Basic rules of hygiene
There are basic rules of hygiene for the tissues of the eyes and surrounding skin, subject to which they will remain healthy:
- Hydration. The mucous membrane of the eyes should always be covered with tear fluid. If it is absent or slightly reduced, injuries and microcracks may form on the cornea. To correct the situation, the doctor may prescribe moisturizing drops that will promote the regeneration of damaged tissue.
- Daily eye treatment. For these purposes, you cannot use antiseptic agents or soap, as they contribute to dryness of the thin skin of the eyelids and irritate the eyes. It is recommended to use regular running water if the patient is healthy. When infectious and inflammatory conditions develop in the eye area, in addition to daily treatment with water, antibacterial agents are added. In this case, the patient’s hands should be clean, washed with soap.
- The appearance of diseases. If a patient develops a viral, infectious-inflammatory, or fungal infection, it is recommended to immediately consult an ophthalmologist. Self-medication can lead to complications. The doctor will select the most appropriate medications.
- Compliance with the rules for using contact lenses. To install and remove them, a person must have cleanly washed hands and short-cut nails. This prevents mechanical damage and infection into the superficial layers of the eyeball. The lenses are stored in a container filled with saline solution. It is changed daily, otherwise pathogenic microorganisms and foreign substances will accumulate in it.
- The selected optics for the eyes must strictly correspond to human vision. If a person decides to choose lenses or glasses on his own, visual acuity may deteriorate and intraocular pain and headaches will appear.
- Workplace. To maintain visual acuity, you must maintain distance when working at a computer or papers. It must be at least 40 cm.
- It is not recommended to read or work in moving vehicles. This leads to eye strain and nausea.
- If a person's eyes become very tired, it is necessary to take a break. At this time, you can look out the window at distant objects and use eye exercises.
- The room where a person is and works must be well lit. To do this, use daylight from a window or artificial light from a lamp.
- Protect your eyes from exposure to bright sunlight. Sunglasses are used for this. They help reduce the number of long waves entering through the pupil.
- If permanent diseases develop in the organs of vision, or a person’s regenerative function is reduced, the doctor will prescribe vitamin complexes. They contain microelements that have a beneficial effect on eye tissue. In addition, it is recommended to use creams and ointments that promote tissue restoration.
When using all of the above rules, the risk of developing ophthalmic diseases is reduced.
Simple rules of visual hygiene.
Each of us has known about the basic rules of visual hygiene since our school days: as they say, we have encountered them. Since then, I have remembered that the light of a table lamp must fall from the left side, and the distance from the eyes to the notebook should ideally be 40 cm.
Sometimes the whites of the eyes became red and itchy. Mom shook her head: “Conjunctivitis... I told you not to put dirty hands in your eyes!” And there was only one remedy for this trouble: washing the eyes with a strong tincture of tea. If a stye appeared on the eyelid, the first thing to do was to show the fig directly in the eye of the sufferer. And it passed! In a week. Or as luck would have it. In rare cases, they consulted an ophthalmologist. It was believed that such trifles could be dealt with perfectly using unconventional methods and folk recipes. And they really worked. Or the pain went away on its own.
“It will go away on its own” is generally a unique word form that has become entrenched in the minds of many people and, oddly enough, works on the principle of setting oneself up for recovery.
A lot of time has passed since then. Oculists have become ophthalmologists, and we no longer bypass their offices. And we don’t casually throw the dispensary sheet on the table: “I just need a stamp.” Attention to eye health has become more serious. Treatment methods for the organs of vision have improved, and diagnostics have become more accurate. And the demand for specialist consultations has increased significantly.
The statistics are inexorable: approximately 90% of people living in developing countries experience certain problems and disorders of visual function.
Moreover, 80% of all eye diseases are successfully cured. But it’s better to prevent their occurrence. And although eye pathologies may have hereditary or age-related prerequisites, ophthalmologists recommend paying serious attention to issues of prevention and rules of visual hygiene.
Visual hygiene is a set of preventive measures and rules aimed at preserving and strengthening visual function, as well as the health of the visual organs.
