Detailed description of the study
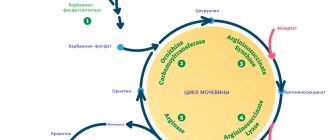
Protein is the main biochemical component of the human body, the basis of which is amino acids consisting of nitrogen, carbon, oxygen and hydrogen. Normally, protein metabolism is closely related to the liver, where their formation and breakdown, or deamination, occurs. The latter process is represented by a cascade of reactions, as a result of which urea is formed.
Urea, or carbamide, is the end product of protein metabolism, formed from ammonia, which is toxic to humans. Urea is the main nitrogen-containing substance in the body - it contains about 90% of the nitrogen from all broken down proteins. After formation in the liver, urea enters the blood, as well as other liquid media, and is excreted by the kidneys along with urine.
In the kidneys, urea, together with creatinine (the end product of metabolism in muscles), goes through the stages of filtration and reabsorption - reabsorption into the blood. Normally, most of the urea is excreted from the body through urine. The level of urea depends on the nature of the diet - the more protein food in the diet, the more it is formed and excreted. The reasons for the increase in urea can also include: a feverish state, strong physical exertion, the postoperative period, as well as taking hormonal drugs (thyroid hormones, adrenal glands) or increased activity of the hormones of these organs.
Also, the level of urea (in blood and urine) changes with kidney pathology, especially if the filtration process is disrupted, and liver - against the background of severe diseases in which liver cells cannot convert toxic ammonia into safe urea. In diseases that occur with renal failure, there is an increased level of urea in the blood and a decreased level in the urine. When the liver is damaged, urea decreases in both the blood and urine. Extreme renal failure, or uremia, is accompanied by a multiple increase in the level of urea in the blood and, if not properly treated, can lead to serious consequences.
The study of urea in urine is presented in two forms - in daily urine collected over 24 hours, and in a single portion. The choice of the form of analysis depends on the indications and, as a rule, remains with the attending physician due to the individual characteristics of each patient. It is most informative to take any analysis of urea in urine together with an analysis of urea in the blood, which allows for a more complete assessment of disorders of protein metabolism in the liver or the excretion of urea by the kidneys.
Causes of liver cirrhosis
It has been scientifically proven that regular consumption of alcohol over several years (10 or more) causes 60-70% of diagnosed cases of liver cirrhosis. Fibrosis originates from progressive alcoholic hepatosis. It is not without reason that those suffering from alcoholism are at risk of developing cirrhosis.
The prerequisites for the pathological process and the development of liver cirrhosis include:
- Chronic viral hepatitis C, B, D, G. More aggressive - type C. Virus carriage may not manifest itself for a long time, which is why in 97% it leads to massive death of hepatocytes.
- Autoimmune aggression provoked by a disorder in the immune system. Appears against the background of exposure to a virus or occurs independently.
- A parasitic infection that lasts for a considerable period of time.
- Long-term use of hepatotoxic drugs.
- The influence of toxic elements - work in hazardous industries, with reagents, chemicals.
- Development of bile duct obstruction.
- Chronic diseases of the heart and blood vessels cause venous stagnation and the formation of foci of necrosis.
The disease is asymptomatic and people are unaware of the existing threat. Progression is accelerated by a combination of several damaging factors. For example, alcohol addiction together with hepatitis C will quickly lead to a complicated course. Knowing the first signs and thinking about liver treatment is important. And yet, cirrhosis of the liver is not a death sentence and this disease is treatable and preventable.
References
- Clinical guidelines for chronic kidney disease, 2021. - 156 p.
- Guyton, A.K., J.E. Hall. Medical physiology / trans. from English; edited by IN AND. Kobrina. - M.: Logosphere, 2008. - 1296 p.
- Pérez, V., Barrera, G., Hirsch, S. et al. Efficacy of urine urea nitrogen measurement to assess the compliance with protein restricted diets. - Nutr Hosp., 2021. - Vol. 36(3). — P. 714-717.
