Removal of the epiretinal membrane - This is a surgical intervention to excise the pathological film located above the macula. A similar procedure is prescribed if the patient’s vision is significantly reduced and there is a risk of irreversible damage in the macula area. The operation to remove the epiretinal membrane is performed in several stages. At the first stage, an inspection of the intraocular cavity is carried out, then the vitreous body is removed, and then a direct excision of the fold of the macula is carried out. Among the surgical complications are: infection, disruption of the integrity of the retina and its detachment, uncontrolled increase in IOP and the new appearance of the epiretinal membrane. Vision in the postoperative period is restored gradually over 4-6 months, which depends on the patient’s age, the area of excision and the presence of concomitant diseases.
A little history
Among the methods of treating retinal pathologies, operations to remove epiretinal membranes are considered relatively new. Such interventions are usually performed as planned and are classified as high-tech. They require modern, expensive equipment and highly qualified surgeons, which makes it possible to carry out such operations only in large specialized medical centers.
Performing effective operations in the retina became possible only with the development of vitreoretinal surgery. Therefore, diseases accompanied by the formation of epithelial membranes in the macular zone until the middle of the last century were the cause of blindness.
The method of removing the epiretinal membrane was first proposed by the American ophthalmic surgeon, Professor Charles McCamer in the 70s of the last century. Subsequently, the technique of this operation was constantly improved and today it is successfully used even with large-area growths in the macula area. Today, removal of the epiretinal membrane can be performed by two methods - classical, using an ophthalmic scalpel, and innovative, using laser radiation. The use of a laser to excise the macular fold is more gentle and effective. However, the high cost of the operation significantly limits the spread of this technique.
Prevention and methods of prevention
It is quite difficult to prevent the occurrence of fibrosis, since it is practically impossible to follow the dynamics of the growth of scar tissue. However, the use of preventive measures will help minimize the likelihood of the disease occurring and slow down its progression. To do this you need:
- To refuse from bad habits;
- Maintain a sleep and rest schedule;
- Use healthy eating rules in your daily diet;
- If you have diseases of the visual organs, systematically undergo scheduled examinations with an ophthalmologist (twice a year) and use corrective means;
- Timely stop and eliminate systemic diseases, monitor the dynamics of their development.
It is especially important to follow these recommendations in old age, since after 60 years the risk of fibrosis increases several times in men and women. If you notice unpleasant sensations, as well as a sharp drop in severity, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible
The earlier the disease is detected, the higher the chances of recovery.
Indications for surgery and possible limitations
Surgery to remove the epiretinal membrane is only necessary if there is a significant decrease in visual acuity or serious distortion of visible objects. The indication for its implementation is the rapid growth of the macular fold, when there is a threat of irreversible changes in the retina. Contraindications to removal of the epiretinal membrane are retinal tumors and diagnosed optic nerve atrophy. Restrictions to surgical intervention are:
- Acute infections of the eyes or eyelids.
- Blood clotting disorders.
- Relapses of chronic diseases.
- Feverish conditions.
In this case, the operation may be postponed for a certain period.
General information
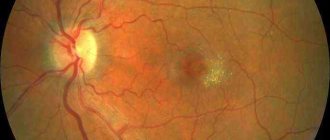
Epimacular fibrosis is a slowly progressive age-related pathology that causes severe visual impairment. A characteristic feature is the presence of an epiretinal membrane (thin film), localized mainly in the central region of the retina. Because of this, the most characteristic symptom is a decrease in visual acuity, but there are other manifestations of the pathology.
The exact cause of the development of epimacular fibrosis is unknown. Risk factors for the development of the disease include previous eye injuries, surgical interventions, pathological systemic changes, etc.
Statistics indicate that epimacular fibrosis develops more often in older people.
Thus, in a sample of patients under the age of 50 years, the incidence of the disease does not exceed 2%. In persons aged 75 years - 20%.
Now the relevance of the issue of timely diagnosis and selection of the most effective treatment method is increasing.
At the moment, only surgical intervention is an adequate treatment tactic with a pronounced positive effect.
Preparing for surgery
Preoperative preparation of the patient for removal of the epiretinal membrane includes a complete ophthalmological examination with examination of fields and visual acuity, as well as hardware examinations: electroretinography, ultrasound and CT of the eyes. The patient also undergoes laboratory tests: general and biochemical blood tests, coagulogram, HIV, RW, hepatitis. In addition, ECG and lung fluorography data will be needed.