Due to the fact that our eyes are exposed to heavy visual loads during the day, first of all we need to take care of the proper organization of our workspace:
- Lighting. The lighting in the room should be moderately bright, and the light should be soft and constant - without flickering. When working at a desk, the light source should be on the left (for left-handed people - on the right) and behind your back, but in such a way that your shadow does not cover the working area of the table. At night, general background light is added to the directional light to create a smooth transition from one type of lighting to another. If the desk is located near the window, then some time of sunlight will be enough to maintain optimal light conditions. The main thing is that the light does not hit your eyes and does not blind you. The distance from the eyes to the surface of the table or book should be 30-40 cm;
- Working at the computer. When working at a computer, dim ambient light is sufficient. However, a desk lamp can be directed towards the keyboard area to illuminate it. You should not sit at the monitor in pitch darkness - due to the high contrast, your eyes become overstrained and quickly get tired. The optimal distance from the eyes to the monitor is at least 50 cm;
- Breaks and visual rest. During prolonged visual stress, it is necessary to pause and rest your vision every 40-60 minutes. Ideally, you need to do a few eye exercises that will relieve tension and relax the eye muscles. This can be strong squinting, small blinking, movements of the eyeballs up and down, left and right. It is useful to look into the distance and do a delicate eye massage with your eyelids closed. You can also perform a special set of exercises to restore vision;
- “No” to bad habits. If you are an ardent fan of literature and cannot imagine your life without books, you should take care of your reading culture. It is recommended to avoid reading on the go, while lying down, in transport, or in a dimly lit room. Your eyes, of course, will serve you well, but it would be wiser and more correct to take care of them;
- Moisturize your eyes. People who spend a lot of time at the computer, as well as students whose visual stress is very high, often experience the so-called “dry eye syndrome”. It is associated with insufficient production of natural lubrication, which is needed to wash and moisturize the eye. As a result, a person may experience discomfort, dryness, pain and a feeling of sand in the eyes. This phenomenon is also common among people who wear contact lenses for a long time: they dry out the eye and reduce the ability of the tear gland to produce natural secretions. The best solution is to consult an ophthalmologist about this problem. He will prescribe special drops that activate the production of lubricant or recommend the use of “artificial tears”;
- Stop, infection! Maintaining a minimum of hygiene will protect you from problems such as eye infections. The eyes are very vulnerable to various types of infections, including dust, dirt, sand, and smoke. Conjunctivitis, stye, blepharitis - this is not a complete list of diseases that affect not only children, but also adults who have the habit of rubbing their eyes with dirty hands. Seasonal allergies and hay fever, which also affect the eyes, are worth a separate discussion. Golden rule: wash your hands. And if a speck gets into the eye, it should be carefully removed with the edge of a clean napkin or handkerchief;
- Washing and daily hygiene. You need to wash your eyes at least twice a day: morning and evening. Warm lotions or compresses made from chamomile decoction help relieve tired eyes. Black tea bags can also be used;
- Gentle cleansing. Girls who wear cosmetics should always remove their makeup before going to bed, no matter how tired they are. Just imagine the combination of eye shadow you've been wearing all day, mascara and sebaceous gland secretions. This whole “cocktail” is one big breeding ground for bacteria on your face. Cleansing your face and removing all impurities from eyelashes, eyelid folds, and eyebrows is a mandatory procedure that should end your day;
- Glasses. All accessories that you wear must be properly selected and of high quality. This applies to both prescription glasses and sunglasses. There are a huge number of the latter on the market, but not all of them meet sanitary and hygienic standards. Inexpensive products are made from low-grade plastic and do not provide the protection your eyes need from UV filters. It is wisest to purchase sunglasses in specialized optical stores. They perfectly protect against bright sunlight, ultraviolet radiation and dust and dirt getting into the eyes. As for glasses for vision correction, they should be selected by an ophthalmologist personally for you. The same goes for contact lenses;
- Gymnastics for the eyes. An excellent preventive remedy for adults and children is eye gymnastics. Today, there are several popular techniques that share one goal: to support visual function. It is believed that the main reason for decreased visual acuity is visual strain, which must be relieved with the help of relaxing eye exercises. Performing eye exercises really helps with slight deterioration of vision, and helps primarily with myopia (myopia), and also helps relieve spasm of accommodation. Among the most famous gymnastics for the eyes are gymnastics according to E. Avetisov, W. Bates, M. Norbekov. The exercises are accessible to everyone and easy to do. After just a week of regular training, vision improvement and relief of eye tension are noted;
- Vision and diet. As children, mothers and grandmothers carefully persuaded us to eat carrots so that our eyes could see better: after all, this is vitamin A! And no wonder. A high-quality, balanced diet is the key to health, including eye health. Sources of vitamin A are also bell peppers, rose hips, pumpkin, eggs, green vegetables, milk, butter, and egg yolk. Vitamin D is also an “eye vitamin”. To replenish its reserves in the body, you need to include in your diet foods such as beef liver, cod liver, eggs, fatty fish and fish oil, as well as blueberries, black currants, peaches, and apricots. In the off-season, you can take a course of eye vitamins, which your doctor will recommend;
- Compliance with safety regulations. Protect your eyes from injuries, bruises, scratches and abrasions. When working in dusty conditions (repairs, hazardous industries, etc.), use special safety glasses. Avoid getting foreign bodies into your eyes;
- Prevention from an early age. Teach children about visual hygiene from an early age. In a playful way, tell and show them how to properly keep their eyes clean and healthy. Visual loads in children of primary and secondary school age must be dosed - they must be alternated with a change of activities;
- Prevention and timely treatment. If you experience discomfort in the eyes, rapid fatigue, spots, fog, decreased visual acuity and other unpleasant symptoms, you must make an appointment with an ophthalmologist. You should not self-medicate or hope that the symptoms of discomfort will go away on their own. Eye infections tend to subside, and then become more active with renewed vigor, transforming the disease into a chronic condition. Even if there are no complaints, it is recommended to have your eyes checked by a doctor once a year.
