Different eye color or heterogeneity in its distribution in one eye is called heterochromia.
This anomaly occurs in 1-2% of people in the world, in both sexes.
The explanation for the phenomenon lies in the content of melanin in the iris of the eyes - its excess or deficiency leads to heterochromia. It has several classifications - according to type, causes and extent of distribution. Statistics say that the anomaly is more common in women, but its manifestations are unusual in men.
Causes of heterochromia
The most common cause of heterochromia is heredity. Less often, trauma becomes the decisive factor - hemorrhage occurs in the eyeball or sclera. Exposure to chemical reactions following foreign body entry is another type of precipitating injury.
Eye diseases can also provoke heterochromia of the iris:
- hemorrhages in the eye or sclera;
- glaucoma;
- neurofibromatosis – the distribution of melanin is stopped;
- Waardenburg syndrome - melanin is unevenly distributed in the upper layer of the iris;
- inflammation with complications.
Sometimes heterochromia appears in the postoperative period if complications arise from glaucoma or cataracts. Ophthalmologists distinguish several types of heterochromia.
Cause for concern?
The phenomenon itself is considered abnormal and atypical for the structure of the human eye, but at the same time, if it is not caused by diseases or damage, then in itself it is not a cause for concern. In order to exclude all possible associated complications, a medical examination is a priority. It will be carried out to detect hereditary diseases and anomalies in the development of the body. With hereditary causes, different eye colors are often adjacent to a gray strand of hair on the top of the head or forehead. A similar condition is observed when a person’s skin is uniformly covered with a coffee-milk stain or patchy coating. The sclera and iris of the eye are also covered.
You should also consider going to the clinic if there is minimal damage to the eye from debris, scale, or as a result of strong blows to the head and eyeballs. Concussions are the most common indication for eye examination.
Classification of heterochromia
An anomaly with uneven eye color is divided into several varieties due to its occurrence and extent of distribution. The differences affect not only the appearance, but also the health of the eyes - perhaps a parallel course of other diseases.
Heterochromia comes in the following forms:
- The state of complete heterochromia is characterized by completely different eye colors, while both look aesthetically correct, there are no aberrations. A common combination is brown and blue eyes.
- Sector heterochromia is the coloring of one eye in several colors. The structural distribution of color can be different - parts in different proportions or waves - an extremely rare phenomenon. The anomaly forms in the first six months of life, when there is an uneven distribution of melanin in the iris. There are gray-brown and green-blue combinations. The partial form of heterochromia is temporary - by two years the distribution of melanin is normalized.
- The central form is common and involves a change in the color of the iris of one eye. The eye looks aesthetically acceptable, the second organ is colored monotonously. It is extremely rare that the color around the eye is distributed in the form of two rings - a phenomenon almost impossible.
Mechanically acquired heterochromia occurs when copper or bronze shavings or iron filings get into the eye. A small particle of metal gets stuck in the sclera or upper layer of the iris, and no pain signal comes from there. The scale is tiny in size, it stays there and does not cause discomfort. Soon, oxidation begins in a humid environment - pigment is formed in the iris. It has a light green or rusty tint; even after removing the scale, the color does not return to natural.
Varieties
Simple heterochromia appears from birth and is not associated with injuries or diseases. One eye must be brown, the other can be green or blue. The main reason is a genetic predisposition to the anomaly, but it also occurs as a consequence of Horner's syndrome. It is expressed in weakness of the cervical bundle of nerves. The only side effects are astigmatism and slight squinting of peripheral vision in a light-colored eye.
Much more dangerous is complicated heterochromia, which develops as a result of Fuchs syndrome. A severe inflammatory process in the upper layers of the iris and sclera affects one eye and causes a decrease in visual acuity. The organ is saturated with lymphatic connections, which is why the color of the iris becomes lighter. Diagnosis is difficult, treatment is even more difficult. The symptoms of this variety are as follows:
- vision decreases over short periods, in jumps;
- the lens becomes cloudy;
- if you look closely at the color of the iris, it becomes lighter, “speckled.”
The worst manifestation of the disease is blindness. Ophthalmologists identify a third type of heterochromia – acquired. It can be caused by injuries, tumors and inflammation, as well as chemical burns.
