Varieties
There are 4 types of exophthalmos:
- Permanent , in which neoplasms appear after an injury to the hand, eyes or brain herniation.
- Pulsating , after injury to the eyes and skull.
- Intermittent , manifests itself after tilting the head.
- Progressive malignant , occurs due to dysfunction of the thyroid system.
Also, it can be one- or two-sided , pronounced or inconspicuous .
Edema exophthalmos
Exophthalmos itself is not a disease, it is only a symptom . Therefore, in order to successfully treat the disease, it is worthwhile to better understand the true reasons that led to the appearance of this deviation from the norm.
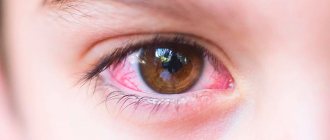
Attention! Edema exophthalmos is one of its most dangerous forms, in which the eyeballs literally dislocate from the sockets , which leads to disability of the patient.
Complex forms of protrusion are extremely rare . Most often, everything is limited to quite severe swelling and protrusion of the eyeballs.
Edema exophthalmos develops in patients whose age exceeds forty years. It can occur equally in both men and women. Patients often complain of increased intraocular pressure.
Edema exophthalmos can be either unilateral or bilateral .
Diagnostics
To diagnose this type of disease, the latest equipment available in modern eye clinics is used.
With the help of this kind of equipment, it becomes possible to determine intraocular pressure during exophthalmos, as well as the degree of vascular damage, which necessarily occurs during protrusion phenomena.
Of great importance is an external medical examination , which can and should be performed by a professional doctor.
Symptoms
If we talk about the symptoms of this disease, we can distinguish the following types :
- Severe pain that can only be relieved with severe analgesics or even drugs. This kind of pain is explained by the fact that as a result of exophthalmos, the nerve fibers are compressed. They are the ones who give the body a signal in the form of pain.
- Edema of the orbital eyelids. Also, the phenomenon of edema can spread to the periorbital area. This kind of edema is quite developed in order to instantly attract the attention of a doctor.
- Complete or partial loss of visual functions. This type of loss is due to the fact that as a result of protrusion, multiple optic nerves are compressed in order to make significant adjustments to the patient's visual pattern.
Treatment
Unfortunately, medicine does not have adequate methods for treating exophthalmos. This disease poses a significant danger to its carrier. Therapy should be carried out by an experienced ophthalmologist, as well as an endocrinologist. Most often, drugs are prescribed that stabilize the patient’s hormonal levels. Here we are talking about prednisolone , which is prescribed in dosages reaching 1200 mg.
The prescription of drugs that contain the active substance “thyroidin” is also of great importance. If we talk about prednisone, then this medication is necessary to relieve the inflammatory process, which always manifests itself with exophthalmos. Thyroidin is able to normalize the functions of the thyroid gland , which is also of great importance for the successful fight against symptoms of diseases.
It is worth noting the importance of local treatment, which consists of prescribing various kinds of eye drops, as well as local drops. Here, most often, we are talking about prescribing a series of hormonal drops, such as Dexamethosone , which help relieve inflammatory processes.
Photo 1. Dexamethasone eye drops 0.1%, 10 ml, .
Also very popular is the use of ointments that contain an antibiotic. Let's say tetracycline ointment.
Treatment of thyroid eye disease
If thyroid eye disease is left untreated, the inflammation should resolve on its own within a few months or years. However, symptoms caused by swelling (such as bulging eyes) may remain permanent because some of the tissue that has been stretched may not always return to its original shape. The goal of treatment is to limit the damage caused during the period of inflammation. Treatment of thyroid eye disease requires joint efforts of an ophthalmologist and an endocrinologist.
Drugs for the treatment of thyroid eye disease
At an early stage of the disease and when the disease is mild, artificial tears are used, but they may not be enough. As the disease progresses, you may need immunosuppressants, a family of drugs that suppress the immune system that produces abnormal antibodies. Commonly used immunosuppressants are steroids such as prednisolone. You may also need to take certain other medications (omeprazole protects the stomach lining) to counteract some of the more common side effects of steroids. If you have a very severe illness, your doctor may prescribe a course of steroids given through an IV.
