What are styes and chalazions?
Stye is a very common disease, it is difficult to find anyone who has not experienced it at least once.
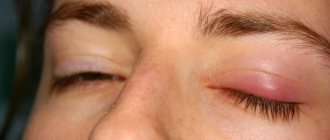
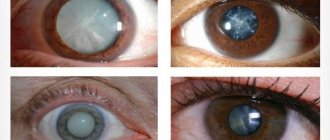
Stye, or hordeolum, is an inflammatory disease of the eyelid. This is a purulent process that begins as a result of infection and is localized in one of the hair follicles of the eyelashes, the Zeiss sebaceous gland or a lobule of the meibomian gland. Depending on its location, it can be external (on the edge of the eyelid) or internal (on its inner surface).
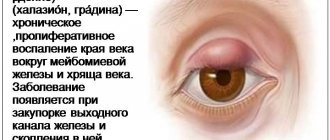
Chalazion, or chalazion, hailstone, is, unlike barley, a chronic disease. This is a tumor-like formation that slowly increases due to blockage of the outlet channel of the meibomian gland and the accumulation of secretory fluid in it.
Visually, barley and chalazion may look similar at the beginning of the process. But in essence these are completely different diseases.
Signs of chalazion:
- the appearance of a “ball” in the thickness of the eyelid;
- the eyelid turns red and swells;
- possible slight inflammation of the conjunctiva (the mucous membrane inside the eyelid and on the white of the eyeball);
- soreness and feeling of sand in the eye;
- photosensitivity;
- lacrimation with internal chalazion;
- decreased vision with large or multiple chalazions.
When entering the chronic stage, the disease can last for years. The addition of pathogenic microflora contributes to the development of purulent inflammation - an abscess. The skin over the chalazion turns red, hurts, swells, and your health worsens. To prevent this, you need to start treatment in a timely manner.
Difference in causes
Barley occurs due to two reasons:
- infection inside the eyelid;
- weakening of the immune system.
In the vast majority of cases, the causative agent is Staphylococcus aureus. Its distribution routes are: airborne, household contact, medical or nutritional. Usually, violation of personal hygiene rules - rubbing the eye with dirty hands - leads to infection of the eyelid if the body is weakened due to the following factors:
- Malnutrition or vitamin deficiency.
- The presence of an infectious, viral, cold disease or recovery period after it.
- Side effects of certain medications.
- Smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Stress, lack of sleep, chronic fatigue.
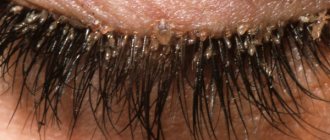
- The presence of eye diseases such as conjunctivitis, keratitis, blepharitis, as well as some common diseases - diabetes mellitus, gastrointestinal pathologies, demodicosis, seborrhea, furunculosis, elevated lipid levels.
The causes of chalazion are many and in most cases they are unclear. It often develops after general hypothermia of the body.
Barley is also common in children.
Wearing contact lenses is considered a provocative factor. In addition, the following conditions may cause blockage of the sebaceous meibomian gland:
- congenital pathologies of the gland (its improper development);
- endocrine system disorders (diabetes mellitus), genetic predisposition, increased oily skin;
- too much decorative cosmetics on the eyes and neglect of hygiene rules when removing them;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- decreased immunity.
Despite some similar causes of both diseases, the main difference is the presence of infection and purulent inflammation in barley. In rare cases, untreated stye may develop into a chalazion. In this case, these will be two different diseases superimposed on each other.
What diseases provoke the development of hordeolum?
It is believed that the main cause of barley is hypothermia and associated colds. The inflammatory process often develops due to weakened immunity, which cannot fight bacteria and viruses. Pathologies of a bacterial and viral nature that cause inflammation include diseases such as:
- sinusitis;
- ethmoiditis;
- tonsillitis;
- sphenoiditis;
- frontitis.
