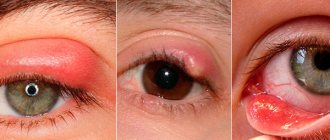
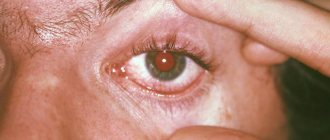
Types of fungal eye diseases
Oculomycosis is a fungal infection of the eyes. There are several types:
- Candidal blepharitis. The disease spreads only on the eyelids.
- Scleritis. A fungal infection affects the sclera and multiplies successfully in it.
- Conjunctivitis. The mucous membrane is affected.
- Keratitis. The disease affects the cornea.
- Endophthalmitis. The avascular gelatinous substance that fills the eye cavity suffers.
On a note! The most unsafe diseases of a vital organ are those that can enter the sclera and vitreous body. Microorganisms can infect fragile capillaries and nerve endings.
Types of mycoses on the eyes
This infection has several pathogens. Mycosis is divided into several types, depending on the type of fungus.
- Candidomycosis. This type of mycosis is in the form of yeast-like fungi. There are a lot of spores of these fungi in the environment, and they are also found in the microflora of the human body.
- Actinomycosis. The causative agents are considered to be radiant fungi similar to anaerobic bacteria. This type of mycosis is the most common. Actinomycetes are found everywhere: the mucous membrane, in the gastrointestinal tract of humans, in many animals, and spores can also be in the air or on plants.
- Sporotrichosis. Caused by dimorphic fungi. Infection occurs through plants and soil. Carriers can be both people and animals.
- Aspergillosis. The conjunctiva or skin is affected by mold fungi.
Causes
This type of disease can occur as a result of microorganisms from the environment entering a vital organ.
Also, infection from mycotic foci located on the surface of the body can penetrate into nearby tissues.
Routes of infection
Depending on how the fungi got into the eyes, there are 2 ways of infection:
- endogenous route of infection;
- exogenous route of infection.
The first route of infection is based on the fact that the pathogen spreads from other affected parts of the body. Distribution occurs through blood circulation. The endogenous or hematogenous route of infection is considered the most dangerous and is quite rare.
Causes:
- otitis;
- sinusitis;
- onychomycosis;
- frontitis.
The disease may be accompanied by candidiasis of the nasal and oral cavity.
Exogenous or contact occurs as a result of the penetration of the fungus into the eye tissue from the environment.
Sources of infection:
- use of unsterile instruments;
- mycosis in the eyebrow area;
- dirty hands;
- fungal infections in the form of inflamed spots on the surface of the body.
The household route of infection can occur as a result of the ingestion of spores of certain fungi.
Who is at risk
The distribution area of fungi is soil, so people living in villages and urban-type settlements are most often susceptible to fungal eye diseases. The risk group includes such occupations as workers in mills, elevators and feed mills. While drying grain, foreign bodies and dust may get into your eyes.
Teenagers and schoolchildren are also at risk because they are in large groups.
How to treat eye fungus
For eye infections, medications with antifungal action are prescribed
Eye fungus will not go away on its own. He will need treatment anyway. It is based on the patient's use of antifungal medications. In most cases, patients with this diagnosis are treated as inpatients.
Treatment of fungal infection of the visual organ and area around the eyes is based on several principles:
- To enhance the effect of therapy, the simultaneous use of systemic and local drugs is required. Doctors prescribe tablets and solutions for intravenous administration. Eye injections, drops and ointments are also required;
- Anti-inflammatory therapy, which is based on glucocorticoids, improves the patient's condition. It is used at almost all stages of development of infection in the organ of vision;
- In particularly difficult cases, surgical treatment of inflamed tissues located inside the visual apparatus is prescribed.
On the recommendation of the attending physician, the patient begins to fight the infection with medications. The doctor should tell the patient in detail about how to treat the fungus.
Amphotericin B, Itraconazole and Griseofulvin help suppress the activity and proliferation of mycosis in the eye area. Nystatin is also recommended for use if the patient has been diagnosed with a candidiasis infection.
Eye drops with an antifungal effect must be combined with systemic drugs that fight the pathogen from within the body.
Surgery is prescribed for a fungal infection only if the patient has corneal ulcers or serious damage to the intraocular tissues. Keratoplasty is performed if local treatment does not bring a positive result, and the patient’s condition only worsens.