How color is formed
- 2.1 Central heterochromia
- 3.1 Simple form
- 4.1 Therapeutic treatment
- 5.1 Video: Heterochromia
Chromatophores, cells containing a pigment called melanin, are responsible for creating the color of the iris. But not only their presence/absence/quantity is important, but also the order of distribution, how exactly the chromatophores are located in the mesodermal layer.
Heterochromia
By the way. The mesodermal is the anterior iridescent layer, and there is also a posterior, ectodermal, which consists of cells with fuscin; it is dark in everyone except albinos.
Iris of the eye (iris)
Three pigments form the primary colors of the iris.
- Yellow.
- Brown.
- Blue pigment.
Eye color, what does it depend on?
How high the concentration of each is and how they are proportionally distributed - this factor forms the color. Depending on which color is dominant, the eyes will look like.
Sectoral heterochromia
When translated from the Greek language, the “diagnosis” of heterochromia sounds like a different color. In this context, the iris of one eye does not match the color of the second eye. This is a genetic trait that can pass from one generation to another or appear over a number of generations. There is also a purchased option.
By the way. Eyes of different colors are not so rare; they occur in ten people out of a thousand. That is, about one percent of all inhabitants of the globe have this anomaly.
So, heterochromia - a congenital disorder of pigmentation of the iris - does not threaten any health consequences
This amazing feature is perceived by many carriers of the anomaly as a defect, but there are people who are proud of their different eye colors, which makes them stand out from the crowd and gives their appearance something unusual, mystical, inaccessible to mere mortals. In ancient times, it was believed that a person with different-colored eyes had special knowledge, and it was not “from God” at all, but “from the devil.” Such people were considered children of the devil, and since there were no color-correcting contact lenses that could hide this “flaw,” they were tracked down and burned at the stake, or at least expelled.
By the way. Mothers who gave birth to babies with different eyes, even if they themselves had normal eyes, were considered to have entered into a relationship with Satan with all the ensuing consequences for them.
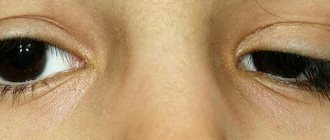
Child with different eyes
Many conspiracies and prayers have been preserved that protect against meeting a person with “devilish” eyes, in order to avoid the troubles and misfortunes that he can bring. The formation of the opinion about heterochromia as a deficiency and defectiveness comes from the Middle Ages, and superstitious and insufficiently educated people are still susceptible to it. Scientists, having thoroughly studied this phenomenon, gave it a simple and understandable explanation - the amount of melanin is minimal in relation to the average norm or exceeds it.
Heterochromia is not a disadvantage or defect
Video: 5 facts about heterochromia to know and not be afraid of
Diagnosis and treatment
Even partial heterochromia is noticeable to the naked eye, so primary diagnosis is carried out visually. When a change in the color of the iris of one eye is detected, the ophthalmologist prescribes an examination. The following methods are used:
- biomicroscopy – finding clots and foreign bodies;
- ophthalmoscopy - gives a picture of the blood vessels and retina;
- campimetry checks the reaction of the pupil to light and color;
- ultrasound and electrophysiological examination - determines the condition of the pupil and lens, as well as the chemical balance of the iris
To treat Fuchs syndrome, a vitrectomy is performed to remove scars, blood clots, and abnormal vitreous tissue from the eye. Metallosis requires removal of the foreign body and long-term drug therapy. The congenital form of the anomaly does not need to be treated - it does not harm the health of the eye. You can change the color using laser correction, which is not always safe and effective.
Mechanism of heterochromia
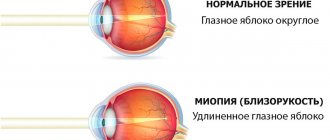
Eye color is determined by the content and distribution of a special substance in the iris - melanin. The more pigment, the darker its color. If there is little pigment, the eyes (or part of the iris) will be very light.
With heterochromia, melanin is distributed unevenly: its concentration is greater in one of the irises or in the area of the iris of one eye. The causes of heterochromia of the eyes can be hereditary factors (most often the feature is a consequence of congenital anomalies), certain diseases (cataract hemorrhage) or injuries received during life.
