Indications and contraindications for
Scintigraphy is not necessary for all groups of patients with thyroid diseases. The study is carried out exclusively according to the indications of an endocrinologist. Indications for examination are:
- hormonal disorders that are practically not amenable to drug therapy;
- severe dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- determination of the location and size of the gland in the presence of formations in it;
- abnormalities of gland development (presence of additional glandular lobes, etc.);
- anomalies in the position of the organ (retrosternal location of the lobes, etc.);
- diagnosis of “active” and “inactive” neoplasms in gland tissues;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- suspicion of malignant processes in the gland;
- postoperative monitoring of the condition of the gland (presence of remnants of pathological tissues after their removal, etc.);
- inflammatory processes in glandular tissues;
- undergoing radiation therapy and chemotherapy treatment.
Contraindications to this examination are pregnancy, regardless of duration (the radioactive drug can penetrate the placenta to the fetus and cause malformations) and infancy.
The procedure should be performed with caution in those patients who have a tendency to develop allergic reactions, since it is very difficult to predict how the body will react to the administration of a radioactive drug before the procedure
Indications for osteoscintigraphy
Which doctor prescribes the procedure and why?
Scintigraphy of skeletal bones is performed to identify various pathological processes in bone tissue.
A referral for the procedure is usually prescribed by a rheumatologist in the following cases:
- establishing the cause of long-term pain in the bones;
- clarification of the results of x-ray examination for fractures;
- determination of the degree of complexity of fractures (detection of fragments in soft tissues);
- identification of bone metabolism disorders (metabolism) - foci of necrosis, Paget's disease;
- diagnosis of osteomyelitis (in adults), rickets (in children);
- suspicion of bone cancer or the presence of metastases in them;
- monitoring the effectiveness of treatment of malignant diseases of the bone skeleton.
How to behave after the procedure?
Thyroid hormone T4
Thyroid scintigraphy is a safe method. It does not cause any particular negative consequences. But radiotherapy drugs are dangerous to the patient's health, since the radiation can seriously affect the cell's DNA.
To prevent complications, you must behave correctly:
- Women of reproductive age should undergo scintigraphy 20 days after the last day of menstruation. This will avoid the risk of conducting research during an unplanned pregnancy.
- The dose of radiotherapy for children is adjusted according to their body weight.
- Nursing mothers should undergo scintigraphy or suspend the lactation period.
- A person who is constantly in contact with children, pregnant or lactating women should stay away from them. The substances used for research are radioactive.
Myocardial scintigraphy for congenital heart defects
What is a hypoechoic thyroid nodule?
Myocardial scintigraphy in children is performed mainly to identify the origin of the left coronary artery from the pulmonary trunk. 201T1 is administered intravenously at rest, after which scintigraphy is performed in several projections or single-photon emission tomography. If there is a defect, a segmental perfusion disorder is detected.
This study allows us to differentiate between anomalous origin of the left coronary artery and other causes of impaired myocardial contractility in infants - myocarditis and dilated cardiomyopathy. In addition, scintigraphy is performed to detect myocardial ischemia and infarction in Kawasaki disease.
The gallium isotope 67Ga selectively accumulates in foci of acute and chronic inflammation of both bacterial and non-bacterial origin. 67Ga uptake has been described in many inflammatory heart diseases, including infective endocarditis, myocardial abscesses, and pericarditis.
Animal experiments have shown that 67Ga accumulates in the myocardium during myocarditis, and clinical trials have shown a strong relationship between 67Ga accumulation and morphologically confirmed myocarditis.
In case of morphologically confirmed myocarditis, scintigraphy with labeled antibodies to myosin has diagnostic value. In myocarditis, they accumulate in foci of necrosis, in contrast to 67Ga, which is tropic towards foci of inflammation. Scintigraphy with 201T1 in myocarditis has been studied very little. Focal perfusion abnormalities were identified, which, however, did not correspond to the distribution of blood vessels.
Factors influencing study indicators
Thyroid hormone tests: norms and interpretation
To obtain the most realistic results, the following indicators are taken into account:
- presence of a diagnosis of myocardial infarction;
- recent inflammatory process;
- presence of a pacemaker;
- consumption of caffeine-containing drinks the day before the examination;
- taking beta blockers.
If the patient is aware of the presence of these factors, he should inform the medical personnel conducting the study or the attending physician. In addition, you will need to report all medications you are taking, including information about possible allergic reactions to medications.
