Pyelonephritis
Diabetes
Hepatitis
Rheumatism
42017 October 27
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. We remind you that independent interpretation of the results is unacceptable; the information below is for reference only.
Urea in the blood: indications for prescription, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and normal indicators.
Additional examinations
General and biochemical blood tests are not enough.
This is only a small fraction of the measures that are required to establish the true causes of the increase in urea. Without them it is impossible to say anything concrete. An extended list might look like this:
- Oral interview with a specialist. You can't do without it. Because it is necessary to identify all possible health complaints. Then systematize them and put forward hypotheses regarding the nature of the phenomenon.
- Anamnesis collection. The nature of daily activity, diet and dietary habits, bad habits, family history, past and current disorders. Also other factors. All this needs to be installed.
- Ultrasound of the liver, kidneys. Ultrasound technique is one of the main ones in the examination process. Gives an idea of the state of these organs.
- Hormonal tests are performed as needed.
- If diabetes mellitus is suspected, it is necessary to evaluate the functional integrity of the pancreas. Through special tests.
- MRI, CT as needed.
- The same applies to assessing the condition of the heart.
Diagnostics is carried out by a group of specialists. Depending on the cause, disruption of the biochemical process.
Complexes with this research
Women's check-up No. 1 38 studies for annual preventive examination RUB 19,290 Composition
Expanded hospital complex Expanded infectious screening for prevention and hospitalization RUB 7,700 Composition
Entry into IVF Examination when a woman enters the IVF procedure RUB 23,020 Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Diabetes monitoring RUB 1,900
- Biochemistry of blood. 8 indicators 990 R
- Biochemistry of blood. 13 indicators 3,490 RUR
- Healthy interest 4,250 RUR
- Examination during pregnancy. 3rd trimester 9,620 RUR
Causes of increased urea in the blood
Subjective factors are the most common. Including in healthy patients (no matter how paradoxical this combination sounds). In this case, a group of specific moments is determined.
As a rule, people can cope with them on their own; neither the participation of specialists nor medical assistance is required. Except in rare situations.
Consuming large amounts of alcohol
Causes short-term biochemical changes. At a high concentration of ethanol, the process of breakdown of nerve tissue begins, which enters the bloodstream and is metabolized by the liver.
These necrotic structures break down into urea, which is then eliminated in urine. The whole process takes no more than a day. Plus or minus.
If the blood is tested at this point, the levels will be inappropriately high. But in such a situation we are talking about a variant of the norm. Everything will return to acceptable limits on its own.
Ample consumption of animal protein
The nutritional factor in the development of pathological processes is the main one when the situation is observed in a healthy person.
When receiving a large amount of such food, an increase in urea levels cannot be avoided. The body, however, is capable of adjusting and stabilizing volumes on its own. Therefore, no critical violations are observed. In addition, the disorder quickly disappears on its own.
- Amylase. Normal blood levels in women, men, children by age, table. What does it mean increased, decreased, treatment
Attention:
Treatment is required only for pathologies of the kidneys and excretory tract. In such a situation, consuming large amounts of meat can be dangerous.
Subjective causes of increased urea are the least threatening among all those described, since they rarely require medical intervention.
Liver diseases
Such disorders are extremely common and constitute the top three. Heterogeneous in character.
The patient does not always understand that something is wrong with him. Because the urea concentration increases long before the first symptoms develop. Although not always.
There is also a positive point here: the study of the indicator gives an idea of the early stages of pathologies, even when there is no clinic yet.
Among the specific conditions:
- Hepatitis. Inflammatory disorders. The plural is described because there is a large group of forms. Mostly these are viral diseases.
They typically have a sluggish onset, with scant symptoms leading to late visits to doctors. Urea begins to rise almost immediately after the incubation period is over.
There are alcoholic varieties, as well as dosage forms caused by improper or long-term use of certain hepatotoxic drugs. The approach is differentiated. Depends on the situation.
- If uric acid in the blood is elevated, what are the causes, symptoms and treatment
Excess urea is not always present, only in the early stages of hepatitis, while the organ is still functioning normally.
- Cirrhosis of the liver. The same applies to a similar diagnosis. Its essence lies in the death of organ cells. However, this is not a one-time process. If we don’t talk about an acute condition provoked by alcohol or taking a large number of drugs, poisons, etc.
In the compensated phase, urea increases as soon as the liver stops working quite actively; on the contrary, it decreases. Because the organ can no longer process the same amount of substance. The pattern is simple.
Attention:
Liver disorders can provoke both an increase and a decrease in urea levels, depending on the phase and type of the underlying diagnosis. This creates confusion in the survey questions.
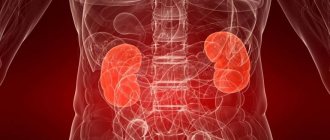
Kidney pathologies
Diseases of the excretory tract are also common. And here the reasons for the development of pathological changes are largely mechanical. The end product of protein breakdown is simply not excreted in sufficient volumes, even with adequate synthesis.
