Stress urinary incontinence in women is manifested by urine leakage when sneezing, coughing, or physical activity, and is often combined with a weakening of the muscular framework of the pelvic organs.
Treatment of stress urinary incontinence when a small amount of urine is lost can be conservative. If conservative treatment is ineffective, getting rid of this pathology is only possible through surgery.
Currently, the most effective and safe treatment for stress urinary incontinence in women is TVT or TVT-O (sling surgery).
Contraindications for sling surgery
- A serious condition caused by exacerbation of chronic diseases, renal, liver and pulmonary failure.
- Pregnancy, postpartum period, condition after recent operations.
- Menstruation.
- Urinary tract infections - in this case, surgery is performed only after treatment of the infectious process.
- Oncology.
- Variants of incontinence not associated with weakening of the urogenital ligament. Such women need to choose other treatment methods.
- Severe prolapse is prolapse of the pelvic organs. In such cases, an operation is performed to return the organs to their physiological position.
How sling surgery combats urinary incontinence
To understand the principle of operation of the sling, you need to imagine the structure of the urinary system. The bladder is a hollow organ that serves as a reservoir for collecting urine. It distinguishes between the apex, body (middle part) and neck (lower narrow part).
Structure of the bladder
In women, this organ is located in front of the uterus below it and, in an empty state, is located at the level of the womb (pubic symphysis) - the place where the pelvic bones connect. The filled bladder rises higher, reaching the middle of the distance between the pubis and the navel.
The urethra (urethra) extends down from the bladder. In women, its length is only 3-5 cm. The urethra is directed downward, curves slightly and opens above the vagina about 2 centimeters below the clitoris.
In the lower third of the urethra there is a special dense structure called the urogenital (urogenital) diaphragm, which is attached to the pubic bones. Its task is to prevent urine leakage.
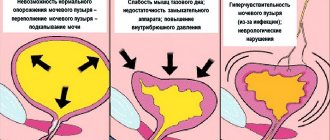
During laughter, coughing, and physical activity, intra-abdominal pressure increases. At the same time, the neck of the bladder lowers, and the urogenital diaphragm pulls the urethra up. As a result, the urethra becomes bent and urine cannot flow out. This is a physiological mechanism that prevents enuresis.
However, sometimes muscle tissue weakens and loses its tone. Most often, this situation occurs after multiple births, especially if they were difficult, sudden weight loss, severe physical activity, and with age due to decreased tissue tone.
As a result, a weak urogenital diaphragm with increased intra-abdominal pressure cannot hold the urethra and pull it up to “lock” urine. The urethra descends following the neck of the bladder and urine begins to flow out of it. Incontinence (enuresis) occurs.
This condition cannot be corrected through exercise, medications or other procedures. All these measures are not effective or give a permanent sustainable result.
The problem of urinary incontinence can be solved with the help of sling surgery. During this procedure, the urethra is supported using a sling - an implant that strengthens the weakened urogenital diaphragm.
After such an intervention, the urethra acquires a physiological position and even during physical exertion, urine does not flow out of it. The unpleasant odor, inflammation of the mucous membrane and other symptoms disappear.
Implantation of an artificial bladder sphincter
Urinary incontinence negatively affects the quality of life of any person, since its involuntary leakage always causes a lot of inconvenience. Various forms of urinary incontinence affect 5 to 10% of the world's population, 70% of whom are women.
Urinary incontinence can be urge or neurogenic. In this case, a person experiences increased contractility of the bladder, and the mechanism for retaining fluid in it is disrupted. This may occur due to insufficient functioning of the bladder sphincter.
Separately, stress urinary incontinence is distinguished, which is associated with true sphincter insufficiency. It is classified as type 3 stress urinary incontinence (International Continence Society classification).
It is known that no more than 50% of people seek qualified medical help regarding their problem. This often happens due to a false sense of shame, or due to an incorrect belief that therapy is impossible. As a rule, from the moment a person first experiences urinary incontinence until he contacts a specialist, an average of 5 years passes. Meanwhile, modern medicine has effective methods for treating incontinence and can help almost every person with this problem.
Urge incontinence is most often treated with medications, but type 3 stress urinary incontinence always requires surgery. One of the leading methods of surgical intervention is the implantation of an artificial bladder sphincter.
What is an artificial bladder sphincter?
An artificial sphincter is a prosthesis that is implanted into the human body. It is necessary for holding urine in cases where your own sphincter cannot cope with this task.
When and why was it created?
The first prototype of a modern device was developed back in 1947 by scientist and urologist FB Foley. It looked like a cuff that was placed around the human urethra. This cuff was connected to a pump syringe, which was kept in the underwear pocket. The idea was very innovative and correct from a medical point of view. However, the level of surgery at that time did not allow the implant to be completely removed from the human body, so its installation was often complicated by purulent processes.
