Classification of the disease
Depending on the area of the lesion, unilateral, bilateral and partial blepharoptosis are distinguished.
Acquired ptosis is classified according to the type of causes that caused the muscle pathology. The cause of the pathology can be uncontrolled use of steroids. Aponeurotic prolapse (muscle weak and inelastic):
- Age-related blepharoptosis is a consequence of biological aging of the body and the epidermis as well. It is diagnosed mainly in old age.
- Traumatic - the result of unsuccessful surgery or previous injuries that led to muscle aponeurosis.
Neurogenic omission (injury to the oculomotor nerve or magnocellular nucleus):
- Damage affecting the nervous system.
- Extensive infectious lesions of the central nervous system of a viral or bacterial nature.
- Some neurological diseases.
- Diabetic polyneuropathy, brain tumors or migraines.
- Injuries to the sympathetic nerve that regulates eyelid movement.
Mechanical ptosis is formed when there are tears or scars on the surface of the eyelid, lesions inside or outside the eyelid adhesions, or due to penetration of a foreign body into the eyeball.
Oncogenic prolapse accompanies all cancers in the orbital area. This type of eyelid ptosis directly depends on the course of the underlying disease and cannot be treated separately from it.
Pseudoptosis or constitutional drooping of the eyelid always affects both eyes and is most often a congenital pathology.
The eyelid hangs symmetrically and sometimes a person does not even pay attention to it. There are several causes of false ptosis:
- excess skin folds;
- insufficient elasticity of the eyeball;
- unilateral exophthalmos of endocrine origin.
After removal of the eyeball, the natural support for the eyelid disappears and anophthalmic ptosis occurs.
Depending on the severity, ptosis is divided into three degrees: 1. Partial
- the skin covers the iris of the eye by one third;
2. Incomplete
- the skin covers the iris by two thirds;
3. Full
- the entire pupil is blocked.
Causes of ptosis
Factors that provoke ptosis in a child depend on the form of the disease. The table shows the types of ophthalmological defects and the causes of their occurrence:
| Type | Causes |
| Congenital | Weak development or absence of the muscle that lifts the upper eyelid as a result of genetic abnormalities |
| Underdeveloped oculomotor nerve as a result of neurological pathologies in the fetus | |
| Acquired | Injuries |
| Neurological pathologies | |
| Diseases of internal organs | |
| Medical procedures |
Upper eyelid ptosis
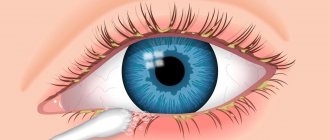
The normal condition is a slight overlap of the iris of the eye by the upper eyelid. When the overlap exceeds two millimeters, the initial stage of ptosis of the upper eyelid is diagnosed.
Unilateral or bilateral congenital ptosis of the upper eyelid is more often diagnosed in childhood. With a slight prolapse, the disease is sometimes left for further monitoring and observation. If there is significant prolapse, mandatory medical intervention is required.
If treatment is not timely, there is a risk of complications such as a significant decrease in visual acuity and strabismus.
The most common symptoms of the development of ptosis of the upper eyelid include:
- Drooping eyelid in one or both eyes.
- Irritated eyes. Unpleasant sensations intensify with each closing of the eyelids.
- It becomes difficult to keep your eyes open, which leads to rapid eye fatigue. Prolonged course of this condition leads to frequent headaches.
- To improve visibility, a person is forced to tilt his head back.
Drooping eyelids cause double vision. Due to disruption of the blinking process, the cornea dries out, which leads to dry eye syndrome or infectious lesions.
The main causes of noncongenital drooping eyelids are age-related disorders or acquired injuries.
Symptoms
It is easy to determine pathological disorders of the eyelid in a child. This is noticeable visually without special examination. But there are several degrees of ptosis of the upper eyelid.
- In the first degree of pathology, the upper eyelid covers 1/3 of the pupil. This degree slightly impairs the baby’s vision.
- The second degree of ptosis is characterized by closure of 2/3 of the eyelid.