- Chin, H., Kim, D., Park, J. et al. Effect of urine urea nitrogen and protein intake adjusted by using the estimated urine creatinine excretion rate on the antiproteinuric effect of angiotensin II type I receptor blockers. - Nutrition, 2015. - Vol. 31(11-12). - P. 1333-8.
Symptoms of liver cirrhosis
According to statistics, up to 80% of people who fall ill do not experience any significant changes in their health. A decrease in detoxification function provokes weakness, muscle pain and heaviness on the right side, under the lower rib after fried and fatty foods.
Undamaged cells are able to compensate for the work of dead cells up to a certain point. This condition lasts up to several years. Some patients experience dyspeptic disorders after drinking alcohol, even in small doses. Possible nausea, vomiting, pain in the epigastrium, flatulence, diarrhea. Once the symptoms are eliminated, everything stops.
Doctors distinguish three stages of liver cirrhosis with characteristic signs:
Compensated
- moderate pain in the right hypochondrium;
- feeling of bitterness in the mouth;
- disturbance of sleep and concentration;
- external phenomena - spider veins on the skin in the upper part of the body.
Subcompensated
- an increase in neurological symptoms - drowsiness, forgetfulness, handwriting changes, fingers trembling;
- skin manifestations - spider veins in the shoulder girdle area, itching, redness of the palms, pale nails, crimson tongue;
- baldness of the armpits and pubis;
- passing episodes of water retention, flatulence, diarrhea;
- increased bleeding;
- hormonal disorders - gynecomastia in men, menstrual irregularities in women.
Decompensated
- weight loss and loss of appetite;
- osteoporosis;
- muscle weakness;
- ascites that cannot be cured;
- darkening of urine and discoloration of feces;
- yellowing of the skin and sclera;
- increased body temperature;
- hepatic encephalopathy - dizziness, heaviness in the head, confusion, possible coma;
- the addition of infection and the occurrence of pneumonia, sepsis;
- varicose veins of the digestive tract.
External signs of liver cirrhosis - “stars, red palms, a bright shade of the tongue - are associated with an excess of female sex hormones. An imbalance that occurs during the breakdown of hormones is to blame for this. Therefore, they accumulate and expand the capillaries.
When palpated in the area of the right hypochondrium, in 30% of patients, an uneven, knotty surface of the deformed gland is revealed. In 70% it is enlarged, and in 50% an enlarged spleen is added. At the stage of decompensation, a decrease in size below normal is noted. This is due to the greater coverage of fibrosis.
There are active and inactive forms. The first is characterized by slow growth of connective fibers, which lasts up to several years. Sometimes - decades. The second is characterized by progression. In the presence of provoking factors - drinking alcohol, smoking, etc., it quickly passes into the decompensated phase. Concomitant HIV infection also contributes to rapid progression.
Special methods are used to detect dangerous violations.
Treatment of liver cirrhosis
The main condition for successful therapy is the elimination of the causes that led to the pathological condition. This includes giving up alcohol, stopping hepatotoxic drugs, compensating for heart failure, eliminating infection, and following a diet.
If you start the fight when there are no obvious manifestations, you can achieve lasting improvement. Tactics are selected by the doctor individually. But there are unifying principles.
Nutrition and daily routine
For the fastest recovery, you need to eat right. Diet No.5 is prescribed. It excludes fried, spicy and smoked foods. Fatty foods - meat, fish and animal fats in any form remain prohibited. Low-fat protein foods are limited. Industrial canned food, offal and meat, fish, and mushroom broths will have to be put aside. Dishes made from legumes and high in spices are not allowed.
The doctor will recommend a decoction of rose hips or dried fruits to normalize digestion and reduce swelling. Salt is also limited. You need to eat up to 6 times a day in small portions, preferably at the same time. The daily routine includes naps and walks in the fresh air. Physical activity is limited. Lifting heavy objects and walking long distances is avoided.
