The Hirschberg strabismus angle is determined in order to determine how much the disease has progressed. This diagnostic method is one of the most accurate, so it is mandatory for patients. How far the eyeball deviates from the midline is calculated in degrees. Depending on the data obtained, a decision on the treatment method will be made. Today we would like to talk in detail about how to determine the angle in patients and what is required for this.
What to look for when making a diagnosis
When determining the diagnosis, it is necessary to pay attention to the medical history, namely:
- The time when strabismus appeared indicates the etiology. The earlier it occurs, the greater the likelihood of surgical intervention. With late onset, the chances of an accommodative component increase.
- Angle variability is an essential criterion, since the periodic appearance of strabismus makes it possible to understand that binocular vision has been preserved.
In the case of alternating strabismus, symmetrical visual acuity is assumed in each eyeball.
- The general condition or abnormal development is of great importance. For example, attention is drawn to the frequency of strabismus in a child suffering from cerebral palsy.
- The specialist needs to check the birth history, become familiar with the indicators during pregnancy, the baby’s weight at birth, pathologies during intrauterine development, or during childbirth.
- Hereditary history also has a strong influence, since in most cases this disease is a congenital pathology.
- As part of testing sensory functions, the level of stability of binocular vision is determined, its acuity, and the presence or absence of bifoveal fusion are revealed. Attention is drawn to the functional scotoma of suppression, the nature of diplopia, and fusion reserves.
When checking motor functions, the doctor analyzes the degree of mobility of each eyeball, characterizes the deviation, and determines the complexity of disturbances in the work of the extraocular muscle of each eye separately.
Definition of strabismus
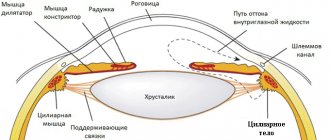
Strabismus, or strabismus, heterotropia, is a common eye disease that is associated with incoordination of the activity of the extraocular muscles. The function of these muscles becomes clear from the name. They are responsible for the movement of the eyeballs.
Due to the fact that these muscles are innervated by the III-IV pairs of cranial nerves, not only ocular pathology, but also direct disorders of the functioning of the central nervous system are responsible for changes in their coordinated activity.
With normal vision, the eyes are focused on a specific point in space and at the same time transmit an imprint of the image from each side to the brain. And with strabismus, one eye deviates to one degree or another from this point.
And then the image entering the brain from the deviated eye does not correspond to the other, which also enters the brain, but from a healthy and normally located organ of vision.
Receiving such inconsistent information, the nervous system excludes from perception the image that comes from the squinting eye. A three-dimensional image is not created in the brain and a person who has strabismus (as well as heterophoria) sees a flat image.
Subsequently, due to the fact that the eye that squints ceases to participate in the process of vision, “lazy myopia” or amblyopia develops.
It should also be noted that strabismus can be:
- Congenital (as a result of exposure to genetic factors or unfavorable conditions during pregnancy).
- Acquired (if the angle of vision is impaired while reading, watching television, as well as with certain diseases of the central nervous system and other factors).
And strabismus is also divided into friendly and unfriendly.
Therapy in the ophthalmology department
Ophthalmologists at our clinic treat:
- myopia (myopia);
- astigmatism;
- farsightedness;
- amblyopia;
- glaucoma;
- cataracts;
- retinal dystrophy and detachment;
- diabetic retinopathy;
- blepharitis;
- demodicosis;
- diseases of the cornea;
- conjunctivitis;
- destruction of the vitreous body;
- dry eye syndrome;
- computer vision syndrome.
You should seek medical help from an ophthalmologist if:
- vision has deteriorated;
- received an eye injury, chemical or thermal burn;
- discomfort is felt when a foreign body enters;
- the eye hurts, is swollen, red, watery and itchy;
- after waking up, the eyelashes feel “sticky” and pus is released from the tear ducts.
Depending on the identified problem, the causes of its occurrence and other individual characteristics of the clinical case, the ophthalmologist may prescribe:
- correction of visual acuity through the selection of glasses or lenses;
- eye drops – to relieve accommodation;
- physiotherapy;
- laser vision correction is a modern and very effective technique that eliminates retinal dystrophy, corrects severe farsightedness, myopia and other eye pathologies;
- carrying out reconstructive surgery after injury to the organs of vision.