Surgical treatment of thyroid eye disease
About 5 in 100 people with thyroid eye disease have a severe form of the disease, which causes the optic nerve (the connection from the back of the eyeball to the brain) to shrink. This can damage your entire vision. In this case, the doctor may decide to organize decompression. This is a procedure that creates space in the orbit for inflamed tissue to spread. This relieves pressure on the nerve. In some cases, surgery may be performed to move the eyeballs back. Sometimes surgery to remove pulled muscles allows you to return everything to its place. If there are problems with elongated tissues that need surgical correction after the inflammation has passed, surgery is done in the orbit and then on the muscles.
Other Treatments for Thyroid Eye Disease
If double vision (diplopia) develops, your doctor may prescribe modified glasses that block vision from one eye; or cover your eyes with a special prism to stop diplopia. Radiation therapy (treatment by exposure to a radioactive substance) may be used for some people. The goal is to reduce swelling in the eye. It is used along with other forms of treatment. There are a number of new treatments for thyroid eye disease that are being studied. In addition, the doctor will treat abnormal thyroid function. For this purpose, medications (radioactive iodine) or thyroid surgery will be prescribed.
Advice for patients with thyroid eye disease: 1) Smoking worsens the course of the disease, so give up this bad habit. 2) Bright light can irritate the eyes, in which case sunglasses will be useful. 3) If you drive a car and have double vision, be sure to control it with prism glasses.
Complications of thyroid eye disease. Most people do not develop permanent complications. However, they do occur in some people, especially those whose treatment is delayed or whose disease is severe. More often, complications occur in older people, as well as in smokers and patients with diabetes. Possible complications: 1) damage to the cornea; 2) constant squint or double vision; 3) damage to the optic nerve, which leads to decreased vision or color perception; 4) unsightly appearance.
Complications due to treatment: 1) side effects due to the use of immunosuppressive drugs. 2) side effects due to surgery: double vision (in 15 out of 100 people with thyroid eye disease); loss of vision (less than 1 in 1,000 people with thyroid eye disease).
Thyroid eye disease is a long-term illness. The period of inflammation lasts from several months to several years (usually about two years). However, for most people the condition is mild and requires only the use of artificial tears and regular eye exams. Then this disease goes away on its own. For patients with severe thyroid eye disease, the prognosis depends on how early the diagnosis is made and how intensively treated. About 1 in 4 people will eventually have reduced vision.
Thyrotoxic exophthalmos
Thyrotoxic exophthalmos is a consequence of a disease called thyrotoxicosis . It is important to note that this type of disease most often develops in women whose age exceeds fifty years. The phenomena of protrusion are often accompanied by redness of the lower eyelid, as well as inflammatory processes that occur in the eye orbit.
A huge number of visual and computer techniques are used for diagnosis. In particular, the patient is sent to undergo ultrasound, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging . All these methods can provide true information about the condition of the patient's fundus, as well as the condition of the orbital and periorbital areas of the eyes.
Signs
Symptoms that can provoke this disease:
- Increased fatigue and irritability. These symptoms should be classified as general, which are the result of a serious illness.
- tremors .
- Swelling of the lower eyelid.
- Redness of the lower eyelid.
- Serious changes in the fundus of the eye, which lead to increased intraocular pressure.
- Increased sleepiness.
- Serious pain syndrome, which consists of unbearable dull or throbbing pain that may be characteristic of this disease.
How to treat thyrotoxicosis
Treatment of thyrotoxic exophthalmos can be carried out using a wide range of different methods. No method can completely eliminate this type of disease. The first and most common method is that the doctor prescribes conservative treatment , which can and should include a wide range of medications.
Medicines
An endocrinologist may recommend using a common and very inexpensive drug called L-thyroxine. This drug is used to treat endocrine diseases and is successfully used in patients who have certain thyroid diseases. As a result of the influence of this drug, the background of thyroid hormones , and the phenomena of exophthalmos may decrease.
In addition, an ophthalmologist can prescribe medications that can reduce swelling and inflammation. Here we are talking about local therapy. As such therapy, Dexamethasone is prescribed, which successfully fights inflammation.
Treatment methods for thyroid diseases
It is important to begin treatment of thyroid diseases as early as possible, when the morphological changes in the gland are still minor. Medical assistance at this stage will allow you to get a quick and noticeable effect. In order not to miss the development of the disease, consult a doctor when the first alarming symptoms appear. It is also advisable to undergo an annual preventive examination.
Drug treatment
Treatment of hormonal disorders in the thyroid gland is carried out using drug therapy.
