Role, function
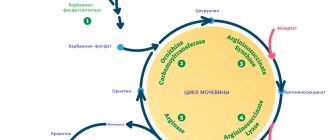
This is an organic substance formed in the liver after the breakdown and processing of ammonia. This process requires more than one step. As a final product, it passes from the liver into the bloodstream. It is excreted with waste products through the kidneys.
If it fails to break down ammonia, it begins to poison the body due to its toxicity.
Therefore, it is important that the content of this compound in serum is within normal limits.
Urea itself is not important, but the body needs it to safely eliminate nitrogen, which is its main function.
This relationship is an indicator indicating a certain imbalance in the functioning of all systems and organs, and indirectly characterizes the activity of the liver and kidneys.
What is urea
Urea is one of the products of protein metabolism. Otherwise, this compound is called urea. During gestation, the metabolism of proteins (proteins) is significantly accelerated, since these substances are necessary for the placenta and normal development of the embryo.
Urea is the end product of protein metabolism. This substance is excreted from the body mainly through the excretory organs. The accumulation of such breakdown products is harmful. Urea is an ammonia compound and is toxic to both the expectant mother and the fetus. This applies to increased levels of urea. However, a low level of urea in the blood during pregnancy also indicates pathology.
During the gestational period, the body contains a large amount of fluid. In addition, the excretory organs try to dispose of harmful substances as quickly as possible in order to protect the fetus. These factors lead to a decrease in blood urea during pregnancy. However, a drop in urea levels is not always due to natural causes. In some cases, this may be caused by various pathologies.
Norms
This substance is constantly created and eliminated from the body, so its correct content is important for humans.
Changes in levels can be used for monitoring
- performance of the renal and excretory systems;
- the presence or absence of liver dysfunction;
- condition of muscle tissue because it contains protein, which when broken down produces urea.
The normal value is almost independent of gender, but differs in adults and children:
- in newborns - 2.0-7.3 mmol/l;
- In children under 14 years of age - 1.4-6.4 mmol/l;
- from 15 years old - 2.5-7.3 mmol/l.
In infants, elevated levels are caused by excess fluid in the body. 7-10 days after birth, the urea level corresponds to the child norm.
Elevated levels are sometimes observed in older people (up to 8.3 mmol/L), but this is not considered abnormal because it is associated with age-related decline in kidney function.
Biochemical blood test indicators
Biochemical blood test is a comprehensive study consisting of many tests.
Total protein and albumin
Total protein shows the content of all types of proteins in the blood serum. Proteins are responsible for transporting nutrients, protecting the body from infections, serving as building materials for cells, tissues and organs, and maintaining hormonal balance in the female body.
During pregnancy, protein levels may decrease. This occurs due to the consumption of the substance to build fetal cells.
Pathological causes of protein reduction may be:
- liver and kidney diseases;
- malfunction of the thyroid gland;
- internal bleeding.
Protein concentration increases during inflammatory processes, systemic pathologies, autoimmune diseases, and acute intestinal infections.
Albumins are proteins with a small molecular weight. The concentration of these substances affects the osmotic pressure of the blood, which regulates water exchange between tissues and blood.
Albumin is not a mandatory test parameter. It is mainly determined in pregnant women in the following situations:
- when swelling occurs;
- with gestosis;
- with an increase in total protein levels.
Urea and creatinine
Urea and creatinine are chemical compounds that are formed as a result of the breakdown of proteins and are excreted from the body by the kidneys. The concentration of these substances allows us to evaluate the functioning of the urinary system. For example, with kidney dysfunction, protein metabolism products accumulate in the blood, causing intoxication of the body. High levels of urea and creatinine can cause pathologies dangerous for the pregnant woman and fetus.
During pregnancy, the risk of kidney disease increases significantly. This happens for the following reasons:
- Due to hormonal changes, immunity decreases and the body becomes susceptible to viruses and bacteria. As a result, the likelihood of developing pyelonephritis and other inflammatory kidney diseases increases;
- the enlarged uterus puts pressure on the ureters, which leads to stagnation of urine in the kidneys.
High urea and creatinine can be observed in pregnant women with urolithiasis, renal failure, diabetic nephropathy, and inflammation of the urinary tract.
In addition, the concentration of urea and creatinine makes it possible to monitor the condition of other organs. For example, low urea content is observed in liver pathologies.