- In the third degree, the pupil is almost completely covered by hanging skin. The child sees almost nothing with one eye.
It is difficult for a baby to blink with any degree of ptosis of the upper eyelid. He has to tense his facial muscles, including his eyebrows and forehead. The eye not only does not open completely, but also does not close if the pathology is congenital. Because of this, irritation of the eyeball occurs.
Diagnosis of ptosis of the upper eyelid in a child
The doctor will be able to determine the diagnosis during the initial examination. The doctor needs to diagnose ptosis and identify the exact cause of its occurrence.
- During a visual examination, the doctor assesses the condition and mobility of the damaged eyelid.
- It is necessary to compile an anamnesis. The doctor collects data about the baby’s family and takes into account hereditary factors.
- The size of the hanging skin fold is determined.
- The strength of the eye muscles is taken into account.
- The doctor evaluates symmetry during eye movements, and the mobility of the eyebrows is also taken into account.
- It is necessary to measure the child's intraocular pressure.
- Children's visual acuity is assessed.
- It is necessary to determine possible strabismus or amblyopia in the baby.
Congenital pathology can be distinguished from acquired pathology by the mechanism of pupil closure. With congenital ptosis, the eye will not be completely closed, unlike acquired ptosis. Depending on the cause of the disease, the necessary treatment will be prescribed to eliminate sagging skin above the eye.
Lower eyelid ptosis
Ptosis of the lower eyelid is much less common than ptosis of the upper eyelid.
In the early stages, the disease manifests itself as bags and swelling under the eyes, which significantly spoil the appearance. Over a long period of time, the ciliated edge of the eyelid gradually separates from the eyeball. In the future, eyelid inversion may develop, followed by infection of the mucous membranes. Ptosis of the lower eyelid is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Decreased visual acuity.
- Difficulty blinking.
- Frequent recurrences of infectious eye diseases (for example, conjunctivitis).
- Sensation of a foreign body in the eye.
- Increased lacrimation.
The main cause of lower eyelid ptosis is biological aging of the body. At a young age, there are no accumulations of fat cells and skin on the surface of the eyelid, and the muscles are quite elastic and are able to maintain the eyelids in tone. Over the years, the skin and orbital muscles become inelastic, the subcutaneous fat layer atrophies and moves downward. Relaxation of the orbital septum leads to excessive protrusion of orbital fat and the formation of “bags” under the eyes. Weak muscles and ligaments, stretched and sagging skin spoil the appearance and create unnecessary strain on the eyes.
Surgical intervention
It can be performed for any type of ptosis, especially if conservative therapy is ineffective. The duration of the operation is about 30-60 minutes under local or general anesthesia.
2-4 hours after the intervention, the doctor allows you to remove the bandage. The wound is painless and does not require analgesics. After surgical intervention, re-formation of the disease practically does not occur.
There are methods that allow a person with eyelid ptosis to avoid surgery. To obtain a visible effect, they must be performed correctly and after consultation with a specialist. If the drooping of the upper eyelid is the result of any disease, it is necessary to treat it so that there are no relapses of ptosis in the future.
Related articles:
- Glaucoma: causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention
- Optic neuritis: types, symptoms and treatment
- Colorblind. What colors do these people not distinguish?
- Optic nerve atrophy: ICD-10, symptoms, causes, how to treat
Gravitational ptosis
Gravitational ptosis refers to a change in the condition of facial skin under the influence of gravity. Over time, the skin begins to sag, firmness and elasticity decrease. Skin that has lost its elasticity begins to sag under the influence of gravity.
The first manifestations of gravitational ptosis are observed after 35 years and are associated with the aging process.
The upper layer of the epidermis noticeably slides and falls. Deep wrinkles begin to form. The manifestations of symptoms depend on the stage of ptosis. Main features:
- Drooping corners of the mouth that completely change the facial expression.
- Formation of folds on the upper eyelid.
- The skin under the eyes takes on a dark tint.
- Blurry oval face.
- The bend of the brow ridges changes.
- The level of the outer corner of the eye decreases.
