A rare genetic disease characterized by the absence of the iris is called aniridia (irideremia). Patients suffering from this pathology are at risk, as they may develop concomitant eye diseases: cataracts, glaucoma, horizontal nystagmus. As a rule, congenital aniridia is diagnosed. In other cases, the disease develops under the influence of external factors. Both men and women are equally susceptible to this disease, regardless of racial differences.
Structure of the iris
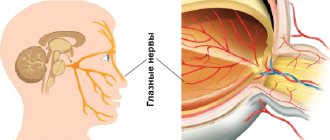
As you know, the eye has a rather complex structure. The iris is the anterior part of its choroid. It acts as a barrier to excess light, like the diaphragm in a camera. The iris, together with the lens, separates the anterior and posterior chambers of the eyeball. To make it clearer, let us explain: the anterior chamber is located between the cornea and the iris, and the posterior chamber is behind the lens. The transparent liquid filling these cavities allows light to pass inside without hindrance.
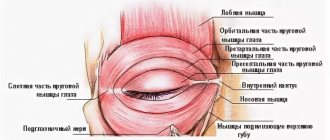
The iris of the eye consists of two layers. The base of the upper leaf is a stroma, consisting of blood vessels and covered with epithelium. The surface of the iris has a lace relief pattern, individual for each person.
The bottom layer consists of pigment and muscle fibers. Along the edge of the pupil, the pigment layer comes to the surface and forms a dark-colored border. There are two muscles in the iris, they have different directions. The sphincter, a circular muscle along the edge of the pupil, ensures its narrowing. Dilator – radially arranged smooth muscle fibers. It connects the sphincter and the root of the iris and is responsible for the dilation of the pupil.
Diseases, anomalies, their causes and symptoms
The presence of infection is accompanied by inflammation.
The inflammatory process in the iris is called iritis. This is an eye disease in which infection can occur through the blood. The basis for the development of the disease are:
- viruses;
- fungal infections;
- bacteria;
- rheumatic pathologies;
- diabetes;
- tuberculosis;
- Bekhterev's disease:
- venereal diseases;
- herpes;
- parasites;
- allergens.
The presence of an inflammatory reaction in the eyes is determined by the following signs:
- pain in the area of the affected organ of vision;
- photophobia;
- reducing the sharpness of the visible image;
- increased lacrimation;
- blue-red spots on the whites of the eyes;
- greenish or brown tint of the iris;
- deformed pupil;
- severe headache, especially in the evening and at night.
Other diseases
The disease occurs against the background of pathological growth of blood vessels.
- Coloboma is the absence of the diaphragm or part of it. It can be acquired and hereditary. The embryo develops a bubble at week 2, which by the end of week 4 takes the shape of a glass with a slit at the bottom. In the fifth week, it becomes clogged, and its development is inferior, when the iris is formed at the 4th month of intrauterine development. It manifests itself in the formation of a depression, which makes the pupil pear-shaped. Coloboma entails changes in the fundus of the eye, which receives excess light.
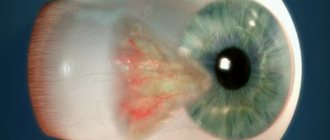
- Iris rubeosis (neovascularization) is a pathology characterized by the appearance of newly formed vessels on the facial surface of the iris. Has the following manifestations: visual discomfort;
- fear of light;
- decrease in visual acuity.
Multi-colored eyes are a rare pathology that does not affect visual acuity.
Other diseases acquired as a result of trauma to the visual organs and abnormalities in the development of the pigment layer:
- delamination;
- dystrophy;
- different color of the membrane of the right and left eyes;
- red eyes due to albinism (lack of natural pigment);
- stromal hyperplasia or hypoplasia;
Pathologies of the pupil:
- “double eye” - the presence of several, but perhaps complete absence;
- the presence of fragments of the embryonic membrane;
- deformation;
- deviation from normal location;
- unequal diameter.
Functions of the iris
- A thick pigment layer protects the eyes from excess light.
- Reflex contractions of the iris regulate the light in the eye cavity.
- As a structural element of the iridolenticular diaphragm, the iris holds the vitreous body in place.
- By contracting, the iris participates in the circulation of intraocular fluid. It also plays a significant role in accommodation, that is, focusing on a specific object.
