Pollakiuria is a urological pathology, the main symptom of which is frequent urination, accompanied by discomfort. This condition can be a symptom of a variety of diseases, so if it does not stop for a long time, there is no need to endure it. It is worth contacting a specialist such as a urologist.
Symptoms of pollakiuria
The following manifestations may indicate that the patient has pollakiuria:
- Frequent urination during the day. It is normal if a person urinates on average up to 10 times a day (or more if an increased amount of fluid is consumed).
- Increased urge to urinate at night - more than 2 times.
- Passage of small amounts of urine.
- Feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
- Despite the fact that a person has an increased urge to urinate, the total amount of urine does not exceed normal volumes.
Frequent urge to urinate is a reason to consult a doctor
Problems with urination can cause a person great psychological and physiological discomfort. Frequent urge to urinate is not a fatal problem, but quite unpleasant. Urinary incontinence, a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder, difficulty urinating - such disorders do not always occur only in older people; such delicate problems can arise at different periods of life in both women and men. A urologist at any medical center can provide assistance if there are disorders in the genitourinary system. How much urination is normal is very subjective for each person; it all depends on many factors - age, physiological characteristics, the presence of diseases, even nutritional conditions and others. The urge to urinate can be considered frequent if the number of trips to the toilet at night or during the day has increased significantly compared to previously observed and causes discomfort. The normal amount is considered to be up to 10 times during the day, and no more than 1-2 times at night.
Causes of urological disorder
There can be many reasons for pollakiuria. They can be divided into several categories:
- Hormonal disorders. They may be accompanied by a state of dysbacteriosis, urolithiasis, frequent bowel movements or constipation, frequent fatigue, and poor appetite.
- Tumor formation in the lower abdomen. Possible accompanying symptoms are pain in the affected area, blood in the urine, fatigue, swollen lymph nodes, fever, unexplained weight loss.
- Endocrine disorders. For example, diabetes increases the frequency of urination. This pathological condition is also characterized by dry mouth, frequent thirst, itchy skin, drowsiness, and fatigue.
- Urogenital infections.
- Diseases of the urinary and reproductive system - urethritis, cystitis, kidney inflammation. In men – prostatitis, prostate adenoma.
- A number of factors can also provoke pollakiuria : stress, drinking large volumes of liquid, pregnancy, hormonal changes in a woman’s body due to the menstrual cycle, taking diuretics, increased physical activity, hypothermia, drinking alcohol and certain foods.
Causes of pain when urinating in women
There are several reasons that influence the appearance of pain and discomfort when urinating. The most common among them are the following:
Cystitis
Cyctitis is an inflammatory process affecting the walls of the bladder.
Under normal conditions, urine is sterile. If a woman’s body functions normally, the immune system suppresses the growth and development of dangerous flora. However, with impaired immunity, rare emptying of the bladder, hypothermia, and stagnation of blood in the pelvic organs, favorable conditions can be created for infection and the onset of the inflammatory process. The infection can enter the bladder in several ways: through the kidneys (descending infection), from the genital tract and intestines through the urethra (ascending infection), through the lymph (lymphogenous route) and blood (hematogenous infection). One of the main signs of cystitis is a frequent urge to urinate, small portions of urine, and a feeling of fullness even after emptying the bladder. During and after urination, women experience pain in the lower abdomen - strong, sharp, cutting, aching or sharp. In addition to dysuria, other symptoms of cystitis are noted: general weakness, increased body temperature, chills, lethargy, and malaise. Expert opinion
There is such a phenomenon as postcoital cystitis: after the end of sexual intercourse, a woman feels the need to empty the bladder, during which pain and discomfort appear. If you encounter a similar problem, contact a gynecologist or urologist.
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category Oksana Anatolyevna Gartleb
Sexual infections (chlamydia, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, candidiasis, etc.).
These can be not only sexually transmitted diseases, but also infectious processes caused by the pathological growth of opportunistic and pathogenic microflora of the vagina. In such cases, additional symptoms are added to the complaints - burning, swelling, dryness, soreness and itching of the genitals, as well as vaginal discharge that has an unpleasant odor, color or consistency.
Hormonal changes
Pain in the vagina when urinating is a frequent accompaniment of menopause. Due to a decrease in the amount of estrogen, the vaginal mucosa becomes drier, prone to the formation of microcracks and scratching. Because of this, the release of urine leads to irritation of the mucous membrane, itching, burning and pain when urinating. The intimate moisturizing gel “Gynocomfort” helps to cope with them. Its use promotes the regeneration of minor injuries and scratches of the mucous membrane. In the absence of contraindications, long-term correction of the condition of the mucous membranes of the genitourinary system is carried out using creams containing estriol, for example, “Orniona”, which will be a therapy that eliminates the cause of atrophy.
Stones
Sand, small and large stones can form in the kidneys, ureters and bladder.
This occurs due to metabolic disorders, hypovitaminosis, chronic and acute diseases of the genitourinary system, and poor nutrition. One of the signs that helps identify urolithiasis is bloody urine and severe pain when urinating. There may also be paroxysmal pain in the lumbar region and lower abdomen, and frequent urges to deurinate, which do not bring satisfaction. Painful sensations intensify during physical activity, when walking, when changing body position. In especially severe cases, severe weakness, fever, dizziness, chills, vomiting, and nausea occur.