Stye is one of the common consequences of many chronic diseases. They not only lead to inflammation, but also complicate its diagnosis and treatment. In some diseases, it is very difficult to get rid of barley forever, as they predispose to relapses of the inflammatory process. Such pathologies include:
- anemia;
- gastritis;
- diabetes;
- stomach ulcer;
- hyperlipidemia;
- peritonitis;
- furunculosis.
The body must regularly receive the amount of vitamins required for its normal functioning. The development of the inflammatory process is often associated with a deficiency of vitamins A, B and C.
Sometimes stye occurs due to disorders that many people think do not pose a health risk. For example: helminthiasis, skin tendency to become greasy, acne formation.
How to distinguish diseases by symptoms?
A clear difference between barley and chalazion.
Barley has the following clinical manifestations:
- at the very beginning of the development of the inflammatory process - a feeling of discomfort, itching, sensation of a foreign body in the eye, then acute pain when blinking, increased tearfulness;
- swelling of the eyelid, hyperemia of the mucous membrane, formation of a compaction with a purulent top;
- after a few days - opening of the “head” with pus and necrotic core coming out of it;
- reduction of swelling, reduction and complete disappearance of painful or unpleasant symptoms.
If your immune system is very weakened, the following symptoms may also occur:
- increased body temperature;
- headache;
- general malaise, lack of appetite, nausea;
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes, usually in the neck.
Manifestations of chalazion at the initial stage have similar features:
- the formation of a pea-sized lump over several weeks (the skin over it is mobile, the conjunctiva is hyperemic and has a small gray area in the center);
- the formation does not cause pain, except that if the lump is large, the feeling of pressure on the cornea may be unpleasant (it can cause astigmatism of the eye);
- If, due to non-compliance with hygiene rules, the chalazion becomes infected, suppuration, pain, and redness of the skin of the eyelids are possible.
Externally, the disease looks only like a rounded formation at the edge of the upper or lower eyelid.
The symptoms of the diseases vary enough that you can independently determine what exactly is bothering you: stye or chalazion.
Features of barley
Barley is a purulent inflammation of the hair follicle of the eyelash or Zeiss (sebaceous gland), which affects the bulb of the eyelash. Read more about the disease here.
Related material: 9 ways to quickly get rid of stye
Symptoms of stye are:
- painful swelling;
- edema;
- redness of the eyelid.
As a result, after 2–4 days a yellow purulent head is formed, which is removed with particles of dead tissue. In some cases, complications such as headaches, increased body temperature and swollen lymph nodes are possible.
It is contraindicated to squeeze out pus yourself! This can lead to dissemination of the infection and the appearance of new styes.
Also read: Features of treatment of stye on the eye during pregnancy
Reasons for appearance. Prevention. Treatment
Risk factors are:
- frequent hypothermia;
- disruption of the digestive tract;
- avitaminosis;
- weak immunity;
- Staphylococcus aureus.
The condition of the eyelids themselves plays a significant role; the presence of dermatological diseases aggravates the risk of stye.
To prevent and treat the disease, it is necessary to follow the rules of personal hygiene and not touch your eyelids with dirty hands.
In the initial stage, barley is lubricated with a 1% solution of brilliant green 3 to 5 times a day. They also make drip injections of medicines into the conjunctival cavity of solutions:
- sulfacyl sodium 20%;
- erythromycin solution 1%;
- dexamethasone 0.1%.
They also use ointments that are lubricated on top of the eyelid and placed under it. Treatment usually lasts up to 2 weeks.
Features during the course of diseases
Barley “gives” quite acute pain, sometimes even low-grade fever. When a chalazion develops, they are absent, apart from discomfort if the granulation is large enough.
Symptoms of chalazion develop over at least a month, or even two. The ulcer “ripens” in a couple of days.
The formation with barley is softer to the touch than with chalazion. Barley most often opens spontaneously; after the pus is released, there are no scars left. In the case of hailstones, if infection occurs and pus forms, it can escape through the fistula tract and continue to form.
Differences in symptoms
The main reason why people confuse chalazion and stye is the similarity of symptoms of these diseases. But there is a way to distinguish ophthalmological pathologies by symptoms.
