Peripheral vision
Peripheral (side) vision refers to the type of visual perception that is provided by separate areas of the retina. This type of visual function is necessary to provide a complete picture and complete orientation of a person in space.
A characteristic feature of peripheral vision is the difference between objects when light hits them. Moving or changing objects, as well as black and white colors, are best perceived with lateral vision.
Peripheral vision is less sharp than central vision. Its deterioration or absence is always associated with the presence of any pathologies of the visual apparatus.
Good peripheral vision is important for representatives of certain professions. To improve it, there are special sets of exercises.
Tunnel vision
Against the backdrop of the development of tunnel (tubular) vision, a person loses peripheral vision and loses the natural ability to see objects located on the sides. If this pathology progresses, the patient sees only those objects that are located directly in front of him.
More frequent detection of the disease in men is associated with physiological characteristics. Representatives of the stronger sex are characterized by focusing their gaze on the target, while the female half of the population has a clearer lateral view.
Tunnel vision is divided into 2 types:
- one-sided;
- bilateral.
Pathology can also be short-term and stable. In the first case, the disorder is associated with asphyxia and sudden changes in blood pressure (sometimes the anomaly is observed in astronauts and pilots). With a persistent disorder, the negative processes occurring in the retina of the eye become irreversible.
During the course of the disease, patients experience significant discomfort - they constantly bump into various objects, lose the ability to independently drive vehicles, or move without assistance not only on the street, but also at home.
With early diagnosis and effective therapy, the disorder can be eliminated and full vision can be restored. Long-term progression of the disease is fraught with many irreversible complications.
What can you do to improve your sleep quality?
1. Your pillow should be firm enough to keep your spine straight.
2. You should fill the space between your neck and mattress to keep your head and neck in a neutral position.
3. If you have shoulder pain, try placing a pillow in front of your body and resting your arm on it. This will help relieve the pain.
4. To avoid or get rid of hip pain, try placing a pillow between your knees to keep your hips level.
5. To avoid sagging breasts, try placing a small pillow under them to prevent the ligaments from being stretched. Or just sleep on your back.
6. If you wake up in the morning with a puffy face, puffy eyes and deeper wrinkles than last night, you should change your sleeping position. Sleeping on your back can prevent unwanted contact between your face and your pillow.
7. A good mattress is the most important thing when it comes to healthy and restful sleep. If you're a side sleeper, you'll want to choose a mattress with good shoulder and hip support and a medium to firm firmness. Foam mattresses and mattresses that can “remember” your body position (viscoelastic) are the best options as they are very effective at relieving pressure points.
Of course, other reasons can cause pain and swelling. Therefore, do not immediately think about your sleeping position; maybe the problem is completely different, and the wrong position simply aggravates the situation.
Swelling, for example, can be caused by drinking large amounts of water before bed and/or consuming salty and spicy foods.
In any case, sleep in a way that suits your body to avoid any consequences.
Causes
Ophthalmologists identify many causes of tubular vision:
- degenerative processes occurring in the retinal area;
- eye diseases (glaucoma, cataracts);
- mechanical injuries to the eyeballs;
- the presence of benign or malignant tumors in the visual system;
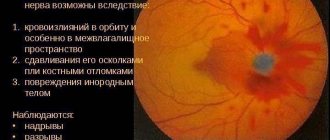
- inflammatory disorders in the optic nerve;
- frequent increases in intraocular pressure;
- oxygen starvation.
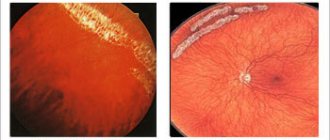
One of the common causes of abnormal vision is considered to be retinal pigment degeneration, a genetically determined disease that occurs with the formation of an annular scotoma. The pathology requires intensive treatment at an early stage of its development, in the absence of which it can cause complete blindness in the patient.
Loss of lateral visual function can occur after poor-quality laser photocoagulation, intoxication with alcohol, nitrogenous substances, or prolonged use of psychotropics. Sometimes the deviation is associated with the presence of inflammatory processes in the brain, multiple sclerosis, head injuries, and chronic diseases of the ENT organs.
Tube vision is not a hereditary disorder. Some ophthalmological diseases caused by genetics can provoke its appearance.
If there are pathologies that can cause limited vision, it is necessary to periodically visit a specialist. Only through regular medical examinations and timely implementation of medical measures can one resist an irreversible loss of vision.