- Since there are many vessels in the iris, it performs trophic and thermoregulatory functions.
Diagnostic methods for iris damage
If the patient has signs of iris damage, a number of examinations should be performed;
- Visual inspection under side lighting conditions;
- Biomicroscopy;
- Pupillometry (measuring the diameter of the pupillary opening);
- Fluorescein angiography, which uses contrast to visualize the blood vessels.
To summarize, it should be remembered that the iris plays an important role in creating visual images. It regulates the amount of light that enters the retinal plane, which is achieved through the work of two muscles (sphincter and dilator). In diseases affecting the iris, not only its function is disrupted, but also other structures of the optical system.
What determines eye color?
Each person has a unique iris pattern. The color scheme is also different and depends on the melanin pigment, more precisely, on its amount in the cells of the iris. The more it is, the richer the colors. It has long been noted that the color of the iris of the eye is associated with the climatic zone where a person lives. During evolution, more pigment appears to have been produced in those exposed to intense sunlight. Therefore, representatives of northern peoples more often have light eyes, and southerners have dark ones. But there are exceptions: Chukchi and Eskimos have brown eyes. However, this only confirms the rule, because snowy plains are no less blinding than a desert or a tropical beach.
Eye color is a trait enshrined in genes, but it changes throughout life. Newborn babies have blue-gray eyes; only after three months can you understand what color they will have. In old age, the amount of pigment decreases and the iris of the eye brightens. Diseases can affect eye color. If you protect your iris from the bright sun with dark glasses since childhood, you can slow down its fading. With age, the pupils become smaller; their diameter is reduced by more than a third by the age of 70.
Diagnosis of diseases by the eyes
Even in ancient Egypt, priests associated various marks on the iris with certain health or mental problems. Numerous observations of doctors made it possible to draw up maps that indicate the projection zones of organs.
Iridologists view the eye as a part of the brain brought to the surface of the body. The iris has many nerve connections with internal organs. Any changes in them are reflected in the pattern and shade of the iris.
What does eye color say? Iridologists believe that only brown and blue are healthy. Other shades indicate a predisposition to diseases. The color of the iris is rarely uniform. For example, if it is all dotted with specks devoid of pigment, the body has a high level of acidity. Normalizing it is not difficult at all. You just need to limit your consumption of milk, baked goods and sweets. Changes in health will definitely be reflected in the drawing, that is, the iris of the eye will also change. Diseases of the digestive organs and the accumulation of waste are projected as dark specks. This may indicate a tendency to constipation, gastroenteritis and gallbladder diseases.
How are they treated?
In the fight against iris diseases, ophthalmologists use:
- anti-inflammatory ointments or drops;
- analgesics;
- antihistamines;
- corticosteroids;
- mydriatics that reduce intraocular pressure.
Eye diseases require professional therapy. Self-medication does not matter and can lead to damage to the choroid of the organ, retina, or complete loss of vision. Therapy is carried out in a hospital setting under the supervision of a doctor. If surgical intervention is necessary, the ophthalmologist, based on the results of the studies, refers the patient to a specialized department or eye pathology clinic.
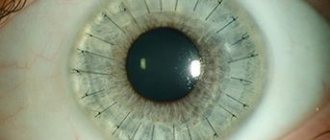
Spots and other patterns on the iris
Specks can be of different sizes and shapes. Here are some signs that a person can use to navigate himself by studying the pattern of his iris.
Circular strokes or half rings mean that their owner is subject to stress. Such a person keeps grievances and other negative emotions to himself. Prolonged stress leads to diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Clear rays from the pupil to the edges indicate that the lower intestines are not working well.
A white stripe along the edge of the iris indicates increased cholesterol levels or even atherosclerosis. If such an arc frames the iris from above, there is a problem with the blood supply to the brain; below, there is a problem with the blood vessels of the legs.
Spots on the iris of the eye indicate diseases of a specific organ. By looking at the projection diagram, you can determine where to look for violations and what examinations should be carried out. If you find a large spot on yourself, there is no need to be alarmed. Size does not always indicate the severity of the problem. Perhaps the disease is still in its very early stages and can be easily cured.
What does the relief of the iris indicate?
This sign denotes heredity and human immunity. A dense, smooth iris shows that its owner initially has high endurance and good health. Any illness is easier to bear and the body recovers quickly. This is a sign of long-livers.
