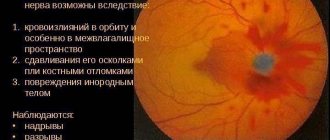
Optic nerve hypoplasia is a developmental anomaly that occurs in newborns. The term hypoplasia is translated from Greek as weakening of formation, in this case, tissue. The pathology occurs mainly in newborns and represents insufficient development of axons in normal supporting tissues.
Reasons for development
Hypoplasia of the optic disc occurs in a child during intrauterine development under the influence of the following factors on the mother’s body:
- smoking;
- alcohol or drug use;
- diabetes;
- hypothyroidism;
- taking medications;
- infection with cytomegalovirus;
- herpetic infection;
- ionizing radiation;
- injuries;
- exposure to high or low temperatures;
- oligohydramnios;
- genetic abnormalities.
Against the background of predisposing factors, ganglion cells in the fetus divide incorrectly. In this case, a violation of the division of ganglion cells of the eye occurs in the 2nd month of intrauterine development or the death of nerve fibers in the last stages of gestation. Often this anomaly is combined with other disorders in the brain and is caused by compression of the optic nerve structures in the process of pathological growth, neoplasms or exudate.
Electrical stimulation of the optic nerve has a positive effect.
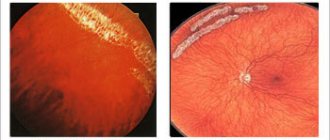
Coloboma of the optic nerve
True, isolated colobomas, in which only the optic nerve is abnormal, are extremely rare.
More often they are combined with scleral ectasia, choroidal and retinal colobomas, as well as other anomalies. The occurrence of optic nerve coloboma, like other colobomas, is associated with a disruption in the process of closing the germinal fissure. Colobomas vary in shape and size. At the site of the optic nerve head, a round, oval or triangular depression with clear boundaries, bordered by pigment, is visible. The dimensions of this recess are 2-3 times larger than the diameter of the disk itself. The true boundaries of the disc are not visible and are only outlined against the background of a large choroidal defect in the upper part of the coloboma.
The vascular bundle is located in various areas and is significantly changed. One part of the vessels (usually the upper ones) emerges from the optic nerve head itself, the other is much lower and bends over the edge of the choroid and retina. The vessels can also emerge in one bundle or evenly along the entire edge of the coloboma. Vision with colobomas of the optic nerve is usually significantly impaired.
A less common form of optic nerve coloboma is called “peripapillary true staphyloma,” in which the normal disc is located at the bottom of a regular cylindrical depression.
Morning glow syndrome
- a congenital developmental anomaly in which the optic nerve head is significantly enlarged, grayish in color, with a deep funnel-shaped excavation, resembling the shape of a flower. In the center of the disc, in place of the missing central vessels, lies gray-white tissue; numerous vessels of reduced caliber emerge along the edge. A wide grayish ring of pigment forms around the disc. Visual acuity is sharply reduced. The anomaly is often combined with persistence of the vitreous artery (posterior portion of the primary hyaloid system), congenital cataracts, high myopia, and astigmatism.
Retinal dysplasia in other animals
Myopia is just the tip of the iceberg. The problem occurs because the sclera is abnormally elastic and does not provide the normal shape and size of the eye. The connective tissue begins to behave like a stretched elastic band on clothing and cannot cope with the load. However, the same myopia usually begins to manifest itself only at the age of 5-7 years. How can you understand that a child is dysplastic and has a high risk of developing myopia in the future?
First, look at your parents. If they have myopia and other symptoms of DSD, then the child’s chances of wearing glasses at school are very high.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=https:accounts.google.comServiceLogin
Secondly, you need to pay attention to those systems that are also affected by imperfect connective tissue. Until the age of 3, no symptoms usually appear clearly. The manifestation of problems coincides with periods of rapid growth of the child. At the age of 4-5 years, heart valve prolapses begin to form. At about the same age, signs of flat feet appear. As a rule, such children are much more flexible than their peers.
The most difficult period for people with DTD is adolescence. The body grows at incredible speed. All cells work in crazy afterburner mode, trying to increase as much mass as possible in a short time. Long, slightly awkward teenagers already suffer from the consequences of this explosive growth, and those with dysplasia also receive in addition myopia, curvature of the spine and other joys.
Once growth is complete, new symptoms usually no longer appear.