Is it possible to get heterochromia?
As is easy to understand from the classification of heterochromia, it can be acquired throughout life. The full form is unlikely, but a partial form may occur due to injury or inflammatory processes. The danger is not the change in color, but the diseases that can affect the eye. Today, different eye colors, complete and central heterochromia especially, are considered attractive. That’s why people often go to eye clinics for laser pigment correction. For example, you can turn “banal” brown into blue in exactly this way.
You will have to take into account the fact that it will be impossible to return the natural color of the eye. The second danger is the occurrence of splitting and pain in bright light. Such sacrifices will not be justified even by spectacular results.
Types of disease
Heterochromia is classified according to several indicators. Taking into account the main factors that provoke the development of the disorder, the disease is divided into hereditary or acquired. Depending on the difference in the shade and color of the iris, experts distinguish hypochromic and hyperchromic heterochromia heterochromia.
Based on the shape and location of iris pigmentation disorders, the following types of heterochromia are distinguished:
- Full. Characterized by the presence of different shades of each eye unit. The irises of each organ of vision have radically different shades. Most often there are cases of combinations of brown and blue shades. Anatomically the functionality of the organs of vision without aberration.
- Partial. Also called sector heterochromia. With this disorder, the iris of the eye has several colors.
- Central. Refers to a common type of heterochromia. With this disorder, there is a change in the color of the iris around the pupil in the form of rings. This phenomenon creates a rainbow effect, which manifests itself in the combination of two areas of different colors in one organ of vision. The second eye may have a clearly defined one shade.
- Metallic. Refers to a unique form of pathology. It provokes the development of mechanical damage to the eyes from metal shavings. When it remains in a humid environment for a long time, oxidation occurs, leading to the formation of pigment. This type of heterochromia is characterized by the presence of a light green or rusty-green tint to the iris.
Despite the fact that each type of heterochromia is characterized by pronounced symptoms, a full examination in special clinics will allow one to correctly determine the form and etiology of the development of this disorder.
Features of people with heterochromia
According to popular beliefs, people with heterochromia have two souls. Such a statement, naturally, finds little confirmation, but characteristic features of such an anomaly are observed. Such people have charisma and a passionate attitude towards what they love. They are somewhat hot-tempered and can make hasty decisions.
Character is also determined by the attitude towards one’s peculiarities. Some people find this aesthetically unpleasant, so they withdraw into themselves and develop complexes. Others may take pride in their differences, thereby acquiring a certain amount of narcissism. In general, such people do not differ from ordinary people with the same eye color.
Treatment methods
Congenital heterochromia is not a pathology and does not require treatment. If the root cause of the disorder is associated with the presence of any pathological processes, then their treatment is mandatory.
In modern ophthalmological practice, several treatment methods are used to restore a uniform shade of the iris.
Medication
If there are indications for therapeutic treatment, doctors prescribe drugs with local and systemic effects:
- Corticosteroid drugs are used in the presence of active foci of inflammation. In this case, either eye drops or ointments are used for application under the conjunctiva.
- Steroid medications are prescribed for injuries to the organs of vision and damage to the integrity of the cornea. Such drugs can be used for local therapy.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of drops and intramuscular injections.
- Antibacterial and antifungal medications, if there are clear indications for their use.
- Miotic drugs for diagnosing glaucoma.
Drug treatment for a person is prescribed by a doctor. The specialist determines its duration and dosage regimen.
Laser
Laser correction of heterochromia is a cosmetic method. Effective when it is necessary to eliminate dark shades of the iris.
The procedure is carried out quickly and consists of several stages. Under the influence of a laser, melanin molecules are destroyed. It is subsequently excreted through the venous sinus drainage system.
Immediately after the correction, the change in eye shade begins with its darkening in the first minutes. Full manifestation of laser color changes is observed 1.5 – 2 weeks after laser treatment.
Laser treatment is characterized by an irreversible effect and the possibility of side effects. Therefore, before using this method of treating heterochromia, it is necessary to weigh the pros and cons.