Eye hazards
The organs of vision are susceptible to environmental factors.
The dangers for them are the following:
- penetration of an infectious, viral, fungal, parasitic agent;
- bright sunlight, which can damage the retina;
- work in enterprises associated with the use of welding, chemicals, woodworking;
- strong wind, which can bring foreign objects into the eyes, causing mechanical damage and infection;
- chronic dry eyes caused by negative environmental factors, decreased function of tear fluid production;
- systemic diseases of the vascular bed (diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis, ischemic disease, thrombosis);
- a systemic disease developing in the organs of vision or brain;
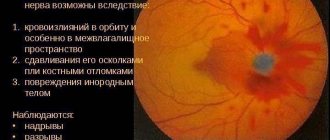
- optic nerve disease;
- mechanical damage to the external structures of the eyes and eyelids.
If one of the above conditions occurs, consult an ophthalmologist or traumatologist. With proper treatment, the possibility of a full recovery increases.
Rules for working at the computer
To reduce the load on your eyesight from computer radiation, it is recommended to follow the following rules:
- the distance from the monitor should be at least 40-60 cm;
- adjusting the brightness of the monitor so that there is no unpleasant feeling when working;
- periodic pauses in work to give the eyes a chance to rest;
- transferring the gaze from the computer to a distant object, preferably out the window;
- use of moisturizing drops for excessive dry eyes;
- reducing time spent working at the computer, if possible;
- periodically perform eye exercises.
If a person’s work involves a computer, it is recommended to periodically examine the organs of vision by an ophthalmologist. Timely detection of deviations in vision functions increases the possibility of their elimination.
Reading rules
To reduce eye strain when reading, it is recommended to follow the following rules:
- read while sitting with a book in hand to reduce the load on the cervical spine;
- the reading room should be well lit with sunlight or a bright lamp;
- It is forbidden to read lying down, this increases the load on the visual organs;
- It is recommended to take a break periodically and perform eye exercises;
- If your eyes are very dry, use moisturizing drops.
If you follow the rules, the load is reduced not only on the eyes, but also on the spine. Therefore, the brain is well supplied with blood.
Baby's visual mode
Try to preserve your child’s vision in the modern world of computers and other similar devices. Dose your baby's visual load, do not let him spend indefinitely with a tablet or smartphone. Alternate periods of intense visual work with active rest. Walking in the fresh air is very beneficial. No one will argue that today our life is unthinkable without the achievements of technological progress: smartphones, tablets, laptops surround us everywhere, including at home. And it is not surprising that they are used not only by parents, but also by their children.
At a very early age, children easily master various gadgets: the child has not yet learned to speak, but already knows how to turn on a game or cartoon on his mother’s tablet.
But is it so harmless for the child’s health? According to experts, technological progress is fraught with certain dangers. Therefore, they have developed recommendations for parents that will help preserve the baby’s vision and at the same time not infringe on his desire to keep up with the times.
Adults who spend a lot of time at the computer are aware of the unpleasant sensations that arise, such as discomfort and fatigue. But the same symptoms are typical for babies! But unlike mothers and fathers, such stress affects young children much more seriously and can cause a sharp decrease in vision.
Parents need to understand that early intensive “exploitation” of the eyes at close range threatens the inevitable deterioration of the child’s vision and leads to the development of myopia, or myopia. The insidiousness of this disease is that the earlier it manifests itself, the faster it progresses.
With myopia, a child has difficulty seeing objects located in the distance. This occurs due to a violation of the optics of the eye, in which the image is formed not on the fundus, but in front of it. If treatment is not started on time, degenerative changes may occur in the retina and fundus of the eye, which can lead to loss of vision.
A child should only draw or sculpt at a table and only in good lighting. The light source should be bright, but not tiring, and located on the left side (if the child is right-handed) so as not to create shadows.
In children under three years of age, there is a high probability of developing myopia, even in cases where the child does not have a genetic predisposition to it. The cause of the pathological condition is constant stress on the eyes, which can be facilitated by loving parents who actively involve their little geniuses in the process of learning about the world with the help of modern technologies.
Between the ages of one and three years, the visual organs actively develop. That is why during this period it is very important to create conditions for the proper functioning of the visual system. The visual load of a small child must be strictly dosed.
Until the age of three, it is better not to watch TV at all. This not only puts unbearable strain on the eyes, but also negatively affects the central nervous system. For an older child, watching children's programs should not exceed an hour a day, and the distance to the TV should be at least 3 meters with an average screen size.