It is also mandatory to visit certain medical specialists, for example a dentist, in order to sanitize the oral cavity and eliminate foci of infection. Permission to perform the operation is issued by the therapist based on the results of the examination. If necessary, he may prescribe additional preoperative treatment.
The operation to remove the epiretinal membrane can be performed under either general anesthesia or local anesthesia. Therefore, the day before the intervention, the patient goes for a consultation with an anesthesiologist, who will determine the method of pain relief. No later than a week before surgery, the patient must give up alcohol and stop taking certain drugs (antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants). On the day of the operation, you should refuse food, limiting yourself to only a small amount of still water. Half an hour before surgery, the patient is given intramuscular painkillers, sedatives and antihistamines.
Treatment of the disease
There are no conservative methods for eliminating epiretinal fibrosis. However, in some situations, medical treatment of the pathology is not required. Therapy is not prescribed for minor disorders of the visual apparatus. In this case, the patient gets used to slight deviations in vision that do not affect his normal life.
Sometimes the membrane spontaneously moves away from the retina, which leads to the resumption of normal functioning of the visual system.
However, scar tissue usually does not shed on its own. In these situations, surgical treatment is required.
Surgical intervention
Before the operation, the patient must undergo a full medical examination by highly specialized doctors who will predict possible postoperative complications:
- endocrinologist;
- cardiologist;
- otolaryngologist;
- dentist
Surgical treatment is performed if epiretinal fibrosis provokes significant dysfunction of the visual organs and affects the patient’s quality of life.
Surgery will help prevent retinal detachment. The most commonly used is vitrectomy - removal of a fragment of the vitreous body in the area where the film is localized, as well as scar tissue. Instead of part of the eyeball, a saline solution is poured in: this will preserve the transparency of the optical bodies and prevent loss of vision. The operation is performed under local anesthesia.
After removing the affected membrane, the use of anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial drops is indicated to help reduce postoperative swelling and reduce the likelihood of a secondary infection.
Vitrectomy is a fairly effective operation, but not in all cases it can restore normal vision.
If the surgery is successful, the patient can go home the same day. The rehabilitation time is approximately three months.
During the recovery period you will need to follow a number of recommendations:
- regularly visit an ophthalmologist;
- stop driving for a while;
- reduce the time spent watching TV and using the computer;
- use sunglasses;
- avoid eye injuries.
Traditional therapy
If the fibrous film does not affect visual function, traditional medicine methods are used. However, in advanced stages they are unlikely to help:
- Herbal infusions made from lemon balm, as well as carrot, blueberry, citrus juices, beets, and cabbage are beneficial for the visual system.
- A composition prepared from burdock, mallow, lemon balm, and birch buds has a beneficial effect on the retina of the eyes. The herbs are mixed in equal proportions. The infusion should be consumed three times a day for 2 months.
- Effectively copes with eye diseases (eyebright). It can be taken orally as an infusion, and can also be used as an eye drop. An infusion of eyebright is consumed three times a day, for a course of 30 days, after which they take a break and repeat the treatment. Drops are applied three times a day for a month.
- Goat milk is mixed with water in equal proportions. The mixture is instilled into the eyes, 3 drops per day.
Before using unconventional remedies, you should definitely consult an ophthalmologist.
Progress of the operation
Removal of the epiretinal membrane is performed in a sterile operating room using an ophthalmological microscope and other special equipment.
The patient is placed on the surgical table, and the area around the eyes is treated with a disinfectant solution. The anesthesiologist prepares the system for intravenous infusion of the necessary drugs. Blood pressure and pulse rate sensors are attached to the patient. The surgeon performs local, usually retrobulbar, anesthesia, installs an eyelid speculum and begins the operation.
The operation process includes three stages. At the first stage, a vitrectomy is performed - the vitreous body is removed. To do this, three incisions are made through which instruments are inserted. The vitreous body is removed using an aspirator, after which the vitreoretinal cavity is inspected. Next, they begin to directly remove the folds on the macula. First, using tweezers, the outer edge of the film is separated and lifted above the surface of the retina. The surgeon then uses a scalpel or laser to cut through the inner membrane and remove it.
The final stage of the operation to remove the epiretinal membrane is a complete inspection of the intraocular space by the surgeon to identify possible violations of the integrity of the retina or hemorrhages into the cavity. Then the removed vitreous is replaced with a gas mixture, perfluoroorganic compound or silicone oil. The instruments are removed and several sutures are placed on the sclera. Before the end of the intervention, the patient is administered antibiotic solutions, and a sterile bandage is applied to the eye. The anesthesiologist provides postoperative pain relief and the patient is transferred to the observation room.