Principles of the procedure
The method is based on the fact that the patient is intravenously injected with radiopharmaceuticals (radiopharmaceuticals), which can accumulate in the area of the body being studied. The substance used consists of a “vector” and a “marker”. “Vector” is capable of “staying” in specified organs and systems. The “marker” is a radioactive tag that emits gamma radiation. The principle is based on the description of the ability of body areas to accumulate markers.
A special device - a gamma camera, based on recorded data on the behavior of the marker, shows the current processes and state of the examined organs, systems or tissues. Depending on the objectives of the examination, the composition of the radiopharmaceutical the patient receives differs.
The radiologist examines the results shown by the equipment. Based on the data obtained, a diagnosis is made. If peak or negative indicators are noticed, uneven distribution of the injected marker with labeled red blood cells, then this indicates the presence of pathology.
The behavior of isotopes in the body varies. In one case, in areas where active growth or restoration is noticeable. This is an indicator for identifying microcracks, arthritis and some types of cancer.
“Cold” areas, on the contrary, accumulate a small amount of isotopes or are not capable of absorption at all. This is typical for diseases of the lymphatic system and indicates the presence of metastases. Such indications indicate the formation of tumors (malignant, benign) and dangerous disturbances in the functioning of the circulatory system.
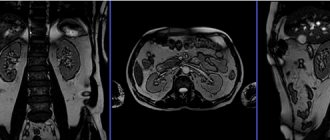
Gamma scintigraphy of the kidneys
In recent years, dynamic computer gamma scintigraphy has been increasingly used in pediatric urology and nephrology, which is a new stage in the diagnosis of kidney and urinary tract diseases. The study is carried out using a gamma camera.
The combination of a gamma camera with a computer device provides recording, storage and subsequent processing of information. The high resolution capabilities of the gamma camera in combination with computer data processing make it possible to identify and study up to 13 areas of interest in each kidney, assessing hemodynamics, secretory and excretory processes in each of them. Gamma scintigrams are obtained as a color image on a display screen or in the form of graphs. A snapshot can be taken from the display screen.
With unchanged renal function from the 3rd to the 15th min. The study makes it possible to visually trace the stages of accumulation of the labeled compound in the renal parenchyma, pelvis, ureters, and bladder.
The time of maximum accumulation of the isotope in the kidney, which is normally 3-5 minutes, and the half-life (6-8 minutes) quantitatively characterize the secretory and excretory processes occurring in the kidneys.
The diagnostic capabilities of computer gamma scintigraphy are so great that they can detect a difference in kidney function of 5%.
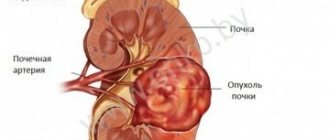
Gamma scintigraphy with 1311-hippuran and especially with 197-promeran is a valuable method for detecting renal tumors and cysts and is significantly superior to excretory urography in this regard. With a kidney cyst, a clear defect in the parenchyma is determined on a gamma scintigram.
A kidney tumor is characterized on a gamma scintigram by a less clear defect in the parenchyma, and with total damage, the kidney does not accumulate the radiopharmaceutical drug.
Gamma scintigraphy is of great importance for diagnosing various kidney anomalies. Thus, in case of anomalies in the position of the kidneys, it is possible to obtain an image of the fused kidneys and determine the degree of functional activity of each half of them and the isthmus, which is necessary to know when performing surgical interventions on such kidneys.
Gamma scintigrams clearly show various forms of kidney dystopia; in addition, they can be used to make a differential diagnosis of dystopia and nephroptosis by examining the child in the lying and standing positions.
In children with double kidneys, this method makes it possible to clearly determine both their size and shape, as well as the functionality of each segment.
Gamma scintigraphy provides valuable information in children with urolithiasis. In case of ureteral stones, the gamma scintigram shows the contours of the kidney and ureter to the level of obstruction by the stone. The ability to study the structure and function of various zones of the kidney using gamma scintigraphy allows for wider use of organ-preserving operations for urolithiasis, specific and nonspecific kidney lesions.
Gamma scintigraphy is a very promising and valuable method for diagnosing urological diseases in children due to its low morbidity, safety for the patient and obtaining extensive information about various aspects of the activity of the kidneys and urinary tract.