Cholesterol
In human blood, cholesterol is contained in the form of complex compounds with special proteins. Depending on the density of complex compounds, cholesterol can be divided into several types:
- HDL is “good cholesterol”, which provides cell membranes with strength and elasticity, promotes the production of vitamin D in the body, and takes part in the synthesis of sex and steroid hormones;
- LDL is “bad cholesterol.” Excess of the substance reduces the functionality of HDL and leads to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of blood vessels. High levels of LDL are observed in hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus, systemic connective tissue diseases, and obesity.
During pregnancy, cholesterol levels increase. This is due to changes in hormonal levels and metabolism in the female body. Therefore, special standards have been developed for pregnant women, which should be taken into account when deciphering the analysis.
Glucose
In a healthy pregnant woman, the blood glucose level (glycemia) is within certain physiological limits. Elevated values may indicate diabetes mellitus type I or II, as well as gestational diabetes (GDM).
GDM is the most common metabolic disorder in pregnant women encountered by endocrinologists and obstetricians-gynecologists. The main cause of the disease is a change in hormonal levels. Most often, with GDM there are no pronounced symptoms, which makes diagnosis difficult. Determining glucose in a biochemical analysis is one of the ways to detect pathology. GDM requires immediate treatment, as it can cause miscarriage and affect the health of the unborn child and the woman herself.
ALT and AST
ALT and AST are enzymes of a subgroup of transaminases, which are considered the main markers of liver disease. When the parenchyma of an organ is damaged, substances enter the blood in large quantities, which indicates the presence of pathology.
In addition, the level of enzymes makes it possible to monitor the functioning of the cardiovascular system and the condition of skeletal muscles.
The synthesis of substances is associated with the content of vitamin B6 in the body. Accordingly, if there is a lack of this vitamin, the values of ALT and AST will be reduced.
Bilirubin
Bilirubin is a substance that is formed when red blood cells break down. This process mainly occurs in the liver, so first of all, the value of bilirubin reflects the work of this organ.
The results of biochemical analysis indicate the values of three types of bilirubin:
- general;
- direct;
- indirect.
Indirect bilirubin is very dangerous: its high content in the blood causes intoxication of the body. Direct bilirubin is soluble in water and less toxic.
If pregnancy proceeds without complications, then the indicators of the three types of bilirubin do not deviate from the reference values. The cause of increased results may be acute and chronic hepatitis, liver tumors. Also, high numbers are observed with severe toxicosis.
Alpha amylase
Alpha amylase is an enzyme that breaks down starch into simpler saccharides and is involved in the digestion process. Without this substance, the body would not be able to absorb carbohydrates, the main source of energy.
An increase in the enzyme during pregnancy may indicate the following problems:
- diabetes;
- pancreatitis - inflammation of the pancreas;
- cholecystitis - inflammation of the walls of the gallbladder;
- renal failure - impairment of all kidney functions;
- ectopic pregnancy - attachment of a fertilized egg outside the uterine cavity.
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
This is the most common enzyme in the body and is present in all tissues and organs. The substance takes part in the transport of phosphorus and accelerates the breakdown of complex phosphoric acid compounds. Determining the amount of enzyme is necessary to assess the condition of the liver, kidneys, gall bladder, bone tissue and other organs and structures.
In the second trimester of pregnancy, placental fetal alkaline phosphatase begins to enter the maternal bloodstream. A woman's ALP level rises and reaches its maximum in the third trimester.
A physiological increase in the concentration of the substance is not dangerous and is not considered a pathology. But if the analysis result significantly exceeds the reference values, then this may indicate the presence of diseases:
- gestational diabetes mellitus;
- gestational dermatosis;
- inflammatory processes of the liver, kidneys, gall bladder.
Microelements
Microelements are substances that ensure proper functioning of the body. A lack of microelements in a pregnant woman can negatively affect the endocrine, nervous, and digestive systems, and also lead to fetal developmental abnormalities. Therefore, it is so important to check the content of these beneficial substances in the body during pregnancy.
Biochemical analysis determines the level of calcium, iron, sodium and other trace elements. When prescribing an analysis, the doctor determines the number of positions to be examined, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient. If there is a deficiency of any substance, a diet correction or taking vitamin and mineral complexes is required.
Online consultation with a gynecologist
Online consultation
During the consultation, you will be able to voice your problem, the doctor will clarify the situation, interpret the tests, answer your questions and give the necessary recommendations.
Indications for analysis
The reasons why a urea level test is performed are as follows:
- disorders of the excretory and urinary systems;
- changes in liver function.
