Dark - abnormal urine color
Disease is most often indicated by pain. However, there are other symptoms that are more subtle and that you may not feel at first. They may be a signal to visit a doctor. One of them is the wrong color of urine.
It is usually colorless or slightly straw-colored. Any deviation from this standard should be cause for concern. Intense yellow color of the liquid may indicate that you are taking too much vitamin B. Foamy and cloudy urine should also be a concern for the patient. If after a urine test the doctor does not notice any abnormalities, you should ask him why it is dark in color.
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
Some sexually transmitted infections (STIs) cause an inflammatory response in the body, which can lead to an excess of white blood cells that end up in the urine. Some STIs also cause an increase in vaginal discharge, which may leak when you urinate and cause cloudy urine. If you have an STI, you may also notice the following symptoms:
- painful or frequent urination;
- itching or redness of the genitals;
- strange discharge from the penis or vagina;
- genital sores or warts;
- bad vaginal odor;
- abdominal pain.
But you should know that STIs can occur, especially at the initial stage, and be asymptomatic. You should definitely talk to your doctor and ask to be examined.
Stones in the kidneys
When kidney stones form, more minerals (salts) are released into the urine, which can cause cloudiness. Many kidney stones will pass without medical attention, but sometimes they cause severe pain and can stop the flow of urine (renal colic). In addition to cloudy urine, signs of kidney stones may include:
- pain in the back or side;
- fever and chills;
- vomiting;
- blood in urine;
- bad smell of urine;
- burning during urination.
For kidney stones that do not pass naturally, there are several treatment options. Doctors may use a shock wave treatment known as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy. They may remove the stone by inserting a scope through the urethra, or they may perform surgery.
Diabetes: type 1 or type 2
People with diabetes may experience cloudy urine for a number of reasons. The kidneys must process excess blood sugar, which can cause dehydration. Kidney damage caused by diabetes can also prevent the kidneys from filtering urine properly. In addition to cloudy urine, symptoms of diabetes often include:
- extremely frequent urination;
- feeling thirsty or dry mouth;
- fatigue;
- blurred vision;
- tingling and numbness in the arms and legs.
About 1 in 4 adults with diabetes will have kidney disease. If a person has diabetes, the doctor may do frequent urine tests to look for a protein known as albumin, which may indicate kidney damage.
Prostate problems
Having an inflamed or infected prostate, sometimes called prostatitis, can cause white blood cells, pus, or discharge to leak into the urine. Additional signs of prostate problems include:
- frequent urination or pain when urinating;
- blood in urine;
- burning during urination;
- pain in the back, hips, or pelvic area;
- painful ejaculation.
If a man experiences any of these symptoms, he should talk to his doctor. The doctor will examine the prostate and prescribe urine and blood tests.
Vaginitis and thrush
Vaginitis is an infection of the vagina caused by a yeast infection, trichomoniasis, or bacterial vaginosis, and these can also cause cloudy urine. Excess white blood cells or other secretions can also change the clarity of urine during vaginitis. Symptoms of vaginitis also include:
- painful urination;
- vaginal bleeding;
- genital irritation;
- increased volume of vaginal discharge;
- changes in the color and odor of vaginal discharge.
The doctor may perform a pelvic exam, check for vaginal discharge, and perform a vaginal pH test. Depending on the cause of the vaginitis, he may prescribe a specific medicine or cream to treat the infection.
Main causes of dark urine
Dark yellow or dark red urine may appear after eating beets, blackberries, or rhubarb. First of all, this indicates a large amount of beta-carotene in the body, which is gradually filtered through the kidneys. Dark urine (brown or dark brown) appears when the patient takes antibiotics.
Dark brown urine usually indicates blood in the fluid. This can happen due to illness or medication. Frequent use of painkillers, sex hormones (especially progesterone) and anesthetics causes dark urine.
Physiological factors
Urine without pathologies is transparent, yellow or straw-colored, with a neutral odor. The shade of urine is formed depending on the content of pigment substances in it: stercobilin, urochrome and urosein. Slight cloudiness of urine in the morning portion is not a deviation from the norm.
Physiological causes of cloudy urine in women:
- Exposure to the external environment: hypothermia provokes the formation of cloudy urine with sediment from minerals and salts;
- Long-term storage of collected biomaterial: after 2 hours, an organic sediment appears in the urine, confirming the unsuitability of urine for analysis;
- Limiting fluid intake, as a result, urine becomes concentrated and slightly cloudy;
- Taking a hot bath, visiting a sauna or bathhouse, this worsens inflammatory processes;
- Violation of the rules of rational nutrition or taking medications that disrupt the urinary process;
- Excessive physical activity, while protein substances penetrate into the urine through the kidney filter.
A woman’s urine becomes cloudy when hygiene rules are violated, after sexual intercourse, and during pregnancy. Drinking alcohol-containing liquids and toxic substances also causes cloudy urine.
What diseases does this urine color indicate?
Dark urine containing blood may indicate diseases such as:
• kidney inflammation (glomerulonephritis); • urolithiasis disease; • cystitis; • kidney cancer; • bladder cancer; • bacterial infection.
Often hematuria is not the only symptom of the disease. It may be accompanied by such ailments as: severe lower back pain, fever, change in stool color, pain when urinating, renal colic or bloating. None of the above symptoms should be ignored by the patient, who should seek treatment from a specialist as soon as possible.