Symptoms
The incubation period for the development of the disease depends on how strong the person’s immunity is. The rate of development is influenced by the general state of health and the presence of pathologies. It can take 10 hours from infection to manifestation of the disease, in some cases up to 3 weeks.
Signs:
- painful sensations inside the eye;
- presence of burning, may itch;
- sharp decrease in vision;
- Various types of ulcers can be seen on the eyelids, the organ also swells, and redness is often observed;
- purulent discharge.
A person may feel a haze before the eyes, which prevents them from clearly viewing surrounding objects. Redness of the white, various inclusions in the eyeball and strong tearing also indicate the penetration of a fungal infection.
In eyes
Mycosis of the eyeball primarily affects the conjunctiva. This is the entire surface of the eye, with the exception of the cornea. The fungus can be spread with dirty hands.
Symptoms of mycosis:
- noticeable redness in the eyeball;
- swelling;
- increased lacrimation;
- discharge with pus.
The cornea is a circular, avascular, transparent tissue. If toxins get onto the front of the eye surface, its surface immediately becomes red and an increased pulsation is felt, causing pain. As a result, vision decreases, a fear of light develops, and the cornea becomes cloudy.
For centuries
Fungal blepharitis or mycosis of the eyelids occurs as a result of the activity of fungi of the genus Candida. The disease most often affects a weakened body. Under the influence of fungi, the edges of the eyelids thicken, which leads to eyelash loss. A crust becomes noticeable along the edge of the eyelids, which peels off and falls off. When scratching, scars and ulcers can form.
The fact that fungus has entered the eyes is indicated by such signs as: rapid blinking, a feeling of dryness in the eye, frequent white discharge that is located in the corners of the eyes.
Symptoms of a fungal infection
Fungus in the eyes gives symptoms specific to this disease. Knowing them, a person can independently suspect its development and promptly seek medical help. The onset of the clinical picture of the disease begins when the infectious agent enters the visual organ from lesions on the body or the environment. If the fungus is not treated, it will continue to grow. The disease itself will become advanced, which will significantly complicate its treatment.
In eyes
Penetration of toxins into the deep layers of the visual apparatus leads to the development of conjunctivitis
The rapid spread of mycotic infection leads to damage to the cornea, lacrimal sacs and the eyeball itself. At the same time, the number of pathogenic microorganisms actively increases, resulting in the inflammatory process. With such a course of the pathological process, a person is worried about the following symptoms:
- Redness and inflammation of the eye membrane;
- The appearance of purulent masses and increased tearing;
- Sharp pain in the eyes and a strong burning sensation;
- Covering the eyeball with a white coating;
- Sensation of a foreign object in the eye.
Additionally, conjunctival ulceration occurs. This is caused by the penetration of toxins into the deep layers of the visual apparatus. If the disease leads to purulent-tear conjunctivitis, then the threat of damage to the blood vessels of the eyes increases several times. This complication is dangerous because it causes damage to the vitreous body.
For centuries
Fungus on the eyelids of both eyes is considered the most common mycosis, which affects the visual apparatus. In most cases, it is caused by a pathogen that belongs to the genus Candida. The viability of this pathogen is regulated by the human immune system. When the body's defenses decrease, the fungus becomes activated and multiplies rapidly.
Fungal infection of the eyelids can be identified by the following symptoms:
- The appearance of scales at the very base of the eyelids;
- Redness of the infected area;
- Filling the corners of the eyes with whitish masses;
- Itching;
- Loss of eyelashes;
- The appearance of ulcers and pustules on the eyelids.
If you discover such symptoms, you must immediately contact a specialist. He will select adequate eye therapy that will help eliminate the symptoms of the disease. With the correct diagnosis and approach, treatment will be successful.
What it is?
Fungal blepharitis Source: drvision.ru One of the varieties of various inflammatory eye diseases is blepharitis.
Accompanied by inflammatory processes along the edges of the eyelid. The disease affects various segments of the population, regardless of gender and race. It is difficult to cure and can last for many years. Manifests:
- peeling of the skin surface and the appearance of plaque on the skin of the eyelids;
- sticking together of eyelashes with yellowish or greenish discharge;
- increased lacrimation;
- the formation of peeling scales in the head and eyebrows.
The pathogenesis of the pathology consists of the development of numerous factors. Staphylococcal, fungal or tick-borne infections and microbial colonies on the surface of the eyelid. Their metabolic products - enzymes and toxins - cause tissue destruction.
