general characteristics
Speaking about the general characteristics of paralytic strabismus and the treatment of pathology, it is worth noting its main features.
The problem in question manifests itself visually - the person begins to noticeably squint one eye. As for the patient himself, he can diagnose the presence of such a problem independently, without the help of strangers, because with this pathology there is a significant distortion of the visible picture of the surrounding world. Practice shows that if the defect in question is present, a person cannot normally perform even the simplest work.
Experts in the field of ophthalmology say that if you ignore the problem, you can get serious problems with vision, up to its complete loss. However, it is worth noting that with timely and competent elimination of the pathology, such a danger can be guaranteed to be avoided.
Prevention and prognosis
To prevent the development of paralytic strabismus, the following preventive measures must be observed:
- monitor eye hygiene;
- avoid excessive strain on the visual organs;
- avoid head and eye injuries;
- correctly distribute time of work and rest;
- timely treatment of infectious pathologies;
- undergo regular medical examinations with an ophthalmologist, especially if there is a hereditary predisposition.
The prognosis for paralytic strabismus is favorable in most cases. The greatest effect from conservative treatment can be achieved with timely consultation with a specialist. After surgery, the cosmetic defect is eliminated and visual functions are restored.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Definition of pathology
How is the violation in question determined? It is worth noting that the diagnosis of paralytic strabismus can be made even visually, however, any ophthalmologist, conducting an examination, is obliged to study the problem in more detail, making a series of specific measurements, as well as assessing the visual field. All of the above actions are carried out by carrying out the following procedures in the prescribed manner:
- Examination of the eye using an ophthalmoscope and determining the angle of vision by measuring the angle of reflection of light.
- Assessment of the field of binocular vision using a synoptophore.
- Using a prismatic compensator, determine the angle of deviation from the norm.
In the process of diagnosing pathology, multi-dot color text can be used to study the nature of binocular vision impairment. Regarding the process of separating the fields of the right and left eyes, the ophthalmologist can use coordiometry skills.
It should be noted that after all the procedures necessary to establish paralytic strabismus and confirm the problem, the patient must be referred to a neurologist.
How to diagnose paralytic strabismus
When examining a patient, the ophthalmologist uses many methods. This includes a visual inspection and carrying out various tests with tables and other devices. But the most effective is Chess coordiometry. In this case, special filters of two colors are used - red and green. In addition, glasses and flashlights of the same shade are used. The patient should look at a graphed screen with small squares. The sides of each square are equal to 3 degrees of angle. In short, this method allows you to accurately determine which nerves and muscles are affected.
Equipment used for diagnostics
To more accurately determine the characteristics of visually observed pathology, as well as the reasons for its formation, modern medicine uses several types of equipment. Most often, to investigate the nature of the problem, the following is prescribed:
- computed tomography of the brain or its examination using MRI;
- computed tomography of the orbit;
- electromyography.
It should be noted that any of the listed procedures must be performed along with the diagnostic measures for the disease in question described above. When studying the results obtained during diagnostic procedures, the presence of some other specialists is important, including professionals in the field of neurology and infectious diseases.
Symptoms of pathology
The problem in question has a number of symptoms by which it can be quite easily identified. These include the following indicators:
- lack of eye mobility (or observation of low mobility);
- double vision of objects before the eyes;
- constant presence of deviation;
- presence of a difference in deviation angles (primary is less than secondary);
- presence of dizziness;
- observation of arbitrary deviation of the head towards the affected muscle (torticollis).
It should be noted that in fact there is a basic difference between paralytic and concomitant strabismus. It lies precisely in the last presented feature. This is due to the fact that with concomitant strabismus, involuntary turns of the head are not observed.
Signs and symptoms of heterotropia
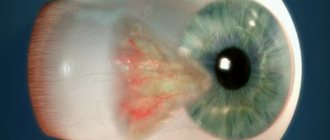
Paralytic heterotropia, as mentioned above, occurs due to dysfunction of the optic nerve or the muscles that it innervates. These muscles are responsible for the mobility of the eyeball. Pathological manifestations are immediately noticeable. The eyes lose the ability to focus on an image or object, which is why they move towards the temples or nose.
In a short time, vision decreases and myopia or hypermetropia develops. To restore full vision, you should immediately contact an ophthalmologist. The necessary studies will be carried out and competent treatment will be developed to return 100% vision to the patient.