Diagnosis of epiretinal fibrosis
To diagnose the disease, it is enough to perform an ophthalmoscopy and carefully examine the structures of the fundus. To establish the correct diagnosis, it is also necessary to perform angiography. In advanced cases, various changes are revealed, including macular edema.
Additional fluorescein angiography helps exclude other ocular pathologies. Optical coherence tomography can also be done to help measure the thickness of the macula and look for signs of macular edema.
Postoperative period and possible complications
After surgery to remove the epiretinal membrane, the duration of the rehabilitation period is strictly individual and directly depends on the preoperative state of the patient’s visual functions, his age and the presence of chronic diseases. After the procedure, the patient must wear a sterile bandage over the eye, replacing it with a new one every day. After being discharged from the hospital, it is necessary to undergo weekly scheduled ophthalmological examinations and instill reparative, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory eye drops prescribed by the doctor.
To protect your eyes from light, it is recommended to wear dark glasses outside. In addition, you need to stop playing sports and limit general activity. For several weeks it is forbidden to lift weights, visit baths, saunas, swimming pools, and open reservoirs. Avoid eye fatigue when reading, watching TV, or working at close range. By following these simple recommendations, in 80-90% of cases it is possible to avoid possible complications. Vision improvement occurs gradually and reaches the maximum possible within 4-6 months.
Undesirable reactions when removing the epiretinal membrane can occur both during the operation and in the long term after it. Surgical complications include hemorrhages into the inner space of the eye and under the retina; it is also possible to disrupt the integrity of the retina and a sharp increase in IOP. In the postoperative period, there are infectious lesions of the organ of vision, as well as retinal detachment. Complications of the long-term postoperative period include the occurrence of cataracts and the development of glaucoma. In 10-12% of cases, a relapse of the disease occurs, accompanied by the growth of a new membrane of even greater density.
Etiology
Most often, epiretinal fibrosis of the retina develops as a result of age-related changes in the body: during the aging process, the risk of pathology increases.
In addition, the disease can be triggered by the following factors:
- genetic predisposition;
- previous inflammatory diseases of the conjunctiva, for example, uveitis;
- retinal disinsertion;
- eye surgery;
- vascular disorders leading to a failure of the blood supply to the inner membrane (retinopathy);
- type 2 diabetes;
- macular holes;
- central vein thrombosis;
- eye damage, postoperative changes in the organs of vision.
There are two types of fibrosis:
- Focal. Most often detected in the early stages of pathology. Occurs in the form of foci of film growth.
- Diffuse. The film forms on most of the macula, accompanied by elongation of the hyaloid membrane.
The appearance of epiretinal fibrosis does not depend on the person’s gender, and can occur in both women and men.
Cost of surgery to remove epiretinal membrane
The cost of surgery to remove the epiretinal membrane depends on the extent of the intervention and the chosen surgical method. Thus, excision of pathology using a laser is a more modern, low-traumatic and expensive technique. In our clinics in Moscow and Naro-Fominsk, surgical interventions to remove the epiretinal membrane are performed using modern equipment, with the involvement of highly qualified specialists. The cost of removing the epiretinal membrane at Dr. Shilova’s Clinic ranges from 35,000 to 69,000 rubles.
Manifestations of epiretinal fibrosis
With epimacular membrane, visual function is impaired, which suffers to varying degrees (ranging from minor deviations to severe dysfunction). Patients often complain of decreased image clarity and distortion of the contours of surrounding objects. Difficulties may also arise when reading, especially small print, and it becomes difficult for patients to see small objects. The blind spot may increase in size. Most often, epiretinal fibrosis is located only on one side, and pathological changes do not progress over time.
Causes
To correctly diagnose and combat the disease, it is important to determine not only the forms of its manifestation, but also the causes. In most cases, epiretinal ocular fibrosis develops idiopathically. There is no reason for its occurrence. Doctors conclude that this occurs against the background of age-related changes in the body.
However, in some cases there are factors that give impetus to the development of the anomaly. Their determination is important for correct diagnosis and treatment prognosis.
There are cases where a disease such as uveitis caused epiretinal fibrosis of the eye. What it is? Inflammation of the choroid of the eyeball. Uveitis is a collective name for a group of inflammations. The pathological process can be localized in different parts of the eye shell.
Other causes of epiretinal fibrosis of the eye are:
- retinal detachment;
- previous ophthalmological surgeries;
- retinopathy caused by diabetes mellitus;
- injuries.