There are several specific conditions:
- Nephropathy. Large category of disorders. Presented with a wide range of deviations. There are usually no specific manifestations.
- Inflammatory processes. Pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis. Infectious, autoimmune disorders, it doesn't really matter. More importantly, these deviations cause filtering problems.
With a low degree of dysfunction, this is not so noticeable. Urea in the blood is increased, but symptoms are still absent or scant. Which becomes a false indicator of a stable state.
In typical cases, pathologies of the profile in question should be suspected immediately. So as not to miss the moment and be on the safe side.
- Blood sugar 34 - what does it mean and what to do?
- Kidney failure. Typical condition. A characteristic feature is a critical reduction in the speed and quality of filtration. The most dangerous complication of the problems mentioned above.
Injuries, damage
The connection between the change in the biochemical indicator and the injury suffered is obvious, so conclusions can be drawn immediately. The cause of high urea levels is the death of cells that need to be disposed of.
Since they consist of protein compounds, processing occurs in the liver. Ultimately, this ends with an increase in the indicator.
Injuries can be very different:
- Burns.
- Violation of the integrity of soft tissues.
- Other problems.
Iatrogenic factors
The cases where doctors participate in the mechanism stand out. We are talking about operations and traumatic diagnostic procedures.
The more dangerous the procedure, the higher the number of injured tissues and, accordingly, the concentration of the said substance will be relatively high.
In the context of the situation, if the urea is elevated, this means that the damage was serious, but specialized correction is not required. Everything returns to normal on its own, without medical measures.
Endocrine diseases
Pathological processes associated with hormonal levels can also cause increased urea in the blood.
- Diabetes. In general, it provokes protein metabolism disorders. Regardless of the flow phase. The only way to normalize the condition is to keep the glucose concentration within adequate limits.
- Thyroid diseases. Excessive production of specific compounds. T3, T4, partially - pituitary TSH.
- Pathologies of the adrenal glands, in which the concentration of steroid substances increases.
All of them require urgent treatment, since without it they provoke serious complications. Up to and including disability.
Consequences of pregnancy
Normally, protein breakdown products decrease during gestation, sometimes reaching a minimum. But the increase in values lies in developmental disorders of the fetus, liver or kidney dysfunction in the mother. These are the most common sources of the problem.
Heart disorders
For example, a heart attack. A state of acute death of cells in the muscle layer of an organ. Accompanied by a short-term but significant increase in the indicator. Since the signs are quite bright, the connection level does not matter much.
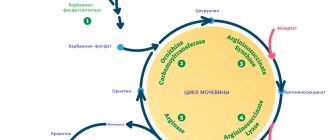
Why is urea produced?
Increased production of urea is associated with the presence of rich protein foods in the daily diet, but under the condition of impaired renal function.
Production occurs in several stages:
- Eating protein foods.
- Breakdown and further absorption of proteins and other nutrients by active enzymes and gastric juice.
- The final stage of protein breakdown in the liver, the transformation of nitrogenous elements into urea.
- Transfer of urea into the bloodstream, further filtration in the renal structures.
- Removal of the resulting biochemical substance with urine.
Stages of formation and excretion of urea
Normally, urea contains about 46% nitrogen. With prolonged abstinence from protein foods, a low urea content is observed, both in the blood serum and in urine.
Symptoms
Clinical manifestations depend on the specific pathological process. As such, an increase in urea does not make itself felt. It can only be detected through laboratory evaluation. For the rest, you need to build on other manifestations.
The following signs are present against the background of liver diseases:
- Pain on the right, under the ribs.
- Feeling of fullness in the abdomen.
- Bloating, increased production of intestinal gas.
- Bitterness in the mouth.
- The shade of the dermis and sclera of the eyes may change to yellowish or greenish. This is the result of the release of bilirubin into the tissues and bloodstream.
- Digestive problems.
- Increased body temperature.
- Stool disorders. A change in its shade to light or complete absence of pigmentation.
When it comes to kidney disease, the following are typical symptoms:
- Dysuria. Frequent false urge to empty the bladder.
- Increased daily diuresis. The so-called polyuria. When too much substance comes out: more than 2 liters. Occurs in the initial stages of the pathological process.
- Oliguria, the opposite phenomenon, is observed as soon as the disorder reaches a certain point.
- Pain in the lumbar region.
- Increased body temperature.
- Weakness, sthenic phenomena.
- Blood pressure surges.
- Heart rhythm disturbances.
There are many more options. It all depends on the primary diagnosis and the severity and decompensation of it.
Deviations caused by natural factors, for example, poor nutrition, do not make themselves known. Unless some anomalous condition is connected in parallel. Accordingly, treatment as such is not required.
The same applies to physiological fluctuations after heavy drinking, some other conditions, and physical activity (it can also provoke temporary deviations).
All questions are considered during the diagnostic process.
Medicines that lower urea levels
If urea in the blood is elevated, an integrated approach is necessary to normalize its levels. Combined treatment includes prescribing certain medications and performing artificial blood purification in order to remove toxic breakdown products.