Chronic meibomitis and seborrheic dermatitis aggravate this process. Pathology can be caused by many reasons, but the main causative agent is considered to be the eyelash mite, which lives on the skin and is part of the skin microflora - the acne gland (Demodex folliculorum).
The development of the disease and its progression leads to multiple pathologies:
- inflammation and loss of optical transparency of the vitreous body of the eye;
- formation of induced astigmatism; corneal perforation.
Inflammation of the eyelids
In order to understand what blepharitis is, you need to have a good understanding of how the human eyelid works and why, what functions it performs. The main task of the eyelid is to protect the eyeball from drying out and adverse environmental influences, such as wind, sun and even just dust.
This determines its structure:
- the upper layer of the eyelid is covered with skin, along the edge of which there are eyelashes;
- in the ciliary bulbs and between them there are exits of the sebaceous glands;
- the second layer consists of muscles, which allows you to close/open your eyes;
- The plate connecting the upper and lower eyelids is located even deeper;
- The plate contains the so-called lacrimal glands.
The skin around the eyes is so thin that its thickness is only 0.3 - 0.5 mm. Subcutaneous tissue is loose. This structure is designed to ensure the mobility of the eyelid, but because of this it is easily susceptible to swelling and injury. It is this feature that makes plastic surgery possible.
Diagnostics
You cannot independently determine the complexity of the lesion. Only a consultation with an ophthalmologist and dermatologist will help make an accurate diagnosis.
To identify the pathogen, doctors prescribe bacteriological culture.
An accurate diagnosis is made as a result of the following instrumental studies and diagnostics in laboratories:
- Refractometry. The optical system of the eye is examined. As a result of the study, the refractive power is determined. An automatic refractometer is used to determine it.
- Study of visual acuity. For diagnostics, an optotype table and a special projector are used. With fungal infection, visual acuity decreases below v=1.
- Ophthalmoscopy. A fundus lens or ophthalmoscope is used to examine the fundus of the eye.
- Biomicroscopy. As a result of a non-contact method using a binocular microscope and a slit lamp, individual ocular structures are examined.
- Angiography. Photography or video is being taken. As a result of the procedure, the quality of the vessels is assessed.
Treatment
Fungal infections are less treatable than bacterial infections. This is due to the structure of the fungal cell, which is in many ways similar to the structure of human cells. Fungi develop strong immunity to modern fungal drugs.
Do not think that antifungal drugs are completely harmless. Therefore, self-treatment is strictly prohibited.
Before drug treatment is prescribed, it is important to conduct a series of laboratory tests to accurately determine the diagnosis.
Whether the treatment was chosen correctly or not can be judged within a week from the start of treatment. Therefore, you must strictly follow the doctor's instructions.
Medication
Depending on the severity of the disease, doctors prescribe certain drug therapy.
Antibiotics are used to treat keratitis. In addition, the doctor prescribes antiviral and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Drug treatment is prescribed depending on what kind of infection has gotten inside.
Folk remedies
The remedies used by traditional healers are not inferior in quality to pharmacological drugs and are used to treat fungal diseases.
- Children often experience eye inflammation. For comfortable treatment, you can use herbs. A decoction of oak bark, St. John's wort, chamomile or calendula will help relieve inflammation. You need to rinse your eyes every hour.
- Baking soda will help quickly relieve the symptoms of inflammation, but it is powerless against mycosis. To wash the eyes, take 1/3 tsp. soda and dilute it in 100 ml of warm water.
- A bag of used tea leaves also helps in the fight against eye diseases. It should be applied warm to the closed eye. The procedure should be repeated at least 4 times a day.
To avoid diseases, it is important to adhere to preventive measures.
Inexpensive but effective drugs
To avoid relapse, it is important to strictly follow the recommendations prescribed by the ophthalmologist. Drug therapy is usually carried out at home. Patients with complications are admitted to the hospital.
Conservative treatment involves taking tablets orally and using drugs applied to the surface of the body. These include ointments and drops.
- Okomistin. A drug against mycosis. The composition includes miramistin. Drops against mycosis are prescribed mainly after planned operations. Also used in cases of infection. Treatment lasts a week. A similar drug is Dismistin.
- Floconazole ointment. Fungal infection of a vital organ can be treated with this ointment. It needs to be placed under the lower eyelid. Duration of treatment – 2 weeks.