In 1972, the device was improved by urologist FB Scott. It was this American doctor who created the prototype of the modern artificial sphincter. It consisted of three elements: a cuff that encircled and compressed the urethra, two pumps that inflated and deflated it, and a reservoir to collect fluid. The success of surgical intervention to install the first three-component sphincter in those days reached 60%.
The device was later improved by the American Medical System, which happened back in 1983. Until now, doctors have successfully used artificial AMS sphincters, which have undergone only minor modifications.
Efficiency of the operation.
The success rate of installing a modern artificial bladder sphincter is 75%. Moreover, 90% of people who use these devices are absolutely satisfied with their performance. In no more than 20% of cases, a repeat operation is required, which is performed in order to eliminate deficiencies in the operation of the device.
Indications and contraindications.
Indications for installation of an artificial bladder sphincter vary. The absolute indication is irreversible disturbances in the functioning of the own sphincter, against the background of normal functioning of the bladder. In this case, the patient should not have a urinary tract infection or obstruction of the urethra.
In men and women, there are different indications for surgery, which are presented in the table.
| Men | Women |
| If urinary incontinence develops after undergoing radical prostatectomy due to prostate cancer. After undergoing transvesical adenectomy or retropubic prostatectomy, intraurethral resection of the prostate due to benign prostatic hyperplasia. | Urinary incontinence of a neurogenic nature due to trauma, disease of the brain or spinal cord, myelomeningocele, sacral origin, peripheral neuropathy. |
| Previous pelvic trauma, surgical reconstruction of urethral stricture. | Type 3 stress urinary incontinence that has not been resolved with less invasive procedures. |
| Congenital malformations of the urethral neck and bladder. | |
| Neurogenic dysfunction of the bladder sphincter due to brain injury or due to congenital malformations. |
Absolute contraindications to the operation are:
- Stricture urethral disease.
- Recurrence of stricture.
- Urinary tract infections.
- Urethral diverticula.
- Unstable or overactive bladder.
- Shriveled bladder.
- Low bladder capacity.
Relative contraindications include:
- Vesicoureteral reflux of the second stage and higher.
- Urolithiasis, bladder cancer and other conditions that require surgical treatment.
- Stenosis of the bladder neck, its contracture.
If relative contraindications can be eliminated, then the installation of an artificial sphincter becomes possible. It is important that the person has the necessary mental and physical abilities to control the operation of the pump. Before the operation, a detailed consultation with a doctor is required about all the nuances of working with the sphincter.
What examinations do you need to undergo before bladder sphincter implantation surgery?
Firstly, the patient discusses with the doctor all the nuances of the upcoming intervention. Secondly, he undergoes a physical examination, which is aimed at identifying indications and contraindications for surgery.
It is mandatory to undergo a general urine test, urine culture, blood tests, and possibly an ECG.
In some cases, cystography, urethrography, urethroscopy, cystoscopy and other highly specialized tests are required. The better the patient is examined, the higher the chance that the operation will be successful.
Progress of the operation.
The operation can be performed through the angle of the penis and scrotum (penoscrotal approach), or through a perineal incision (performed under the scrotum). If the access is penoscrotal, then one incision is sufficient to install the implant. If the approach is perineal, an additional incision is required to install the reservoir. In this case, the patient spends 1 to 3 days in the hospital. The catheter from the urethra will be removed the next day after the operation.
The sphincter is activated after its installation 6 weeks later. This time is necessary for it to take root. Under the supervision of a urologist, a person is trained to work with the device. In the future, you will need to visit a doctor once a year.
Preparing for sling surgery for urinary incontinence
First, the doctor must make sure that the woman has stress incontinence. A cough test is performed - the patient is placed on a gynecological chair or couch and asked to cough. If the function of the urogenital diaphragm is impaired, urine begins to be released from the urethra.
A pelvic ultrasound is performed, during which the doctor examines the bladder. This allows you to ensure that there are no other pathologies that could cause urine leakage.
The doctor must interview the woman to find out the reasons for the involuntary release of urine. In favor of stress incontinence they say:
- Urine leakage during coughing, sneezing, or physical activity.
- Absence of incontinence during sleep, at rest and during sexual intercourse.
- No signs of frequent urination.
The operation is performed only in cases of stress incontinence or combined variants with a stress component. In other cases, other treatment methods are selected.
Before the intervention, the woman undergoes tests:
- Blood and urine - general examination.
- Blood tests for syphilis, AIDS, hepatitis, clotting and bleeding duration.
- Smear of the genital tract and urethra for flora and STDs
According to indications, cystoscopy is performed - examination of the urethra and bladder using a special device equipped with a camera and a light source.
Other diagnostic methods may be prescribed - biochemical blood tests, ECG and other studies.
