- Primary appointment with a urologist-andrologist
1900 ₽ - Repeated appointment with a urologist-andrologist
1700 ₽
Urology is a field of medicine whose specialists determine the causes of the development of pathologies, identify symptoms, carry out diagnosis, and then treatment. New, modern methods of providing qualified medical care to patients are constantly being developed and put into practice. Urologists have all the skills to detect diseases affecting the kidneys, bladder, urethra, and ureters.
There are many urological pathologies, so in this area of medicine there are the following highly specialized sections:
- andrology, whose specialists treat pathologies of the male genitourinary system;
- urogynecology, which deals with the detection and treatment of diseases in women;
- oncourology, which determines the causes of the formation of malignant tumors in the genitourinary system;
- urogeriatrics, focused on the study, prevention and treatment of diseases in old age;
- phthisiurology, aimed at the diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis of the genitourinary system.
Moscow employs experienced specialists whose practical work experience averages 26 years. These are doctors of the highest category and candidates of medical sciences who are engaged not only in daily practice, but also in scientific work. During their training, urologists thoroughly study gynecology, oncology, nephrology, and surgery. We guarantee our patients a comfortable psychological environment, sensitive and attentive attitude, as well as the effectiveness of diagnostic and treatment procedures.
Take the test and find out if you need to see a urologist?
Take the test
Introduction
Phenazopyridine has been registered in the Russian Federation since 2021 [1]. It began to be used abroad almost a century ago and is still prescribed today. Phenazopyridine has been known as an azo dye since 1914. Phenazopyridine was thought to have antiseptic properties and was prescribed to treat urinary tract infections (UTIs) caused by Staphylococcus, Streptococcus
and
Escherichia coli
, but the medical and scientific community later abandoned the view that phenazopyridine was bactericidal effect, defining its purpose - relief of dysuric symptoms in UTI as part of combination therapy with various antibiotics [2].
Currently, phenazopyridine is used as a uroanalgesic that relieves the symptoms of UTI (burning, pain, frequent urination), as well as for pain relief for urinary tract injuries, surgical interventions, endoscopic procedures, and the use of a probe or catheter [1, 2].
It is important for the practicing physician to remember that the use of phenazopyridine to relieve symptoms of dysuria in UTI should not delay the diagnosis and pathogenetic therapy. Phenazopyridine is prescribed for symptomatic pain relief and is not a substitute for specific antimicrobial therapy.
Review of preclinical and clinical studies of phenazopyridine
Phenazopyridine is a dark red microcrystalline powder. It is poorly soluble in cold water and easily soluble in hot water, alcohol and glycerin, creating an acidic urine reaction. Phenazopyridine, excreted in the urine, acts on the mucous membrane of the lower urinary tract, where it has a local analgesic effect. Phenazopyridine and its metabolites are quickly excreted from the body by the kidneys (when taken 600 mg/day, phenazopyridine is 90% excreted within 24 hours, with 41% as unchanged drug, 49% as a metabolite) [1, 3].
Phenazopyridine colors urine (in an alkaline reaction) dark orange or reddish, and feces orange-red. The appearance of a yellowish color to the skin or sclera when using phenazopyridine may indicate its accumulation as a result of impaired renal function or overdose, which requires discontinuation of the drug. It is not recommended to wear reusable contact lenses while taking the drug, since phenazopyridine can cause staining [3].
Drugs for the treatment of kidney failure
There are many drugs for kidney failure, but a specialist always prescribes only the drug that will be effective in a particular case.
Medicines that are used to treat kidney failure may include:
- Diuretics (increase urine flow, remove excess sodium from the body).
- Medicines to control blood pressure.
- Medications to control high potassium levels.
- Medicines to treat anemia.
- Products to control high phosphorus levels.
Mechanism of action of phenazopyridine
A possible mechanism for the analgesic effect is inhibition of voltage-gated sodium channels and mechanosensitive nerve fibers of group A [3].