- The skin of the face sags and its contour changes.
The described symptoms gradually intensify towards the age of 50. The aging process cannot be prevented, but it can be significantly delayed and slowed down. The development of gravitational ptosis is influenced not only by lifestyle, but also by proper skin care. Also, the deformation of facial contours is promoted by the psycho-emotional state and genetic predisposition.
Ptosis in children
Ptosis in children is divided into congenital and acquired. Ptosis is often combined with other disorders of eye functionality, among which the predominant ones are:
- heterotropia - a pathology that makes it difficult to concentrate both eyes on one object, with a violation of their coordination;
- Amblyopia is a deviation in which one of the organs of vision is not involved and the brain receives different pictures that it cannot connect into a single whole;
- anisometropia - a disease characterized by a significant difference in eye refraction, which can be combined with astigmatism and occur without it;
- Diplopia is a disorder that causes all objects in the field of vision to double in size.
Ptosis can be a manifestation of common diseases. The main prerequisites for the development of the disease in children include:
- trauma received during the passage of the birth canal;
- dystrophic type of myasthenia gravis - related to severe forms of autoimmune lesions affecting muscle fibers and nerves;
- neurofibromas - a neoplasm that occurs on the nerve sheaths of the upper eyelid;
- ophthalmoparesis – partial immobilization of the eye muscles;
- hemangioma is a tumor-like formation that forms on blood vessels.
Congenital ptosis
It has classification features associated with the root causes of the development of a pathological condition in childhood:
- Dystrophic form is one of the most frequently recorded, occurring:
- in case of deviation from the standard development of the structures of the upper eyelid;
- with weakness of the muscle elements of the upper muscle;
- with dystrophic changes in the levator;
- with blepharophimosis - genetically predisposed to insufficient development of the palpebral fissure.
- Non-dystrophic form - characterized by stable performance of the muscles of the upper eyelids.
- Congenital neurogenic - formed due to paresis of the third pair of cranial nerves.
- Myogenic - transmitted along the hereditary line from mother to child.
- Pathology combined with the Marcus Hun phenomenon is a condition characterized by spontaneous raising of the upper eyelids, formed when opening the mouth, swallowing movements, moving the lower jaw to the side (any functions performed by the masticatory department).
Favorable option
Ptosis of this type in children has its own prerequisites for formation and subtypes:
A deviation that arose as a result of a defective aponeurosis, characterized by the presence of excess skin folds and frequent swelling of the eyelids. Almost all recorded variants affect both eyes.
Neurogenic ptosis has its own varieties and causes:
- damage to the motor pathway located in the region of the third pair of cranial nerves;
- congenital Horner's syndrome - characterized by traumatization at the time the child passes the birth canal or other unknown origin;
- acquired Horner's syndrome - as a sign of damage to the nervous system, formed after surgical interventions in the chest area or due to neuroblastoma (a malignant neoplasm that develops exclusively in childhood).
Myogenic ptosis – recorded in the presence of pathological abnormalities:
- with existing myasthenia gravis – arising against the background of underdevelopment and neoplasms in the area of the thymus gland, characterized by lesions of the eye muscles, double vision of anteriorly located objects and asymmetry;
- with progressive external ophthalmoplegia - partial paralysis of the cranial nerves responsible for the innervation of the eye muscles.
Mechanical - formed as a result of scar tissue and neoplasms on the skin of the upper eyelid.
False – fixed in case of disorders and disturbances in the movements of the eyeball up and down, in the presence of excess skin folds in the upper eyelid and in case of tumor-like formations on the vessels (hemangiomas).
Symptomatic manifestations and treatment regimen in childhood are practically no different from adults. Surgical procedures for the treatment of blepharoptosis in children are performed after they reach three years of age and subject to general anesthesia. Until the age of three, children develop their visual organs and the operation makes no logical sense.
Treatment of ptosis
In cosmetology, there are many methods for treating all types of ptosis aimed at getting rid of defects or reducing them. The final result depends on the degree of damage to the skin.
