How is the examination carried out?
To perform kinetic perimetry, a special device is required - a perimeter.
The perimeter can be arc (desktop), projection or computer. This research method is carried out for each eye separately, while a bandage is fixed on the second eye. When performing perimetry, the patient looks at the indicated point without looking away. The doctor is on the side, moving the object along the meridians from the periphery to the center. In this case, the patient needs to catch the moment when, with his gaze fixed on a point in the center, he sees a moving object.
The size of the object used depends on the visual acuity. For high visual acuity, an object with a diameter of 3 mm is used; for low visual acuity, an object with a diameter of 5 to 10 mm is used. Usually the study is carried out along eight meridians, sometimes for a more accurate picture - along 12 meridians.
There is no color perception in the peripheral parts of the retina. The extreme periphery perceives only white color; as you approach the central zones, the sensation of yellow, blue, green and red colors appears. And only the central zone perceives all colors.
The technique for studying visual fields may differ depending on the device intended for perimetry. First of all, a study is carried out towards the white color using the perimeter.
The other eye should look at the white mark, which is located in the middle of the perimeter. A person needs to look at this very point throughout the entire procedure. After about ten minutes, the patient is reminded to fixate his gaze on this mark. Immediately after he sees a dot in motion, he should tell the doctor about it.
After completing the examination, the doctor should schematically display the visibility of the patient's visual fields. After this, perimetry occurs using multi-colored markers. However, the subject should not know in advance which color he will work with.
During the procedure, the patient will need to not only determine the location of the mark, but also recognize its color. If a person does not guess, then the mark moves further from the border. The doctor often uses scarlet, green, yellow or blue objects.
I would like to draw your attention to the effective Amsler test, which acts as a type of perimetry. The procedure requires the patient to focus on the middle of the image
How to perform perimetry
Depending on which device is used to perform the procedure, the technique for examining visual fields differs.
Förster perimeter
Perimeter survey
First, a study is carried out on white :
- The patient is asked to sit next to the device with his back to the light source. The chin is placed on the device's stand. One eye is covered with a blindfold, and the other looks at a white mark placed in the central part of the perimeter. It is at this point that a person will have to look throughout the entire procedure.
- After several minutes allocated for habituation, the patient is informed that he is fixing his gaze on a stationary mark, and after he notices a moving point on the periphery, he needs to tell the specialist about it.
- The doctor begins to move the mark along the meridians in the direction from the periphery to the central part, and the person being examined lets him know when he sees the object.
- The doctor turns the device alternately by 45˚ and 135˚.
- The same actions are carried out with the other eye as with the first.
Upon completion of the examination, the specialist creates a schematic representation of a person’s visual fields.
Then perimetry is carried out using color marks .
- The subject should not know which color will be used for the procedure. Therefore, during the examination, a person needs not only to mark the mark, but also to correctly determine its color.
- After this, the boundaries are indicated on the schematic representation of the visual fields. If the patient makes a mistake with the color, the tag moves further until the specialist gets the correct answer.
The most commonly used colors are red, yellow, green and blue. The procedure is performed with 8 meridians and an interval of 45˚ or 12 meridians and 30˚.
Computer-assisted research
- The patient sits near the device. A shutter is installed over one eye, and the chin is placed on a stand.
- Objects move chaotically on the monitor, and the patient, having seen the object, must press the mouse button.
Computer perimetry of the eye takes longer - about 5-10 minutes. The essence of the procedure is that the brightness and size of a static object are constantly changing. The study determines the sensitivity of the retina to color in any of its zones.
The data is considered more accurate than the study conducted by Förster's perimeter. The results obtained are saved on the computer, and if necessary, you can view and evaluate them again.
What may prevent you from receiving correct data:
- Ptosis of the upper eyelid;
- Overhang of eyebrows into the visual area;
- Deep-set eyes;
- The presence of a high bridge of the nose.
If a person has such symptoms, it is recommended to undergo an examination using a computer device and perimeter. This will allow you to get more accurate results.
Diagnostic methods
Different methods are used for the study, and each eye must be diagnosed separately. The doctor will ask you to look at one point, noting the appearance of an object in nearby areas.
Basic diagnostic techniques:
- Control – allows you to make an approximate assessment of the visual field, does not take much time and does not require the use of special equipment. The main control in this case is the normal field of view of the specialist conducting the diagnosis. You will need to close one eye with your palm, and use the other to fix the open eye of the doctor sitting opposite you. During the inspection process, the appearance of fingers, pens and other objects entering the field of view is noted.
- Kinetic – it is carried out using a manual perimeter (a screen shaped like a hemisphere). The chin is placed on the stand of the device, and the corresponding mark is fixed with the eye being examined. As soon as you see a luminous object with your peripheral vision (it can move from the periphery to the center or vice versa), tell the doctor that you see it. In this case, the boundaries of the field of view are taken to be the points at which the object disappears or appears.
- Static - this type of perimetry is carried out using an automatic perimeter. The chin is placed on a stand, and the eye being examined fixes the mark. The computer starts showing a glowing object in different parts of the screen and increases its brightness until you notice it and press the corresponding button.
- With double frequency - in this case, the subject examines black and white vertical stripes that flicker at a high frequency (due to this, the effect of doubling them occurs). If vertical stripes are not visible at certain frequencies, this indicates pathology of the optic nerve or retina. The technique is highly effective in the early stages of diagnosing glaucoma.
Types of perimetry
Determining the boundaries of the visual field can occur in two ways:
- Control - by comparing the boundaries of the field of vision of the patient and the doctor;
- Instrumental - with a projection of the boundaries of vision onto a flat surface or hemispherical perimeter (perimetry).
To instrumentally determine the field of view, special devices are used - perimeters. Depending on the type of device, several types of perimetry can be distinguished, each of which has its own technique. The two most popular methods are kinetic and static threshold. Together they help to identify patterns of visual disturbances associated with pathologies of the choroid, retina and optic nerve.
Kinetic perimetry
Movable markers – achromatic (white) or colored – are used as test objects. Measurements are carried out in 8 meridians of space, gradually moving the test object from the periphery to the center at a speed of 2° per second. The kinetic technique is carried out primarily using arc perimeters. The simplest is the Förster manual perimeter, which consists of a fixed arc with movable test objects. During the examination, the patient sits motionless and looks at the central point, while the doctor moves marks along the arc line and records the reaction of the subject.