Radioisotope method for diagnosing vesicoureteral reflux. To diagnose vesicoureteral reflux, radioisotope cystorenography is used, which consists of simultaneous recording of radioactivity levels over the bladder and kidneys when a labeled compound is introduced into the bladder (A.F. Vozianov, V.P. Ishchenko, 1968).
Normally, the level of radioactivity over the kidney area when a labeled compound is introduced into the bladder increases slightly and corresponds to the background of the body, and the amplitude of the bladder curve is much higher than that of the kidneys. In this case, as the bladder is filled with an antiseptic solution, the nature of the curves does not change.
When vesicoureteral reflux occurs, the level of radioactivity on the affected side increases and a synchronous decrease in the vesical curve is observed.
Radioisotopic cystorenography allows you to determine the time of onset of reflux depending on the degree of filling of the bladder, indicates the side of the predominant lesion in a bilateral process, and clarifies the state of outflow from the upper urinary tract.
To diagnose vesicoureteral reflux, cystorenoscintigraphy is also used, in which the process of penetration of the bladder isotope into the ureter and pelvis is recorded using a gamma camera detector (N. A. Lopatkin, 1977). The cystorenoscintigram not only detects the moment of onset of reflux, but also obtains an image of the bladder, ureter and pelvis.
Technique of the procedure
The radiopharmaceutical, which is given intravenously, produces energy called gamma waves. The recording apparatus (gamma camera) receives the indicator signals, and the system converts the information into an image. This makes it possible to see how certain areas of the myocardium are supplied with blood. From many images taken in different projections and at different angles, a computer can create a 3D model of the heart.
The radiologist and cardiologist give an opinion based on the image obtained. The basic principle of assessment is as follows: areas of the myocardium that are well supplied with blood are shown light, and those where perfusion is low are dark.
The patient is given intravenous radiocontrast, after which it is necessary to wait about 40-60 minutes. This is necessary so that the substance passes through the liver during metabolism, since the accumulation of the drug in it will give an image similar to the glow of the heart and interfere with adequate assessment of the results.
Myocardial scintigraphy exists in two versions:
- SM at rest is a one-day procedure;
- Weight-bearing SM - requires a 2-day clinic visit for bicycle ergometry.
If you are planning a diagnosis with a pharmacological load and the patient is taking medications that act on the cardiovascular system, you cannot do without consulting your doctor. Taking such drugs can blur the clinical picture and give false results, which will lead to incorrect treatment or the need for repeated testing. Such medications should be discontinued three days before the procedure.
On the eve of testing, you should give up coffee and tea, chocolate and cocoa, as well as Coca-Cola and energy drinks, i.e. products with caffeine.
Myocardial scintigraphy with stress provides more accurate data on the state of the heart vessels than studies at rest. To do this, the patient is asked to make a certain number of revolutions on a special exercise bike while simultaneously recording an electrocardiogram. ECG significantly expands the possibilities for diagnosing ischemic disorders in the myocardium.
If physical activity is contraindicated, drugs are used to increase blood flow to the heart, which mimics the heart muscle's response to exercise.
When the images obtained from scintigraphy are the same at rest and during exercise, it means that blood flow in the coronary arteries is normal. The test may show adequate supply at rest, but after physical stress, a “perfusion defect” (blackout) sometimes appears due to the lack of radiotracer in an oxygen-deprived area of the myocardium. If a dark area is visualized at rest and after exercise, it is a sign of a previous heart attack with the formation of scar tissue.
Methodology
The radiopharmaceutical is administered intravenously. After the injection, the patient is allowed to go home for 3 hours or is asked to wait on the territory of the medical center. During this time, it is advisable to drink 1-1.5 liters of water to speed up the removal of radionuclides that are not absorbed by bone tissue. Immediately before the procedure, you need to empty your bladder.
Bone scintigraphy is performed in a sitting or lying position. The patient must remain completely still and cannot talk during the entire procedure (from 30 minutes to 1 hour). The medical staff of the diagnostic room is located in an adjacent room, from where they monitor the process and condition of the patient through a special window.
The gamma camera used for scanning is a large (50 cm in diameter) crystal that captures and records radiation across the entire surface of the patient’s body. The obtained data is processed by a special program and displayed on the radiologist’s computer monitor.
Where is scintigraphy done?
It is better to undergo scintigraphy at a medical center that specializes in radiodiagnostics.