The only thing that is necessary for the patient is to listen to the recommendations of the ophthalmologist.
In the presence of paralytic strabismus, the following signs are noted:
- the eyes do not move towards one or more affected muscles or move in a limited manner;
- the primary deviation angle is less than the secondary one;
- inability to clearly see the image with both eyes at the same time, split images;
- tilting the head in the direction where the muscle is affected;
- vertigo.
People of all ages are susceptible to paralytic strabismus. It occurs due to injuries, toxic poisoning, etc.
Reasons for education
Experts in the field of medicine name a number of reasons why the pathology in question may arise. Among the main causes of paralytic strabismus in adults it is worth highlighting:
- the presence of purulent inflammation in the area close to the optic nerve;
- toxic damage to the eyeball;
- presence of eye injuries;
- the presence of diseases whose action is aimed at damaging the central nervous system (in particular, the optic nerve);
- the presence of various types of tumors;
- myositis;
- neuritis.
Experts in the field of ophthalmology note that the most common cause of the pathology in question is injury to the eyeball. As a rule, the causes of this type of dysfunction can be both domestic and industrial.
Treatment of convergent strabismus in the MGK
At the Moscow Eye Clinic, patients with convergent strabismus are provided with a wide range of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Diagnostics are performed by qualified specialists with unique clinical experience. When prescribing treatment, a strictly individual approach is used. The clinic has an extensive methodological and hardware base for the treatment of such pathologies. These techniques are suitable for both children and adults:
- Infrared laser therapy (exposure to infrared radiation on the organ of vision at close range), the procedures of which make it possible to improve the hemodynamics of eye tissue and relieve spasm of accommodation.
- Laser therapy sessions designed to improve spatial vision and accommodation functions.
- Exercises on the device “Synoptophore Sinf-1”. This device is the main one for stimulating vision, necessary for strabismus and other types of binocular vision disorders. It allows you to carry out sets of special exercises aimed at merging images, which makes it possible to train vision impaired by strabismus. In addition, such training significantly increases visual reserves and improves eye mobility.
- Treatment with the Spekl-M device, using two types of laser, which is indicated for clouding of optical media, amblyopia and strabismus of various origins.
- Especially for young patients with strabismus, MGK offers training with the Rainbow BZR-1 kit. This kit, in a playful way, helps restore central fixation and other functions of binocular vision.
Doctor of Medical Sciences Svetlana Gavrilovna Chernysheva deals with the problems of all types of strabismus at the Moscow Eye Clinic. Svetlana Gavrilovna is an ophthalmic surgeon, professor, the best specialist in Moscow in the field of diagnosing binocular oculomotor pathology in adults and children, as well as its functional and surgical treatment. Proficient in various methods of surgical treatment of all types of strabismus.
You can find out the cost of a particular procedure or make an appointment at the Moscow Eye Clinic by calling 8 8 (499) 322-36-36 (daily from 9:00 to 21:00) or using the online registration form.
Yakovleva Yulia Valerievna
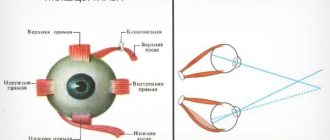
Types of pathology
It is worth noting that paralytic strabismus that develops in humans can take on different types. Currently, in medical practice, there are several variants of the pathology in question, the classification of which is made depending on the location of the pupil of the eye and the possibility of its movement. Among the varieties of paralytic strabismus, it is worth highlighting:
- horizontal (when the pupil deviates to the left or right);
- vertical (in case of pupil deviation down or up);
- permanent/temporary;
- bilateral, unilateral or intermittent.
The types of pathology under consideration can be either acquired or congenital, but each of them always affects only one eye.
As for the forms of pathology, depending on the location of the pupils, it can be characterized as:
- vertical;
- divergent;
- convergent.
As for divergent strabismus, this pathology, as a rule, occurs against the background of myopia. In such a situation, the patient's eye is directed towards one of the temples. In the absence of myopia, the manifestation of this form of pathology is usually associated with infection. When the eye is squinted up or down, the strabismus will be called vertical.
As for convergent paralytic strabismus, it is observed, as a rule, in childhood. Practice shows that such pathology is often temporary and in the first stages is quite easy to completely treat. When observing such a problem with the eyes, the pupils of a person are directed towards the nose. In adults, this type of pathology is often associated with farsightedness.