In addition, referral for testing is recommended if a person:
- have heart problems, arterial hypertension;
- joint diseases of a rheumatic nature;
- there is intoxication of the body (alcohol, chemicals), hunger;
- The digestive tract is disrupted, which prevents the absorption of nutrients.
This laboratory test is necessary for athletes due to large muscle mass, which causes an increase in nitrogen compounds, as well as due to the intake of biological protein supplements.
How to normalize carbamide levels
If a decrease or increase in urea is caused by pathologies, then it is necessary to undergo additional examination. Then, based on the test results, the doctor prescribes treatment.
When carbamide decreases, the patient is also advised to pay attention to her diet. You need to eat as much protein food as possible. If urea is elevated, then a diet is prescribed with limited protein-rich foods.
After completing the course of treatment and adjusting the diet, the urea level returns to normal. During pregnancy, it is very important to pay attention to the biochemical composition of the blood. After all, any deviation from the norm can negatively affect the condition of the fetus, and then the health of the newborn.
Symptoms of low concentration
If a low level of urea is detected, it means that there is a possibility of certain pathologies of organs and systems. When the level decreases, there are no obvious symptoms, but indirectly it is:
- loss of appetite, bitterness when belching;
- feeling of heaviness under the ribs on the right side;
- bloating accompanied by pain;
- muscle weakness, swelling of the limbs;
- frequent urge to urinate, flatulence.
The person also feels constant fatigue, decreased performance, and unexplained weight loss occurs.
Complexes with this research
Examination during pregnancy.
1st trimester 11,430 RUR Composition Preventive check-up Universal annual preventive screening 7,730 RUR Composition
Kidneys. Extended examination RUB 1,340 Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Expanded hospital complex 4,910 RUR
- Pregnancy planning. Clinical indicators 4,350 R
- Kidney screening RUR 780
- Entry into IVF RUB 16,590
- Examination during pregnancy. 3rd trimester 6,310 RUR
Reasons for falling rates in adults
Low urea levels are a less common occurrence. This is not always a symptom of some disease.
These causes may not have negative consequences and do not require treatment:
- A vegetarian diet or a diet with insufficient amounts of protein foods;
- after hemodialysis (blood purification device);
- excessive amounts of body fluids administered intravenously.
Negative factors that reduce concentration in men and women include:
- liver damage - tumors of a benign or neoplastic nature, cirrhosis, hepatitis of any type, necrosis;
- the presence of helminths, poisoning of the body;
- diseases of the thyroid gland associated with insufficient synthesis of hormones and leading to a failure in the formation of urea;
- complications after surgical interventions (surgeries on the liver and intestines).
A low level of urea is observed in cases of poisoning with phosphorus compounds, arsenic, excess growth hormone in the body, and poor intestinal absorption of nutrients.
The use of certain hormones containing testosterone, somatropin, and insulin reduces this indicator.
In men
In addition to the above factors, urea levels often decrease in men:
- due to abuse of alcohol-containing drinks, which often leads to alcohol intoxication;
- as a result of increased physical activity aimed at increasing muscle mass.
As a result of high sports load, all the protein entering the body with food is spent on building muscles and accelerating the increase in their mass, and is not left for the synthesis of urea.
In women, including during pregnancy
Physiological and pathogenic factors affecting the concentration of urea in the blood in women are the same as in men. However, for an expectant mother, a value below normal is considered normal, and even 4 mmol/l is acceptable.
Urea levels drop during pregnancy because:
- The synthesis of proteins is higher than the rate of their breakdown, because everything goes towards building fetal tissue;
- physical activity decreases, muscle work slows down;
- the kidneys and excretory system work harder.
Despite the fact that a decrease in the level of nitrogenous substances in an expectant mother is not considered pathological, women with a history of diabetes mellitus, nephrolithiasis, or pyelonephritis are carefully monitored.
What is the importance of the study?
The pregnant woman's body is subjected to severe stress and significant changes.
This often leads to exacerbation of chronic diseases and the emergence of new pathologies. A biochemical blood test is an important element of screening during pregnancy. The analysis allows:
- assess the functions of internal organs;
- determine violations of water-salt metabolism;
- identify micronutrient deficiencies;
- diagnose diseases in the early stages.
For what indications should a pregnant woman get tested?
The doctor does not need any reasons to prescribe a test. The analysis is mandatory and is carried out several times during pregnancy: in the first trimester when registering, as well as in the second and third trimesters. For certain indications, additional testing may be prescribed.
Low value in children
It is considered correct to reduce the level of urea in a child in infancy (up to 12 months), which is associated with natural processes and does not threaten his health. During this time, most of the protein is spent on the further formation and development of systems and organs.