The most effective and efficient is surgical intervention. Various types of facelifts successfully relieve ptosis. This method is considered deeply invasive and may have contraindications and low risks of complications. Therefore, surgical treatment should be used only at the last stage of the disease, in the absence of alternatives.
Treatment of ptosis of the upper eyelid without surgery (massages, peeling, facelift, injections) is the most common method of treating the disease.
Conservative treatment methods include:
- Hardware and therapeutic treatment. Modern massage techniques are used to enhance the tone of the facial muscles. Peels from chemical to more gentle. To strengthen the structure of the facial muscles, hardware facelift procedures are prescribed. Microcurrent and laser therapy will also be effective. Directed current or laser beams are able to penetrate into the deep layers of the epidermis and stimulate a natural increase in muscle tone.
- Injection procedures. The effect on the skin is carried out after anesthesia, and the drug for injection is selected individually for each patient. This could be Botox, hyaluronic acid or a “cocktail” of nutrients.
Treatment optimally selected by a cosmetologist can significantly slow down the aging process. Conservative methods have virtually no contraindications.
Treatment of the impending century
Differentiation of congenital and acquired forms, determining the causes of the disease help the doctor select a treatment regimen. Conservative treatment methods include the following physiotherapeutic procedures:
An important part of the treatment of such pathology is special gymnastics.
- physiotherapy;
- exposure to direct electric current (galvanization);
- ultra-high frequency therapy;
- massage;
- application of paraffin applications.
If after 6-9 months conservative methods of therapy do not produce an effect, then, in the absence of contraindications, surgical intervention is prescribed. If a disease has been identified that provoked ptosis, then the underlying disease is treated first. Surgical intervention is performed for partial drooping of the eyelid at the age of 13-16 years, and for complete drooping in preschool children due to the threat of amblyopia.
Before surgery, the affected skin fold is fixed with a plaster to prevent the appearance of strabismus. In children, surgery is performed under general anesthesia. Excess skin is removed, the corresponding muscles are tightened, a cosmetic suture is applied, and then a bandage is applied, which is removed after a few hours. Postoperative hematomas and swelling on the face disappear in about a week.
Ptosis after Botox
The most common adverse reaction after Botox injections is drooping eyelids. No doctor gives a guarantee that such an effect will not occur. Ptosis after Botox has quite strong external manifestations and is considered a serious cosmetic defect. However, this condition is temporary and is completely reversible.
Drooping eyelids are manifested by a sharp decrease in muscle tone. The process affects not only the eyelids, but also the brow ridges, which, when lowered, increase the asymmetry of the face. The skin on the forehead and eyelids swells; excess moisture causes drooping eyelids and narrowing of the eye slits.
Causes of adverse reactions
Individual characteristics of the body
. Unpredictable reaction to drug administration. The risk increases in proportion to the number of procedures performed. In this case, it would be advisable to reduce the number of injections and the treatment area.
Exceeding the dosage of the drug
. This can happen if the solution is diluted incorrectly or injections are performed incorrectly. An attempt to increase the dose of the drug in order to enhance the effect ultimately results in the development of ptosis.
Incorrect injection site selected
. If the procedure was carried out without taking into account the anatomical characteristics of a particular person, there is a possibility of ending up in dangerous areas. In this case, the injection injures the muscle and provokes unwanted reactions.
Features of Botox absorption in tissues
. The solution must be individually selected for the specific type of problem. Otherwise, excessive diffusion will result in undesirable areas being affected.
Causes of the disease
Let us examine in detail the reasons for which ptosis occurs.
Innate
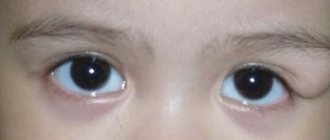
Congenital ptosis occurs in children due to underdevelopment or even absence of the muscle that should be responsible for raising the eyelid. Congenital ptosis sometimes occurs together with strabismus.
When ptosis treatment is not treated for a long time, the child may develop amblyopia (lazy eye syndrome). Congenital ptosis is most often unilateral.
One of the most common eye diseases is pterygium. Read on to learn about its correct diagnosis, treatment and prevention.