Main symptoms
Underdevelopment of the optic disc causes the development of such clinical signs in children as:
The optic disc pathology is noticeable in the baby by strabismus.
- strabismus;
- nystagmus;
- violation of orientation in space;
- double vision;
- dizziness;
- inability to fix gaze;
- headache;
- reduction in the size of the eyeball;
- field disturbance and blurred vision;
- inability to distinguish colors;
- increased fatigue;
- decreased visual acuity.
The onset of symptoms is noted immediately after birth and manifests itself in the deviation of the eyeballs in one or different directions, as well as when turning the head to select the point of best vision of an object. An increase in symptoms is observed with anxiety, poor health, or after infectious and viral diseases. With ophthalmoscopy, a noticeable decrease in size and gray color of the optic nerve head is observed, and atrophy of the retina and its structures is observed around it.
Heterotopia of the optic disc
Optic disc aplasia
- its congenital absence is a rare unilateral or bilateral anomaly. It is often combined with other malformations of the eye and central nervous system. In cases of true aplasia, the optic disc and fibers, retinal ganglion cells and retinal vessels are absent. There are no visual functions.
One variant of the anomaly is aplasia of nerve structures with normal development of mesodermal elements in the optic nerve trunk and central vessels. This abnormality is called aplasia of the disc or third neuron, retina.
Optic disc hypoplasia is more common than optic disc aplasia, but is also quite rare. With hypoplasia, the optic disc in one or both eyes is reduced in size to 1/3-1/2 of its normal size.
It is often surrounded by a zone of pigmentation. The vascular system of the disc is normally developed; tortuosity of the vessels is less common.
X-ray examination sometimes reveals a decrease in the size of the optic foramen, which indicates the spread of hypoplasia in the proximal direction.
Hypoplasia of the optic disc is often combined with microphthalmos, aniridia, and underdevelopment of the orbit. At the same time, delayed psychophysical development and hemiatrophy of the face on the affected side may be observed.
Visual functions are severely impaired and depend on the degree of hypoplasia. When optic disc hypoplasia is combined with nystagmus and strabismus, as well as its mild severity, it is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis with amblyopia.
Several cases of disc placement in unusual positions, sagittal on the nasal or temporal side, have been described. In these cases, the macula is usually also displaced, the eyeball deviates, forming an angle y.
Congenital excavation of the optic disc is an oblique arrangement of its scleral canal, externally similar to glaucomatous excavation. It is formed due to the oblique course of the optic nerve canal, while the disc has the shape of a vertically located oval, its nasal edge is pushed forward and overhangs somewhat, the course of the vessels passing through it is the same as during conventional excavation.
Often combined with refractive errors.
Duplication of the optic nerve head is often combined with duplication of the nerve itself along a certain length. A rare anomaly, it is often unilateral.
Two discs are revealed in the fundus, each with its own vessels. The additional disk is usually smaller, often connected to the edge of the main disk, and can be located in any position.
The degree of doubling may be less pronounced: ophthalmoscopically, on one disc, the retinal vessels emerge from two different recesses.
Congenital pseudoneuritis (false neuritis) is one of the most commonly observed anomalies of the optic nerve (up to 0.2% in the population). In most cases, the anomaly is bilateral (up to 80% of cases). Sometimes it manifests itself as a family pathology. The morphological basis of the anomaly is hyperplasia of glial and connective tissue in the intraocular portion of the optic nerve.
The clinical picture is represented by signs of neuritis: the optic disc is hyperemic, with unclear boundaries. With small degrees, only the nasal border of the disc is unclear, in a pronounced form - all borders are washed away. Atypical branching and tortuosity of the vessels on the disc are often observed, but their caliber is not changed. In most cases, high degree hypermetropia is observed.
Pseudoneuritis must be differentiated from true neuritis, papillitis, in contrast to which in pseudoneuritis there is no peripapillary edema, hemorrhages and exudate on the disc, vessels of normal caliber, the process does not progress, visual functions are not impaired.
Visual acuity in pseudoneuritis can be reduced due to refractive error and increases with its correction. Children with pseudoneuritis should be under medical supervision and should be consulted by a neurologist and otolaryngologist.
Myelinated optic disc and retinal fibers are one of the most common anomalies in which myelination involves the optic nerve fibers and extends beyond the cribriform plate into the eye into the disc and retina.
A characteristic ophthalmoscopic picture is observed: shiny white spots with jagged, uneven edges, shaped like flames, fox tails, fan-shaped from the disc to the retina, covering its vessels.