N. Aizawa et al. (2010) studied the effect of phenazopyridine on the afferent innervation of the rat bladder in comparison with lidocaine and acetaminophen (paracetamol) in an experiment with direct measurement of Aδ- and C-fiber activity. The study was conducted on Sprague-Dawley rats. Under urethane anesthesia, single nerve fibers, mainly originating from the bladder, were identified in the L6 dorsal root by electrical stimulation of the left pelvic nerve and distension of the bladder. Based on conduction speed (2.5 m/s), the fibers were divided into Aδ- and C-fibers. Afferent innervation in response to chronic bladder filling was measured before drug administration. Phenazopyridine (0.1–3 mg/kg), lidocaine (0.3–3 mg/kg), or acetaminophen (1–10 mg/kg) was then administered intravenously. After drug administration, the afferent innervation of the filled bladder was again measured. The study found that all drugs significantly increased bladder elasticity. The effect was dose-dependent. 28 nerve endings were localized (Aδ-fibers: n=13, C-fibers: n=15). Intravenous administration of phenazopyridine significantly and dose-dependently reduced the activity of only Aδ-fibers, but did not affect C-fibers. Acetaminophen also significantly reduced Aδ fiber activity only, but the effect was not dose dependent. Lidocaine inhibited the activity of both Aδ and C fibers. The researchers concluded that phenazopyridine could directly inhibit mechanosensitive Aδ fibers in the normal rat bladder. This finding may explain the clinical effect of the drug in conditions of bladder hypersensitivity [4].
Phenazopyridine and urinary tract infections
Phenazopyridine is recommended as symptomatic therapy for rapid relief of pain.
For urinary tract infections, phenazopyridine should be prescribed simultaneously with antibacterial agents; the course of phenazopyridine should not exceed 2 days (since with properly selected antibiotic therapy, after 2 days the need for further use of the uroanalgesic should disappear) [5].
C. Deepalatha et al. (2011) conducted an open-label, randomized trial to compare the effectiveness of 3 treatment regimens in relieving symptoms of uncomplicated UTI when treatment was initiated within 48 hours of diagnosis. In group 1, patients received only phenazopyridine at a dose of 200 mg 3 times a day for 48 hours. In group 2, patients were prescribed phenazopyridine and antibiotics (ciprofloxacin, doxycycline). In group 3, patients received a drug for the treatment of nephrolithiasis of plant origin (3 times a day for 48 hours). The results of the study showed that the combined short-term use of phenazopyridine as an analgesic and antibiotics (ciprofloxacin, doxycycline) for 48 hours led to a significant reduction in burning during urination by 91% and a decrease in pain intensity by 89%. When using phenazopyridine in monotherapy, the burning sensation decreased by 73%, the intensity of pain during urination - by 80%, while when using a herbal preparation, these indicators decreased by 53 and 44%, respectively [6].
Thus, phenazopyridine is effective as a uroanalgesic for short-term use in the treatment of uncomplicated UTIs.
G. Marcelin-Jiménez et al. (2006) presented the results of a double-blind, crossover, randomized study of the pharmacokinetic interactions of ciprofloxacin with phenazopyridine. The project involved 24 healthy male Mexican volunteers who, depending on the study period, received oral ciprofloxacin (500 mg) or a combination of ciprofloxacin and phenazopyridine (500 mg + 200 mg, respectively). The simultaneous use of phenazopyridine significantly increased the bioavailability of ciprofloxacin and its mean residence time (MRT) in the blood [7].
Phenazopyridine and sling operations
Surgeries using a free synthetic loop are the main method of eliminating urinary incontinence in women [8]. OF Dueñas-Garcia et al. (2017) conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to study the effect of phenazopyridine on the prevention of urinary retention in the early postoperative period in women undergoing sling surgery. The authors showed that the use of phenazopyridine at a dose of 200 mg before surgery allowed a statistically significant reduction in the incidence of urinary retention (p = 0.01) compared with the rate in patients who did not receive this drug [9].
What treatment methods do urologists use in our clinic?
Pharmacotherapy. Drug treatment is widely used in urology. Depending on the disease, the doctor may prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics, uroseptics, ointments and solutions with antiseptic action, multivitamin complexes and other drugs. Medicines can eliminate foci of infection, reduce the manifestation of unpleasant symptoms, and suppress the activity of pathogens.