A loose iris of the eye (photo) shows that a person is susceptible to depression and nervous breakdowns under heavy stress. In response to stress, heart pain, spasms of internal organs, and irritability occur. But if you take care of your health and don’t expose yourself to unnecessary stress, there won’t be any special problems.
A very loose iris, with a large number of indentations, indicates a weak immune system. Diseases cling to the body at the slightest stress.
Iris map
In iridology, it is common to depict the iris as a clock face. This makes it more convenient to designate the zones of various organs. For example, the right iris in the 11-12 o'clock sector reflects the work of the brain. The health of the nasopharynx and trachea is indicated by the zone from 13 to 15 hours, and the right ear is characterized by the sector 22-22.30. The left iris is a mirror image, which means you need to look for the other ear on it. Any point on the iris of the eye indicates which organ is worth paying attention to.
The iris is divided into three rings. The internal one - around the pupil - shows the work of the stomach and intestines. The middle ring reflects the health of the pancreas, gallbladder, heart, adrenal glands, autonomic nervous system, muscles, bones and ligaments. In the outer zone there are projections of the liver, kidneys, lungs, anus, urethra, genitals and skin.
Modern iridology
For some time now, ancient methods of research and treatment have been returning to us. Of course, modern doctors are endowed with a large amount of knowledge and convenient equipment. To diagnose diseases using the iris, conventional ophthalmic examination lamps and an iridoscope are used.
Doctors distinguish between signs responsible for hereditary predispositions and marks acquired during life. An experienced diagnostician can determine when a little prevention is enough and when serious treatment is necessary.
The iris can tell about health, past and future illnesses. It is believed that it contains information for four generations ahead. But despite the public maps, reading them is somewhat difficult. Therefore, you should not “rely on your eye” in such a matter as iridology. If you want to find out something about yourself based on your iris, contact a specialist.
Treatment of eye melanoma
Medicine is developing rapidly; methods have been developed to help rid a person of eye melanoma and prevent tumor growth.
An effective way to remove melanoma is eye surgery. The point is to remove damaged tissue. The disease is likely to continue to progress and become cancer, leading to death. The patient, wanting to increase the chances of recovery, must undergo disease prevention. You need to be in the mood for a speedy recovery.
Treatment of the disease by type: close-focus therapy, laser therapy, diathermocoagulation and cryodestruction surgery. The methods do not involve pain relief, it is not required. This means that there are no contraindications. If the disease is in the penultimate stages, the person’s eye and inflamed nodes are removed. This applies to cases where melanoma turns into late-stage cancer. After removal, the patient remains in the hospital for three days.
Late stages of the tumor do not require removal surgery. Therefore, the patient is offered pain relief procedures to remove eye irritation and tissue damage. A person is obliged to take drugs that normalize the functioning of organs. You need to see a doctor in time, which turns out well, and your chances will increase by at least 30%.
Types of eye melanomas
Also, for patients with severe eye cancer, several types of surgeries are provided that are appropriate for the disease.
- The first is to remove some of the iris to help relieve pain. Also, in 10% of cases, if necessary, the patient has the ciliary body removed.
- The second method proposed by doctors is resection of part of the eye with blood vessels.
Sometimes eye removal is used. For example, when the size of the tumor is extensive or a person’s chances of recovery become less, i.e. The area of the eye is affected and the person no longer sees anything.
Consequences
But cancer treatments are dangerous and come with consequences. For example, bleeding, cataracts, complete loss of vision, etc. Eye surgery is painful, traumatizes the organ, which will lead to discomfort when blinking or closing the eyes. However, the chance of recovery after surgery is high.
If there is a predisposition to the appearance of a cancerous tumor in the eye, disease prevention is necessary to reduce the risk of the disease. Predisposition factors for the disease include:
- Working outdoors, which involves exposure to dust, small particles, sunlight, or irritation of the retina by light, heat or cold.
- The skin color is too white, as is the hair (or red), the eyes are blue or green.
- The number of moles and birthmarks on the body, which contribute to the appearance of eye tumors, turning into skin cancer.
- Genetic predisposition to ocular melanoma or diseases of this type.
- Number of burns on the skin.
- Aging.
- Leading an unhealthy lifestyle.
- Poor care.