Initially, barley shows itself very clearly with the following signs:
- feeling of discomfort in the eyelid area;
- itching of the skin at the site of inflammation;
- feeling of a foreign body in the eye.
After some time, swelling of the eyelid appears, and uncomfortable symptoms increase. Discomfortable sensations (pain, itching) are very disturbing, sometimes low-grade fever (37-38 degrees) occurs, and the lymph nodes located near the ears become enlarged. On the 3rd or 4th day, a compaction forms at the site of greatest irritation of the skin, which gradually develops a purulent apex. After a few more days, the top breaks through and pus flows out. After this, the inflammatory process subsides, and soon the sore heals completely.
Read in a separate article: Tumor on the eyelid: causes and types
The difference between a chalazion and a stye is that initially a dense tubercle appears on the upper or lower eyelid, which does not cause severe pain when palpated. The skin behind it moves easily, it does not fuse with it. With barley, this process is accompanied by itching, profuse lacrimation, and sometimes there is pain of a pulsating nature. With the development of a chalazion, practically no painful symptoms are noted. With barley, over time, the head of the abscess appears, and the chalazion remains just a hard lump.
Treatment of stye and chalazion
If you consult a doctor in time, the risk of surgical treatment becomes minimal.
In 25% of cases, if the chalazion is not complicated by an inflammatory process, a few days after formation it begins to resolve and goes away on its own. If it occurs regularly, you should definitely consult a doctor to identify the causes and effective treatment.
An ophthalmologist can prescribe eye ointments and drops that promote the process of tumor resorption and restore the functioning of the meibomian gland duct, and also, depending on the degree of development of the process, recommend the following treatment options:
- Traditional medicine methods are effective in the case of treating a one-time or rare chalazion that is not complicated by infection - they use compresses from a warm infusion of chamomile and calendula flowers, as well as a light massage of the tumor in a circular motion (if localized on the lower eyelid - the direction of movement is upward, on the upper - downward) several times a day.
- Steroid injections directly into hailstones. This method works well to reduce inflammation.
- Surgical option. A large chalazion that constantly recurs can be removed with an incision and curettage. Performed under local anesthesia, without pain.
If a chalazion forms regularly, you should definitely undergo an examination, which will be prescribed by a therapist. The problem may be caused by the presence of another chronic pathology.
Stye is treated with antibacterial drops and ointments for a week. The abscess usually opens up on its own earlier, but in order to avoid relapses, you need to endure the full period of using the drugs.
Clinical picture
Barley is a purulent inflammation of the glands of the eyelid. It has an infectious basis, most often the causative agent of the disease is Staphylococcus aureus. There are two forms of the disease: external and internal. In the first case, a purulent formation occurs on the edge of the eyelid at the location of the excretory ducts of the glands. The inner stye on the eye can only be seen by turning the eyelid itself out.
Chalazion does not have an infectious basis, and therefore is not a disease contagious to other people. It is a small thickening of the eyelid that may disappear on its own a few days after formation.
Prevention: prevention is better than cure
What is common in the prevention of both diseases is:
- maintaining personal hygiene (use a personal clean face towel, do not touch your eyes with dirty hands);
- strengthening the immune system (hardening, taking the necessary medications in consultation with the doctor).
In case of frequent relapses of diseases, you need to be examined by a therapist and, if necessary, by specialized specialists (dermatologist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist).
In the video below, experts talk about the symptoms and treatment methods for barley:
How does stye differ from chalazion: how to identify the disease
Many people, noticing a slight redness on their eyelids, in place of which a compaction in the form of a ball or hailstone gradually forms, believe that it is a stye that has popped up and begin to treat it on their own. But there is another ophthalmological disease that has a similar manifestation, clinical picture, and symptoms. This is a chalazion. Despite the external similarity of barley and chalazion, they have significant differences, identifying which can quickly get rid of the problem. How barley differs from chalazion will be discussed further.