Physiotherapeutic treatment. Prescribed for chronic diseases of the urinary system. A urologist can use the entire range of physical procedures: exposure to currents of various frequencies, magnetic fields, ultrasound, etc. The procedures help reduce pain and eliminate inflammatory processes by increasing blood supply to organs and relieving muscle spasms.
Minimally invasive operations. Endoscopic techniques are used not only for diagnosing diseases of the urinary system, but also for their treatment. Minimally invasive surgeries are performed on the lower (urethra, bladder) and upper (kidneys, ureters) urinary tract.
Complex surgical operations. They are carried out in case of detection of congenital defects in the development of organs of the genitourinary system, in case of serious injuries, in the detection of oncological diseases, necrosis of varying degrees of severity. Radical and organ-preserving surgeries are performed at the Miracle Doctor urology clinic. We have created all the conditions for performing surgical procedures of almost all profiles.
To successfully identify diseases at the initial stage, our clinic offers patients from Moscow and the region a comprehensive program in urology “Men’s Health”.
Phenazopyridine and cystoscopy, chromocystoscopy
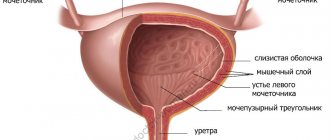
The properties of phenazopyridine, such as the ability to anesthetize the bladder mucosa and color urine orange-red, have been studied in relation to cystoscopy and chromocystoscopy. Cystoscopy is one of the most informative and frequently used methods for examining urological patients; It also serves to carry out some therapeutic manipulations in the bladder cavity under visual control, and is an integral part of other diagnostic procedures, such as chromocystoscopy. Typically, chromocystoscopy involves intravenous administration of the dye indigo carmine, followed by observation of its removal from the orifices of the ureters using a cystoscope. Used to study renal function and determine ureteral patency [10].
The effectiveness of identifying the ureteric orifices using urine staining with phenazopyridine was demonstrated in the work of A. Rehfuss et al. (2018). Patients took phenazopyridine 200 mg at 19:00 on the eve of surgery (13–17 hours before cystoscopy). The authors concluded that phenazopyridine can be successfully used to locate the ureteral orifice. At the same time, in a third of patients the staining of urine was so strong that it made it difficult to examine the mucous membrane of the bladder [11]. Preoperative administration of phenazopyridine has been successfully used for intraoperative assessment of ureteral patency during gynecological surgery. A single dose of 200 mg of phenazopyridine was effective in 91.8% of cases; if ineffective, sodium fluorescein was administered during surgery [12].
The analgesic effect of phenazopyridine during cystoscopy was studied in a randomized, prospective, placebo-controlled trial conducted by Tae Nam Kim et al. (2006). The study included 63 patients who underwent cystoscopy. In the main group, patients received lomefloxacin and phenazopyridine 200 mg 3 times a day for 4 days, and the control group received antibiotics (lomefloxacin) and lactobacilli 3 times a day. Analgesic effects were assessed using the Numerical Pain Intensity Scale (NPIS) and the 4-point Categorical Scale (CAT) (in both cases, higher scores corresponded to greater pain intensity). The observation period was 7 days. The intensity of pain decreased gradually from the 1st to the 7th day of observation. The NPIS score in patients from the main group was significantly lower than in patients from the control group, especially on days 1 and 2 after cystoscopy (p <0.05). The CAT score in patients from the main group was also lower than in patients from the control group, especially on the 1st day after cystoscopy (p<0.05). Some patients had previously undergone cystoscopy. In the phenazopyridine group, 84.7% of patients responded that cystoscopy was less painful, 11.5% - the same as before, 3.8% - more painful. In the control group, 8.7% of patients said that cystoscopy was less painful, 82.6% said it was the same as before, and 8.7% said it was more painful. Side effects were not observed in any case. The researchers concluded that phenazopyridine is an effective and safe analgesic for cystoscopy [13].
Drugs for the treatment of urinary incontinence
Urinary incontinence can be caused by various reasons, depending on which the doctor prescribes treatment.