Prerogative aspects
Scintigraphy is a study intended not only to determine cardiac pathologies. With its help, the skeletal system, thyroid and parathyroid glands, abdominal organs, and other body systems are examined. The advantage of cardiac radionuclide diagnostics lies mainly in the identification of severe complications of ischemia and the ability to predict their further development. IHD (coronary heart disease) is determined at an early stage, as well as in cases where the latent form of the disease prevents its determination using other examinations.
Other prerogatives include:
- safety. The dose of radioisotopes absorbed by the heart muscle does not harm the body and does not entail any consequences of radiation;
- no penetration into the body (non-invasive);
- painlessness;
- the procedure causes virtually no side effects.
There are no special measures to prepare the body for the examination.
Story
The art of shorthand already existed, as can be concluded from some data, among the ancient Egyptians, where the speeches of the pharaohs were recorded with a conventional sign; From the Egyptians this art passed on to the Greeks and Romans, who had cursive writers. December 5, 63 BC e. The first known use of shorthand in history took place in Ancient Rome. According to the ancient historian Plutarch, on this day, at a meeting of the Roman Senate, where the fate of the conspirator Catiline was decided, Cato the Younger made an accusation. In the 1st century BC. e. The Roman grammarian Tiron invented a special method of shorthand, called Tyronian icons
(notae Tironianae); these icons were formed from Roman capital letters by shortening and simplifying them; in combination with each other, the icons underwent certain changes and mergers, symbolic designations were used for some vowels; sometimes letter designations were used to designate whole words; some letters were omitted, although without a specific system. Among the Romans, cursive writers (notarii) used such icons to record public speeches and minutes of meetings. During the empire, this shorthand was studied in schools, and subsequently it was used by the Christian Church.
With the fall of the Roman Empire, this art also fell, although it continued to exist until the time of the Carolingians, then it completely disappeared. The number of signs was very large: Seneca counted them up to 5000, in Carolingian times there were up to 8000. Manuscripts written in Tyronian signs have survived to the present day.
In the Middle Ages, after the disappearance of the Tyronian icons, only the attempt of the English monk Johann Tilbury to compose a new Latin shorthand (in the 12th century) is mentioned. In the Middle Ages and at the beginning of the New Age, speeches were written down in the ordinary alphabet, but with abbreviations, which were then supplemented.
At the end of the 16th century, the art of shorthand reappeared in England and received special development at the end of the 18th century. From England, shorthand spread, starting in the 17th century, to the continent. Shorthand reached its greatest development in the North American United States, England, France, Germany, Switzerland and Austria-Hungary.
Resulting Images
- static - the result is a flat (two-dimensional) image. This method most often examines bones, thyroid gland, etc.
- dynamic - the result of adding several static curves to obtain dynamic curves (for example, when studying the function of the kidneys, liver, gall bladder)
- ECG-synchronized study - ECG synchronization allows you to visualize the contractile function of the heart in tomographic mode.
Scintigraphy is sometimes referred to as a related method, single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), which allows one to obtain tomograms (three-dimensional images). When using SPECT/CT technology, a hybrid tomographic study of a given area is recorded, producing fusion images that combine isotope tomography (SPECT) and computed tomography (CT). As a result, the functional image is combined with the anatomical one, often increasing the sensitivity and specificity of the detected changes. Using SPECT technology, studies of the myocardium and brain are carried out. SPECT/CT is used in the study of skeletal bones, thyroid and parathyroid glands, lungs, liver, as well as in studies with tumor-specific drugs (octreotide, sestamibi, MIBG, etc.)
Features of scintigraphy of skeletal bones:
The study is carried out 3 hours after administration of the radiopharmaceutical. Takes from 10 to 30 minutes. The conclusion is issued on the day of the study.
When patients come for the study, they must have with them extracts from their medical records or an outpatient card, conclusions (if available) based on the results of X-ray studies, CT, MRI, as well as the results of previous scintigraphic studies.
Radiopharmaceuticals (RPs) used: diagnosis of skeletal bone diseases is carried out with labeled phosphate complexes, which strongly bind to hydroxyapatite crystals and immature collagen. 99mTs is used as a tag, which has a short half-life - only 6 hours. Gamma quanta leave the body and are registered by the detectors of the device, resulting in an image after computer processing.