Static perimetry
The visual field is measured using a stationary test object. Inside the hemisphere of the device, where the patient places his head, luminous points periodically flash in different parts of the space. Noticing them, the patient must immediately press a special button, recording the result. The gaze should remain motionless and focused on one point strictly in the center of the field.
Each luminous mark is located in a certain area of the field of view. If the patient registers its presence, then this part is visible to him. To consolidate the result, each mark is duplicated again. The result of the study is a schematic image of the visual field, where the areas visible to the eye are indicated in white, and the invisible areas in black.
Static perimetry is performed according to two different programs - screening and threshold. Screening diagnostics takes no more than 5–7 minutes and gives a general idea of the state of peripheral vision. Threshold – implies a deeper study of the pathology and can last up to 30–40 minutes.
Threshold perimetry
The threshold perimetry strategy requires increased concentration from the patient, so it is not suitable for everyone, but if used successfully, it gives more accurate results. It is used to obtain additional information on already diagnosed vision defects. The technique is based on measuring the sensitivity threshold for each point of the visual perimeter.
Computer perimetry
Research can be carried out either manually or using computer equipment. Often, methods are used simultaneously to verify the reliability of results in controversial situations.
Computer perimetry of the eye excludes the direct participation of an ophthalmologist - all diagnostics are performed by computer equipment according to the programmed program. Static threshold computer perimetry has gained the greatest popularity in recent years. It allows you to obtain data on the state of the visual field without the active participation of the patient - the computer records all reactions of the eye independently. The method is based on changing the position, size and brightness of stationary test objects. When the patient's eye notices the appearance of an object, the computer records its location relative to the central point of the eye's field of view.
What can autorefractometry reveal?
Autorefractometry helps detect visual impairments, such as:
- Myopia is an eye disease in which a person sees close objects well, even the smallest ones. In the distance, the picture looks blurry and the further away the object is, the blurrier it is visible. This is due to the elongated eyeball, in which the image arrives in front of the retina rather than through a specific area.
- Farsightedness is a refractive error in which a person sees objects both at a great distance and very close and blurred. The only exception is age-related farsightedness, in which the patient recognizes objects far away. This happens due to a shortened eyeball, in which the image passes not through a certain area of the retina, but into the plane behind it.
- Astigmatism is an ophthalmological disease that damages the cornea and lens. Because of this, a person can see some objects near and far well, but others poorly. The reason for this is the disruption of the spherical surface of the cornea and lens. In its normal state it has an even coating, but with astigmatism its sphericity is disrupted and images are focused in front of the retina, others after, and some in it, as it should be.
According to doctors, about 75% of people suffer from astigmatism, but not everyone pays attention to this, because
it may be quite small. This disease is diagnosed even at an early age. And the sooner correction and treatment begin, the higher the chances of getting rid of the disease.
Perimetry
Perimetry is a diagnostic method that allows you to determine the state of the visual field. The visual field is that part of the surrounding space that a person sees at the same time when the eye is completely motionless. Visual field defects are a symptom of problems with the retina or optic nerve and make it possible to accurately diagnose a number of dangerous eye diseases, often leading to complete blindness. Perimetry plays a particularly important role in establishing the diagnosis of glaucoma.Indications for perimetry
: • glaucoma; • retinal dystrophy; • retinal disinsertion; • retinal hemorrhage; • oncological eye diseases; • damage to the optic nerve; • hypertension; a brain tumor; • traumatic brain injuries.
Kinetic perimetry
This type of research is based on the use of moving objects of different colors. It is performed using perimeters specially designed for this purpose. They can be table-top, in which an object moved by the doctor is used during testing, or projection-based, in which a light object is used.
The examination requires maximum concentration, since visual fields are determined based on the patient's responses. It is performed for each eye separately. The patient sits in front of the perimeter. While the study continues, it is necessary, without stopping, to peer at a given point in the center of the perimeter. An object of a certain diameter and color moves from the periphery to the center of the perimeter. The patient should report when he notices the object in peripheral vision and when the object disappears. The doctor puts these marks on a special table. Then the marked points are connected and the missing areas are shaded. Based on the data obtained and the necessary additional examination, the doctor can determine the nature of the problems that have arisen, establish a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Static perimetry
When performing static perimetry, the object is motionless, only the degree of its illumination changes. This makes it possible to determine the reaction to light of those areas of the retina that are primarily affected by glaucoma. For this study, special computer perimeters are used. The patient fixes his gaze on a luminous point in the center of the perimeter. Then the program starts and light points, brighter or dimmer, begin to appear alternately around the entire perimeter. When the patient notices such a point with peripheral vision (without taking his eyes off the focal point in the center), he must press a button on the joystick. After completing the study, the doctor makes a diagnosis based on the results issued by the device.
Donders method
Peripheral visual fields are determined using the Donders method. This is a control study in which no instruments are used. It consists of sitting opposite the patient at a distance of about half a meter. The patient closes his left eye, while the doctor should close his right eye. Each of them looks with an open eye into the eye of the person sitting opposite. The doctor's field of vision is a reference for the patient's field of vision. The doctor begins to show his fingers, moving his hand. If the doctor and the patient notice the fingers with peripheral vision at the same time, it means that the patient’s field of vision is not changed. The patient's left eye is examined in the same way.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis is based on patient complaints and perimetry. When visiting an ophthalmologist, it is necessary to describe as accurately as possible all the negative manifestations that diagnostic equipment cannot detect. Such manifestations include:
- headache;
- feeling of pressure on the eyeballs;
- dizziness;
- imbalance;
- fog in the eyes;
- light sparks in the field of view.
If you have floaters before your eyes, then read the article.
Carrying out perimetry
All these symptoms will help the doctor make an accurate diagnosis, and, if necessary, prescribe additional consultations with a neurologist and neurosurgeon. To determine the impairment of visual fields, loss of individual zones and precise localization of areas, the Perimeter ophthalmological device is used. The device has several modifications, but computer perimetry is considered the most accurate diagnostic method. Since the human eye does not respond equally to the colors of the spectrum, visual field loss testing is usually performed for all primary colors.