Before the operation, you need to cleanse the intestines with an enema and remove hair in the pubic and groin area. The intervention is carried out on an empty stomach.
Cost of the operation
Some operations may be carried out according to government quotas. To receive them you need to submit an application and wait in line.
The quotas include:
- Sling operations.
- Abdominal and laparoscopic surgeries.
- Installation of sphincter prostheses for men (it is possible that you will have to pay for the prosthesis yourself).
If a person does not want to wait in line, then he can go to a private clinic and pay for the procedure he needs on his own.
- Installing a sling on average costs 80,000-100,000 rubles. If the latest generation sling is used for the operation, the price can increase several times.
- Vaginal plastic surgery costs women 50,000-200,000 rubles.
- Colposuspension using the laparoscopic method costs about 150,000 rubles.
- Bladder sphincter implantation can cost about 500,00 rubles.
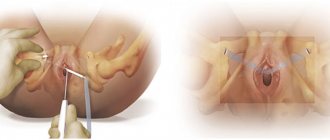
How is sling surgery performed for urinary incontinence in women?
The operation is performed under general anesthesia. It is possible to use spinal and epidural anesthesia, during which an anesthetic is injected into the spine, turning off the sensitivity of the lower body. Therefore, the patient does not feel pain.
The operation is monitored using ultrasound and other methods. This eliminates traumatic damage to the urinary system.
A catheter is inserted into the urethra, through which urine will flow during installation of the implant. This allows the doctor to monitor the integrity of the urethral tissue.
An incision is made on the upper wall of the vagina. A surgical instrument is inserted into it, which moves up towards the abdomen and comes out through the skin, in which small incisions are made in advance. The sling is pulled through the resulting channel.
The result is two very small incisions in the lower body, which are located:
- In the groin - this method is called transobturator suburethral.
- On the pubis - this technique is called retropubic.
The choice of surgical method depends on the woman’s condition, the location of her pelvic organs and other factors. The Center for Aesthetic Medicine practices an individual approach to each patient, so in case of urinary incontinence, doctors will select the most suitable option for sling surgery.
To tighten and hold the urethra, different types of slings are used:
- TVT – used when performing an operation with the tape coming out into the pubic area.
- TVT-O, TOT - used during an operation in which the tape is brought to the groin area.
Outer sling
Inner sling
At the end of the operation, the sling is tightened, giving the urethra the desired position. A suture is placed on the upper wall of the vagina, and the ends of the tape going up are tucked under the skin and also sutured. Gradually, the tape fuses with the tissues and is retained in them. The neutral plastic from which it is made is well accepted by the body.
After the operation, a catheter remains in the urethra for some time, and a tampon is left in the vagina to absorb blood. They are removed during the day.
Progress of surgery
Sling operations last about forty minutes. The doctor implants a synthetic sling between the urethra and the vaginal wall in the form of a hammock. This helps restore the normal angle between them, which prevents urine leakage.
Operations differ by access type:
- TVT – transvaginal. The surgeon works through two incisions over the vaginal wall and pubic bone. The loop is tightened towards the suprapubic abdomen.
- TOT (TVT-O) – transobturational. The doctor makes one incision in the vaginal wall and two in the obturator muscles. The ends of the sling are brought out into the inner sides of the thigh incisions.
The synthetic implant does not cause allergic reactions and does not affect blood flow in the internal organs.
The effectiveness of treatment after slig implantation is assessed. To do this, the bladder is filled with saline solution. The patient is asked to cough. If the sling is installed correctly, urine leaks will not occur.
Afterwards, the doctor installs a catheter to drain urine. A tampon is placed in the vagina in case of bruising, which is possible. They are removed one day after the intervention.
The choice of technique depends on the health, age and presence of concomitant OMT diseases in the patient. Sling operations are performed under the control of a cystoscope, which eliminates complications by 99%.
Advantages of sling surgery in the treatment of urinary incontinence in women
- The sling method is a modern operation that leaves no scars on the body. Small cuts where the tape exits gradually become almost invisible.
- The operation does not require long-term rehabilitation or hospital stay. After some time, the woman can go home and periodically come to see the gynecologist.
- The duration of the operation is short – only 20-30 minutes.
- No need for bed rest.
- There is no need for long-term catheterization. The catheter is removed the same day and the patient goes to the toilet as usual.
- Complications after such an intervention are extremely rare. Their prevalence does not exceed 3-4% and is mainly associated with improper behavior of women after surgery.
- The effectiveness of the operation is very high and is in no way inferior to extensive interventions. However, much depends on the skill and experience of the surgeon. Therefore, it is advisable to do it in a good clinic, where doctors who are well familiar with this technique work.
In St. Petersburg, such a clinic is the Center for Aesthetic Medicine. Doctors who have extensive experience performing a wide variety of gynecological and urological operations work here.