The distance from the baby’s eyes to the computer monitor or gadget screen should be at least 30-40 cm at rest.
The use of gadgets in transport is extremely undesirable, since the distance to the screen changes when moving, which causes fatigue of the ciliary muscle responsible for accommodation.
If a child sees well, then during long classes he must nevertheless take breaks every 15-20 minutes.
Make sure your baby maintains correct posture. It is known that curvature in the cervical spine can cause visual impairment.
A balanced diet will help maintain good vision. Be sure to include more fish, cottage cheese, nuts, and honey in your baby’s menu (if you are not allergic to these products).
With a congenital pathology, a small child may not complain about decreased vision, because he does not know what it means to see clearly. Only a pediatric ophthalmologist can make a diagnosis.
Therefore, children from one to three years old must be shown to a pediatric ophthalmologist for an ophthalmological examination once every six months.
For myopia, treatment is aimed at stopping its progression and preventing the development of complications.
Therapeutic treatment can be carried out on a child from the age of two. To achieve the required effect, 3-4 courses of treatment may be needed over the course of a year.
All therapeutic measures, including the prescription of spectacle correction and conservative methods of training visual functions, must be carried out by a qualified pediatric ophthalmologist.
Don't be afraid of getting glasses. For mild myopia, they are prescribed only for distance, so that the child feels comfortable. For constant wear they are prescribed only for high myopia.
In our practice, in 82% of cases it is possible to stabilize myopia. This is achieved through the joint work of the ophthalmologist, parents and young patients.
Carefully monitor your baby’s behavior: if he starts squinting, complains of fatigue and headaches, or squints his eyes, urgently take him for a consultation with a pediatric ophthalmologist. These complaints may be the first symptoms of vision loss! Now parents have a choice: they can treat their child in a clinic at their place of residence or in non-state specialized children's eye clinics. Moreover, some clinics accept children for free, under a compulsory health insurance policy. Treatment of eye diseases in children is more effective at an early age, until the visual system is fully formed. Therefore, it is very important to identify the disease in time and immediately take measures to correct the situation. To stabilize myopia, therapeutic treatment is carried out - as a rule, this becomes possible from the age of two. The treatment course includes techniques to restore normal accommodation (the ability of the eye to switch focal length), metabolic processes and improve microcirculation in the eyeball. This treatment is painless, well tolerated by young children and may even include play components.
Gymnastics for the eyes
Gymnastics for the visual organs is performed in several stages:
- moving the gaze from a near to a distant object;
- circular eye movements to the right, then to the left;
- moving the eyes up and down in turn;
- alternate squinting and widening of the eyelids;
- blink very quickly for 30 seconds;
- strong tension in the muscles of the face and neck, then relaxation.
Eye exercises help relax the muscles around and inside the eyeballs. Using the method, blood flows and the lens relaxes.
STRUCTURE AND HYGIENE OF THE VISUAL ANALYZER.
Purpose of the lesson : To get acquainted with the structure of the visual analyzer, the mechanism of its functioning, age characteristics and hygiene.
1. PROGRESS OF WORK
1. Consider the structure of the visual analyzer, find its main sections: peripheral, conductive and cortical (Atlas
1, p. 102).
2. Familiarize yourself with the auxiliary apparatus of the eye (upper and lower eyelids, conjunctiva, lacrimal apparatus, motor apparatus).
3. Examine and study the membranes of the eyeball; location, structure, meaning. Find the yellow and blind spot (Atlas
2, p. 331).
. 4. Consider and study the structure of the nucleus of the eyeball - the optical system of the eye, using a collapsible model of the eye and a table (Atlas, P. 100)
— Sketch the structure of the eye, identifying all the membranes and elements of the optical system (Atlas 2, p. 331).
5. Find and examine the structure of the conductive section! (Atlas 1, p. 100, Atlas 2, p. 332-338).
6. Explain the mechanism of formation of visual sensations.
7. The concept of refraction, types of refractions. Draw a diagram of the path of rays for different types of refraction (Atlas 2, p. 334) - IT’S BETTER TO PLACE THIS DIAGRAM IMMEDIATELY IN THE MANUALS
8.Name the age-related features of the visual analyzer.
9. Hygiene of the visual analyzer.
10. Determine the state of some visual functions: visual acuity, using the Golovin-Sivtsev table; blind spot dimensions
2. Theoretical material
2.1. Concept of a visual dialyzer
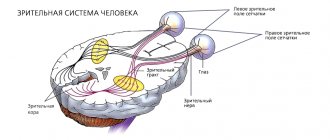
The visual analyzer is a sensory system, including a peripheral section with a receptor apparatus (eyeball), a conducting section (afferent neurons, optic nerves and visual pathways), a cortical section, which represents a set of neurons located in the occipital lobe (17,18,19 lobe) cortex of the large hemispheres. With the help of a visual analyzer, the perception and analysis of visual stimuli is carried out, the formation of visual sensations, the totality of which gives a visual image of objects. Thanks to the visual analyzer, 90% of the information enters the brain.