Surgical
Surgical treatment of eye heterochromia is carried out if there are clear ophthalmological indications for intervention. The most common procedure is vitrectomy. Depending on the method of implementation, the following types of operations are used:
- Rear.
- Front
- Microinvasive.
Also, surgical treatment of this disorder involves surgery using the Rosenthal method. The operation involves restoring the correct shape of the pupil and changing the color of the eyes by installing a silicone implant.
Treatment methods for partial heterochromia of the eyes in people are selected taking into account the root cause of the development of this pathological condition.
What to do with heterochromia?
The first step when heterochromia is detected is to contact an ophthalmologist for advice, regardless of the patient’s own assumptions about the origin of this phenomenon.
Impaired pigmentation of the irises may indicate a serious disease; timely diagnosis will help identify the disease before its main manifestations begin.
Heterochromia in celebrities
Many celebrities live with heterochromia. Such as:
- Ekaterina Guseva (actress);
- Milla Jovovich (actress);
- Demi Moore (actress);
- Mila Kunis (actress);
- Kate Bosworth (actress and model);
- Elizabeth Berkley (actress and model);
- Henry Cavill (actor);
- Max Scherzer (baseball player);
- Josh Henderson (actor, singer).
Contrary to popular belief, David Bowie does not have heterochromia, but anisocoria (this is when a person has different pupil sizes in the right and left eyes).
When he got into a fight at school and was punched in the eye, after this injury his pupil remained dilated forever.
David Bowie
What types are there?
Most often you can find owners of complete heterochromia, which is striking.
The form of the disease is characterized by two-colored eyes; they have completely different colors. This type of disease is considered the most common, and most often people are born with a genetic pathology. It is almost impossible to acquire this form of heterochromia. It is an absolute contrast when two eyes are different colors, for example blue and brown, green and black.
Partial
It is also called sector. This species is characterized by not one, but two colors of the same iris. This means that the eye has two or three colors: it can be brown, gray and blue, blue with white splashes. Often this type of heterochromia occurs as a result of mechanical trauma and is a complication of a previous illness.
Central
Another name for heterochromia is circular. With this form, the iris of the shell consists of several circles and they clearly differ in color. According to the results of numerous studies, it was found that this type of pathology is more common in women, and less common in the stronger half of humanity.
Have you ever met people with different colored eyes? One look at such a person makes you stop your gaze on him, arousing great interest. The combination of brown and blue eyes is impossible not to notice. Nature has endowed such people with a special charm, however, there are only one percent of them in the world. Why is the iris of the eye different colors in one person? We will try to explain this to you.
In science, this phenomenon is called heterochromia. It is explained either by the presence of an excess or, conversely, a deficiency of a pigment called melanin. The most important thing you need to know is that different eye colors are not a disease, but just a gift of nature.
There are also two states of heterochromia. If the irises of the eyes have different colors, then this is complete heterochromia. Partial heterochromia is caused by a two-color iris of one of the human eyes. However, partial heterochromia is extremely rare. In addition, different-colored eyes in a person can be an acquired phenomenon, due to a head injury or after recovery from a serious illness.
Nowadays, science explains this phenomenon, and people with different-colored eyes live peacefully. In the old days, this caused fear. It was believed that multi-colored eyes were a sign of dark forces and such people were avoided. Today, a person with different colored eyes is always the center of everyone's attention. Psychologists have even compiled a special psychological portrait for people with this phenomenon. As a rule, these are sincere, brave and sometimes unpredictable people. Since childhood, feeling different, they are always the center of attention and surround themselves with only a small circle of friends. Maximalists by nature, they always strive to be the first in everything.
“Mosaic People,” as they are called, often use colored lenses to hide their phenomenon from strangers
Excessive attention can sometimes be tiring, which may be why they hide their individuality. The average person, on the contrary, is jealous of the mosaics
After all, being different from others is a reason for pride.
If you find an error, select a piece of text containing it and press Shift + E
or, in order to inform us!
How to deal with circles under the eyes?...
Is heterochromia dangerous?
Genetic heterochromia does not affect human eye health in any way. This is an absolutely harmless anomaly. The prognosis for the acquired form will depend on the timely identification and treatment of the main cause that caused the anomaly. After timely therapy, the prognosis for life and preservation of vision is positive.
