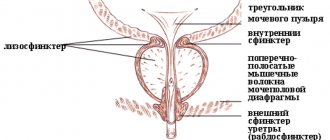
When they talk about such a phenomenon as blood from the urethra
, often involve bleeding from the urethra that occurs between trips to the toilet. They indicate damage to the urethra itself and are not associated with the overlying parts of the genitourinary system - the kidneys or bladder. However, oozing blood may also stain the urine red.
Bloody discharge varies in strength and color. When mixed with other organic substances and mucus, they can acquire pinkish or brownish tints. With intense bleeding, the color becomes bright scarlet - the patient loses a lot of blood. Sometimes the presence of mild bleeding can be judged only by a caked crust around the urinary canal, but even in this case, medical intervention is required.
Causes of bleeding
Discharge of blood from the penis can be caused by:
- shortened bridle;
- unsuccessful poses and sudden movements during sexual intercourse;
- violations of the anatomy of the penis;
- chemical and thermal burns;
- inflammatory diseases of the scrotum and pelvis - urethritis, prostatitis, cystitis, epididymitis, urolithiasis, pyelonephritis;
- STI;
- benign or malignant neoplasms.
The timing of bleeding plays an important role. If they appear during or immediately after sexual intercourse, there is a high likelihood of injury. Blood in urine or semen is a sign of sexually transmitted infections and inflammatory diseases.
Diagnosis of diseases that cause blood in urine
In order to carry out effective therapy for the disease that caused the appearance of blood in the urine of a man, urologists at the Yusupov Hospital conduct a comprehensive examination of the patient using the latest equipment from the world's leading manufacturers and laboratory tests. If blood appears in a man’s urine without pain, doctors use those diagnostic methods that are necessary in the presence of one or another cause of hematuria.
Asymptomatic microhematuria can develop with chronic kidney disease, infectious or viral diseases, menstruation that has begun or recently ended, or after recently performed urological manipulations (catheter installation). In this case, hemostatic therapy and repeated urine analysis are performed.
When examining a patient with blood in the urine visible to the naked eye, a general urinalysis is performed. Worm-shaped clots may form in the urine, indicating their formation in the upper urinary tract. Large, shapeless clots form in the bladder.
Blood in the initial portion of urine appears after injury, as a result of inflammation or tumor growth of the urethra. With total hematuria, all portions of urine are uniformly stained with blood. This symptom is characteristic of diseases of the kidneys, ureter, prostate and bladder. In men, blood is released at the end of urination in the presence of a tumor of the bladder neck, prostatitis, inflammation or tumor of the seminal tubercle.
Pain combined with bloody urine in men may indicate a possible cause of bleeding. If there are stones in the ureter, pain appears in the lumbar region on the affected side before the onset of hematuria. If the ureter is blocked by blood clots, men experience pain after bleeding in the urine. With bladder tamponade, pain occurs after the appearance of blood in a man’s urine.
During the initial examination of the patient, doctors pay attention to the following symptoms:
- Hemorrhagic rashes on the skin and mucous membranes indicate possible diseases of the blood coagulation system, hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome;
- Edema that increases blood pressure indicates kidney disease;
- An increase in body temperature can be caused by an infectious disease;
- Lymph nodes can become enlarged due to blood diseases, cancer, and infectious diseases.
For men, when blood appears in the urine, urologists perform a digital rectal examination and examination of the external opening of the urethra.
An accessible and sensitive diagnostic method is urine testing for the presence of hemoglobin. False-positive results are possible with myoglobinuria and hemoglobinuria, false-negative results are possible when patients take vitamin C and acetylsalicylic acid preparations. The positive result obtained from this diagnostic method is confirmed by doctors at the Yusupov Hospital with the data of a general urine analysis and sediment microscopy. In some cases of blood in the urine of men, Nechiporenko studies may have additional diagnostic value.
Microscopy of sediment using a modern phase contrast microscope allows for topical diagnosis of hematuria. If laboratory technicians detect unchanged red blood cells in the urine, there is a high probability of a urological disease with the source of hematuria located in the collecting system, ureter or lower urinary tract. The presence of altered red blood cells and casts in the sediment indicates kidney disease.
In order to determine the source of blood in the urine of men, a three-glass test is performed. If the source of bleeding is located in the male urethra, blood will be in the first portion of urine. In the case of isolated hematuria in the third portion of urine, the pathological focus is located in the neck of the bladder.
For microscopic examination, men collect an average portion of urine freshly released during urination, which laboratory assistants immediately centrifuge for 10 minutes in a 15-mm flask at a speed of 2000 per minute. During a microscopic examination, at least 10-20 fields are evaluated under four hundred times magnification. The presence of three or more red blood cells in the microscopic field is evidence of microhematuria.
In the presence of gross hematuria, nephrologists at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe the following instrumental studies:
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys, bladder, prostate;
- Excretory urography (performed with normal levels of creatinine and blood urea);
- Cystoscopy (performed after exclusion or in the absence of suspicion of the presence of an acute inflammatory process in the organs of the genitourinary system).