Vision is usually not impaired, the blind spot is enlarged. Visual acuity may be reduced when myelin fibers are localized in the macular area.
Pigmentation of the optic disc is characterized by the deposition of pigment clumps on the disc, most often in the area of the vascular funnel, along the vessels. Less commonly, the entire disc is covered with pigment. Visual functions are usually not impaired.
The anomaly is characterized by the presence of round reflective formations on the disc. According to some authors, drusen consist of hyaline (hyaline bodies), others believe that they are formed from cellular substance.
It is believed that optic disc drusen are a consequence of embryonal mesodermal dysplasia; appear at different ages. The anomaly is usually bilateral, but the drusen are located asymmetrically in both eyes.
There are superficial (explicit), deep, hidden and amputated drusen. Superficial drusen are whitish or yellowish, translucent, round, single or multiple, in the form of conglomerates, protruding above the surface of the disc.
They are most often localized at the nasal edge of the disc or near the vessels; they can be located in the center of the disc, as well as in the peripapillary region. The edges of the disc are irregularly shaped due to protruding drusen, which are better visible in indirect red light.
With a pronounced process, the disc is enlarged and protrudes into the vitreous body. Deep drusen are not visible with conventional ophthalmoscopy and are not detected with oblique illumination in indirect red light. Hidden drusen are located deep in the optic disc tissue and appear only in the pathological prominence of the disc.
Treatment methods
Treatment may be necessary if severe deformation occurs, patency is impaired and blood flow begins to flow poorly. The patient requires surgical treatment if there is a threat of ischemic stroke.
Drug treatment
Glycine tablets Phezam (capsules) Mexidol injections Complex therapy is prescribed with the help of pharmacological drugs. They help blood circulation function normally, strengthen the walls of blood vessels, and stimulate metabolism in cells. Medicines prescribed by a specialist:
- nootropics;
- blood flow regulators;
- metabolism accelerators;
- vasodilators.
If the tissues are affected, the patient has severe hypoxia, then the following drugs are suitable: Actovegin, Reomacrodex.
Surgery
Surgery is necessary for people whose large aortas are damaged. The size and type of deformity is diagnosed, and then specialists decide whether surgery is necessary. The decision is influenced by the patient’s well-being and possible risks.
During the operation, deficiencies are corrected. After about 3 months, it is necessary to check the operated area. Doctors do this using the instrumental method.
Folk remedies
Recipes for folk remedies are used for symptomatic treatment at the initial stage of pathology. In severe cases, traditional medicine methods do not bring the desired effect. For additional therapy that will improve immunity, you can prescribe decoctions or tinctures, lemon, olive oil and chamomile flowers help. Folk remedies have sedative, antihypertensive and vasodilating properties. Suitable:
- infusions and decoctions of rose hips and hawthorn;
- lemon balm and mint teas;
- extract of valerian, motherwort.
Consequences and complications
The patient's problem is often complicated by retinal atrophy. Optic disc hypoplasia causes a number of unpleasant phenomena. Most often these include severe strabismus and decreased visual acuity in one or both eyes. Underdevelopment of nerve fibers leads to atrophy of retinal structures and loss of the ability to see even minor elements. Progression of ophthalmological disorders is also possible, so maintenance therapy is necessary to prevent blindness. One of the main complications of optic nerve hypoplasia is endophthalmos, scleritis and other inflammatory lesions of the eye, which are caused by a disorder of the trophism of its structures. Often the pathology is combined with the absence of a lens or congenital malignant tumors of the brain.
Pathogenesis
The pathogenetic mechanism is directly related to the disruption of the division of ganglion cells of the inner membrane of the eye at 4-6 weeks of embryogenesis. Amacrine and horizontal cells are not affected. According to another pathogenetic theory, the disease is caused by the phenomenon of axonal regression at 16-31 gestational weeks. When the disease is combined with other anomalies of brain development, the leading role in the formation of defects is assigned to retrograde degeneration, caused by the predominance of encephaloclastic processes. Impaired differentiation of hemispheric structures and optical fibers is often associated with pathology of regulatory processes. The mechanical theory is based on compression of the optic pathway by a malignant neoplasm formed by exudate and blood clots.