Contraindications
Contraindications to perimetry are:
- aggressive behavior of the patient;
- mental retardation of the patient, which does not allow him to undergo examination;
- alcohol or drug intoxication.
We recommend the article - Diclofenac eye drops, instructions, indications, contraindications and dosages.
In what cases it is worth using tetracycline eye ointment, you can find out from this publication.
Contraindications to perimetry.
There are several conditions in which perimetry (static and kinetic) is contraindicated:
- aggressive behavior on the part of the patient;
- drug or alcohol intoxication (even in the smallest doses);
- mental retardation that does not allow you to follow the doctor’s instructions.
It is also necessary to take into account factors that may affect the final indicators and simulate deviations from the perimetry norm. These include:
- strongly drooping eyebrows;
- drooping upper eyelid;
- irritation in the area of a large vessel in close proximity to the optic nerve;
- deep planting of eyeballs;
- high bridge of the nose;
- very low vision;
- low-quality vision correction;
- some types of eyeglass frames that cause interference.
How to prepare for research
To conduct computer perimetry, no special preparatory measures are required. Still, it is worth considering some factors that can affect the final results of the procedure:
- High bridge of the nose;
- Very low visual acuity;
- Drooping of the upper eyelid;
- Irritation in the area of the eyeball at the border with a large vessel;
- Carrying out the procedure
The patient is seated in front of a special device, given a joystick in his hands and asked to fix his gaze on one point of light. Then, around the light point where the patient’s gaze is fixed, lights light up at different speeds and in a chaotic manner. The subject's task is to press the joystick button at the moment when he notices the newly appeared light. During the procedure, a computer program records the degrees at which each of the objects marked by the patient was located. Based on the information obtained in this way, computer perimetry is deciphered.
The procedure is carried out for each eye in turn. Its total duration does not exceed 20 minutes. Computer perimetry is completely painless, cannot cause any complications, and no rehabilitation is required after it.
The result of deciphering computer perimetry is an accurate map of the visual fields, which includes all the studied indicators, thanks to which the ophthalmologist makes a conclusion about the state of the visual system in general and the presence of possible problems.
Decoding the result
Based on the results of the examination, the doctor fills out a special form indicating the extreme points of limitation of the visual field.
The form is deciphered by a specialist, taking into account the following factors when assessing:
- number and size of blind spots;
- scotomas - areas that do not coincide with the periphery;
- the state of the retina in the central region of the visual field.
The interpretation of the examination results is carried out taking into account the individual characteristics of the structure of the visual system, so the interpretation of the readings is done by a doctor, and not by a computer program. The obtained data is combined into a complex, and only after a comparative analysis the state of the patient’s visual field is assessed.
The following indicators are considered normal:
- acceptable scotomas;
- absence of a certain number of areas in the field of view.
The following indicators indicate pathology:
- a large number and expanded blind spots;
- some scotomas are a sign of the onset of glaucoma;
- detection of narrowing of visual fields.
An important factor in assessing the results of perimetry is scotomas. This is the name for discrepancies between the contour and boundaries of the visual periphery. Scotomas can be:
- positive – discernible by the patient;
- negative – detected only during the examination;
- relative - representing a decrease in sensitivity, in which only large and bright objects are detected;
- absolute - in the case of complete loss of all objects from the field of view, regardless of their brightness and size.
By analyzing scotomas, a specialist makes a diagnosis. The detected boundaries of the narrowing of the visual field are considered by the doctor on an individual basis. With normal results, the number of scotomas is small. The presence of scotomas in places of vascular formations is also considered normal; they are called angioscotomas. Detection of other blind spots that do not correspond to the normal indicators is equivalent to deviations.
Graphically, a person’s visual field is represented as a three-dimensional visual hill, the boundaries of which are its base, and the height is the degree of light sensitivity of the retinal sectors. With normal vision, the height of the hill decreases from the center to the periphery.
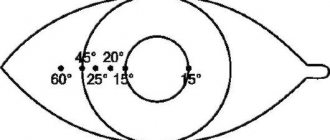
Norm of peripheral boundaries:
- top – 50°;
- lower – 60°;
- internal – 60°;
- external – less than 90°.
Interpretation of perimetry results
The results of perimetry are recorded in the form of a map on which the extreme values (boundaries) of the field of view are marked. Normal indicators: the upper limit of the visual field is 50°, the lower is 60°, the inner limit is 60°, the outer is more than 90°.
The central part on the visual field map displays the state of the photoreceptors of the macular region of the retina. Some areas of the visual field may fall out, while they are surrounded by areas with preserved vision. Such zones, the contours of which do not coincide with the peripheral boundaries of the visual field, are called scotomas. Normally, there are several physiological scotomas on the visual field map. Thus, in the area of projection of the optic nerve head there is the so-called blind spot - an area devoid of light-sensitive cells. Normally, the map also displays areas of projection of retinal vessels (angioscotomas). In all other cases, areas of loss of visual function are pathological.
Scotomas can be positive (when the patient notices loss of the visual field) and negative (identified only during examination), absolute and relative, and have different shapes, localization and size. There are types of pathological scotomas characteristic of certain diseases (glaucoma, migraine).
Another type of change detected by perimetry is a narrowing of the visual fields. Certain characteristics of the narrowing of the visual field (size, localization) correspond to different levels of damage to the optic tract. The narrowing can be one- or two-sided, concentric or sectoral. If defects are noted in only one half of the visual field of each eye, this condition is called hemianopsia, which in turn can be homonymous (when visual defects are determined in opposite areas of both eyes) and heteronymous (when visual defects are localized in the same areas of the visual fields). Depending on the size of the lost areas, hemianopia can also be complete, partial or quadrant.
Indications for the study
The doctor will recommend examination using the refractometry method in the following cases:
- Myopia and farsightedness. To prevent further development of the pathology, early diagnosis is important, so the procedure is prescribed even for minor impairments in visual function.
- Double vision.
- False myopia. Pathology occurs as a result of spasm of the eye muscle. if a person is forced to focus his vision for a long time on objects that are distant or located too close.