Treatment in the ophthalmology department is carried out in comfortable conditions of a day hospital. The use of minimally invasive, non-traumatic techniques and modern, high-quality drugs can significantly shorten the rehabilitation period, and the patient very quickly returns to his normal lifestyle.
To make an appointment with a specialist in the ophthalmology department, call or fill out an application on the website.
Types of research - how to test yourself for strabismus, what norms and deviations exist
To establish an accurate diagnosis and measure the angle of strabismus, specialists can resort to various diagnostic methods. This material will tell you about heterophoria in adults and children.
These include the following:
- determination of the strabismus angle according to Hirschberg;
- study with synoptophore;
- Belostotsky-Friedman color test;
- Wars test;
- raster haploscopy.
Let's look at each of the methods in more detail.
Determination of the strabismus angle according to Hirschberg
As part of the diagnosis, an ophthalmoscope is used. The scheme includes the following stages.
- Turning on the device.
- Direction of the patient's gaze to the hole located in the central part of the device.
- Fixing the location of light glare by an ophthalmologist.
- The glare on the healthy eye is located strictly in the central part of the pupil.
- The diseased eye demonstrates fixation of glare at some distance from the pupil.
- Measuring the deflection angle.
- Switching off the device.
This article will tell you about concomitant strabismus and how it manifests itself.
The angles of strabismus can be different, depending on the location of the flare. The standards are as follows:
- if the glare does not leave the pupil, the angle is at 10 degrees;
- when the light point is located at the edge of the pupil, the deviation angle will be 15 degrees;
- when the highlight is in the middle of the iris, the angle varies from 25 to 30 degrees.
After the diagnosis is completed, the specialist compares the primary and secondary strabismus angle. Primary is the angle affected by strabismus, secondary is an indicator of a fully functioning eye. Conclusions are drawn about the need for surgical intervention. Find out what orthoptics and diploptics are here.
If the reading exceeds 15 degrees, surgery is performed. In other cases, vision is corrected using hardware.
How to determine the angle of strabismus with Synoptophore
Synoptophore is one of the most popular devices for haploscopic diagnostics. The device mechanically separates the fields of view. For this purpose, two optical movable tubes are provided. With their help, testing is carried out using paired test objects.
The use of the device is also practiced for the purpose of conducting a set of orthopedic exercises.
Inside the device, test objects can move in the vertical, horizontal direction, counterclockwise and clockwise. They differ in the type of control elements for each eye. By combining paired drawings, you can understand whether binocular fusion is present or absent. If it is absent, this indicates the presence of a functional scotoma. Having discovered that there is still a fusion, fusion reserves are determined. To do this, the test objects are brought together or separated until doubling of the test objects appears. The presence of positive or negative fusion reserves is determined. Is it possible to get a license with protanopia? Find out here.
The use of Synptophor makes it possible to establish the angle of strabismus (objective or subjective), determine the ability to merge images of objects, establish fusion reserve, and detect functional scotoma.
Bialystotsky-Friedman four-point color test for binocular vision analysis
As part of the Belostotsky-Friedman four-point color test, two blue or green circles are used, the rest are red and white. The patient looks at them through red-green glasses. A red filter appears near the right eye, and a green filter appears near the left eye. The white circle located in the center, when viewed through green and red filters, will be perceived as red or green, based on how dominant the vision of the left or right eye is. If there is monocular vision in the right eye, the subject will see two red circles (when viewed through a red glass). In the case of the left eye, only three are green. Simultaneous vision involves viewing five circles - 3 green and 2 red. Simultaneous vision is characterized by viewing four circles - a pair of green and red.
Using polaroid or raster Bagolini filters, as in the case of using a color device, there is a common object to merge, as well as several objects that can be seen with only one eye.
Note that color tests are used not only to determine strabismus, but also to identify color blindness. For this purpose, a table of color perception for drivers with answers can be used.
The methodology for analyzing binocular vision differs depending on the degree of “dissociating” action. In color equipment it is characterized by greater severity, while in raster and polaroid tests it is less pronounced. The reason is that with glasses the conditions become as natural as possible.
Worth's test - a method for testing vision in adults and children
The Wars test is carried out using a sign projector. It allows you to evaluate the nature of vision when both eyes are open. The test allows you to determine what kind of vision children and adults have - monocular, simultaneous or binocular type. The technique also helps to identify vertical phoria.