2.2. Peripheral department of the visual analyzer
The peripheral section of the visual analyzer is the organ of vision of the eyes. It consists of the eyeball and an auxiliary apparatus. The eyeball is located in the orbit of the skull. The auxiliary apparatus of the eye includes protective devices (eyebrows, eyelashes, eyelids), lacrimal apparatus, and motor apparatus (eye muscles).
The eyelids are semilunar plates of fibrous connective tissue; they are covered on the outside with skin and on the inside with mucous membrane (conjunctiva). The conjunctiva covers the anterior surface of the eyeball, except for the cornea. The conjunctiva limits the conjunctival sac, which contains tear fluid that washes the free surface of the eye. The lacrimal apparatus consists of the lacrimal gland and lacrimal ducts.
The lacrimal gland is located in the upper-outer part of the orbit. Its excretory ducts (10-12) open into the conjunctival sac. Tear fluid protects the cornea from drying out and washes away dust particles. It flows through the lacrimal canaliculi into the lacrimal sac, which is connected by the nasolacrimal duct to the nasal cavity. The motor apparatus of the eye is formed by six muscles. They are attached to the eyeball, starting from the tendon end located around the optic nerve. Rectus oculi muscles: lateral, medial superior and inferior - rotate the eyeball around the frontal and sagittal axes, turning it inward and outward, up and down. The superior oblique muscle of the eye, turning the eyeball, turns the pupil down and outward, the inferior oblique muscle of the eye - upward and outward.
The eyeball consists of membranes and a nucleus. Shells: fibrous (outer), vascular (middle), retina (inner).
The fibrous membrane in front forms the transparent cornea, which passes into the tunica albuginea or sclera. This outer shell protects the core and maintains the shape of the eyeball. The choroid lines the albuginea from the inside and consists of three parts that are different in structure and function: the choroid itself, the ciliary body located at the level of the cornea and iris (Atlas, p. 100).
The choroid itself is thin, rich in blood vessels, and contains pigment cells that give it a dark brown color.
The ciliary body, which has the appearance of a roller, protrudes into the eyeball where the tunica albuginea passes into the cornea. The posterior edge of the body passes into the choroid proper, and up to 70 ciliary processes extend from the anterior one, from which thin fibers originate, the other end of which is attached to the lens capsule along the equator. At the base of the ciliary body, in addition to the vessels, there are smooth muscle fibers that make up the ciliary muscle.
The iris or iris is a thin plate, it is attached to the ciliary body. In its center is the pupil, its lumen is changed by the muscles located in the iris.
The retina lines the choroid from the inside (Atlas, p. 100); it forms the anterior (smaller) and posterior (larger) parts. The posterior part consists of two layers: pigment, fused with the choroid, and medulla. The medulla contains light-sensitive cells: cones (6 million) and rods (125 million). The largest number of cones is in the central fovea of the macula, located outward from the disc (the exit point of the optic nerve). With distance from the macula, the number of cones decreases and the number of rods increases. Cones and net glasses are photoreceptors of the visual analyzer. Cones provide color perception, rods provide light perception. They contact bipolar cells, which in turn contact ganglion cells. The axons of ganglion cells form the optic nerve (Atlas, p. 101). There are no photoreceptors in the disk of the eyeball, this is the blind spot of the retina.
The nucleus of the eyeball is the light-refracting media that form the optical system of the eye: 1) aqueous humor of the anterior chamber (it is located between the cornea and the anterior surface of the iris); 2) aqueous humor of the posterior chamber of the eye (it is located between the posterior surface of the iris and the lens); 3) lens; 4)vitreous body (Atlas, p. 100). The lens consists of a colorless fibrous substance, has the shape of a biconvex lens, and is elastic. It is located inside a capsule attached to the ciliary body by filiform ligaments. When the ciliary muscles contract (when viewing close objects), the ligaments relax and the lens becomes convex. This increases its refractive power. When the ciliary muscles relax (when viewing distant objects), the ligaments become tense, the capsule compresses the lens and it flattens. At the same time, its refractive power decreases. This phenomenon is called accommodation. The vitreous body is a colorless, gelatinous, transparent mass of spherical shape.
2.3. Conductive section of the visual analyzer. The conductive section of the visual analyzer includes bipolar and ganglion cells of the retinal medulla, optic nerves and visual pathways formed after the optic chiasm. In monkeys and humans, half of the optic nerve fibers intersect. This provides binocular vision. The visual pathways are divided into two roots. One of the nicks is directed to the superior colliculus of the midbrain, the other to the lateral geniculate body of the diencephalon. In the optic thalamus and lateral geniculate body, excitation is transferred to another neuron, the processes (fibers) of which, as part of the optic radiation, are directed to the cortical visual center, which is located in the occipital lobe of the cerebral cortex (fields 17, 18, 19).