We continue our analysis of eyelid diseases! The news contains all the main causes of stye on the eye.
Acquired
Acquired ptosis develops for several reasons and is divided into:
- aponeurotic ptosis , which is associated with the weakening or stretching of the aponeurosis of the muscle that should raise the upper eyelid. This type includes senile ptosis, which is one of the processes during natural aging of the body, ptosis that appears after eye surgery.
- neurogenic ptosis associated with damage to the nervous system after diseases (stroke, multiple sclerosis, etc.) and injuries. Ptosis can appear with paralysis of the sympathetic cervical nerve, since it is the muscle that innervates the levator pallidum. Along with ptosis, constriction of the pupil (or miosis) and retraction of the eyeball (or enophthalmos) occur. A syndrome that combines these symptoms is called Horner's syndrome.
- with mechanical ptosis, the cause is mechanical damage to the eyelid by foreign bodies. Athletes are at risk because eye injuries are quite common.
- false ptosis (apparent ptosis), which appears with excess skin folds on the upper eyelid, as well as hypotonia of the eyeball.
Determining the cause of ptosis is an important task for the doctor, since the surgical treatment of acquired and congenital ptosis is significantly different.
An interesting fragment from the program “Live Healthy” about ptosis of the upper eyelid
Exercises for eyelid ptosis
Acquired ptosis is best treated at home. If you start gymnastics at the first signs of drooping eyelids, you can significantly improve your appearance and avoid the need for surgical intervention.
Four simple exercises that will help with eyelid ptosis:
1.
Make several circular movements with your eyes, then close your eyes tightly. Repeat at least three times.
2.
Open your eyes as wide as possible and maintain the position for 15 seconds. After this, close your eyes tightly for 10 seconds. Repeat 5 times.
3.
Press the brow ridges with your index fingers and try to bring your eyebrows together. Do the exercise until your muscles become tired.
4.
Massage your eyebrows with your index fingers. You should start with light touches, gradually increasing the pressure. Finish the massage with the appearance of unpleasant sensations.
Therapeutic exercises have a positive effect on blood circulation and stimulate the facial muscles. Exercises can be done at any convenient time, preferably at least three times a week.
Methods for treating eyelid ptosis at home
Non-surgical treatment is possible for the neurogenic type; for the rest, the methods listed below are unlikely to give any result.
There are a whole host of different techniques that promise to get rid of drooping upper eyelids without surgery. This includes physiotherapy, exercises, massage, and folk remedies. But, in fact, these methods are more suitable for prevention rather than treatment. It is hardly possible to achieve great results with their help, but a small result may be pleasing if ptosis is at an early stage.
Today, surgery is the most effective method for eliminating ptosis.
Traditional methods
It is recommended to use the proposed products immediately, without leaving a portion for next time:
- Egg and olive oil mask. You will need 1 raw egg and 1 tbsp. oils Mix the ingredients thoroughly and apply to the skin around the eyes using a brush. After 15 minutes, wash with water.
- Grape seed oil. The product can be applied after using any serum. It tightens the skin well.
- A mask of potatoes (1 small tuber), sauerkraut juice (1 tbsp) and oatmeal (a pinch). Peel, wash, grate the potatoes on a fine grater. Then add cabbage juice and oatmeal. Mix everything and apply to the area of closed eyes. After 5 minutes, wash off the mixture.
- A mixture of olive oil (1 tablespoon), banana pulp and ginger juice (half a tablespoon each). Mix the ingredients and apply to the area around the eyes. After 10 minutes, rinse off.
- Compress from a tea bag/infusion (for example, chamomile tea). Squeeze out excess liquid from the tea and wrap the bag in gauze. You need to keep the compress for no more than 10 minutes, and then blot off any remaining moisture with a napkin. The bags must cool to room temperature before the procedure! To prevent drops running down your face from staining your sofa or bed, place a towel under your head.