The test involves two green figures perceived by a person through green glass. There is also one red figure, which the patient looks at through red glass. A white figure is visible with both eyes at once.
With binocular vision, a person sees four figures at once, and five at the same time. Monocular vision involves recognizing either three green or two red shapes.
The four-point test is one of the most popular. Before the test, the patient must move 1-5 meters away. The doctor puts on glasses with light filters. Their right side is equipped with a red lens, the left - green.
Raster haploscopy (Bagolini test)
The Bagolini test involves the use of striped glass in several copies. They are located in a trial frame in a mutually perpendicular direction. The patient wearing these glasses must look at the light source located at a point. Vision is assessed as binocular if, during testing, a person clearly recognizes one light source, and two rays intersect on it, resembling the shape of a cross. In the presence of simultaneous vision, the patient also clearly sees a cross-shaped figure, but the number of sources is increased to two. Monocular vision, accordingly, involves viewing only one beam or two alternating ones in the presence of alternating monocular vision. Read about paralytic strabismus in adults at this link.
Determination of the strabismus angle according to Hirschberg
Description of the method: the patient looks directly at the hole of the ophthalmoscope located in front of him, and the doctor notices how the light glare from the device is located on each eye. On an eye that stands straight, the highlight is located exactly in the middle of the pupil. The highlight on the squinting eye is offset from the center and can be located:
- Within the pupil (angle less than 15 degrees)
- At the edge of the pupil (corresponds to a squint angle of 15 degrees)
- In the middle of the iris (corresponds to an angle of 25-30 degrees)
There are two types of deviation angles: primary - the angle at which the squinting eye deviates, secondary - the angle of deviation of the healthy eye, when the squinting eye becomes fixating.
Method using perimeter
During the diagnosis, the patient fixes his gaze on a candle fixed in the horizontal part of the frame perimeter. In this case, the doctor determines the level of the mark where the second candle should be placed so that it is symmetrically reflected in the other pupil. The study should be carried out in a darkened room. It is advisable to fix the subject's chin on the stand.
During the examination, the patient looks into a special device, while combining two images by moving the handles. Pictures can look different (for example, a dog with ears and a tail, or a circle with a square), they are placed in cassettes, the optical heads of which move until the patient's visual axis coincides with the light beam.
To eliminate adjustment eye movements, you should alternately turn the pictures on and off. The squint angle will be displayed on a special scale.
During the diagnosis, the patient fixes his gaze on a candle fixed in the horizontal part of the frame perimeter. Along with this, the doctor determines the level of the mark where to place the second candle so that it is symmetrically reflected in the other pupil. The study should be carried out in a darkened room. The subject's chin must be fixed on the stand.
During the study, the patient observes through a special device, combining at the same time two pictures by moving the handles. The pictures can be viewed in different ways (for example, a dog with ears and a tail, or a circle with a square); they are placed in cassettes, the optical heads of which move until the patient’s visual axis coincides with the light beam.
To eliminate the installation eye movements, turn the pictures on and off alternately. The squint angle will be displayed on a special scale.
Pathology treatment methods
Treatment of a patient with strabismus is aimed at restoring normal binocular vision. There are several effective treatment methods in this case:
- Correction using glasses and contact lenses. This method is used for any deviations. Its essence lies in the fact that special glasses or lenses are selected that help restore visual acuity, convergence of the eyes and accommodation. This treatment is indispensable for strabismus caused by myopia, farsightedness, and other pathologies of accommodation.
- Hardware therapy. The use of specialized devices helps stimulate the visually impaired, amblyopic eye. The most common are computer programs, photo, magnetic, laser stimulation, and vacuum ophthalmic massage.
- Wearing an occlusive dressing. A special bandage is applied to the healthy eye. The patient only looks sick. This promotes stimulation and increased stress on the pathological eye. That is, the healthy, fixating eye is excluded from the visual process. This principle is the basis of hardware therapy and the use of computer programs.
- Surgical intervention. Surgical treatment is used in situations where other treatment methods do not produce a positive result over the course of 1-1.5 years, and the patient’s condition does not improve during this time. The optimal age for the procedure is 3-5 years. First, the tendon is cut or the muscle is transferred to weaken muscle regulation. The second step of the operation is to enhance the action of the extraocular muscle by shortening it.
Another additional method for correcting strabismus is eye exercises. They are effective for patients with a slight deviation of the strabismus angle from the central axis. Visual gymnastics helps restore binocular vision and strengthen the eye muscle.