Causes of chalazion and stye
The tear fluid protects the eyes from dryness. To prevent it from evaporating from the surface of the eye, there is a special sebaceous secretion secreted by the meibomian glands, located throughout the edges of the eyelids. This secretion creates a thin lipid layer on the conjunctiva, protecting tears from rapid evaporation. If, due to poor hygiene, excessive accumulation of fat mixed with dust, particles of the epidermis, the glands become clogged, blocking the release of sebum, they become denser, and a hard ball appears - a chalazion (“hailstone”). When an infection gets into the gland or another part of the eyelid, a compaction with purulent contents appears - barley (hordeolum).
Chalazion affects the edges of the eyelids due to stagnation in the outlet channel of the meibomian gland of fatty secretion, which is necessary to lubricate the eyelashes, the edges of the eyelids, and the cornea to prevent friction of the eyelids against the eye during blinking. If the meibomian gland duct is blocked, fatty secretions accumulate in it. In this case, the immune system surrounds it with a fibrous capsule, but the secretion continues to accumulate in it and the hailstone grows. The prerequisites for the appearance of chalazion and stye have their own similarities and differences.
Barley often develops due to the following provoking factors:
- weakened immune system;
- metabolic diseases;
- constant hypothermia;
- infectious, viral diseases;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- avitaminosis.
Chalazion and stye have both similarities and differences depending on the cause of their occurrence.
Predictive factors include:
- genetic predisposition;
- improper eyelid skin hygiene or lack thereof;
- oily facial skin;
- endocrine diseases;
- chronic gastrointestinal diseases;
- weakened immunity;
- use of low-quality decorative cosmetics;
- daily use of contact lenses that are stored, put on and removed without proper hygiene.
Differences in the clinical picture
Barley is an acute inflammation localized in the ciliary follicle, the Zeiss sebaceous gland or the meibomian gland. A chalazion is a tumor-like compaction that slowly develops due to blockage of the outlet channel of the meibomian gland and the accumulation of secretory fluid there. These two ophthalmological diseases are very similar in appearance, but in essence they are completely different pathologies.
Barley is infectious in nature and its main causative agent is Staphylococcus aureus.
It can be internal, when the seal can be seen by turning the eyelid, and external, in which purulent inflammation develops on the edge of the eyelid from the outside at the point where the inflamed gland is located. The lump matures in 3-10 days, filling with pus and causing great discomfort to the person. As the seal matures, it opens on its own and after the pus flows out, the wound heals without a trace.
Unlike barley, chalazion does not have an infectious nature; it is not contagious. Patients are mainly concerned about aesthetic discomfort associated with the appearance of an unsightly formation in a visible place. Only as the hailstones increase in size can pressure be felt on the eye, which can lead to damage.
Chalazion develops slowly over a month or even two. The seal may disappear on its own, but if an infection gets inside and pus forms, a fistula occurs, through which the purulent mass will be released, but the chalazion will continue to form.
Differences in symptoms
The main reason why people confuse chalazion and stye is the similarity of symptoms of these diseases. But there is a way to distinguish ophthalmological pathologies by symptoms.
Initially, barley shows itself very clearly with the following signs:
- feeling of discomfort in the eyelid area;
- itching of the skin at the site of inflammation;
- feeling of a foreign body in the eye.
After some time, swelling of the eyelid appears, and uncomfortable symptoms increase. Discomfortable sensations (pain, itching) are very disturbing, sometimes low-grade fever (37-38 degrees) occurs, and the lymph nodes located near the ears become enlarged. On the 3rd or 4th day, a compaction forms at the site of greatest irritation of the skin, which gradually develops a purulent apex. After a few more days, the top breaks through and pus flows out. After this, the inflammatory process subsides, and soon the sore heals completely.
The difference between a chalazion and a stye is that initially a dense tubercle appears on the upper or lower eyelid, which does not cause severe pain when palpated. The skin behind it moves easily, it does not fuse with it. With barley, this process is accompanied by itching, profuse lacrimation, and sometimes there is pain of a pulsating nature. With the development of a chalazion, practically no painful symptoms are noted. With barley, over time, the head of the abscess appears, and the chalazion remains just a hard lump.