- Presbyopia. In this case, a person cannot see small objects located nearby, for example, the font of a book or newspaper.
- To clarify the diagnosis and determine the degree of pathology
- When monitoring the situation after ophthalmological operations.
Indications
Patients are prescribed computer perimetry if certain eye diseases are suspected, including:
- Increased intraocular pressure and glaucoma;
- Inflammation of the optic nerve head;
- Retinal damage and detachment;
- Vascular fundus abnormalities;
- Oncological diseases affecting the eye;
- Organic pathology of the central nervous system (hypertension, hemorrhagic stroke, tumor processes, multiple scerosis).
What you need to know about perimetry
The visual field is the space that a person recognizes when his gaze is fixed and his head is still. If you look at a certain object, in addition to its clear image, a person sees other objects located around. This is called peripheral vision, and it is not as clear as central vision.
Perimetry is an ophthalmological study that allows you to examine the boundaries of the visual fields through a projection onto a spherical surface. There are kinetic and static perimetry. Kinetic research involves using a moving object, while static research involves varying the illumination of an object in one position.
The study helps to analyze changes in the visual field and determine the localization of the pathological process (retina, optic nerve, visual pathways, visual centers in the brain). Most often, a narrowing of the visual field and loss of some areas (scotoma) are detected.
Indications for perimetry:
- retinal pathologies (tears and detachments, dystrophy, hemorrhages, burns, tumors);
- diagnosis of macular pathologies, including toxic lesions;
- detection of retinitis pigmentosa;
- diseases of the optic nerve (neuritis, trauma);
- diagnosis of pathologies of the visual pathway and cortical centers in the presence of neoplasms, injuries, stroke, severe malnutrition;
- a brain tumor;
- hypertonic disease;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- signs of cerebrovascular accident;
- confirmation of glaucoma, tracking the dynamics of the process;
- checking patient complaints (aggravation factors);
- preventive examination.
Perimetry is contraindicated if the subject is under the influence of alcohol or drugs, or has mental illness. The procedure does not cause any complications.
What can distort perimetry results:
- drooping eyebrows;
- deep planting of eyeballs;
- drooping eyelid;
- height of the bridge of the nose;
- exposure of the irritant to large vessels near the optic nerve head;
- low visual acuity;
- poor quality correction;
- rim glasses.
False visual field defects can also appear due to the structural features of the face and pupil width. To eliminate false defects, repeat testing is carried out in the same program. In order for dynamic observation to be reliable, the same perimetry conditions must be observed (size of objects, lighting, time and colors).
Computer perimetry of the eye: what is it, how it works and diseases that can be identified -
The eye has a complex structure. Therefore, there are dozens of diseases associated with impaired visual function. But fortunately they are all diagnosed. But different techniques may be required to identify them. One of them is computer perimetry of the eye.
What is eye perimetry?
These are studies of peripheral vision. The decoding gives an idea of the consistency of the visual function and whether it is within normal limits. So, in a healthy state, the eye should cover a certain surrounding space.
Often, perimetry violations go unnoticed by humans. He perceives objects in a narrowed range and does not notice it. Therein lies a serious danger. After all, pathology can develop in the future.
Visual field assessment is required. A computer method is used for this. The study is carried out on special equipment, which is a hemisphere. The patient needs to place his head there. Inside it there is a field on which luminous points appear. They flare up in different places in this space.
Accordingly, when the patient sees such a point, he presses a special button. In this case, it is not allowed to shift your gaze; it must be directed strictly to the middle of the field. Based on the results of the study, a color scheme is drawn up. This is a transcript of the study, where those parts of the visual fields that are no longer accessible to the patient are visible. This means a deviation from the norm.
| This kinetic examination principle allows for a very accurate assessment of the state of the visual fields. |
Operating principle of the device
As stated above, it reacts to parts of the field visible to the eye. Each flashing dot means one or another part of the space; if the patient reacts to it, then this part is visible to him. In this case, the analysis is carried out on the basis of repetition of flashing points, which appear in the same places during the examination.
The duration of the procedure is 5–7 minutes. A printout of the results with a picture is made for each eye separately. At the same time, the figure shows the eye condition in the peripheral vision. For clarity of results, those areas that are visible are marked in white, and those that are not are marked in black. This ophthalmological examination allows you to identify pathologies of the optic nerve.
What diseases can be detected using perimetry?
This procedure is part of a complete examination of the patient's eye condition. This method is the most accurate diagnosis. It makes it possible to detect optic nerve atrophy.
If the boundaries of visibility are deviated from the norm and there are areas inaccessible to the eye, this means the presence of a number of diseases: First of all, this is optic nerve atrophy. It is associated with a narrowing of the visual field, a decrease in the degree of viewing. In fact, the optic nerve dies. The result is complete blindness in the affected eye.
The presence of a scotoma gives reason to suspect myopia. This is what is called myopia in medicine. After all, the dots may not be visible due to weakened vision. Studying the table with the results of the study allows you to identify glaucoma.
It is expressed in increased intraocular pressure. In general, such a study shows the condition of the right and left eyes. It demonstrates the achievement of the threshold level of peripheral vision.
If it is exceeded, then treatment, including surgery, should be started immediately.
Therefore, timely detection of these pathologies can save the eye. And it is especially important to conduct research in children. The resulting photos and videos will make it possible to monitor and study your health status and respond to its changes in a timely manner.
Types of violations
The main violation in the perimetry of the eye is the perception of the visible area by the gaze. There is a certain norm, which is marked by the flashing dots indicated above. If the patient does not see any of them, this means that he does not notice this area of space in front of him.
| As a rule, flashing marks indicate that distant peripheral areas are inaccessible to perception. |
Types and purpose of perimetry
There are two main methods to consider. These are computer and static perimetry. It is important to note that both types are based on the use of computer technology.
Static perimetry
It consists of showing the patient a stationary object that appears at different points. Doctors monitor the reaction to them. The results of the study are indicated by numbers indicating the percentage of scotoma. The result has a color image.
A darker tone means absolute scotoma, that is, areas inaccessible to the eye’s perception. When the test is completed, the doctor records the results and fills out a standard template.