Almost all manipulations are based on alternate observation with the eyes of the movement of objects in various directions. To achieve a positive result, you need to practice daily according to a scheme developed by an ophthalmologist on an individual basis.
Strabismus can also be treated with folk remedies, which can serve as an auxiliary method of therapy:
- Calamus root. An infusion must be prepared from this ingredient. You should take 10 g of root, pour it with 1 glass of boiling water, and leave to infuse for 1 hour. Take 50 ml 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals.
- Cabbage leaves. You need to put a few leaves in boiling water and cook until they are completely boiled. Remove from the water and knead a little. Use the prepared pulp 3-5 times a day in small portions, washed down with the remaining cabbage broth.
- Rose hip. You need to take 100 g of rose hips, pour 1 liter of boiling water, and simmer a little over low heat. Leave to brew for 5-6 hours. Drink 1 glass of the prepared decoction 3-4 times a day; for greater effectiveness, you can add a little honey.
- Schisandra chinensis . You need to chop 100 g of fruits, pour in 0.5 liters of vodka. Mix the ingredients thoroughly, leave to infuse for 10 days, and shake the tincture every day. Take the finished medicine 1 tablespoon 3 times a day.
Initially, heterotrophy becomes an aesthetic defect, which significantly spoils the quality of life, damaging the patient’s self-esteem and activity in general. However, over time, ignoring the disease worsens the condition. A person faces serious visual impairment, even disability. Therefore, you should know that strabismus responds well to treatment in the initial stages.
To avoid the development of heterotrophy, it is necessary to pay attention to preventive measures in both adults and children. Women become especially vulnerable during pregnancy. The main prevention of strabismus is regular examinations by an ophthalmologist. The doctor will be able to promptly identify the pathology and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Useful video
Determination of the strabismus angle according to Hirshberg, features of the procedure:
Methods for identifying pathology and measuring the angle of strabismus at home
With congenital strabismus, you can notice the presence of a problem from the very first days. If the disease is acquired, it is unlikely to immediately notice a slight deviation, given the fact that people rarely go to the clinic for a routine medical examination. After this, the doctor can prescribe treatment at home. To determine pathology, it is not always necessary to visit a clinic - the test can be done at home. To do this, you need to lean back on a chair, fixing your head in a motionless position. Next, the person looks at a stationary object in the window - for example, a sign or a satellite antenna. Focusing of vision on the selected object occurs for 1-2 seconds.
Next, covering his eye with his palm, the person examines the same object for 1-2 minutes. If the fixed object does not jump in different directions when each eye opens, you don’t have to worry about the presence of strabismus - it is simply absent. This is a very simple test, but to obtain more detailed information regarding the condition of the eyes, you should still seek help from an ophthalmologist. He will independently carry out the inspection using appropriate diagnostic equipment and modern techniques. And if, after opening the eye, the object begins to jump from side to side, you definitely cannot do without the help of a specialist - you will have to carry out hardware or surgical vision correction. Maybe,
Strabismus in a 1.6 month old child
Hello, I'm so glad I came across this site. thank you very much for your help)))
My daughter and I are beginners with glasses ((((We live in Samara. She is now 1.7 months old.
I'll start the question from the very beginning.
I had a rapid labor. As a result of which I injured the child’s neck (I sat on her head 2 times when I moved from the couch to the birthing table. A minute later, as I sat up, my baby’s scream was heard). Diagnosis by ultrasound was a dislocation of the cervical vertebrae.
At 3 months I was given a DTP vaccine, it was very difficult (it hung in my arms like a rag). After that, I stopped turning over.
At 6 months they had an infanrix in the hospital (we stayed in the day hospital for two days). It was also difficult, but easier.
Until one year, we visited ophthalmologists 4 times, no deviations were noticed.
At 1.6 she started to roll up and walk on her toes.
We immediately went to the doctors.
The neurologist diagnosed PCNSL at the cervical level. Treatment was carried out: Massage, paraffin with ozokerite and Cortexin injections and electrophoresis. Socks and rolling up are over.
At the same time, we went to the ophthalmologist.
Diagnosis
hypermetropia stage I right eye. hypermetropia II degree left eye.
Dysbinocular amblyopia. Partial accommodative entropy of the left eye.
OD 2, OS 4
Strabismus angle 10, 15
after cycloplegia, the strabismus angle decreased by 5 degrees.