2.4. Mechanism of light and color perception.
The light-sensitive cells of the retina (rods and cones) contain visual pigments: rhodopsin (in rods), iodopsin (in cones). Under the influence of light rays penetrating through the pupil and the optical system of the eye, the visual pigments of the rods and cones are destroyed. This causes excitation of light-sensitive cells, which is transmitted through the conductive section of the visual analyzer to the cortical visual analyzer. In it, a higher analysis of visual stimuli occurs and a visual sensation is formed. Light perception is related to the function of rods. They provide twilight vision. Light perception is related to the function of cones. According to the three-component theory of vision put forward by M.V. Lomonosov, there are three types of cones, each of which has increased sensitivity to electromagnetic waves of a certain length. Some cones are more sensitive to the waves of the red part of the spectrum (their length is 620-760 nm), another type is more sensitive to the waves of the green part of the spectrum (their length is 525-575 nm), the third type is more sensitive to the waves of the violet part of the spectrum (their length is 427-397 nm ). This provides color perception. The photoreceptors of the visual analyzer perceive electromagnetic waves with a length from 390 to 760 nm (1 nanometer is equal to 10-9 m).
Impaired cone function causes loss of correct color perception. This disease is called color blindness after the English physicist Dalton, who first described this disease in himself. There are three types of color blindness, each of them characterized by a violation of the perception of one of three colors. Red-blind people (with protanopia) do not perceive red color; they see blue-blue rays as colorless. Green-blind people (with ditteranopia ) do not distinguish green from dark red and blue. People with trianopia do not perceive blue and violet rays of the spectrum. With a complete impairment of color perception (achromasia), all colors are perceived as shades of gray. Men* (8%) are more likely to suffer from color blindness than women (0.5%).
2.& Refraction
Refraction is the light refractive ability of the optical system of the eye when the lens is maximally flattened. The unit of measurement for the refractive power of any optical system is diopter (D). One D is equal to the refractive power of a lens with a focal length of 1 m. When viewing close objects, the refractive power of the eye is 70.5 D, and when viewing distant objects, it is 59 D.
Passing through the light-refracting media of the eye, light rays are refracted and a sensitive, reduced and inverse image of objects is obtained on the retina.
There are three types of refraction: commensurate (emmetropia), nearsightedness (myopia) and farsightedness (hypermetropia).
Commensurate refraction occurs when the anterior-posterior diameter of the eyeball is commensurate with the main focal length. The main focal length is the distance from the center of the lens (cornea) to the point where the rays intersect, with the image of objects located on the retina of the eye (normal vision).
Myopic refraction is observed when the anteroposterior diameter of the eyeball is greater than the main focal length. The image of objects is formed in front of the retina. To correct myopia, diverging biconcave lenses are used, which increase the main focal length and thus transfer the image to the retina.
Farsighted refraction is observed when the anterior-posterior diameter of the eyeball is less than the main focal length. The image of objects is formed behind the retina. To correct farsightedness, converging biconvex lenses are used, which reduce the main focal length and transfer the image to the retina (Atlas 2, Fig. 333).
Astigmatism is a refractive error along with myopia and farsightedness. Astigmatism is the unequal refraction of rays by the cornea of the eye due to its different curvature along the vertical and horizontal meridians. In this case, the rays are not focused at one point. A small degree of astigmatism is characteristic of the eyes even with normal vision, because The surface of the cornea is not strictly spherical. Astigmatism is corrected with cylindrical glasses that align the curvature of the cornea along the vertical and horizontal meridians.
2.6 Age characteristics and hygiene of the visual analyzer.
The shape of the smooth apple in children is more spherical than in adults; in adults, the diameter of the eye is 24 mm, and in newborns - 16 mm. As a result of this shape of the eyeball, newborn children have farsighted refraction in 80-94% of cases. The growth of the eyeball continues after birth and long-sighted refraction is replaced by proportional refraction by 9-12 years. The sclera in children is thinner and has increased elasticity. The cornea of newborns is thicker and more convex. By the age of five, the thickness of the cornea decreases, and its radius of curvature does not change with age. With age, the cornea becomes denser and its refractive power decreases. The lens in newborns and preschool children is more convex and has greater elasticity. With age, the elasticity of the lens decreases, so the accommodative capabilities of the eye change with age. At 10 years old, the nearest point of clear vision is 7 cm from the eye, at 20 years old - 8.3 cm, at 50 years old - 50 cm, and at 60-70 years old it approaches 80 cm. Light sensitivity increases significantly from 4 to 20 years old , and after 30 years it begins to decline. Color discrimination increases steeply by age 10, continues to increase until age 30, and then slowly declines in old age.