- Clotrimazole ointment. Use late in the evening as short-term blurred vision may occur. A cotton swab is used to apply the ointment around the eyes.
Folk remedies to speed up treatment
At the initial stage of development of eye fungus, you can try to stop its spread using traditional methods. The following unconventional means can cope with this task:
- Spilled tea. Freshly brewed tea is not suitable for treatment, since it does not have time to form substances useful for this procedure. The drunken drink is used for compresses and lotions. They can be done several times a day. A folk remedy will not help to completely cure a fungus. But with its help it will be possible to reduce the severity of the symptoms of the disease;
- A decoction of calamus and yarrow. To use this product, you need to mix the plant material in equal quantities. After 2 tbsp. l. The resulting mass needs to be poured with 500 ml of boiling water. After cooling, the resulting decoction can be used to wash the eyes;
- Fresh cucumbers. Another proven and safe method of treating eye fungus. To prepare this remedy, you need to peel and chop a fresh vegetable. Afterwards, pour 500 ml of boiling water. It is recommended to add 0.5 tsp to the same mixture. soda The infusion should stand for 1 hour. Afterwards, you need to moisten a clean swab and apply it to the sore eye for 15 minutes.
Folk remedies must be combined with drug treatment. They are used until the patient achieves recovery.
Useful video
From this video you will learn more about how fungal skin diseases occur:
Whatever the cause of such a disease, it is necessary to begin treatment as quickly as possible, and it is not recommended to use any means at your own discretion: the entire treatment process must be supervised by specialists .
Fungus on the eyelids is a common disease that causes discomfort and discomfort in the eye area. It occurs for many reasons, one of which is poor-quality eyelash extensions and non-compliance with hygiene rules.
Types of eye fungus
A fungal infection that actively develops in the eyes comes in several types. It can be caused by the following pathogens:
- Aspergillosis. These are molds that can live on human skin. They successfully multiply on the mucous membranes of the visual organ and only occasionally penetrate into the depths of the eye;
- Candidomycosis. A yeast-like form of fungus that lives in the human body or in the surrounding area;
- Actinomycosis. Fungi of this species live in large numbers in the body. They actively reproduce when they move to the mucous membranes;
- Sporotrichosis. They can become infected through contact with contaminated soil or animals. People can also be carriers of the fungus.
A fungus of any of these types finds the least protected place in the eye area and penetrates the organ through it. Afterwards, it begins to multiply, thereby contributing to the development of an infectious disease.
Forecast
The sooner you start treating the disease, the more effective the prescribed treatment will be and the result will not be long in coming.
You should prepare yourself for the fact that fungal therapy takes a long time; you should not count on immediate results.
Possible complications
If fungal eye infections have reached an advanced stage, the development of complications is possible.
In patients whose keratitis is not treated, corneal perforation may occur, followed by surgery to perform a corneal transplant.
Prevention and possible complications
The presence of fungus on the body is under the control of the immune system, but with the weakening of the body’s defenses, active reproduction begins, resulting in eye damage. The development of the disease can be prevented by preventive measures aimed at maintaining immunity:
- adhere to a healthy lifestyle;
- do not drink alcohol, cigarettes or drugs;
- proper nutrition;
- maintaining hygiene;
- walks in the open air.
In the absence of proper care and timely treatment, unpleasant consequences are possible, which will require more effort and time to combat. The following complications are possible:
- deformation and scarring of the eyelids;
- sepsis;
- loss of eyelashes;
- in rare cases, meningitis.
To avoid serious problems, treatment should be started on time. Self-medication is considered dangerous, as it aggravates an already serious condition.
Ketoconazole
The drug is available in the form of an ointment, as well as tablets, from which antifungal eye drops are made as prescribed by a doctor.
The properties of the solution allow you to get rid of most pathogens. The active component is ketoconazole, which is an analogue of imidazoledioxolane. The substance has fungistatic and fungicidal properties against pathogenic fungi.
Eye drops are recommended to be used only as an aid. For fungal diseases, it is necessary to take the medication orally.
The recommended dosage of the drug for children and adults should not exceed 1 tablet per day. To prepare the drops, you must first grind the pill to a powder state. The finished powder must be combined with 5 ml of boric acid (concentration 4.5%) and stirred until the medicine is completely dissolved. The resulting liquid is dropped into the eyes at least 4-5 times a day.