When something went wrong
We are all susceptible to mutation, despite the biological equivalents of the Reed-Solomon code and checksum verification. And, as a rule, these mutations do not make you a superhero at all. Alas. Systemic connective tissue dysplasia (SCT) is just one of the types of genetic failure when the source code for protein synthesis turns out to be buggy.
DST has differences from many other anomalies associated with a crooked genetic code. For example, in sickle cell anemia, only one “bit” is defective. This is a point mutation. With systemic dysplasia, each time it is a unique combination of several defective genes that the child received as a gift from his parents.
In the “factory” of the mutant fibroblast, the very program for creating collagen is unpredictably broken. As a result, either there is not enough collagen at the output, or the cell confuses the stages of fiber weaving, or forgets that it is necessary to cross-link the molecules. The result is fragile and poorly structured.
However, this does not bother the cell and it continues to stamp the defective fiber further. The more defective genetic pieces a person gets, the more severe the consequences for the body. For example, the problematic locus rs143383 of the GDF5 gene and rs35068180 of the MMP3 gene will almost certainly lead to severe myopia. Some particularly unsuccessful mutations even lead to death at a young age.
Diagnostic measures
Hypoplasia of the optic disc can be suspected by the presence of clinical signs characteristic of this disease in the child. To confirm the diagnosis, it is recommended to conduct a large number of laboratory and instrumental studies. Since the disease is hereditary or genetically determined, if the pathology is present in close relatives, a screening test is carried out in utero, which makes it possible to identify underdevelopment of the optic nerve. They also perform electroretinography, which makes it possible to assess the degree of visual impairment.
This pathology is well visualized during MRI.
Characteristic changes are in the fundus of the eye, which can be easily determined by ophthalmoscopy. Computer and magnetic resonance imaging of the head helps to detect concomitant pathology. Histological examination of a retinal biopsy sample reveals a reduced number of light-sensitive cells. Visiometry is used to determine visual dysfunction.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, a physical examination and a special ophthalmological examination are used. If parents or close relatives have pathology, genetic screening is carried out at 16 weeks of intrauterine development. In the postnatal period, diagnosis is based on:
- Electroretinography.
Using an electrophysiological study, a decrease in the amplitude of the electroretinogram due to transsynaptic degeneration is determined. Registration of potentials emanating from the retina makes it possible to assess the degree of visual dysfunction. - Ophthalmoscopy
. A “double ring” effect is observed, in which a layer of pigmentocytes is visualized along the periphery of the optic disc, which is reduced in diameter. The differentiation of foveolar and macular reflexes is very difficult. The diameter of the retinal vessels is not changed, but they have a corkscrew-like course. - CT scan of the head
. Computed tomography reveals a narrowing of the diameter of the optic nerve canal. In the unilateral form, the difference in the size of the canals on the healthy and affected side exceeds 20%. A thin nerve in the orbital part is visualized. - Histological examination
. There is a decrease in the number of retinal ganglion cells with a normal content of horizontal and amacrine cells. - Electron microscopy
. A decrease in the number of astroblasts, atrophic and degenerative changes in axons are visualized. The presence of fluid between the axolemma and the nerve sheath indicates axonal and periaxonal edema. The pathology of the structure of the myelin sheath is determined by reducing the total number of astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. - Visometry
. The severity of visual dysfunction varies widely, as it depends on the severity of nerve underdevelopment.
Additionally, the calculation of the ratio of the distance between the optic disc and the macula to the diameter of the disc, which is normally less than 3, is shown. Differential diagnosis is carried out with aplasia and atrophy of the optic nerve. Characteristic ophthalmoscopic signs of atrophy are a waxy tint of the optic disc, excavation of its surface, narrowing and reduction in the number of retinal vessels. With aplasia, the complete absence of the optic disc is determined against the background of weakly expressed pigmentation of the inner membrane of the eyeball. The macula cannot be differentiated. Only choroidal vessels are visualized.
Collagen under a microscope
Source
Connective tissue is one of the most important tissues in our body. This is a frame that forms the foundation for attaching various cells. There are many different proteins that give the necessary properties to our connective tissue - tensile strength, flexibility, extensibility. The key structural protein is collagen.
These proteins are found almost everywhere. Thanks to them, our skin can stretch and return to its original shape, ligaments prevent the joints from dislocating under load, and the connective tissue of the sclera of the eye guarantees the constancy of its geometry, which is important for normal focus.