Anyone can understand its contents, precisely due to the color display of inaccessible areas of vision.
Computer perimetry
Using this procedure, you can accurately determine not only the location, but also the depth and size of the visual defect. This is a quick, painless and reliable method for detecting visual field disorders.
Graphic interpretation of perimetry results
Decoding is expressed in text and graphic form. The latter, in turn, is a scale with marks for normal, relative and absolute scotoma.
Perimetry indicators: normal or deviation?
The average limits of vision are as follows:
| Up: 55°;Up and out: 65°;Outside: 90°; Down and out: 90°; | Down: 70°; Down inside: 45°; Inside: 55°; Up and inside: 50°. |
If after the examination you find any deviations from the norm, there is no need to panic right away. These could be age-related changes or a defect that is easily corrected. In any case, the doctor will explain the results to you and tell you what to do.
Indications and contraindications
If we talk about the perimetry procedure, it is completely safe. There is no intervention and no medications are required. Therefore, there are simply no contraindications. After all, the computer mechanically sends a signal to the screen, and the patient responds to it by pressing a button.
Indications include loss of vision and disturbances in the perception of objects. For example, one eye sees more space than the other.
| In addition, perimetric studies are also necessary for prevention. After all, timely identification of problems will allow you to solve them and restore health. |
Drug therapy
the danger of atrophy lies in its further development. The reason for this is increased intraocular pressure. This condition is called glaucoma. Accordingly, it is necessary to reduce the pressure on the optic nerve. Then it will not be damaged and the development of atrophy will be stopped.
Therefore, drops are used to reduce it. For example, “Dorothy Plus” or “Prolatan”. They should be taken in doses recommended by your doctor.
Surgical methods
Ways to overcome glaucoma include performing a puncture in the back wall of the eye. That is, as a result of the operation, a small hole is formed. Excess fluid must escape through it, which leads to pressure.
This is the only option for eliminating glaucoma. However, it is impossible to isolate it, since it is an eye condition, not a disease. And it can only be maintained by removing dangerous factors.
Prevention
It is necessary to monitor visual acuity. After all, everything in the eye is interconnected. Therefore, its decrease may indicate the onset of glaucoma. You should watch the pupil. If it is greatly dilated even in the light, this indicates high eye pressure. It must be remembered that acute conditions will lead to total blindness.
Average cost of research in the Russian Federation
It all depends on the region of residence. If it is a small town where they use old equipment, then the cost of the procedure will be approximately 300-350 rubles. If you live in Moscow or similar cities, then the price will accordingly be approximately 1500–3000 rubles, since the study will be carried out using new, modern technology.
Source: https://zdorovoeoko.ru/diagnostika/kompyuternaya-perimetriya-glaza/
Types and methods of perimetry
| Type/method | Distinctive features |
| According to the method of conducting the study | |
| Static perimetry | Involves the use of a stationary object, the illumination of which changes during the research process. This computer perimetry of the eye has proven itself well in observing disorders in the form of scotomas or narrowing of lateral vision, as well as monitoring the optic nerve and retina. |
| Kinetic perimetry | Involves the use of a moving object whose color changes. The process involves the perimeter: the object is moved to the center of vision from the side until the patient fixes it with peripheral vision. The procedure is repeated from different directions using different test objects and their colors. |
| Depending on the equipment used | |
| Touching the screen | The simplest visual field perimetry, which involves moving a black white or colored pin across the screen. |
| Automated perimetry | Diagnostics involves the use of an automated installation in the form of a white hemisphere, with the middle facing the patient. Inside it there is a target located in the center. The patient should not take his eyes off it during the examination. He is given a button that he must press every time he sees flashes appearing inside the hemisphere. All signals are recorded by a computer, which carries out the corresponding calculations. |
| Goldman perimeter | Diagnostics is carried out using the Goldmann perimeter, which is a white hemisphere onto which light spots of different sizes and brightness are displayed, which can remain in one place or move. This technique allows you to test the entire range of lateral vision and is widely used for monitoring the condition of patients suffering from glaucoma. |
| Microperimeter | Involves the use of a computer to evaluate the function of the spot. Microperimeters are involved in the process. |
| Based on the purpose of the study | |
| Monocular perimetry | The field of view is determined for each eye separately. |
| Binocular perimetry | The common field of both eyes is determined. |
Useful video
From this video you will learn what perimetry is:
In any case, it is not worth saving on such a procedure, since perimetry can help identify many dangerous pathologies .
And a correct and timely diagnosis means effective and quick treatment.
When a person begins to notice a narrowing of his visual fields or is diagnosed with general diseases that in one way or another affect the organ of vision, an eye doctor or other specialist prescribes perimetry.
Let's take a closer look at what the procedure is and what it defines.
Eye perimetry is a method for determining visual fields using a special instrument or computer device.
Most often, the visual field is affected by the following diseases:
- Pathological processes in the optic nerve: trauma, neuritis.
- Glaucoma at any stage of development.
- Retinal detachment, hemorrhages and neoplasms in it.
- Brain injuries.
- Neoplasms of the central nervous system.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Poor blood circulation in the brain.
- Hypertension.
- Preventive examinations (for example, for the driver).
Depending on which device is used to perform the procedure, the technique for examining visual fields differs.
Förster perimeter
Perimeter survey
First, a study is carried out on white :
- The patient is asked to sit next to the device with his back to the light source. The chin is placed on the device's stand. One eye is covered with a blindfold, and the other looks at a white mark placed in the central part of the perimeter. It is at this point that a person will have to look throughout the entire procedure.
- After several minutes allocated for habituation, the patient is informed that he is fixing his gaze on a stationary mark, and after he notices a moving point on the periphery, he needs to tell the specialist about it.
- The doctor begins to move the mark along the meridians in the direction from the periphery to the central part, and the person being examined lets him know when he sees the object.
- The doctor turns the device alternately by 45˚ and 135˚.
- The same actions are carried out with the other eye as with the first.
Upon completion of the examination, the specialist creates a schematic representation of a person’s visual fields.
Then perimetry is carried out using color marks .
- The subject should not know which color will be used for the procedure. Therefore, during the examination, a person needs not only to mark the mark, but also to correctly determine its color.