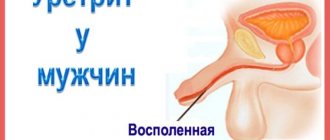
Urethritis
Urethritis is a disease caused by an inflammatory process that is localized in the urethra. The danger of this disease is that the infection can spread towards the kidneys, causing further damage to them. In addition to a possible ascending infection with urethritis, there is a possibility of disruption of the vaginal microflora and the onset of inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs. As for the manifestations of the disease, female urethritis rarely has pronounced symptoms (unlike male urethritis). However, if you notice that pain occurs when urinating, there is uncharacteristic discharge from the urethra (even purulent), or a pulling sensation appears, be sure to consult a doctor: these signs may be manifestations of urethritis.
Inflammatory processes in the kidneys
This may be pyelonephritis. Signs of kidney inflammation include aching pain in the lumbar region, increased body temperature, a decrease in the volume of urine produced, general intoxication of the body, decreased appetite, headaches, diarrhea, vomiting, sweating, pain when urinating. In women, at the end (and in some cases, at the beginning) of the urination process, hematuria (Haematuria) is observed - the appearance of blood in the urine, a change in the color of urine from yellow to brown, brown or red.
Disturbance of vaginal microflora
Normally, the vagina should maintain an acidic environment (from 3.8 to 4.4 pH). However, in case of improper intimate hygiene, washing with inappropriate gels and hormonal imbalance, the vaginal microflora becomes more alkaline. This leads to the formation of microcracks and scratches caused by itching and burning in the labia and vagina. When urine hits damaged areas, it causes irritation and pain when urinating.
Childbirth
During childbirth, numerous tears, abrasions and cracks of the genital organs are formed, including the urinary canal. As a result, after childbirth, a woman may experience pain and pain when urinating until the body recovers.
Features of the treatment of pollakiuria
In medical diagnostics and treatment, high-class professionals are involved. Experienced urologists and doctors of other specializations will find out the cause of pollakiuria and, if it is hidden in a pathological condition, they will use classical and innovative methods to eliminate it. Careful monitoring of the progress of treatment and its effectiveness will help to cope with the disease and return the patient to a decent quality of life without urological problems.
Andrologist in Lipetsk: +7 (4742) 90-40-50, and you can also make an appointment online
Pain when urinating: etiology
Etiology of pain when urinating
can be different: characteristic, only for women or only for men, as well as for both sexes. Most often, discomfort can be caused by inflammatory processes against the background of weakened immunity, stress and hypothermia. Hygiene also plays an important role: its unsatisfactory quality can lead to increased development of pathogenic bacteria and their penetration into the urogenital tract. The reasons that cause discomfort after and during urination are presented in our table:
| Category | Etiology | Peculiarities |
| Common causes, regardless of gender | Inflammatory processes of the urethra due to damage by pathogenic viruses and bacteria. | The pain is cutting in nature and is accompanied by purulent discharge, redness and sticking of the edges of the external opening and further damage to the overlying parts in the absence of timely treatment. |
| Inflammation of the bladder (cystitis) develops due to various reasons. | The acute form is characterized by pain during urination, which radiates into the rectum, frequent urges (sometimes every 5 minutes), and the appearance of blood in the urine. | |
| Urogenital chlamydia due to chlamydial infection | Painful symptoms during bladder emptying are accompanied by mucopurulent discharge in women and bleeding between menstruation and glassy discharge in men, itching and burning, pain in the lower back and scrotum. | |
| Gonorrhea - characterized by damage to the mucous membranes of the urinary organs | Burning and pain in the urethral canal are complemented by a frequent urge to empty the bladder, which is very painful. | |
| Bladder neoplasms of benign or malignant nature | The tumor puts pressure on the bladder and ureter, causing pain. | |
| Pain when urinating in women | Thrush/candidiasis due to infection by Candida fungi | It is characterized by pain during urination and sexual intercourse, burning and itching in the external genital area and a cheesy white discharge. |
| Diseases of the genital organs of an inflammatory nature | Painful sensations and cramps during emptying of the bladder are accompanied by itching and burning of the mucous membrane, and vaginal discharge. | |
| Pain when urinating in men | Acute form of prostatitis - inflammatory damage to the prostate gland | Dysuria: pain, cramping and burning during bladder emptying, which are manifested against the background of symptoms of general intoxication of the body, i.e. lethargy, headaches, fever. |
| Malignant neoplasms of the prostate | Frequent urge and difficulty urinating, pain not only during the process, but also constantly. | |
| Nephrolithiasis - deposition of kidney stones | Acute attacks of spastic pain, accompanied by the presence of blood in the urine. |
Pain when urinating: diagnosis
In order for the treatment of pain when emptying the bladder to be successful, it is important to eliminate its cause. This is impossible without a correct diagnosis. The list of diagnostic studies depends on the age and gender of the patient, the presence of established concomitant diseases. It may include the following:
- Examination by a doctor and medical history;
- General blood and urine tests;
- Tests for the presence of sexually transmitted infections;
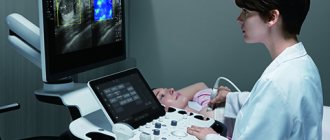
- Ultrasound examination of the genitourinary system;
- X-ray of the lower spine;
- Cystoscopy.