Doppler ultrasound is performed to assess blood flow in the renal vessels. The morphological diagnosis is clarified using a biopsy of the kidney, pelvis, bladder, ureter, urethra, and prostate. Using computer and magnetic resonance urography, the anatomical features of the urinary tract are visualized in detail. Retrograde ureteropyelography and ureteropyelocalicoscopy are used if the source of blood in the urine is suspected to be papillary tumor diseases of the upper urinary tract.
When blood appears in the urine in men suffering from systemic diseases, severe proteinuria, elevated creatinine and urea levels are detected in patients with hematuria, patients are consulted by a nephrologist. A consultation with a hematologist is prescribed if men with blood in the urine have an enlarged liver and spleen, or subcutaneous hemorrhages. When hematuria is combined with diarrhea, patients are advised by an infectious disease specialist. If men have blood in their urine in combination with persistent pyuria that is resistant to antibiotics, a consultation with a phthisiatrician is prescribed.
Associated symptoms
Most often, bleeding from the penis is accompanied by other symptoms:
- pain,
- pain when urinating,
- swelling of the scrotum and its increase in size,
- frequent urge to go to the toilet,
- pulling sensations in the lower abdomen and lower back,
- a rise in temperature and signs of intoxication - severe weakness, high fatigue, chills.
If at least one of these symptoms occurs, it is important to make an appointment with a urologist as soon as possible. Early contact with a specialist will help to identify the disease in time and provide treatment in a short time.
Treatment – prescription and over-the-counter medications
Acute cystitis is not serious, but it is a rather unpleasant disease. In addition, treatment should be started as soon as possible due to possible complications.
The most common treatment for this disease is antibiotics and chemotherapy (due to the bacterial nature of most bladder infections).
The most commonly prescribed (prescription) antibiotics for cystitis are:
- Amoxicillin
. This is a semi-synthetic penicillin. It is used for acute cystitis, as well as for pyelonephritis or asymptomatic bacteriuria. It is an antibiotic with a very wide range of uses - it also helps fight bacteria that are resistant to other antibiotics; - Fosfomycin
. Synthetic antibacterial drug (phosphonic acid derivative). This active substance is often combined in medications with trometamol; - Cephalexin
. Semi-synthetic cephalosporin antibiotic. Because it is very effective against coliform bacteria, it is prescribed for most urinary tract infections, including acute cystitis.
Amoxicillin
It is important to note that you should always take the full dose of the antibiotic even after apparent recovery. Improvement in well-being occurs quickly after taking the first dose. Otherwise, bacteria may become resistant to a particular antibiotic, and the disease may return.
The second group of agents used for acute cystitis are chemotherapy agents, which are over-the-counter medications. They have a strong bactericidal effect, similar to antibiotics. Among them are popular over-the-counter drugs (containing substances from the group of chemotherapeutic agents) based on furagin, ciprofloxacin and nitroxoline. They help relieve symptoms and speed up the healing process.
If cystitis is accompanied by fever or severe pain, your doctor may advise you to take painkillers and antipyretics.
The treatment process for acute cystitis itself lasts up to about 10 days - usually from 3 to 5. After treatment, your doctor may order a urine test to determine the effectiveness of the treatment.
Diagnosis and treatment
As part of diagnosing the causes of blood discharge from the penis, a man is prescribed:
- blood tests - for STIs, tumor markers,
- urine tests - biochemical and general clinical,
- Ultrasound of the pelvis, penis, scrotum, abdominal cavity,
- spermogram,
- smears from the urethra,
- cystoscopy and urethroscopy,
- if necessary, MRI or CT.
Based on the results of a comprehensive examination, the urologist-andrologist chooses treatment tactics. For STIs and inflammatory diseases, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and physical therapy help cope with bloody discharge. Injuries involving damage to the penis and scrotal organs may require surgery.
Have you noticed bloody discharge from the urethra? Don't put off visiting your doctor. Specialists at our andrology clinic provide therapy for STIs, prostatitis, surgical treatment of varicocele and other diseases. Make an appointment by phone.
What causes blood to be released
The release of blood or blood-colored urine from the urethral canal occurs in two cases. These include hematuria - the presence of red blood cells in the urine as a result of inflammatory diseases or injuries to the kidneys and bladder and hematorrhea - urethral bleeding, which is what we are talking about.
If we exclude hematuria, the appearance of blood is caused by the following reasons:
- Mechanical damage to the mucous membrane as a result of medical manipulations: catheterization, bougienage, careless taking of a smear. Typically, such wounds heal quickly without causing complications.
- Injury from falls or impacts. It is fraught with ruptures of the urethral mucosa.
- The appearance of neoplasms, both malignant and benign (polyposis).
- Inflammation of the urethra during infection, leading to erosion. With them, purulent discharge or ichor is mixed with the blood, giving a brown or pink tint.
As you can see, the discharge of blood from the urethral canal is explained by a variety of reasons. With mild mechanical injuries to the mucous membrane, it is prone to fairly rapid recovery. If symptoms increase, accompanied by an inflammatory process, medical care becomes a necessity. Also, with severe injuries to the urethra (ruptures), the bleeding is not always intense, since its ends may be displaced. Therefore, it should be taken into account that the severity of the disease sometimes does not correspond to its manifestations.
You can make an appointment with a venereologist from our consultants by calling +7 (495) 125-49-50
Prices for venereologist services Addresses of clinics Pain during urination Smear from the urethra Ultrasound of the appendages Urologist at home