Normal scintigram of skeletal bones in anterior and posterior projection:
Scintigraphy
Bone scintigraphy (osteoscintigraphy)
The purpose of bone scintigraphy is to diagnose back pain, lower back pain and other pain that may be caused by bone diseases. Bone scintigraphy can detect bone damage, bone cancer or cancer metastasizing to other organs in the bone, as well as infectious and traumatic bone lesions (for example, fractures that do not show up clearly on x-rays). Bone scintigraphy often helps diagnose the disease a month earlier than, for example, bone x-ray.
For bone scintigraphy, a radiotracer is injected into a vein and gradually penetrates into the bone tissue. This may even take several hours. A special camera takes a photo, the image on which allows for diagnostics. Areas that receive little or no penetration of the indicator appear as dark or “cold” spots. This, for example, may indicate certain types of cancer. Bright and "hot" areas may indicate arthritis, a tumor, a fracture, or a bone infection.
Do I need preparation for bone scintigraphy? No special preparation is required for bone scintigraphy. However, you may be advised to drink plenty of fluids before the procedure to speed up the penetration of the indicator into the tissue. Typically, with a bone scan, you must wait 1 to 3 hours after the tracer is administered before the doctor begins taking pictures. In some cases, the picture is taken immediately during the introduction of the indicator, immediately after this, and then after 3-5 hours. During bone scintigraphy, you must lie still to avoid blurry images.
Myocardial scintigraphy - cardiac scintigraphy.
Myocardial scintigraphy is performed to determine how well the heart muscle pumps blood through the vessels to organs and tissues. In addition, myocardial scintigraphy (heart scintigraphy) allows you to check the size of the heart chambers, diagnose certain diseases (heart disease, aneurysm), and detect pathologies in the movement of blood between the chambers of the heart.
Preparation for myocardial scintigraphy includes avoiding drinking coffee and cigarettes 4-6 hours before the study. Sometimes your doctor may ask you not to eat or drink anything. Many medications can affect the results of myocardial scintigraphy (heart scintigraphy), so if you are taking any medications, you should tell your doctor. In some cases, myocardial scintigraphy under load is more effective. In this case, you will have to do some physical exercise in between shooting.
Scintigraphy of the gallbladder.
Scintigraphy of the gallbladder is aimed at checking its functioning. Scintigraphy of the gallbladder allows you to detect blockages in the bile ducts that go from the liver to the gallbladder and duodenum, determine the cause of pain in the right upper part of the abdominal cavity, jaundice, and diagnose the release of bile. You may need to prepare for a gallbladder scintigraphy. Depending on the purpose of the gallbladder scintigraphy, the doctor will recommend not eating 4-12 hours before the procedure. The first images of gallbladder scintigraphy are taken immediately after the indicator is inserted into a vein in the arm. The gallbladder scintigraphy procedure takes approximately 1-2 hours.
Renal scintigraphy.
Kidney scintigraphy can be done in order to assess their condition and detect pathological processes such as kidney stones, traumatic and infectious kidney lesions. Kidney scintigraphy can track blood flow in the kidneys, look at the shape and size of the kidneys, and evaluate how the kidneys make and excrete urine. Depending on the purpose of renal scintigraphy, different types of radiotracers are used. If the kidney area appears as bright areas on an image, it may be a sign of kidney cancer; dark areas may indicate narrowed or blocked blood vessels, cysts, some types of cancer, scarring, or infection. Kidney scintigraphy may also be done to check how well the kidneys are functioning, i.e. track the period of time during which the indicator passes through the kidneys and is collected along with the urine in the bladder.
Before having a kidney scintigraphy, you may be asked to drink several glasses of water. The kidney scintigraphy procedure usually lasts from 30 minutes to 1 hour.
The essence of the method
Thyroid scintigraphy is a radionuclide method for assessing the functional activity of the thyroid lobes (TG), based on the properties of its tissues to absorb iodine and use it to produce hormones. The use of radiopharmaceuticals (RPs) in the diagnostic process - chemical compounds perceived by organ tissues as a necessary participant in metabolism and containing radioactive isotopes in their structure, makes it possible to record the intensity and uniformity of absorption, accumulation and distribution of the substance in the thyroid gland.
In the absence of alternative imaging modalities available to diagnostic medicine today, such as ultrasound, MRI or CT, scintigraphy was the only way to obtain an image of an internal organ. Today, using all of the above methods, it is possible to obtain maximum useful information about the shape, structure and location of the thyroid gland, however, none of them is able to assess its functional state.