Heterochromia of the iris is an ophthalmological phenomenon characterized by different pigmentation of the iris or heterogeneous filling of certain sectors of the iris with melanin in only one eye.
Many people believe that this is one of the great mysteries of nature, an unusual feature of the body. The hereditary form of the anomaly does not pose a threat to vision, but if the eye color was the same, but began to change, this is a cause for concern; you should immediately consult an ophthalmologist!
Heterochromia of the eyes: how to get sick?
Modern society treats heterochromia as a certain feature that gives the owner of eyes of different colors a magical look. The creators of anime and computer games who give their characters heterochromia are trying to emphasize their mystery. Perhaps this is why the fashion for multi-colored eyes arose.
Many people deliberately try to change their eye color to achieve the effect of heterochromia. In this case, you can use multi-colored lenses. It is impossible to become infected or intentionally become ill with heterochromia .
Thus, if a person has eyes of different colors, then this phenomenon is not considered dangerous to health. The cause of heterochromia can be either a hereditary factor or various diseases. Thanks to the emerging fashion for eyes of different colors, many people specifically wear contact lenses that differ from each other in shade.
Is heterochromia curable?
If heterochromia occurs as a result of pathology, it requires treatment; only congenital heterochromia is safe.
After diagnosing and establishing the cause of heterochromia, the ophthalmologist prescribes treatment. The types depend on the severity of the anomaly:
- Laser correction is a surgical operation. Modern and effective treatment. The method is safe. The recovery period is minimal.
- Steroid therapy is a group of drugs. Used in the treatment of a number of diseases of the organs of vision. Steroids destroy enzymes in the eye fluid and change the amount of outflow.
- – ophthalmic surgery. Prescribed when treatment with steroids fails. Consists of complete or partial excision of the vitreous substance.
- A surgical operation is performed in cases of a sharp decrease in visual acuity and progressive cataracts.
In society, people with unusual eyes are treated with genuine interest and kindness. Different colors of irises do not spoil, but on the contrary, complement the external beauty of a person.
Freckles
The cause is a congenital change in the structure of melanocytes, which, under the influence of the sun, produce more pigment.
Dyschromia in the form of freckles is more common in blue-eyed people with reddish hair and light, thin skin. With a rich arsenal of cosmetic products known to mankind, a unique remedy for removing freckles has not yet been invented. Even removing them is always one-time, that is, skin whitening does not lead to the fact that there will be no more freckles. Once the sun warms up, they are right there again. Spot whitening will also not help if you have dyschromia: in this case, areas of the skin from which freckles have been removed look faded, gray and only spoil your face.
Causes of the phenomenon and its signs
Scientists and doctors note that the cause of discord is a lack or excess of a special pigment - melanin - in the mesodermal, that is, the front layer of the iris. It is this substance that determines the color and pigmentation of human skin, hair, and the shade of a person’s eyes. The pigment may be missing or it may be contained in excess in the iris. At the same time, with discord in the eyes, there is generally an incorrect redistribution of the melanin present in the body. The shade of the iris, by the way, is formed in the very first months of a child’s life, and it will become final only by 1-2 years.
On a note! Heterochromia also includes different skin or hair color options. But in this case we will only consider disagreement.
Typically, heterochromia is a congenital anomaly. But in certain cases, it can be obtained as a result of injuries, the development of a number of eye diseases, including cataracts, due to hemorrhages in the eye tissue, etc. Differences in eyes also form with Fuchs, Waardenburg, and Recklinghausen syndromes.
American film actress and fashion model Katherine Anne "Kate" Bosworth
The main symptom of the pathology is just a different color of the irises. In general, no further deviations or changes in the visual organs are noted. But in some cases (for example, with Bernard-Horner syndrome), patients complain of changes in skin color, narrowing of the pupil, problems with sweating, and changes in the position of the upper eyelid. All these signs are observed only on the side of the body that is affected by the syndrome.
With Fuchs syndrome, clouding of the lens and atrophy of the iris are also observed. The patient may develop and progress cortical cataracts, and precipitates are observed - small whitish inclusions.