Medicines
Therapy is prescribed by a specialist. Self-medication will lead to delaying time and worsening the situation. The doctor will draw up a suitable rehabilitation program, taking into account the information received. The treatment complex includes:
- Hepatoprotectors restore damaged hepatocytes and protect against damage. Preparations of ursodeoxycholic acid, essential phospholipids, and milk thistle are mainly prescribed. They stimulate the secretion of bile and reduce intoxication. This improves well-being, eliminates cramps and nausea, and improves digestion.
- Diuretics reduce swelling and remove fluid accumulated inside the peritoneum. If there is no effect, then the contents are pumped out through a puncture in the abdominal wall.
- Antibiotics are prescribed to prevent peritonitis and bacterial infection.
- Beta blockers - Atenolol, Propranolol, reduce pressure in the portal vein.
- Containing lactuose - Duphalac, Normaze, Prelaxan. Neutralizes amino acids in the intestines that cause encephalopathy.
- Complexes of vitamins B, A, C, E, P, cocarboxylase and alpha-lipoic acid improve metabolism and exhibit an antioxidant effect.
- Reducing ammonia levels - Ornilatex, Hepa-Merz, zinc preparations.
- Lipotropic agents - Heptral, Lecithin, Betargin stimulate lipid metabolism, reduce “bad” cholesterol, stimulate lipid oxidation and prevent their deposition in the cell.
- Enzymes – Mezim, Pancreatin, Creon, Micrasim, etc.
- Plant-based soothing tablets – Novopassit, Persen, Valerian and Motherwort extract. Tinctures are contraindicated here, but water infusions of medicinal herbs will be beneficial. But, before use, you will need to consult a doctor.
The result depends on the psychological mood and the efforts made. It is necessary to strictly adhere to the recommendations and medication regimen, and monitor body weight daily.
Surgical
Surgery is performed for varicose veins of the esophagus. During the manipulation, vascular anastomoses are performed and the affected areas are removed.
If the results of MRI and CT scans reveal oncological tumors, they are removed surgically. But, intervention is allowed only at the compensation stage.
Transplantation
In advanced situations, with severe damage, a liver transplant is performed. Sometimes, this is the only chance to save the patient. Unfortunately, the operation does not always end successfully.
According to the Russian Transplantation Center, Research Institute of Emergency Medicine named after. Sklifosovsky, survival rate in the postoperative year is 91%, in the next year - up to 82%. The disadvantages of this method include a large list of contraindications and high cost.
Preparation for analysis
Blood test : blood from a vein must be taken on an empty stomach (do not eat, do not smoke), 8 to 14 hours must pass from the last meal. You can drink some clean water. On the eve of the analysis, you should not overexert yourself physically and mentally, or consume heavy food or alcohol.
Stool and urine tests : to collect biomaterial, disposable containers should be purchased at the pharmacy. On the eve of testing, you should not consume coloring foods (beets, carrots, etc.), activated carbon, laxatives and diuretics.
For urine analysis, morning urine is taken, that is, urine accumulated in the bladder during night sleep. After performing a thorough toilet of the external genitalia and releasing the first portion of urine into the toilet, you need to collect the middle portion in a container. It is advisable to collect feces in the morning or no later than 8 hours before the test.
Comprehensive diagnosis of liver diseases in MedikCity
- Diagnostics of liver function: Alanine aminotransferase;
- Aspartate aminotransferase;
- Bilirubin total;
- Bilirubin direct;
- Gamma-glutamyl transferase;
- Total protein + protein fractions;
- Alkaline phosphatase;
- Primary diagnosis of hepatitis;
- Alanine aminotransferase;
- Hepatitis A, B, C, D, E Virus (Hepatitis A, B, C, D, E Virus), qualitative determination of IgM class antibodies;
At the Medixity clinic, you can undergo a complete diagnosis of liver diseases and other examinations that interest you on a convenient day and time that suits you. Gastroenterologists are seen daily. Our professionalism and experience are at your service!