The mechanism for obtaining information is the introduction into the body of a radiopharmaceutical (for example, radioactive iodine), which is actively absorbed or not absorbed by the endocrine organ. When subsequently recording the radiation intensity, it is possible to obtain a flat or three-dimensional image (in the case of using an emission computed tomograph), reflecting areas of normal, increased or decreased concentration of the radioactive substance.
Areas with increased radiation, highlighted in color or shading, indicate tissue hyperactivity, and areas with reduced or absent radiation indicate their partial or complete functional failure. The use of scintigraphy is advisable only for the purpose of determining the activity of hormone production of one of the parts of the thyroid gland (node or lobe), the pathological condition of which has already been identified using laboratory or instrumental research methods.
Indications for radionuclide diagnostics
Main goals of the procedure:
- assessment of kidney function;
- search for any abnormalities in the functioning of the urinary organ;
- assessment of the state of renal blood flow;
- determination of glomerular filtration rate (GFR);
- diagnosis of renal artery stenosis;
- detection of arterial hypertension;
- detection of kidney development abnormalities;
- search for tumors and possible metastases;;
- establishing the presence of renal failure and determining its degree.
Modern diagnostic techniques help the doctor identify the presence of indications for surgical intervention for urinary tract obstruction.
Radionuclide testing is widely used not only to assess the functional activity of the kidneys, but also to clarify their anatomical position.
Preparation and performance of lung scintigraphy
This diagnostic method is carried out using modern high-tech equipment - a special device with a unique gamma camera, which is designed to record all changes in the organ and transmit them to a computer monitor. Before performing perfusion scintigraphy, protein particles with radioactive isotopes are injected into the human body. After the accumulation of this component in the pulmonary arterioles and capillaries, radiation occurs, which is recorded by the camera; if this does not happen, then this indicates the presence of a blood clot or other problems in this part of the organ.
During the examination, the patient is in a standing position, because in this way you can get a lot of information about the organ and see the overall picture of its work. If necessary, the doctor can change the examination angle, and the patient can change position. In general, the procedure, from the moment of introduction of radionuclide components, takes no more than 20 minutes.
Ventilation scintigraphy is characterized primarily by the fact that the patient inhales a radioactive inert gas, which should fill the lungs. After this, the specialist has the opportunity to determine the condition of the organ, its shape, the presence of disorders, etc. At the end of the examination, when the patient exhales gas, several more pictures are taken to obtain more information.
Scintigraphy is a modern and absolutely safe method for diagnosing various diseases and pathologies of the lungs. The method is suitable for almost everyone, the only exceptions being pregnant women and patients who are allergic to radionuclide components.
DYNAMIC RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY
xda.su Scintigraphy Dynamic scintigraphy of the kidneys
Scintigraphy
is a modern radiation diagnostic method that is used to assess the functioning of various organs and tissues.
Scintigraphy
- a method of functional imaging that involves introducing radioactive isotopes into the body and obtaining an image by determining the radiation emitted by them.
Scintigraphy is a procedure performed on a gamma ray scanner - a diagnostic radiological device - after injecting a small amount of radioactive substance.
KIDNEY SCINTIGRAPHY (NEPHROSCINTIGRAPHY)
is a diagnostic test that involves injecting a small amount of radioactive medicine (a radioactive tracer) into the body and obtaining images of the kidneys using a gamma camera. The resulting images can help in the diagnosis and treatment of various kidney diseases.
Kidneys
is a paired excretory and endocrine organ that regulates the chemical homeostasis of the body through the function of urine formation.
The kidneys are located in the lumbar region on either side of the spine. The right kidney is slightly lower than the left.
There are two types of nephroscintigraphy:
Static nephroscintigraphy.
Gives an image of the kidneys and urinary system, allows you to assess the condition of the kidney parenchyma, their size, correct or incorrect position, shape. This radiological examination is additional after the analysis of x-rays. Its disadvantage is that the resulting scintigram does not record functional changes in organs and does not allow obtaining a complete picture of the disease.
Dynamic scintigraphy.
After the radiopharmaceutical is introduced into the circulatory system, the gamma camera begins to record the state of the urinary system. Pictures are taken at regular intervals. Thus, it is possible to evaluate the passage of urine from the kidneys through the ureters to the bladder. This allows you to obtain a clear image of the kidneys, their parenchyma, the collecting apparatus and assess functional disorders using graphs and comparison of some indicators.
