh air. After childbirth, swelling will not subside immediately. on the contrary, you may feel that they have become larger. This is all normal, it has something to do with the fact that you have suddenly lost weight and lost a large volume of fluid. . but my swelling subsided already on the third day after giving birth. and when I was discharged, I was actually surprised to see my own bones on my feet) ) Good luck to you and having a healthy baby)
Bee: My sister still has 1.5 months after giving birth. held on.
Svetlana Biryukova: Immediately after the birth we passed, but during pregnancy the doctor constantly put her on unloading.
Natalia Bondareva: I had the last 2 months of pregnancy, immediately after giving birth I started to melt before my eyes) ) In general, swelling is not good
Shrew: They were decent before giving birth (from 36 weeks), especially on their legs, and were already discharged from the hospital.
Sweetie: if there is swelling in the legs, then buy an elastic bandage, but about other aspects of the body, I don’t know how to help, but in general, swelling goes away within a week after giving birth
Elena Udintseva: I had swelling both with the first and with the second, I couldn’t even put on shoes, after giving birth everything subsided on the 3rd day, but you with such swelling should be admitted and treated earlier
Mila-Ya 39rus on RыXika: immediately on the same day and passed
Katerina: In 2 days. Only children are also born swollen; this goes away for them by 1 month.
Lesyona: It’s funny, but right after giving birth... I felt it in my slippers))))
Larisa: With gestosis, I was admitted to the pathologist twice. I didn’t notice any swelling in myself. I felt good. But she went to the hospital. I was very worried about the unborn baby. Therefore, I followed all the doctor’s recommendations. And when the child was 4 months old, he was taken away in an ambulance with an attack of pyelonephritis. The protein was off the charts. My kidneys have never bothered me before. Gestosis is serious. It is necessary to control the fluid consumed and excreted. There must be a balance. If the kidneys do not work well, then the body of the unborn child receives toxins that the kidneys did not remove from the expectant mother. Observe and consult a specialist.
juicy cherry: postpartum period is 2 months, so wait a little
Nikita and Natasha Aliseenko: maybe it’s not swelling but fat, how much did you gain during pregnancy, how much did you lose?
: Check your kidneys. Usually, swelling after childbirth begins to go away immediately and completely disappears after a week.
Gulzira Aliyeva: She’s probably gained weight))), during pregnancy you constantly want to eat
NV: just lose weight. it's not swelling.
Irina: Well, obviously not swelling.
Dream: Throw it off a little and the ring will fit. The swelling can't last that long
Domovicha: Only time, ideally, they say, how many months you wear it, the body will recover.
Curare: my little one is already 2 and 7 months old. I weigh 58 kg with a height of 170, and the ring still won’t fit))) ) There is a reason to go get a new one)
Irina Irina: my sister only got it after six months.
Gold-diamond: after giving birth, my fluid was pumped out with diuretics and everything came right away
: It doesn’t fit either.
Nina Apanchuk: lose weight. I didn't take off my rings during pregnancy)))
When does swelling in a newborn go down?
Published by admin on 03/31/2019
In many cases, cerebral edema in a newborn is a consequence of birth trauma. It is a secondary symptom complex of brain tissue damage. It is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in brain cells and intercellular space, as a result of which the brain increases in size. The child has increased intracranial pressure and impaired cerebral circulation. The outcome of the disease directly depends on the speed and effectiveness of the assistance provided. In addition to trauma during childbirth, other factors contribute to brain swelling.