Diagnostics
Differentiating the types of seal on the eyelid is not difficult for a specialist. No tests are required. Before identifying a chalazion or stye, the doctor examines the lump, asks the patient about troubling symptoms, palpates the sore eyelid with light movements, assessing the degree of lump, and makes a diagnosis.
Treatment of chalazion and stye
The methods of treatment for the two ophthalmological diseases differ, since the nature of their origin is different.
Chalazion
Chalazion is often not treated at all. Some people perceive the first-time “hail drop” as simply a cosmetic defect. But since chalazion is a chronic disease, it recurs. If this happens often, you should consult a doctor to identify the cause of constant relapses and then treat the underlying disease or eliminate the provoking factors that lead to the appearance of chalazion. If the seal does not disappear for a long time, it is possible to use drops or ointments, but only after agreement with the ophthalmologist.
To eliminate unpleasant symptoms, you can use a chamomile decoction by soaking a cotton pad in it and applying it to the inflamed area several times a day, or massage the lump in a circular motion after soaking your fingers in heated linseed or olive oil.
If a chalazion becomes infected, steroid injections are prescribed directly into the lump. If the chalazion has reached too large a size and begins to put pressure on the eyes, surgical intervention is performed, which consists of cutting the seal and scraping out the capsule along with the contents. The operation is performed under local anesthesia and lasts approximately 30 minutes. The doctor cuts the skin on the eyelid and uses a special device to draw out the accumulated secretion. A few hours later the patient goes home. While the wound is healing, anti-inflammatory drops and ointments are prescribed.
Barley
Treatment of barley also differs; it is carried out in slightly different ways. At the beginning of the development of the disease, even before the appearance of the abscess, dry heat (UV heating), washing the eyelids with a furatsilin solution, and the use of antibacterial drops and ointments are recommended.
At the stage of compaction formation, as the head matures, it is burned with brilliant green or alcohol. From folk recipes, it is recommended to wash the eyes with a decoction of chamomile or calendula, use compresses with herbal decoctions, and warm the sore eyelid with dry heat. After the head has ruptured, it is recommended to use antimicrobial and antibacterial ointments and drops for several days to prevent re-entry of infection into the wound.
Prevention
Ball-shaped seals (chalazion or stye) cause a person a lot of discomfort, both physical and psychological. It should be remembered that with weakened immunity, both of these diseases can often appear. Therefore, immediately after the seal is cured, it is necessary to think about preventive measures aimed at preventing their reappearance.
Disease prevention measures are as follows:
- take vitamins;
- enrich your diet with fruits, vegetables and herbs;
- try to avoid hypothermia;
- use only high-quality decorative cosmetics;
- follow the rules for using contact lenses;
- if the skin is prone to oiliness, pay more attention to cleansing it of sebum using special products;
- do not touch your eyes with dirty hands;
- promptly treat infectious and viral diseases;
- Carry a clean handkerchief or napkin with you to, if necessary, wipe the eye or use it to remove a foreign body that has entered the eye.
Despite their external similarity, chalazion and stye have different origins. This is very important for choosing the right treatment tactics. If you pay close attention to your health, you can independently determine the type of ophthalmological pathology. However, it is better to consult a doctor who will make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
glazalik.ru
Symptoms
- Swelling.
- When pressing on the tumor, pain appears.
- Increased lacrimation.
- Redness of the skin of the eyelids.
- Pea formation.
- Itching, stinging, burning.
- Accumulation of pus.
- Visual impairment.
- Formation of a gray or red spot.
Disease prevention
A few simple tips will help you avoid this trouble:
- Try to touch your eyes as little as possible. This can irritate the eyes and increases the risk of bacteria getting into the eye. Before you need to touch him, wash those hands.
- Protect your eyes from dust and dirt. Wear special safety glasses if possible.
- Do not overuse cosmetics. Update them periodically, at least once every six months.
- If you have a tendency to get stye, then you need to wash your eyes regularly with warm water and baby shampoo.
If inflammation appears on the eyelid, you should immediately see a doctor.