It is very important to bring your child to an ophthalmologist on time. A good qualified doctor will be able to easily determine the presence of the disease. As soon as the doctor discovers an emerging pathology, treatment should be started immediately.
It is necessary to understand that it is better to fight the disease using comprehensive measures. You need to sense in time the moment when the time has come to abandon hardware correction and decide on surgical intervention.
An experienced surgeon will be able to accurately determine which type of operation should be performed. Do not be self-willed under any circumstances.
You must spend the entire period that the doctor has prescribed for rehabilitation in accordance with the regimen he has established.
Parents should not despair, because at the end of the treatment course, children experience the following changes:
- The quality of vision increases greatly.
- The position of the eyes becomes normal.
- The perception of the world becomes the same as that of a healthy person.
READ MORE: Strabismus 6 months treatment - All about eye problems
98% of children who underwent complex therapeutic treatment and surgical interventions achieved similar results. Of course, parents and doctors will have to spend a huge amount of time and effort to restore the child’s health. If it turns out that your baby's strabismus has not yet developed to serious stages, then perhaps the doctor will simply prescribe eye stickers that will help correct his vision.
If your doctor prescribes you to wear glasses, then for preschool children it is better to buy ones that are stronger. The fact is that children often break their glasses, and therefore the entire course of treatment goes down the drain.
According to the doctor's recommendation, a sticker should be attached to the lens through which the squinting eye is looking. It will help prevent further deterioration of the situation.
conclusions
- Identifying strabismus is a complex process. To make a full diagnosis, you need to undergo a series of medical tests and collect a complete medical history of the patient.
- When identifying pathology, congenital and acquired factors are taken into account, because In most cases, strabismus is a hereditary disease.
- To correctly prescribe treatment, you need to determine the type and angle of strabismus. For this, the following methods can be used: identification of the strabismus angle according to Hirshberg, study with Synoptophore, Belostotsky-Friedman color test, Worth test, raster haploscopy.
Impact of results on treatment tactics
Determining the magnitude of the strabismus angle allows you to draw up a plan for further treatment:
- if the angle exceeds 15 degrees, then surgical tactics are preferable;
- if the angle is 10-15 degrees, then hardware correction of strabismus is performed.
Hirschberg's technique is simple, but not very informative, so to obtain more accurate results, you should use a synoptophore or perimeters.
Determining the magnitude of the strabismus angle allows you to develop a plan for the upcoming treatment:
- if the angle exceeds 15 degrees, then surgical tactics are preferable;
- If the angle forms 10-15 degrees, then hardware correction of strabismus is performed.
Girshberg's technique is simple, but not very informative; therefore, to obtain more correct results, one should use a synoptophore or perimeters.
READ MORE: Exercises for strabismus - eye gymnastics for strabismus in adults and children
How is the angle of strabismus determined?
In what units of measurement is the angle of strabismus determined? The deviation of the visual axis of the eye is measured in degrees, like other angular parameters. Among the methods used to determine the angle of strabismus, the most common is the Hirschberg method, since it is recognized as the simplest and most effective.
When performing this measurement, the patient is asked to fix his gaze on the opening of the mirror of the ophthalmoscope apparatus. At the same time, the doctor notes how the light from the ophthalmoscope is reflected on the oblique organ.
In the eye where strabismus occurs, a beam of light is reflected at the edge of the pupil and indicates that the angle of deviation of the visual axis corresponds to 15 degrees of angular magnitude.
Whereas in a healthy organ, a beam of light is reflected in the center of the pupil. If this indicator deviates by 25-30°, the light beam will fall in the middle of the iris.
The primary angle of deviation is considered to be that of a squinting eye. And the secondary deviation angle is the healthy angle. Depending on the results obtained from the measurement, a further course of treatment and/or correction is already prescribed. Wherein:
- Angle values greater than 15° indicate the need for surgical treatment.
- Indicators below 10° are a direct indication for hardware vision correction.
Despite its simplicity, Grishberg's method is considered insufficiently accurate. More accurate diagnostic results can be obtained by examining devices such as a perimeter or synoptophore.
Let us briefly describe the method for determining another eye pathology. To detect heterophoria, you need to do some measurements or tests. Thus, measurements to determine heterophoria are carried out with the exclusion of the possibility of binocular vision. That is, one eye is covered with a hand or a spatula during examination.