Collagen synthesis is multi-stage, with many regulatory mechanisms. It is carried out by fibroblasts, as in the illustration above. If everything goes well, then the connective tissue is formed exactly as needed. Normally, the process of creating connective tissue fibers is similar to a large mountaineering equipment factory. We take several Kevlar threads, a little nylon and weave them in a strictly defined way. The result is a strong, durable cable.
How to treat?
Therapeutic measures are carried out in early childhood. This increases their effectiveness, since the nerve structures of the brain are in the process of formation. Patients are prescribed spectacle correction and prevention of amblyopia, which consists of blurred vision in the eye that sees better. Transcutaneous electrical stimulation of the optic nerves, which is prescribed in dosed courses and repeated periodically, has a positive effect. Laser radiation or pleoptics is used, which involves exposing the optic disc to a low-intensity laser with low brightness. In addition, medications are prescribed that improve blood circulation in the fundus tissues, vitamin and mineral complexes with lutein, and drugs that enhance metabolism.
Antioxidants and substances that dilate the vessels of the macula will be useful.
Treatment of optic nerve hypoplasia
Therapy is effective only with early treatment. This is due to the fact that in the first year of life the pre- and postgeniculate pathways, the lateral geniculate body and the cortical centers are at the stage of formation. Treatment includes:
- Transcutaneous electrical stimulation of the optic nerve
. The effectiveness of the method directly depends on the initial visual acuity. Electrical stimulation is prescribed in courses. On average, there are from 3 to 5 courses. - Compensation for ocular deprivation
. To compensate for this phenomenon, the child undergoes spectacle and contact correction of visual acuity. Prevention of the development of amblyopia involves the use of dosed occlusion of the better seeing eye. - Laser pleoptics
. The technique is based on the use of low-intensity laser radiation, which improves microcirculation and metabolic processes in surrounding tissues, increases the activity of DNA, RNA and enzymes, and has a beneficial effect on the energy potential of cells and trophic processes.
Symptomatic therapy is based on surgical treatment of nystagmus and strabismus. Surgical methods for correcting strabismus are used before the age of 5 years. Depending on the type of strabismus, surgeries are prescribed that weaken or strengthen the functions of the extraocular muscles. The goal of treatment for nystagmus is to create a position of relative rest by restoring the physiological position of the muscles. According to individual indications, Botox injections are performed into the orbital cavity to reduce the amplitude of small-scale movements of the eyeballs. Additionally, correction of neuroendocrine disorders (neonatal hypoglycemia, panhypopituitarism, secondary hypothyroidism) is carried out.
Prevention measures and forecasts
Without supportive treatment, optic nerve hypoplasia can lead to complete loss of vision. If the pathology is identified in a timely manner and all necessary therapeutic measures are carried out, the child’s vision may improve slightly, but it is impossible to completely recover from the disease. To prevent underdevelopment of the optic disc during pregnancy, women are prohibited from consuming potent and toxic substances and avoiding stress and exposure to ionizing radiation. It is important not to smoke or drink alcohol.
Causes of optic nerve hypoplasia
Sometimes, with underdevelopment of optical fibers, a mutation of the PAX6 gene is detected at the 11p13 locus, which is usually combined with lens opacification and aniridia. An autosomal dominant type of inheritance has been established. Triggering factors include:
- Impact of teratogenic factors
. It has been experimentally proven that drinking alcohol, consuming drugs (cocaine) and smoking during pregnancy significantly increases the likelihood of developing the disease. - Metabolic disorders
. The pathology is often diagnosed in children born to mothers with type 1 diabetes mellitus and a history of hypothyroidism. - The influence of drugs.
Damage to the optic nerve fibers in the fetus is caused by the mother taking phenobarbital, antidepressants, and quinine during pregnancy. - Intrauterine infections.
The development of the disease is often provoked by infection of the fetus with cytomegalovirus and herpes infection.
Traditional bonuses
Of course, we will not return the shape of the eyes of dysplastic patients, but we can still help get rid of glasses. We have excellent equipment and experienced surgeons for this.
For the new year, we have prepared a 33.673% discount on vision correction using the ReLEx SMILE method. More precisely, previously the price for correction started from 98,000, and now from 65,000. It doesn’t matter how many diopters you have, whether you have astigmatism or not, the price does not change. Discounts end after January 17, 2020.
Contacts: “Ophthalmological Clinic “Sphere” by Professor Eskina” telephone call center address: Moscow, st. Starokachalovskaya, 6