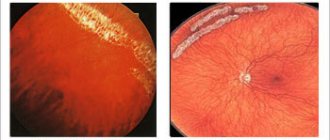
Eye diseases and their prevention. Eye diseases are divided into inflammatory and non-inflammatory. Measures to prevent inflammatory diseases include strict adherence to the rules of personal hygiene: frequent hand washing with soap, frequent change of personal towels, pillowcases, and handkerchiefs. Nutrition, the degree of its balance in the content of nutrients and especially vitamins, is also essential. Inflammatory diseases occur when the eyes are injured, so strict adherence to the rules is necessary when performing various works. The most common visual impairment is myopia. There are congenital and acquired myopia. Acquired myopia is more common. Its development is facilitated by prolonged strain on the organ of vision at close range when reading and writing. This causes an increase in the size of the eye, the eyeball begins to protrude forward, and the palpebral fissure widens. These are the first signs of myopia. The appearance and development of myopia depends both on the general condition and on the influence of external factors: pressure on the walls of the eye from the muscles during prolonged work of the eyes, the approach of an object to the eye during work, excessive tilt of the head causing additional blood pressure on the eyeball, poor lighting, incorrectly selected furniture, reading small print, etc.
Prevention of visual impairment is one of the tasks in raising a healthy younger generation. Almost all preventive work should be aimed at creating favorable conditions for the functioning of the organ of vision. The correct mode of work and rest, good nutrition, sleep, long stay in the fresh air, dosed work, the creation of normal hygienic conditions deserve great attention, in addition, it is necessary to monitor the correct seating of children at school and at home when reading and writing, lighting of the workplace, every 40-60 minutes it is necessary to rest the eyes for 10-15 minutes, for which you need to recommend that children look into the distance to relieve tension in the accommodative muscle.
Practical work
1, Determine visual acuity (Guminsky N.V.. Work No. 522)
2. Determine the field of view (Guminsky N.V. Work N 54)
3. Determine the size of the blind spot.
4. Write data
5. Conduct some experiments with vision.
Visual acuity. Visual acuity is determined using the Golovin-Sivtsev table. It consists of two halves: the left contains letters, the right contains rings with breaks. The letters and rings are arranged in a random order of 12 lines, each containing characters of the same size. When studying visual acuity in preschool children, a special table is used with test objects that are understandable to children (Christmas tree, airplane, mushroom, etc.). Opposite each line on the left is the value of visual acuity in conventional units. The top line corresponds to visual acuity 0.1. The table is designed to test visual acuity at a distance of 5 m.
When determining visual acuity, the table is placed on the side opposite the window, and at the eye level of the subject. The acuity of each eye is set separately, starting with the right. The other eye is covered with a sheet of paper or notebook. Using a pointer or the blunt end of a pencil, letters or rings are shown on the table. If a subject correctly names the signs of the top 10 lines of the table from a distance of 5 m, then his visual acuity is 1.0 and is considered normal.
Example.
The subject from a distance of 5 m reads without errors only the top 5 lines of the Golovin-Sivtsev table. Conclusion. Visual acuity is 0.5.
In the absence of a table, visual acuity can be approximately determined using test objects in the form of the letter “W” of various sizes, which can be cut out of black paper or from Golovin tables. With visual acuity equal to 1.0, the smallest letter can be distinguished from a distance of 5 m (D = 5 m), the middle and large letters, respectively, from a distance of 10 m (D = 10 m) and 25 m (D = 25 m). First, the smallest letter is shown and the distance ( d ) from which it is clearly distinguished by both eyes and each individually is determined. The permissible level of distance reduction is 3 m. If the letter is not distinguishable from this distance, then larger letters are used. Visual acuity is determined using the formula: V (visus) = d :D, where V is visual acuity in relative units; d— _
the distance from which the subject reads the letter correctly; D is the distance in meters from which the letter should be distinguished correctly (5, 10 and 25 m).
Example.
The letter “Ш” of the smallest size can be read correctly from a distance of 4 m. The visual acuity of the subject should be determined approximately.
Solution. V= d: D = 4:5 = 0.8.
Conclusion. The subject's visual acuity is 0.8.
Blind spot. To determine it, you need a small wire pointer with a white circle at the end, a sheet of black paper, and colored chalk.
There are no light-sensitive cells in the area of the retina where the optic disc is located. The optic disc takes up quite a bit of space on the retina. In your field of vision there is an oval zone corresponding to the disk - this is a blind spot.