Characteristic symptoms
The initial symptom of the disease is inadequate visual perception of the surrounding world, the absence of certain objects in the field of view. The defect cannot be eliminated using traditional optical products - lenses or glasses.
Further symptoms are supplemented by the following negative phenomena:
- narrowing of the visual field, leading to the inability to see objects located to the side;
- the formation of scotomas (dark spots) in front of the eyes, indicating severe damage to the optic nerve and active progression of the disease.
The patient gradually loses the ability to fully visualize the objects around him. There is no peripheral view. To examine objects on the sides, the patient has to constantly turn his head in the direction of their location.
In the absence of quality treatment, a person risks losing the ability to perceive light. At an advanced stage of the disease, visual function rapidly deteriorates (the patient may go blind for several weeks),
How can you get rid of the disease?
• taking psychotropic drugs; • nitrogen poisoning; • sudden changes in blood and intracranial pressure; • hypoxic brain damage;
• hereditary degenerative pathologies of the retina; • unprofessional laser vision correction; • open-angle glaucoma; • inflammatory diseases of the eyes, nose, throat; • compression of the optic nerve.
The disease occurs to a greater extent in males, since they are genetically predisposed to have a predominance of central vision, while women use the peripheral field of vision more and see what their gaze is not currently focused on.
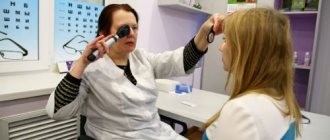
To make a diagnosis of visual field loss, it is necessary to undergo an ophthalmological examination and collect an anamnesis.
In the future, the person will undergo special testing, the results of which will determine the range of vision. Having collected data on symptoms, based on the results of the study, the doctor will identify the reasons that led to the narrowing of the field of vision and prescribe appropriate treatment.
A person with such a vision defect will need help from loved ones at first. Because the treatment may be long-term. It will be necessary to remove from the rooms all objects that a person might stumble upon. Only with time will he be able to get used to it and turn his head in such a way as to see the world around him.
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis requires anamnesis and a detailed ophthalmological examination. To determine the volume of the visible area, special testing is performed. To clarify the existing diagnosis and the stage of the disease, the patient is prescribed perimetry and tonometry.
Treatment of tubular vision requires an integrated approach. The main objectives of the therapeutic course are:
- suppression of inflammatory processes;
- elimination of swelling;
- normalization of blood flow in the optic nerves;
- improving the conduction of nerve impulses.
After eliminating the cause of the pathology, specialists take measures to help restore peripheral vision or maintain the existing range of visibility. The most effective are medications, physiotherapeutic treatment, laser correction, electrical stimulation, and surgery. In addition to the main therapeutic measures, courses with vitamin preparations containing substances important for the visual system (Taufon, Lutein Forte, Emoxipin) are indicated.
Modern researchers are actively developing new treatments for tunnel vision, including special glasses that help restore lateral vision.
Prevention
Patients with an increased risk of loss of peripheral vision are recommended to be examined by an ophthalmologist 1-2 times a year. Prevention is also indicated for men and women over 35 years of age, persons with confirmed glaucoma, and cataracts. To reduce the risk of developing a dangerous disorder, you should minimize visual stress, avoid eye injury, and find time every day to perform special exercises that support the health of your visual organs.
0 0 vote
Article rating
What can you do to improve your sleep quality?
1. Your pillow should be firm enough to keep your spine straight.
2. You should fill the space between your neck and mattress to keep your head and neck in a neutral position.
3. If you have shoulder pain, try placing a pillow in front of your body and resting your arm on it. This will help relieve the pain.
4. To avoid or get rid of hip pain, try placing a pillow between your knees to keep your hips level.
5. To avoid sagging breasts, try placing a small pillow under them to prevent the ligaments from being stretched. Or just sleep on your back.
6. If you wake up in the morning with a puffy face, puffy eyes and deeper wrinkles than last night, you should change your sleeping position. Sleeping on your back can prevent unwanted contact between your face and your pillow.
7. A good mattress is the most important thing when it comes to healthy and restful sleep. If you're a side sleeper, you'll want to choose a mattress with good shoulder and hip support and a medium to firm firmness. Foam mattresses and mattresses that can “remember” your body position (viscoelastic) are the best options as they are very effective at relieving pressure points.
Of course, other reasons can cause pain and swelling. Therefore, do not immediately think about your sleeping position; maybe the problem is completely different, and the wrong position simply aggravates the situation.
Swelling, for example, can be caused by drinking large amounts of water before bed and/or consuming salty and spicy foods.