In young children, this indicator often decreases in parallel with an increase in bilirubin, which indicates the development of pathology in the liver. In such a situation, immediate medical attention and hospitalization are required.
In older children, urea levels decrease due to:
- liver abnormalities;
- intestinal dysfunction;
- increased synthesis of growth hormone - somatropin.
In adolescence, the level decreases due to accelerated growth and buildup of muscle tissue, which “eats” protein, and it does not have time to break down into nitrogenous compounds.
To normalize the situation, a thorough examination is necessary to determine further measures to eliminate the cause of the imbalance.
Table: reference values for biochemical blood tests during pregnancy by trimester
| Indicators | Units | 1st trimester | 2nd trimester | 3rd trimester |
| Total protein level | g/l | 63-83 | ||
| Albumen | g/l | 31-50 | 28-55 | 25-66 |
| Urea | mmol/l | 2,5-7,1 | 2,5-6,2 | |
| Total cholesterol | mmol/l | 6,16-13,7 | ||
| Blood glucose level | mmol/l | 3,5–5,83 | ||
| ALT | units/l | up to 32 | up to 31 | up to 31 |
| AST | units/l | up to 31 | up to 30 | up to 30 |
| Creatinine | µmol/l | 32-70 | 32-50 | 32-47 |
| Total bilirubin | µmol/l | 3,4-21,6 | ||
| Direct bilirubin | µmol/l | Up to 7.9 | ||
| Indirect bilirubin | µmol/l | 3,4-13,7 | ||
| Alpha amylase | units/l | 28-110 | ||
| Alkaline phosphatase | units/l | 40-150 | 40-190 | 40-240 |
| Iron level | µmol/l | 8,93-30,4 | 7,2-25,9 | |
| Sodium level | mmol/l | 135-155 | 135-145 | 135-155 |
| Chlorine level | mmol/l | 98-107 | ||
| Potassium level | mmol/l | 3,4-5,3 | 3,4-5,5 | 3,4-5,3 |
| Phosphorus level | mmol/l | 1-1,57 | 1-1,4 | 0,87-1,47 |
| Magnesium level | mmol/l | 0,85-2 | 0,85-1,7 | 0,85-1,4 |
Normalization methods
To correct a low urea index, the causes of this condition are eliminated. When the imbalance is mild and non-pathological, it is enough:
- adjust the diet, increasing the proportion of protein products in it, and abandon strict diets;
- Discuss with your doctor how to take medications;
- observe the daily amount of fluid consumed.
To normalize urea concentrations, pregnant women sometimes just need to wait until the baby is born, after which the level returns to normal.
But often in severe cases treatment is prescribed.
Medication methods
If it is not possible to completely restore the urea index to normal, it is transferred to the position of stable compensation.
To do this, you should conduct a thorough examination with specialized specialists - a urologist, endocrinologist, therapist, gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist, who will help identify the cause that has a negative impact and prescribe appropriate treatment:
If necessary, medications are prescribed that improve metabolic processes and improve the functioning of the digestive system.
After treatment ends, tests are repeated to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
Nutrition and folk methods
When urea levels are low, it is recommended to increase the amount of protein in the diet. You need to eat meat, dairy products, fish, and legumes.
This is especially important for pregnant women, since the body works for two.
Any traditional methods are in addition to the therapy prescribed by a doctor and cannot be used without his consultation.
Having found out the reason for the decrease in urea levels, the doctor, if necessary, will recommend herbs and a mixture corresponding to the disease - liver, kidneys, stomach and others.
Pituitary and hypothalamic disorders
Diseases of the pituitary gland can also cause a woman to have low urea in her blood during pregnancy. This may be associated with a serious illness such as acromegaly. With this pathology, the patient has an increased level of growth hormone (somatotropin). It suppresses the formation of urea.
The disease manifests itself in the growth of the facial part of the skull, hands and feet. The most common cause of the pathology is a pituitary tumor. The woman needs to consult an endocrinologist and neurosurgeon. If the tumor is large, surgery is performed in the second trimester to remove the tumor. Surgical intervention is performed in the most gentle way - through the nasal passage.
Another reason for a decrease in carbamide may be excessive release of antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin). This substance is produced in the hypothalamus. This condition is called Parhon's syndrome. With this pathology, the level of sodium and urea in the blood drops. The disease is accompanied by sudden weight loss, convulsions and vomiting. It is necessary to limit the amount of fluid consumed and take vasopressin antagonists.