- After this, the boundaries are indicated on the schematic representation of the visual fields. If the patient makes a mistake with the color, the tag moves further until the specialist gets the correct answer.
The most commonly used colors are red, yellow, green and blue. The procedure is performed with 8 meridians and an interval of 45˚ or 12 meridians and 30˚.
Computer perimetry of the eye takes longer - about 5-10 minutes. The essence of the procedure is that the brightness and size of a static object are constantly changing. The study determines the sensitivity of the retina to color in any of its zones.
The data is considered more accurate than the study conducted by Förster's perimeter. The results obtained are saved on the computer, and if necessary, you can view and evaluate them again.
What may prevent you from receiving correct data:
- Ptosis of the upper eyelid;
- Overhang of eyebrows into the visual area;
- Deep-set eyes;
- The presence of a high bridge of the nose.
If a person has such symptoms, it is recommended to undergo an examination using a computer device and perimeter. This will allow you to get more accurate results.
The interpretation of the results depends on how different they are from normal values and the instrument used to perform the test.
- The boundaries of the field of view in relation to the color white , made by the perimeter :
Top – 50˚;
Downwards – 65˚;
Outward – 90˚;
Inwardly – 55˚.
- Normal indicators during computer perimetry :
It is believed that the largest size of visual fields exists for blue, and the smallest for green. This is due to the difference in their wavelengths.
The average values of visual fields for colors are as follows:
Up: 50˚ – blue, 40˚ – red, 30˚ – green.
Down: 50 – blue; red – 40˚, 30˚ – green.
Outward: 70˚, 50˚, 30˚ respectively.
Inwards: 50˚, 40˚, 30˚.
Normal indicators
What is eye pachymetry
Now there are two types of pachymetry in ophthalmology:
- optical;
- ultrasonic
The first option involves non-contact research, but is much less accurate. To conduct the second study, you will need a special ultrasound machine, which will be used to measure the thickness of the cornea. This procedure is called keratopachymetry.
In the case of optical pachymetry, the patient sits in front of a special slit lamp, on which a nozzle made of two plates is installed. It is this attachment that determines the thickness of the cornea in its different places.
Widely used for treatment and diagnosis - eye drops for dilating the pupil.
Autokeratometer with pachymetry function
The ultrasound technique involves contact of the ultrasound machine with the surface of the eye. To ensure that the procedure is painless, the doctor must use local anesthesia. Inocaine is usually used for this. When the anesthesia begins to take effect, the ophthalmologist touches the device to the eye, after which calculations appear on the monitor.
It is extremely important to use the device carefully, as applying too much pressure may cause distorted results. After the procedure has been completed, it is necessary to drip the eyes with moisturizers. This will help avoid irritation
It is very important to remain calm during the procedure as this will reduce the likelihood of corneal injury
This will help avoid irritation. It is very important to remain calm during the procedure as this will reduce the likelihood of corneal injury
After the procedure has been completed, it is necessary to drip the eyes with moisturizers. This will help avoid irritation
It is very important to remain calm during the procedure as this will reduce the likelihood of corneal injury
Ultrasound
When keratotopography is necessary is described in detail in the article.
Kinetic perimetry
When performing kinetic perimetry, visual fields are assessed using a moving light stimulus object of a given brightness. It is moved along given meridians, and the points at which it becomes visible or invisible are marked on the form. By connecting these points, we get the boundary between the zones in which the eye distinguishes a stimulus of given parameters and does not distinguish it - the isopter. The size, brightness and color of objects may vary. In this case, the boundaries of the field of view will depend on these indicators.
Interpretation of autorefractometry results
The patient passed the test and received the results. What can you see there?
- Ref – transcript of the research results.
- R (OD) — visual acuity of the right eye.
- L (OS) – visual acuity of the left eye.
- Sph (sphere) is a parameter that helps determine myopia or farsightedness.
- PD (interpupillary distance) is the interval between the pupils.
- Cyl (cylinder) – a value that reflects the power of cylindrical optics; it is needed to determine the degree of astigmatism of the patient.
- AX (cylinder axis) - measured in degrees, required for the manufacture of glasses lenses to correct the incorrect refraction of light penetrating through a cylindrical lens.
Sometimes you can see this # sign in the results; it indicates errors or unreliable data during research.
In some devices, sphero-equivalent (SE) is determined - this is rounding the value of the strong meridian to a whole number. That is, glasses will be made not according to real results, but according to corrected ones. Many ophthalmologists consider this method outdated, because nowadays you can make glasses with any lenses.
Vision is considered normal when Sph and Cyl are equal to zero, i.e. its acuity corresponds to one. If there are other data next to these indicators, then you should immediately begin vision correction with treatment, lenses or glasses.
Static (quantitative, quantitative) perimetry
Static (quantitative, quantitative) perimetry is carried out using a stationary test object, which is presented to the subject at predetermined points of the arc or hemisphere of the perimeter. The brightness of the test object gradually increases from subthreshold to threshold, at which it becomes visible to the patient. The method is highly informative.
Conditions for performing perimetry. Kinetic and static P. are carried out under conditions of adaptation to different levels of arc illumination (adaptoperimetry): photopic (“daytime”), scotopic (“nighttime”) and mesopic (intermediate) levels. Light levels affect the light sensitivity of the retinal photoreceptors (cones and rods). Thus, under photopic illumination, the most sensitive to light are the cones located in Ch. arr. in the central zone of the retina. P. at this level of illumination makes it possible to identify defects in the central parts of the visual field. Under scotopic illumination, it is most advantageous to examine the peripheral parts of the retina, where under these conditions the sensitivity of the rods is highest. In practice, it is preferable to perform P. under mesopic illumination, that is, under conditions of simultaneous functioning of rods and cones. Color P. must be carried out under photopic illumination, since under these conditions the cone apparatus, which provides color vision, is most active.
Rice. 1. Perimetric form for recording the visual field: dotted lines indicate the normal boundaries of the visual fields of the right eye (dashed line with a dot) and the left eye (dashed line without a dot) when examined using a white test object.