There are several groups of medications, their task is to restore normal nervous regulation of urination. Among them are:
- Medicines that reduce the tone of the bladder wall (reduce the frequency and strength of contractions).
- medications that improve blood circulation in the bladder and relax during the filling phase.
The main method of treating overactive bladder is treatment with mixed-action drugs, anticholinergics, α-adrenergic receptor antagonists, and some antidepressants.
Phenazopyridine in various clinical situations
Autonomic dysreflexia (AD) is a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by hyperactivation of the sympathetic nervous system in response to afferent input resulting from spinal cord injury. It is manifested by headache, sweating, hot flashes, sudden and persistent arterial hypertension, and reflex bradycardia. The most common causes of an attack of VD are distension of the intestine or bladder during urodynamics [9]. F. A. Paola et al. (2003) observed a positive effect of 2-day administration of phenazopyridine to relieve attacks of VD in a 36-year-old man with tetraplegia and increased blood pressure caused by cystitis [14].
Radiation therapy is part of complex treatment for approximately two thirds of cancer patients. One of the complications of radiation therapy is radiation cystitis, which significantly reduces the quality of life of cancer patients. The urgency of the problem is due to the increasing use of radiation therapy and the growing number of cancer survivors. Chronic radiation cystitis most often occurs after irradiation of tumors of the prostate, colorectal, bladder and pelvic organs. In the absence of infection, phenazopyridine can be used to treat dysuria due to radiation cystitis [15, 16].
Why should you contact the urology department of our clinic?
Consultations for adults and children
We help men and women, as well as babies, get rid of kidney and bladder diseases from the first days of life
All types of diagnostics
We have the latest equipment to conduct all necessary examinations of the genitourinary system
Conservative and surgical treatment
We use various methods of therapy depending on the patient’s condition, we carry out planned and urgent operations
24-hour hospital
We provide care for patients after operations and preventive procedures in equipped wards
VIP level service
We accept patients at a pre-arranged time, do not create queues, and provide psychological support during the treatment period
Convenient location
The urology department of the Miracle Doctor clinic is located near the Ploshchad Ilyicha and Rimskaya metro stations in the center of Moscow
The main areas of work of our urology center:
The Miracle Doctor Urology Clinic specializes in the development and improvement of diagnostic methods for urological pathologies. To detect them, high-tech equipment is used here, which makes it possible to establish the localization of pathological foci. The center is equipped with a modern laboratory in which biosamples taken from patients are examined to identify the nature of the infectious process, the severity of inflammation, and tissue degeneration. After diagnosis, comprehensive treatment is carried out for patients with the following diseases:
- tumor of the kidney and upper urinary tract;
- urolithiasis;
- prostate cancer;
- adenoma (hyperplasia) of the prostate;
- bladder cancer;
- hydronephrosis and stricture of one of the ureters;
- urethral stricture and others.
In addition to treatment, the urological center provides rehabilitation for patients after long-term drug treatment or who have undergone surgery. The “Miracle Doctor” will help you recover as much as possible and tell you about ways to prevent a relapse of the disease.
Types of operations performed
Urologists at the Miracle Doctor clinic always try to cure the patient using conservative methods using medications and physiotherapy.
But in severe cases with already developed complications, surgical help cannot be avoided. Our clinic is staffed by highly qualified doctors who specialize in performing any, often the most complex, operations:
- transurethral electroresection of prostate adenoma;
- laparoscopic removal of a kidney tumor;
- laparoscopic resection of the right kidney with a neoplasm;
- mini-percutaneous nephrolithotomy;
- holmium and thulium laser enucleation of prostate hyperplasia;
- percutaneous minipercutaneous nephrolithotripsy;
- retrograde intrarenal lithotripsy;
- contact ureterolithotripsy.
The multidisciplinary clinic practices gentle, minimally invasive endoscopic and percutaneous surgical treatment methods. Only if it is impossible to use them, radical intervention is indicated for the patient.
When should you contact a urology clinic?
