What is strabismus?
Strabismus, or strabismus, is an eye pathology accompanied by deviation of the visual axis from the point of fixation common to both organs of vision. In other words, one eye squints to the side.
In some cases, pathology develops in both visual organs.
With strabismus, it is difficult for the patient to focus on one object and concentrate on it, the resulting image doubles and blurs, and visual acuity decreases. Symptoms of strabismus may vary depending on age. Strabismus in a child under 7 years of age becomes noticeable due to the following signs:
- he constantly tilts or turns his head when trying to look at something;
- the child comes across various objects without noticing them;
- asynchronous and asymmetrical movement of the eyeballs.
It is more difficult for a child at a young age to describe his condition, to tell how he sees and what he feels. Parents should monitor his condition, whose task is to immediately show the baby to a doctor if the first symptoms of strabismus are detected. Strabismus in children of primary school age and in adults is accompanied by such symptoms as:
- rapid fatigue of the visual organs;
- blurred vision;
- dizziness after working at the computer or reading;
- increased sensitivity to bright light;
- diplopia.
A child over 7 years old can describe these symptoms independently. A schoolchild, for example, may complain to his parents about discomfort in his eyes after school or lessons. His complaints should not be ignored.
The appearance of at least one of the above symptoms should be a reason for examination.
Symptoms
A patient with strabismus will complain of blurred vision. It will manifest itself as diplopia (double vision), since in the absence of parallelism of the visual axes, binocular vision cannot be ensured, because the images from the retinas of both eyes do not overlap each other.
Another common complaint is decreased visual acuity in the deviated eye, which can be both a cause and a consequence of strabismus.
In addition, all these visual disturbances, which bring discomfort, can cause headaches, dizziness, asymmetry of tension in the neck muscles as a result of permanent attempts to change the position of the head for a clearer view, etc.
Strabismus in children: causes
Strabismus can be either congenital or acquired. The first type is provoked by a variety of factors:
- heredity;
- alcoholism, drug addiction, smoking and poor nutrition of women during pregnancy;
- the birth of a child prematurely;
- congenital pathologies of the visual organs;
- Cerebral palsy.
The causes of acquired strabismus in childhood are:
- refractive errors such as farsightedness and nearsightedness;
- stress;
- heavy eye strain at school;
- infectious eye diseases;
- eye injuries.
Pathology such as strabismus can also be caused by other reasons. Strabismus can occur in newborns; this phenomenon is considered normal.
If symptoms of the disease are observed in a baby after a year, then it is necessary to urgently begin treatment.
Let's find out how you can cure strabismus in a child.
How to cure strabismus in children?
Strabismus in children can be cured using hardware methods and gymnastics. However, for this you need to consult an ophthalmologist in a timely manner. He will select therapy for the patient, and parents will need to strictly follow all the doctor’s instructions. Whatever method of treating strabismus is used, any therapeutic course will consist of several stages:
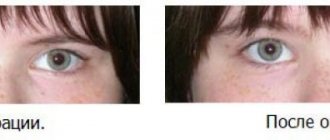
- First, amblyopia—lazy eye syndrome—is treated. At this stage, it is necessary to bring visual acuity to normal. To do this, the patient is prescribed to wear glasses, one lens of which is sealed. For children, special stickers with interesting images are used. In parallel, hardware treatment is carried out.
- At the second stage, the synchronicity of the movement of the eyeballs is restored. Instruments, devices and computer programs help with this.
- The essence of the third stage is to restore the muscular balance between the eyes. If the muscle damage is very severe, surgery may be required at this stage of treatment. Often, in childhood, you can tone the eye muscles at home. For this, the doctor will select a set of suitable exercises.
- At the fourth stage, binocular vision is restored. By the last stage of treatment, the eyes should already be in the correct position. Stereoscopic vision is restored through hardware procedures.
Hardware methods for correcting myopia
One of the effective non-surgical ways to correct refractive errors is hardware correction. Most often this method is used in relation to children and adolescents. Procedures of this kind are painless and are carried out in courses.
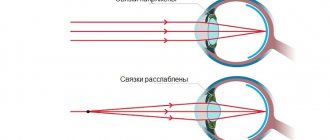
With hardware correction, stimulation is carried out using laser radiation, electromagnetic field, light, ultrasound. The method allows you to slow down the development of myopia, as well as improve accommodation, relieve tension in the eye muscles, and normalize blood circulation in the structures of the eye.
This method is especially effective for mild myopia, but in other cases, hardware procedures can slow down the pathological process. Often, hardware correction is carried out in combination with drug therapy, which gives a more pronounced result. You can undergo hardware treatment for myopia in our eye clinic: https://www.okomed.ru/apparatnoe.html.