When conducting Perimetry, psychology and preparation of the subject are of great importance. Before P., the patient must be explained the objectives and conditions of the study. Unnecessary irritants (light, noise) must be eliminated. To compare P.'s data obtained by different researchers or in the dynamics of the disease, it is important that P. is carried out under strictly identical conditions. The registration perimetric form (Fig. 1) should indicate the patient’s last name, first name, patronymic, date of examination, size, brightness and color of the test object, illumination of the perimeter arc (hemisphere), and pupil width of the subject.
Method Definition
Computer perimetry is one of the most modern methods that allows us to identify many eye diseases. It allows you to detect serious pathologies, which include:
- Glaucoma;
- Initial stages of retinal detachment;
- Inflammation of the optic nerve;
- Tumors of the eyeball;
- Dystrophic pathology of the retina.
Computer perimetry assesses the state of the visual fields. The field of view is a fairly relative value. When a person focuses his gaze at a certain point, he will still see surrounding objects. The picture will be fuzzy and blurry, but it is still perceived by the brain. Moreover, both static and dynamic objects are recorded. Color rendering is perceived correctly.
Since computer perimetry of the eye does not use any drugs and there is no surgical intervention, there are few contraindications for this procedure. Computer perimetry is not prescribed:
- Persons under the influence of alcohol or drugs;
- Patients with mental disorders;
- Persons of degenerative type.
Determination of peripheral vision
Indications for use
Perimetry is indicated in the presence of the following pathological conditions:
- retinal dystrophy;
- hypertonic disease;
- burn eye disease;
- oncological diseases of the eye;
- retinal disinsertion;
- retinal hemorrhages;
- glaucoma;
- brain tumor (particularly in the occipital region);
- trauma, neuritis or ischemia of the optic nerve;
- traumatic brain injury;
- cerebrovascular accidents (transient ischemic attacks, stroke);
- preventive examinations for getting a job (important for types of work that require increased attention).
Why do you need to measure the refraction of the eye?
Each of us has an individual structure of the lens and cornea, the relationship between them, unlike any others, hence the statement that the human optical system is unique. Throughout life, refraction changes and, along with it, the quality of vision. General trends will include:
- newborn babies are farsighted,
- by the age of 20, young people are one third farsighted, and about 40% suffer from myopia, the rest have normal vision,
- Natural aging of the body also affects refraction. Senile farsightedness (myopia) is a very common phenomenon.
Measuring refraction is very important when performing vision correction. It allows you to choose the right glasses and monitor the progress of treatment
This is of particular importance in childhood and adolescence (at this time, vision correction allows you to correct defects and preserve the child’s vision).
It is also important to monitor changes in refraction in old age; diagnostics will help monitor the treatment process or the level of vision loss. Measuring refraction will allow you to plan laser correction and determine its results
Measuring refraction will allow you to plan laser correction and determine its results.
Types of eye refraction
The human eye is very similar in structure to a camera. Light rays pass through the cornea, are refracted, then through the lens and are focused in the center of the retina on the macula (macula). If this is so, then this is the norm and they talk about 100 percent vision (ophthalmologists call it emmetropia). The images perceived at different distances (near and far) are clear and bright, a person sees equally well both in daylight and at dusk.
If the focus, as a result of a defect in the refraction of rays by the lens or cornea, is located in front of the retina (in the area of the vitreous body), they speak of myopia (myopia). With myopia, a person will have difficulty distinguishing objects that are far away and will see relatively clearly those that are close.
If the focus of refraction is behind the retina, then for such a patient close objects will be blurry and indistinct, but those that are far clearer. This type of vision is called hypermetry.
Another type of visual impairment is astigmatism. Here, as a result of the curvature of the sclera or lens, the rays are bent, which distorts the perceived image, causing a loss of clear vision in a certain area. Images may be blurry, unclear, or stretched out.
Myopia, hypermetry and astigmatism require correction and often treatment. In childhood, it is quite possible to preserve vision or even restore it; in old age, a correctly determined refraction will allow for adequate treatment and correction.
Determination of visual fields using perimetry
Material equipment: Forster perimeter, standard forms of visual fields, stamps of different colors, ruler, colored rods.
The field of view is determined using the Forster perimeter. The subject is seated with his back to the light and asked to place his chin in the notch of the perimeter tripod. If the field of view for the left eye is determined, then the chin is placed on the right side of the stand. The height of the stand is adjusted so that the upper end of the tripod is at the lower edge of the eye socket. The subject fixes with one eye a white circle in the center of the perimeter arc, and covers the other eye with his hand. Set the perimeter arc to a horizontal position and begin measuring. To do this, slowly move the white mark along the inner surface of the perimeter arc from 90° to 0° and ask the subject to indicate the moment when the identification mark becomes visible for the first time to a fixed eye. Mark the appropriate angle and check again. Then set the perimeter arc in a vertical position and measure the upper and lower boundaries of the visual fields. The study, as a rule, is carried out in no less than 4, but more often in 8 meridians with an interval of 300. The boundaries of the field of view will be determined more accurately, the more meridians are examined. The data is transferred to standard visual field forms. Connect the exposed points with a line and obtain the boundary of the achromatic field of view.
By replacing the white mark with a colored one, the boundaries of color vision are determined in the same way, while the subject is required not only to see the mark, but also to accurately determine its color.
The field of view for colorless objects extends outward by approximately 90o, inward and upward - up to 60o, and downward - up to 65o. The field of view for blue objects extends outward by approximately 75°, inward and upward - up to 45°, downward - up to 50°. The field of view for red objects is outward to approximately 60°, inward to 40°, upward to 30°, downward to 45°.
Expression of practical result
When examining the visual field in 8 meridians, the following recording is made:
The limit of the achromatic field of vision for the right (and/or left) eye: outward - 90o, downward outward - 90o, downward - 60o, downward inward - 50o, inward - 60o, upward inward - up to 55o, upward - 55o, upward outward - 70o .
They also use the total designation of the size of the visual field, which is formed from the sum of the visible parts of the visual field examined in the meridians. Achromatic field of vision for the right (and/or left) eye: 90+90+60+50+60+55+55+70=530 o, which corresponds to the norm.