You should contact a urologist if you experience episodic or constant symptoms, regardless of their severity. Damage to one of the organs of the genitourinary system of an inflammatory, dystrophic, tumor nature can manifest itself as follows:
- pain in the scrotum area;
- pain in the lumbar spine;
- pain during or after urination;
- difficulty urinating;
- blood in the urine;
- swelling, increase in size of the testicles;
- prolapse of the uterus;
- frequent urination;
- decreased potency.
The Department of Urology “Miracle Doctor” is a structural unit of a multidisciplinary medical institution. Here patients receive comprehensive comprehensive care for any, even the most complex, diseases. The clinic provides affordable high-tech treatment, if necessary, with the most comfortable subsequent hospital stay.
The paid urology clinic “Miracle Doctor” provides emergency and planned care to patients with urological diseases. Its goal is to eliminate negative symptoms, stop pathological processes, and provide high-quality rehabilitation.
What examinations can a urologist prescribe?
Lab tests. They are the starting point for obtaining a general picture of the disease. Most often, the doctor prescribes clinical blood and urine tests that will help identify signs of inflammatory processes in the body. In addition, to determine sexually transmitted infections, smears and scrapings are taken from the vagina and urethra. Before taking the test, be sure not to urinate for more than 1 hour.
Ultrasound. Ultrasound scanning allows you to quickly and painlessly examine the bladder, ureters, kidneys and other pelvic organs. The examination allows us to identify malformations, inflammatory diseases, tumor neoplasms, and traumatic injuries. An ultrasound is performed with a full bladder.
MRI. Magnetic resonance imaging is performed for detailed visualization of the genitourinary system. With the help of an examination, a specialist can identify pathologies of any nature: benign and malignant tumors, kidney and bladder stones, hernias, adhesions, blood flow disorders, injuries and much more.
X-ray (urography). The study can be performed with the introduction of a contrast agent. Urography is prescribed to clarify diagnoses such as nephrotuberculosis, hydronephrosis, nephroptosis, etc. X-ray allows you to visualize the location of organs relative to each other.
Modern urology has an extensive list of methods for diagnosing diseases of the genitourinary organs. “Miracle Doctor” is ready to offer its patients a full range of examinations in accordance with the indications.
Safety of phenazopyridine
When using phenazopyridine according to indications and in accordance with the course recommended in the instructions for medical use of the drug, the frequency of adverse reactions is rare (≥1/10000, <1/1000) and very rare (<1/10000) in accordance with the World Health Organization classification healthcare organizations [1].
Anemia and methemoglobinemia are contraindications for the use of phenazopyridine [2]. Methemoglobinemia is a condition in which more than 1% methemoglobin is detected in the blood. Methemoglobinemia can be congenital or acquired. Acquired methemoglobinemia develops as a result of the action of certain drugs, industrial and ecotoxicants on the body, which either directly oxidize iron, which is part of the hemoglobin structure, or are metabolized in the body to form reactive products that have this property [17]. Phenazopyridine-induced methemoglobinemia is relatively rare, with fewer than 10 cases reported worldwide over the past 35 years [17].
In case of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G-6P-DH) deficiency, phenazopyridine should be taken with caution [2]. Hereditary disturbance of activity or deficiency of G-6P-DG leads to hemolytic anemia. Dapsone, methylthioninium chloride (methylene blue), nitrofurantoin, phenazopyridine, primaquine, rasburicase and tolonium chloride (toluidine blue) have been shown to have adverse effects in individuals with G-6P-DH deficiency [18].
Data indicating that phenazopyridine has a teratogenic effect in the experiment were not obtained when administered together with sulfacytin to rats at a dose of up to 110 mg/kg/day and rabbits at a dose of up to 39 mg/kg/day [2]. Data from clinical observations of 50,282 mother-child pairs have been published, documenting the use of phenazopyridine in 1,109 cases during pregnancy, of which 219 in the first trimester. The results showed no increase in the number of malformations and adverse effects. According to the FDA scale of risks to the fetus when using drugs in pregnant women, phenazopyridine is classified as category B [19]. It is unknown whether phenazopyridine is excreted in breast milk, so its use during breastfeeding is not recommended [1, 20].