Urinary tract infections
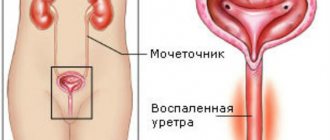
An increased amount of cloudy urine containing blood or pus often occurs when you have a urinary tract infection (UTI). This can happen in both men and women. Excess white blood cells, which the body uses to fight urinary tract infections, can also make urine cloudy or milky white. Urinary tract infections occur when bacteria enter the urethra and enter the bladder. Women have a higher risk of developing UTIs than men. In addition to cloudy urine, signs of a UTI may include:
- pain in the pelvic area;
- constant desire to urinate;
- burning during urination;
- passing a small amount of urine at a time;
- bad odor from urine.
Most UTIs are treated with a course of antibiotics for several days. More complex UTIs can be treated with an initial dose of antibiotics given intravenously, followed by several weeks of oral antibiotics.
Pathological causes
Cloudy urine for several days indicates the beginning of the development of the inflammatory process. There are pathological causes of cloudy urine in a woman: bacterial or viral infections, urolithiasis, lymphostasis, and cancer.
Cloudy and discolored urine indicates that it contains an increased amount of red blood cells, urothelial cells lining the urinary tract, as well as bacteria, fats or salts. Diseases that can cause cloudy urine:
- Pyelonephritis: a condition characterized by damage to the tubular systems of the kidneys. Dull or aching pain in the lumbar region, nausea, vomiting, fever and general weakness are symptoms of the disease. The patient notes frequent urination, pale, opaque urine with a thick sediment consisting of leukocytes, erythrocytes, bacterial mass and epithelium;
- Urolithiasis is the presence of stones of varying sizes and consistency in the renal pelvis and urinary ducts. When moving them, the patient experiences an acute feeling of discomfort in the lower back, often every act of urination is very painful. During the examination, cloudiness of the urine, the presence of salts, mucus and red blood cells in it are noted;
- Cystitis: the disease is characterized by inflammation of the bladder, which is manifested by the following symptoms: cloudy urine with flakes, yellow or reddish in color. In the acute form of the pathology, urination is painful in the morning, difficult, accompanied by pain in the pelvis and lower back. The chronic form of cystitis is characterized by the presence of impurities in urine and the inability to completely empty the bladder;
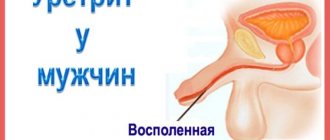
- Urethritis: the disease is based on inflammation of the urethra, which leads to changes in urine: the urine is cloudy with pus, the woman notes the presence of thick discharge, burning and itching in the urethra. Common symptoms of urethritis are weakness, fever and pelvic pain;
- Glomerulonephritis: kidney damage that is immunoinflammatory in nature. Symptoms of the disease are fever, lower back pain, swelling of the eyelids. Urine deep red with sediment. Without timely medical care, there is a high risk of developing complications (renal failure) and the pathology becoming chronic;
- Gonorrhea: symptoms appear 3-5 days after infection. Signs of the disease are burning and itching, discomfort when urinating, women note the presence of purulent discharge. When inflammatory processes enter the chronic stage, the menstrual cycle is disrupted and the chances of conception are reduced.
Very cloudy urine that remains opaque for several days is the reason why you need to see a doctor for diagnostic tests.
Factors that influence the appearance of hematuria
Age. Blood in the urine in men over 50 years of age is very often associated with the development of benign prostate dysplasia. Young men are more likely to suffer from urolithiasis, Alport syndrome, than other age groups. Inflammation of the kidneys after a viral or bacterial infection (post-infectious glomerulonephritis) is considered one of the leading causes of visible blood in the urine in children.
Floor. Blood in the urine in women most often occurs due to urinary tract infections. More than half of all women have experienced cystitis at least once in their lives. This is due to anatomical features: the urethra in women is shorter and wider than in men.
Family history. In 10-15% of cases, hematuria is familial.
Causes of hematuria
The most harmless reason that causes a change in the color of urine is considered to be diet. Blueberries, blueberries, beets, and rhubarb can color the urine, causing false hematuria. Taking certain medications and drugs has the ability to irritate tissues and damage small vessels. Thus, treatment with cyclophosphamide, penicillin, anticoagulants (heparin, warfarin), aspirin can cause bloody urine. Usually in this case, the color normalizes after stopping or reducing the dose of the medication. Another cause of blood in the urine may be severe physical activity, such as long-distance hiking or marathons. In this case, they talk about “runner’s hematuria” or marching hematuria. A similar condition can occur after heavy physical work.
There are many more serious pathologies that are associated with changes in urine color. It can be:
- urinary tract infections;
- urolithiasis disease;
- benign prostatic hyperplasia;
- diseases of the glomerular apparatus of the kidneys - glomerulonephritis;
- hereditary diseases, such as Alport syndrome or sickle cell anemia;
- gynecological diseases, for example, endometriosis spreading to the bladder area;
- papillary necrosis - damage to the renal papillae;
- tumors of the urinary organs - kidney cancer, bladder cancer.
In any case, regardless of the cause, you should consult a doctor immediately after detecting a change in the color of your urine.