Oculus dexter Oculus sinister
Standard form for determining the visual fields of the left and right eyes (normal visual fields for a white object are indicated)
Literature for the section “Practical skills”
Main:
1. Guide to practical classes in physiology // Ed. G.I.Kositsky and V.A.Polyantsev. - M.: Medicine, 1988.
2. Workshop on normal physiology // Ed. N.A. Agadzhanyan. - M.: Higher School, 1983.
3. Workshop on physiology // Ed. K.M.Kullandy. - M.: Medicine, 1970.
4. General physiology: Educational method. manual // Ed. A.I. Kubarko. - Minsk: MGMI, 2000.
5. Physiology of blood. Body fluids: Educational method. manual // Ed. A.I. Kubarko and V.A. Pereverzev. Ed. 2nd, Spanish and additional - Minsk: MGMI, 2000.
Additional:
1. Vinogradova I.L., Glasko E.N., Umnova N.I. and others. Group systems of human blood and blood transfusion complications. - M.: Medicine, 1988.
2. Instruction of the Ministry of Health of the USSR No. 06-14/20 dated November 3, 1976 on the use of a standard universal reagent for determining the Rh factor - Rh0 (D) in test tubes without heating.
3. Kozinets G.I. Study of the blood system in clinical practice. - M.: Triada-X, 1998.
4. Murashko V.V., Strutynsky A.V. Electrocardiography. — 3rd ed., revised. and additional - M.: MEDpress, Elista APP “Dzhanger”, 1998.
5. (Prokop O., Gohler W.) Prokop O., Geler V. Human blood groups. Per. with him. - M.: Medicine, 1991.
6. Standard hemagglutinating sera for determining AB0 blood groups. Brief instructions for use of the USSR Ministry of Health No. 06-14/20 dated 10/14/1976.
7. Sixth Report of the Joint National Committee on the Prevention, Recognition, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (USA) - JNC-6. Presentation of the main provisions // Cardiology. - 1998. - No. 3.
Additional methods in eye diagnostics
Ultrasound of the eyeball
Ultrasound is a popular research tool due to the receipt of accurate and complete information and the high effectiveness of the procedure. Ultrasound examination is necessary to detect eye abnormalities, tumors, and retinal detachment.
Campimetry
The method determines the central field of vision for colors and is used to detect diseases of the optic nerve, glaucoma and retina. The diagnostic kampimeter consists of a special large screen, where the patient looks with each eye alternately through a slit on a black screen.
EFI eyes
The electrophysiological research method has found wide application in the study of the cerebral cortex, retina and levels of damage to the optic nerve, and the function of the nervous department of the optical apparatus.
Keratotopogram
A method that studies the surface of the cornea before laser correction. It is carried out on an automated computer system by scanning to determine the sphericity of the surface.
Tonography
Dynamic study of intraocular pressure. IOP takes about 5 minutes; in such a short period of time, you can obtain important information about the state of fluid outflow inside the eye.
The method allows you to accurately determine the thickness of the cornea; it is necessarily prescribed for laser operations
Fluorescein angiography
Shows the condition of the fundus and retinal vessels. A series of high-precision images are taken after the fluorescent solution is administered intravenously.
The non-contact modern OCT method is used to determine the condition of the optic nerve and retina.
Operational examination under an optical device to detect ticks.
Schirmer test
A procedure that determines tear production. The test is performed for symptoms of dry eye. An ophthalmological test is placed on the edge of the patient's lower eyelid, which can be used to determine if it is wet with tears.
A method for accurately detecting glaucoma using a lens. The angle of the anterior chamber is examined.
Fundus examination with Goldmann lens
It is used for retinal dystrophy and detachment, as well as to obtain data on its peripheral parts that were not detected during a classical examination.
High-precision modern instruments and a variety of techniques allow us to accurately and effectively conduct research on the visual organs at the cellular level. Most diagnostics are carried out non-contact and painlessly, without requiring prior preparation of the patient. In the relevant sections you can learn in detail about the methods for diagnosing eye diseases.
Computer eye perimetry
Computer eye perimetry is an ophthalmological examination that measures the width of the visual field. Peripheral vision allows a person to see objects not only in front of him, but behind and to the side at a certain angle. When pathological changes appear, the width of the visual field narrows or changes. To identify regressive processes, eye perimetry is performed. There are several methods for determining the width of the field of view:
- kinetic (observation of a moving object in low light);
- static (observation of a static object when the light level changes);
- Amsler test (assessing the visibility of a picture);
- campimetry (observation of a white dot in a black square during movement).
Diagnostics are performed using a special device, all results are recorded and processed by a computer program. To confirm the primary data, control measurements are carried out. This method reduces to zero the risk of error and the influence of the human factor.
Main indications
With the help of computer perimetry, pathological changes in the patient’s visual system are detected at an early stage. Regular observations allow you to choose the right course of therapy and monitor the effectiveness of treatment. Indications for the procedure:
- glaucoma, optic nerve damage;
- head injuries;
- brain tumors;
- pathological and dystrophic disorders of the retina;
- hemorrhages, circulatory disorders;
- hypertension;
- eye burn.
It is recommended to undergo appropriate diagnostics when applying for a job that requires increased attention and good breadth of vision.
Perimetry is contraindicated in mental disorders. It is not advisable to perform the procedure if the patient is under the influence of drugs or alcohol. In this state, a person’s reaction is significantly dulled, and the meanings are distorted.
How to prepare for the procedure
Computer perimetry does not require special training. This is a painless and safe procedure. The only condition is that you need to remove your glasses (or contact lenses) before starting the study.
Diagnostic results are influenced by individual characteristics:
- significant drooping of the upper eyelid;
- raised bridge of the nose;
- severe myopia.
Features of the procedure
The patient is positioned in front of the device, the head is fixed motionless. With one eye he fixes his gaze on the object of observation. The second eye is closed with a flap. During measurement, the patient must press the joystick at the moment when he sees the object. The speed and location of the object's appearance change chaotically with acceleration. The results of clicks are recorded. Once completed, the procedure is repeated on the second eye. The study lasts from 10 to 20 minutes. The final result is presented in the form of a visual latitude map, on which areas that fall out of the visibility zone are marked. Based on these data, the ophthalmologist makes a diagnosis.