Make a pointer from thin wire, attach a white circle with a diameter of about 3 mm to its tip. Place a white dot in the center of a sheet of black paper measuring at least 20 - 24 cm. Attach the paper to the wall. Blindfold one of your partner's eyes and sit him down so that the other eye is exactly opposite the fixation point at a distance of 30-35 cm. Let him look motionlessly at this point. Using the white circle on the pointer, guide along a sheet of black paper. First, the subject sees a circle, then it disappears. Mark this place and move the pointer further - the circle will appear again. Mark this place as well. Repeat the procedure in several directions - you will get an oval outline of the blind spot.
Thus, the object is not visible when it is projected onto the optic disc. Measure the marked area of the blind spot. Now calculate the size of the corresponding area at a distance of one hundred meters from the eye. You can hide an entire car.
Experiments with vision.
Thousands of visual illusions are known.
1. Changeling figures:
2. Direction of lines:
The lines appear non-parallel because other lines intersect them at an angle.
a b
3. Dominant eye
Did you know that one eye is your dominant eye?
Take a piece of cardboard with a hole about 2.5 cm in diameter. Hold the cardboard at arm's length and look through the hole at some distant object. Gradually move the cardboard closer to your face until it touches your nose. Then it will become clear that only one eye was looking through the hole, and it is the leading one. By repeating this experiment, determine whether the leading eye is always the same. In some people, the eyes are equivalent and the dominant eye cannot be identified.
4. *Hole* in the palm
Roll up a narrow tube of newspaper and place it over one eye. Place your palm near the end of the tube in front of your other eye so that it obscures the center of that eye’s field of vision. Thus, you turn off the entire periphery of the visual field of one eye and the center of the visual field of the other eye. Look straight ahead. A rather strange image is formed: its periphery is the objects in the room and the palm, and the center is a hole in the palm through which distant objects are visible - and all this makes up a single picture.
This experience once again clearly demonstrates that the integrity of the visual field is such an important condition that all interference with holistic perception is eliminated.
Prevention of ophthalmological pathologies
To prevent diseases developing in the organs of vision, adhere to the following rules:
- the food consumed must contain all vitamins, microelements, minerals, amino acids;
- the use of multivitamin complexes with a reduced amount of any microelement;
- proper rest during the day, sleep at least 8 hours a day;
- visiting an ophthalmologist at least once a year, especially for people who have chronic eye disease;
- using hygiene rules to prevent the introduction of infections and viruses.
Most people will have eye diseases throughout their lives. To prevent them, prevention rules are used. If the doctor has prescribed any medication, you should strictly adhere to the dosage. If there is no effect, only an ophthalmologist can replace the drug. Self-treatment can lead to complications.
Visual hygiene: how to properly care for your eyes
The human eye weighs 8 grams. But in order to save these precious 16 grams, sometimes you have to make significant efforts. Although for most people, for long and happy vision, you need to follow very simple hygiene rules, which we’ll talk about today.
Don't close your eyes when you wash your face! Water should get not only on the eyelids, but also on the eyes.
- We wash ourselves according to science. Eye care is primarily the prevention of infectious diseases. How to properly wash your eyes?
- To wash hands.
- Wash your face at least twice a day.
- You can wash your eyes with clean running water or a decoction of chamomile, mint, or sage.
- When washing your face, you don’t need to close your eyes too much; the water should get not only onto your eyelids, but also onto your eyeballs!
- Dry yourself with a personal towel.
- You can also wipe your eyes with a cotton pad soaked in water or a decoction of herbs. The direction of movement is from the temple to the inner corner of the eye. For each eye - a separate cotton pad.
Useful gadgets for the eyes
Gadgets can not only harm vision, but also work to preserve it. Let's talk about some modern eye aids.
Use the offer store on your smartphone. There will be things useful for your vision there.
- Massager glasses. Manufacturers promise that they will improve blood flow in the eye area, tone muscles, and normalize eye pressure.
- Relax glasses will help relieve eye fatigue and relax the eye muscles.
- Training glasses, perforated. Thanks to the holes, they prevent the eye muscles from atrophying and train them.
- Mobile applications “Eye acuity test” and “iKulist”, with which you can test your vision and identify possible visual impairments.
- Programs with sets of useful exercises for the eyes: EyeCorrector, Vision+.
If you wear contact lenses:
- do not use lenses for more than 19 hours;
- do not sleep in lenses;
- do not swim with lenses on;
- wear lenses according to the manufacturer's instructions and doctor's recommendations;
- wash your hands before putting on or removing lenses;
- refuse contact lenses if you have a cold, when the body is weakened and dehydrated - during these periods the eyes become dry, opening the way for infections.
If you wear glasses:
- use glasses of current diopters;
- Make sure your glasses lenses are always clean;
- Change your glasses every 2–3 years—scratches on the lenses are harmful to your eyes.
Positive effects on eye health:
- balanced diet;
- rejection of bad habits;
- adherence to daily routine;
- good sleep;
- eye gymnastics.
If you have questions about eye hygiene, contact our specialists or ask them during a consultation with an ophthalmologist.