It should be noted that the pathology in question can manifest itself in three other forms, depending on the nature of its origin: orbital, nuclear and stem. Let's talk about them further in more detail.
Types of strabismus
Let's consider the main types of strabismus that are encountered in ophthalmological practice.
The classification was compiled and approved by WHO:
- Children often experience false or imaginary strabismus, which is visually determined due to an immature nasal septum. It is formed due to folds in the corners, which visually give a slight shift of the eyeball inward towards the bridge of the nose. But this condition has nothing to do with the true disease. Once fully formed, this visual effect disappears.
- The true form of the disease can be permanent or manifest itself as a result of severe fatigue or a previous illness. But, regardless of this, this is the disease that occurs most often in adults.
- Accommodative strabismus occurs when the eye muscles accommodate. The disease progresses rapidly in the absence of appropriate therapy. In this case, most often one eye squints. Accommodative strabismus initially appears periodically, but later it can be observed more often. The disease ends with constant squinting of the eyes. Accommodative strabismus is often a consequence of a disease such as astigmatism.
- The form of the disease can be concomitant. This is a separate form of manifestation of the disease. It manifests itself quite late and is considered a consequence of the pathology not being treated in time in early childhood.
- Paralytic strabismus is characterized by the inability to move the eyeball due to the inability of the muscles to perform their functions. There is also a pseudoparalytic type, which is formed when it is impossible to move a muscle due to the formation of a scar on it. Paralytic strabismus requires complex treatment. Correct diagnosis plays an important role here. For long-term illness, surgical treatment is prescribed. If paralytic strabismus is mild, then conservative treatment is used (glasses, exercises, hardware therapy).
- Congenital and acquired strabismus. The first subtype appears after childbirth, which is why it is called congenital strabismus. It often becomes a consequence of labor and prematurity of the child. The transmission of the disease by inheritance plays an important role here. So, if a father had a disease, then the likelihood of such a pathology “inherited” increases several times in his children. But it is not the disease itself that is transmitted, but the predisposition to it. This birth defect is often caused by the fact that one of the parents has astigmatism. In this case, in-depth diagnosis is necessary even in the absence of manifestations of the disease. The causes of the appearance of an acquired disease (the name indicates the factors of the disease) are diseases of the nervous system, stress, and infectious diseases.
- The disease may also be hidden. Only one thing can determine it - an ophthalmological examination (determining the angle of strabismus, the presence of concomitant pathologies: astigmatism, amblyopia). Symptoms of this type of strabismus include double vision and constant eye fatigue.
The angle of strabismus can be quite large, which makes such pathology visually noticeable.
The disease can cause severe headaches as the brain constantly tries to focus the eyeball by straining the muscles.
Against the background of this disease, amblyopia and astigmatism develop very quickly.
Nuclear
The development of this type of strabismus can only be associated with an infectious lesion of the nuclei of the brain, and can also occur with other diseases that have a detrimental effect on the body, striking examples of which include:
- encephalitis;
- multiple sclerosis;
- neurosyphilis.
If, during the examination, diagnostics have identified this particular form of pathology, then the patient should be prepared for the fact that all those changes that will occur at the level of the brain nuclei over a short period of time will have irreversible consequences, as a result of which they may the most tragic consequences will happen.
Diagnostics
Paretic (paralytic) strabismus occurs with the following disorders of the nerves of the oculomotor system:
- nuclear defeat;
- fascicular lesion;
- basilar;
- orbital.
To determine the type of lesion, special studies of the brain are necessary. An ophthalmologist should carry out diagnosis together with a neurologist in most cases.
Impaired mobility of the visual organ, double vision and strabismus often indicate the onset of various abnormal processes in the central nervous system. Since the patient initially turns to an ophthalmologist in cases of visual disturbances, the ophthalmologist must assess the patient’s general condition and obvious symptoms and make a preliminary diagnosis. The doctor determines the number of affected nerves (isolated paralysis or ophthalmoplegia), which ones. Additionally, it is necessary to determine whether cranial nerves that are not involved in oculomotor function are affected.
Isolated paralysis is not difficult to diagnose; it is only necessary to determine in which direction the eye movement is impossible, as well as the muscle responsible for this direction of eye movement and the corresponding nerve.
When it comes to strabismus with a double image, or the limitation of mobility is not defined, as well as vertical strabismus, some studies are necessary for a correct diagnosis, such as:
- test for diplopia;
- eye mobility study;
- electromyography (EMG).