When is strabismus in children treated surgically?
This treatment method is used only as a last resort, when conventional therapy has failed. Also, surgery is prescribed at the stage of restoring the functionality of the eye muscles using conservative methods. The procedure is carried out using a laser machine. For very young children it is done under general anesthesia. Schoolchildren are operated on under local anesthesia. During the operation, the surgeon either relaxes the muscle that holds the eye in the wrong position, or strengthens it if it does not hold the eyeball well.
The procedure is painless. The child will be able to leave the hospital the very next day. But he will remain on sick leave for 2-3 weeks. During this period, you will need to regularly visit your doctor and put antibiotic drops in your eyes. This treatment method is rarely prescribed to children. Let's find out whether strabismus can be cured without surgery if the pathology arose in adulthood.
Preparation for the procedure
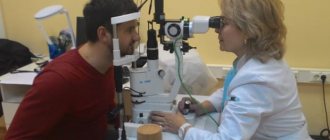
The patient should prepare properly; all recommendations are usually voiced by the doctor before the operation. Using a diagnostic program, preliminary data is analyzed and the optimal result that should be obtained after correction is calculated. The ophthalmologist decides together with the patient which program to use.
After the vision test, the patient is prepared for the procedure. The area around the eyes is cleaned with special products. After this, the patient is invited to the operating room, where the correction will be carried out. Next, special drops with an anesthetic effect are dripped for pain relief. After that, an expander is installed on the eyelids, which makes it possible to keep the eyes open throughout the entire correction process.
The doctor adjusts the laser based on the information obtained during the examination. The microkeratome is placed on the surface of the eye. During operation of the device, the patient feels slight pressure, but not pain. The doctor turns the flap to the side with great care and asks the person to focus his gaze on the red light bulb. In this case, the patient is prohibited from moving his eyes. The procedures are painless and effective with results that last for many years!
How to cure strabismus in adults?
First, let's look at the causes of strabismus that occurs in adulthood. Strabismus in an adult most often appears as a result of:
- cataracts;
- thorn;
- macular degeneration;
- optic nerve atrophy;
- retinal detachment;
- head and eye injuries;
- cranial nerve palsy;
- tumors;
- neuroinfections;
- stroke;
- multiple sclerosis.
The list of factors that can lead to strabismus is quite extensive, so it is incorrect to believe that strabismus is a pathology that manifests itself exclusively in childhood.
Often in adults, strabismus is a concomitant disease. Most of the main ailments are treated with surgical methods.
Is it possible to cure strabismus in adults?
Traditional methods for eliminating strabismus in adults are contact lenses and glasses. If they do not help achieve normal visual acuity, then laser correction is prescribed. In cases where strabismus develops against the background of cataracts, a surgical method is used. Treatment for strabismus depends on the cause that caused it. The doctor must determine the factor that provoked the disease and eliminate it, after which the functionality of the eye muscles is restored and measures are taken to improve visual acuity.
Surgery to treat strabismus in adults is performed under general or local anesthesia. It depends on the nature of the pathology and the clinical picture of the disease. The procedure lengthens or shortens the eye muscles so that the eyes move in a coordinated manner. If both eyes are affected, the operation is carried out in two stages: first one eye is treated, and six months later - the second. After the surgical procedure, conservative treatment continues: eye gymnastics, hardware techniques. Medications may be prescribed.
Surgical techniques (operations to correct strabismus)
The surgery aims to realign the eyes by lengthening, shortening or repositioning one extraocular muscle. Surgery in adults requires local anesthesia and takes 1-2 hours, with recovery lasting about a week or two. The operation in children is performed only under general anesthesia. Large imbalances cannot be corrected with one procedure, so two or three interventions may be needed.
To provide rapid access to the extraocular fibers, the ophthalmologist makes a small incision in the conjunctival area. In order to weaken the muscle, it moves from its usual attachment site closer to the equator of the eyeball. If it is necessary to strengthen weakened muscle fibers, then they are partially resected and reattached.
Additionally, adjustable sutures are applied. If necessary, they are carefully tightened using tools or loosened after a few hours.
Recently, minimally invasive techniques have been used in ophthalmic surgery, in which access to the muscle fibers is carried out through two small holes.
However, manipulation is not capable of “reprogramming” the brain and making an image of an object appear as a single whole.
Surgical intervention has a number of advantages: it improves depth determination, increases stereoscopic perception, and minimizes diplopia. After the procedure, an adult can focus his gaze and maintain visual contact.
Patients may experience slight pain or discomfort in the postoperative period, but this usually goes away on its own or the doctor prescribes Paracetamol tablets for pain relief.
The manipulation does not require hospitalization of the patient in a hospital. To prevent postoperative complications, drops with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.