The following medications are most often prescribed to reduce urea levels:
- Polysorb is a drug from the group of enterosorbents for oral administration in the form of a suspension. One tablespoon of the product is dissolved in a glass of clean water without gas. The prepared solution is taken 3-4 times a day an hour before meals. The course of treatment is from 10 to 15 days. The cost of the drug is approximately 240 rubles.
- Atoxil is a sorbent with intense absorption properties that has antibacterial, disinfectant and wound-healing effects. The drug is able to remove toxic substances from the body and eliminate the symptoms of poisoning. To prepare the solution, thoroughly stir 1-2 sachets of the product in 200 ml of slightly warmed water. Take Atoxil as symptoms develop. The price of the sorbent is about 150 rubles.
- Enterosgel is an absorbent drug in the form of a jelly-like paste. The drug is taken 1 tablespoon 3 times a day 1.5 - 2 hours before or after meals. The course of therapy is designed for 7 - 14 days. The price of the drug is about 230 rubles.
- Silix is a multi-purpose intestinal sorbent in powder form. To prepare the solution, you need to dissolve 12 grams of the product in a glass of warm boiled water. The resulting volume is calculated for a day. It is divided into several stages. The drug is taken for 14 days. The cost is about 190 rubles.
- Lespenefril is an antiazotemic, diuretic agent in the form of an oral solution. The drug activates filtration, reduces urea levels and removes nitrogenous compounds. A single dose is 1-2 teaspoons dissolved in? glasses of water. The treatment course is 3 - 4 weeks. The cost of the drug is about 195 rubles.
- Hepa-Merz is a drug to reduce the concentration of ammonia in the blood. The active substance promotes the production of somatotropin, its own insulin. Has a beneficial effect on liver function. The drug is administered by intravenous drip infusion. To prepare a medicinal cocktail, 40-60 ml of Hepa-Merz are injected into 500 ml of sodium chloride solution. The price of one ampoule of the product is about 630 rubles.
- Ornilatex belongs to the hypoazotemic group of pharmaceuticals. The product promotes the removal of excess urea and the synthesis of its own hormones. The required amount of the drug is injected into 500 ml of saline sodium chloride solution or Ringer's solution and administered intravenously. The price for 10 ampoules of Ornilatex starts from 1,470 rubles.
- Ornitsetil is a detoxifying agent that helps reduce urea levels in the blood and restore liver function. Available in powder form for the preparation of a solution for oral administration. The drug is taken 2-3 times a day, after dissolving the contents of the sachet in 200 ml of water. The daily dosage usually does not exceed 20 grams per day. The price starts from 500 rubles for 10 bags.
- Larnamine is a drug of the hypoammonemic group. It is able to reduce urea levels in the blood, restore the structure of liver tissue, and improve protein metabolism in the body. Can be used orally or by intravenous infusion. For oral solution, mix the contents of the sachet in one glass of water or juice. Take 3 times a day during meals. For intravenous drip infusions, the contents of ampoules (from 4 to 8 pieces) are introduced into a bottle of physiological sodium chloride solution (500 ml). The price of the drug in powder form is from 2,400 rubles per package, in ampoules - from 1,800 rubles for 10 pieces.
Under the influence of medications, the concentration of urea in the body decreases and the breakdown products of nitrogen-containing compounds are eliminated. Medicines are prescribed by the attending physician based on laboratory data, after a detailed analysis of the results of ultrasound diagnostics.
What is urea in the blood?
Urea in the body
Urea is a normal waste product of the human body, formed during the metabolism (processing) of proteins. Proteins are contained not only in food that the body receives from the outside; in addition, all decaying cells of organs and tissues participate in protein metabolism.
Every day, millions of cells naturally “die off” in the body, each of which consists of protein. All unnecessary "debris" generated must be properly processed in order to leave the body, which is when the metabolic processes occurring in the liver come to the rescue. It is there that urea, as well as other nitrogen-containing substances, are ultimately formed from proteins that the body does not need.
Next, urea enters the blood and circulates there until it is excreted by the kidneys. Urea is constantly contained in the blood at approximately the same level, since the processes of breakdown (metabolism) of proteins in the body never stop. Naturally, more proteins break down when eating large amounts of animal foods, as well as after injury or intense physical exertion, when many cells in the body are damaged.
How is urea different from uric acid?
Uric acid and urea are substances that have nothing in common. The significant difference between them lies in metabolic processes. Uric acid is a constituent of urine, which is formed as a result of the breakdown of nucleic acids. The mechanism of its formation involves the blood, liver and brain. The whole process is aimed at neutralizing ammonia. Uric acid is excreted through urine and sweat. Violation of the formation and metabolism of uric acid leads to the development of gout, the deposition of salts in the tissues of internal organs.
Urea is a nitrogen-containing compound that is formed during protein metabolism and the breakdown of amino acids. It is present in small quantities in the general bloodstream, while the main part is excreted from the body in the urine. The presence of urea indicates the development of certain diseases, however, a small amount of it is not harmful to the body.