Orbital
As for the orbital form of paralytic strabismus, its treatment is carried out most successfully and, according to statistics, gives the greatest number of favorable outcomes. The main etiological factor of this type of lesion, as a rule, is a subperiosteal abscess or periostitis. Practice shows that the treatment method for this form of the disease is based on the complete removal of the process that provokes a change in the normal functionality of the organ of vision. Statistics show that after all necessary operations, visual acuity is restored to its maximum or full extent.
Pathology in children
It is known that paralytic strabismus is often observed in children who have just been born. The pathology is classified as congenital and forms in the womb.
The main reason for the appearance of the eye disease in question in a child is the presence of complex infections in the mother’s body, which affect the development of the child’s central nervous system. Also, the cause of this phenomenon may be the mother’s abuse of bad habits during pregnancy.
It should be noted that recently paralytic strabismus has become quite often diagnosed in children - 2-3 times more often than in adults. If the problem is ignored, the baby may experience dysbinocular amblyopia, the development of which at one point begins to occur rapidly.
Treatment
In order to eliminate a visual defect, medical specialists conduct a complete examination of the patient, as a result of which the underlying nature of the disease should be established. Once this is determined, a treatment plan can be developed, which usually includes surgery for paralytic strabismus, which allows you to restore the symmetry of the eyes.
If the problem is not advanced, it can be eliminated with medication. In addition, a number of effective manipulations also include reflexology, electrophoresis and electrical stimulation.
Rehabilitation period
After carrying out all the procedures prescribed in the indicated course, it is necessary to avoid excessive eye strain, as well as regularly perform special exercises prescribed by the ophthalmologist.
Special attention should be paid to the fact that during the postoperative period it is necessary to wear special glasses designed to cover the operated eye from the sun, as well as protect the healthy one.
It should be noted that the procedure for treating strabismus is a rather lengthy process that can take a couple of years; as for the rehabilitation period, it takes about six months.
Traditional methods for improving vision during rehabilitation
During the rehabilitation period, you can take care of your eyes using products prepared according to traditional methods. It should be noted that before using them, you need to consult with your treating ophthalmologist, outlining the features of the composition of each product.
Currently, among the most effective methods for restoring visual acuity in the postoperative period are herbal drops and decoctions made from natural ingredients. Let us consider further some recipes for their preparation.
Phytodrops from dill seeds. To prepare an effective remedy according to this recipe, you need to take 10 g of powder made from dill seeds and pour a glass of boiling water over the component. The infused and strained product should be instilled into the operated eye three times a day, a couple of drops.
Decoction of pine needles. In order to prepare an effective product made from pine needles, you need to pour 100 g of the main component with a glass of boiling water, then let the mixture brew for an hour. After the allotted time, the decoction must be consumed. To obtain a positive effect, the use of the product must be repeated three times a day.
Phytodrops with honey. In order to make effective herbal drops, you need to mix 3 drops of apple and onion juice in one bowl, and then add 1 drop of natural liquid honey to the indicated components. After stirring, pour a spoonful of boiling water into the mixture and let it brew, sealed. The infused remedy should be instilled into the eyes daily before bedtime. Reviews about this method of sharpening vision often say that it becomes clearer in the morning.
Symptoms of the disease
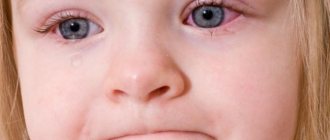
Symptoms appear quickly: usually the mucous membrane is completely infected overnight, and in the morning manifestations of the infection are already visible. They cause great discomfort to a person, as they affect the organs of vision.
In most cases, symptoms appear initially in one eye: with timely treatment, damage to the second may not occur
The first thing you should pay attention to is redness and stickiness of the eyelids in the morning. Other symptoms appear throughout the day, such as watery eyes, a feeling of dryness, swelling of the eyelid and redness of the conjunctiva.
The patient may notice scanty and clear mucous discharge. The feeling of sand under the eyelid and increased sensitivity to light cause even more discomfort when working.
Another symptom of conjunctiva is a rash on the skin around the eye, they are almost identical to a herpes rash. These are small blisters of fluid that cover the mucous membrane of the eye and the area around it.
Thanks to the examination, the ophthalmologist can immediately draw a conclusion about the disease and prescribe proper treatment.