Surgery
In some cases, surgical treatment is indicated. A thyroidectomy (removal of the thyroid gland) is performed. Sometimes only a lobe of the thyroid gland is removed (hemithyroidectomy). Removal of the thyroid gland is required when malignant neoplasms are detected, a large goiter that impairs breathing and swallowing, thyrotoxicosis that cannot be treated conservatively, as well as in some other cases.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Endocrine exophthalmos
Endocrine exophthalmos is associated with a kind of imbalance in the functioning of the endocrine glands . As a result of increased production of thyroid-stimulating hormone, you can often experience the phenomenon of protruding eyeballs.
Endocrine glands can increase or decrease the production of various hormones . In case of increased activity, this can lead to serious deviations in human life.
If we talk about the symptoms of this disease, they show great similarity with those symptoms that were described in the case of thyrotoxic exophthalmos . The diagnostic methods for this disease are also similar to those described above.
If we talk about treatment methods, then in cases of endocrine exophthalmos, a course of corticosteroid therapy . There is also radiotherapy , which involves administering high doses of radiation. In addition, surgical treatment methods are used. These include excision of the eye orbit , as well as its decompression .
Methods for diagnosing thyroid diseases
If thyroid dysfunction is suspected, a set of diagnostic procedures is carried out, which includes, in addition to examination by an endocrinologist, a number of laboratory and instrumental studies. The specific list of studies is determined by the attending physician.
General blood analysis
A general blood test is a mandatory diagnostic minimum test, which is prescribed for almost any disease. A general blood test will help the doctor assess the impact of thyroid disease on the general condition of the body.
More information about the diagnostic method
General urine analysis
A general urine test, as well as a clinical blood test, is a mandatory diagnostic minimum test.
More information about the diagnostic method
Blood chemistry
The purpose of a biochemical blood test is to identify changes in organs and tissues that may accompany thyroid disease. Indicators such as total protein, urea, cholesterol, bilirubin, liver enzymes, and creatinine are assessed.
More information about the diagnostic method
Blood test for hormones
A blood test for hormones is one of the main methods for diagnosing thyroid diseases. First of all, indicators such as free T4 (thyroxine), antibodies to thyroglobulin (AT-TG), TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) are assessed. These three tests constitute a screening study that identifies thyroid pathology. The detailed study includes other indicators in addition to those mentioned.
More information about the diagnostic method
Analysis for markers of autoimmune diseases
A blood test for markers of autoimmune thyroid diseases primarily includes indicators such as antibodies to thyroglobulin (anti-Tg) and antibodies to thyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO).
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland allows you to determine the size of the gland, as well as the presence of nodes in it.
More information about the diagnostic method
Radiothermometry
Radiothermometry can detect areas of increased temperature in the thyroid gland. Higher temperature values indicate an increased intensity of metabolic processes, which is typical for malignant neoplasms.
More information about the diagnostic method
Other instrumental studies
In case of an unclear clinical picture, additional thyroid examinations may be prescribed - computed tomography (MSCT), MRI, scintigraphy.
Thyroid puncture
A puncture of the thyroid gland is performed, the resulting material is examined under a microscope, which makes it possible to study changes in the gland tissue.
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
Pulsating exophthalmos
With pulsating exophthalmos, a significant disturbance occurs in the vascular bed. This kind of disorder manifests itself in the fact that vascular tone in the cavernous sinus is upset. Very often, this kind of disease can be observed in children who have a disease called cerebral hernia . If we talk about diagnostics, the following types are used:
- Ultrasound.
- CT scan.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
The same methods are used as for the types of exophthalmos mentioned above.
If we talk about the main symptoms of this disease, they are similar to the symptoms of thyrotoxic exophthalmos, however, with pulsating protrusion, the patient’s vision does not disappear.
It is disrupted so that the patient has enormous visual discomfort. Often with this disease, we can talk about nystagmus of the eyeballs.
Therapy
The disease is treated with radiotherapy . It is important to use large enough doses of radiation to achieve a significant effect. Small doses of radiation are not able to have a significant effect on this disease.
A radical method in the treatment of pulsating exophthalmos is the method in which the so-called ligation of the carotid artery . As a result of this type of fixation, the pressure on the eyeballs is reduced, which means the symptoms of bulging are reduced.
However, with this surgical method of exposure, serious side effects may occur in the form of increased intraocular pressure. Therefore, the surgeon is obliged to weigh all the pros and cons before performing this type of operation in order to avoid serious complications in the form of complete or partial loss of vision.