- Ice cubes made from herbal infusions . Medicinal herbs help relieve swelling of the eyelids, tighten the skin and get rid of small wrinkles. The following plants are suitable: birch leaves, chamomile, parsley, as well as others with anti-inflammatory and decongestant effects. After preparing the decoction, you need to freeze it into cubes and wipe your eyelids with them daily.
Treatment with folk remedies is not always possible. You need to make sure that there are no contraindications or allergic reactions to the components. In any case, it is recommended to first consult with your doctor regarding their use.
Exercises
Special gymnastics for the eyes can help improve the condition of the muscles and tissues of the eyelids, strengthen the eye muscles and get rid of fatigue and other uncomfortable sensations.
Rotating your eyeballs in a circle, from side to side, up and down, and closing your eyelids are great exercises. You just need to do them every day, for about five minutes. We will not describe the exercises in detail, but we suggest watching a visual video - Facebook building with Galina Dubinina:
Photo of performing eye exercises with drooping eyelids:
Massage
Please note that all procedures give some effect only if performed regularly. If you do it today, and tomorrow or the day after tomorrow you are lazy, then the result will not be the best.
You can massage when applying cosmetics to the area around the eyes. It is performed as follows: you should lightly pat the lower and upper eyelids. At the top, movements should be from the outer corner to the inner, at the bottom - vice versa.
You shouldn't expect a super-WOW effect. The effect can vary greatly from person to person; it depends on many factors (skin condition, consistency and quality of procedures, etc.). This needs to be understood.
In no case should you rub your eyelids too hard, otherwise you risk getting the opposite effect, the skin will stretch and sag even more.
Physiotherapy
The duration of any physiotherapeutic procedure should be determined by your attending physician (ophthalmologist).
It is worth paying attention to possible contraindications:
- cardiovascular diseases;
- hypertension 3 degrees;
- general serious condition;
- psychical deviations;
- exacerbation of infectious diseases;
- presence of a pacemaker.
Naturally, these are not all contraindications. This point needs to be clarified again with a specialist.
The following physiotherapy procedures may be prescribed, see the table below.
| Physical procedure | Description |
| Galvanization | The skin area is exposed to a continuous low-power electrical current. The current is generated by a special device, and it is applied to the skin using electrodes (metal plates). |
| Ultraphonophoresis | During the procedure, medications are introduced into the upper layers of tissue through the sebaceous and sweat glands using ultrasound. The procedure has a cumulative effect. |
| Laser therapy | The procedure is carried out using a device that emits monochrome and coherent light. |
| Ultrahigh frequency therapy | Electromagnetic fields with ultrasonic frequency are used. Using special devices, the desired area is heated with heat. Plates are selected and installed at a certain distance (the closer, the stronger the impact). If the electrodes are installed incorrectly, you may get burned. |
Also, at the initial stage of ptosis, treatment with paraffin masks can be used. They tighten and strengthen muscles. It is necessary to do 1-2 procedures per week, and then 2-3 times a month for prevention.
Botox and other drugs
Botox injections (as well as Dysport, Lantox) can also be used to treat ptosis. However, they often, on the contrary, lead to drooping eyelids. You should very carefully choose a specialist with good reviews. The disadvantage of this method is the short-term effect of medications, after which the eyelid droops again.
If the Botox injections themselves provoked ptosis, you will have to wait up to 5-6 months (until the effect of the administered drug wears off). You can take a course of some kind of physiotherapy, make masks and use a cream with a lifting effect.
A course of vitamin therapy is often prescribed, and agents that improve the condition of tissues and muscles are also indicated.
Some more tips
- Acupuncture. Acupuncture may help if the drooping eyelid is caused by a neuromuscular condition or a stroke. Special needles are placed by a specialist in the face and scalp. The procedure is usually carried out twice a week.
- Vitamin B12. Eat more wild cold-water fish (tuna, salmon, mackerel), chicken broth and organic beef.
- Foods rich in beta-carotene and other carotenoids. Introduce into your diet vegetables and fruits whose flesh is bright yellow, orange or red. These are: papaya, pumpkin, red peppers, carrots, tomatoes, sweet potatoes. They relieve inflammation and improve immunity.