Normally, after the administration of a radiopharmaceutical (hippuran), after five minutes, clear photographs of the parenchyma can be taken; after one to two minutes, the contrast of the image decreases, and the drug is evenly distributed in the pyelocaliceal system.
After about fifteen minutes, the radiopharmaceutical is fixed in the bladder. Any slowdown in excretory processes or a decrease in tissue accumulation of hippuran indicates a pathology of the urinary system or kidneys.
DYNAMIC KIDNEY SCINTIGRAPHY (NEPHROSCINTIGRAPHY)
is a radiological examination of the kidneys by recording the passage of nephrotropic radiopharmaceuticals through the kidneys.
Dynamic nephroscintigraphy is a method that examines not only functional abnormalities, but also the anatomical features of organs. This branch of medicine, called nuclear medicine, uses in its research the properties of radionuclide pharmaceuticals to be distributed and selectively accumulate in the tissues and cells of the body. Together with the use of ultrasound, MRI, PET/CT, such diagnostics provide a complete picture of the disease and allow the most adequate treatment to be prescribed.
Scintigraphy using a drug that is tropic to kidney tissue is used if a tumor of the genitourinary system is suspected.
By observing the process of uptake of radiopharmaceuticals by cells of the urinary system, the radiologist can accurately determine:
The functioning of both kidneys, the functioning of the ureters and bladder.
The nature of the tumor is malignant or benign.
Distinguish congenital abnormalities in the size or shape of the kidney from changes that occur during oncological pathologies.
Condition of the second kidney, if surgery is necessary.
The effectiveness of chemotherapy and other treatments in repeated studies.
Indications for dynamic nephroscintigraphy
Any significant changes or impairment of renal function.
Detected anomalies of organ development.
Second and third stages of hydronephrosis.
Cysts and neoplasms of the kidneys and urinary system (to exclude the malignant nature of the tumor).
Evaluation of the second kidney for renal failure when planning nephrectomy.
Planning organ-conserving surgery on a solitary kidney.
Exclusion or detection of metastases in the kidneys and genitourinary system.
Dynamic nephroscintigraphy is of particular importance when choosing a method of treating kidney cancer. The main indicator when choosing between resection of a kidney affected by a cancerous tumor and nephrectomy is the assessment of the reserve capabilities of the contralateral kidney. In this case, dynamic nephroscintigraphy data allows one to visualize not only the size and extent of the tumor, but also to assess the condition of healthy kidney segments. After introducing a radiopharmaceutical into the circulatory system, the gamma camera records the capture of the drug by three segments of the kidney in turn: first the upper, then the middle and, finally, the lower. At the same time, normal indicators for each of the segments are 14, 18 and 14 units. respectively.
Due to the high accuracy of this radiological study, it is possible to predict the development of such a complication as renal failure in operated patients. The scintigram obtained as a result of diagnosis complements laboratory biochemical analysis, as well as creatinine analysis and x-ray diagnostics.
Dynamic nephroscintigraphy gives more accurate results, since the gamma camera covers the entire lumbar area. It is possible to study while moving and sitting.
Contraindications to dynamic renal scintigraphy
All methods based on recording the capture, accumulation and distribution of special preparations labeled with radioactive isotopes are potentially dangerous. Therefore, some patients have limitations for this radiological examination.
These include:
The patients are in serious condition. Dynamic nephroscintigraphy takes from 45 minutes to one and a half hours. This can be tiring for frail patients.
Pregnant women. Intravenous administration of a radiopharmaceutical increases the risk of radiation exposure to the fetus. In case of confirmed or possible pregnancy, diagnosis is carried out only for vital reasons.
Nursing mothers. Radiopharmaceuticals are short-lived and are eliminated from the body within 24 hours. During this period after diagnosis, you should stop breastfeeding.
Cancer patients after chemotherapy. There may be an increase in the side effects of treatment; therefore, a pause of three weeks before diagnosis is necessary.
Cancer patients after radiation therapy. You should wait two to three months after treatment.
Recently operated patients. Excessive accumulation of radiopharmaceuticals is possible at the surgical site, and therefore the examination is carried out after the recovery period.
Despite the existing contraindications, dynamic nephroscintigraphy is a safe and painless method that gives highly accurate results.
Benefits of dynamic renal scintigraphy
High accuracy and sensitivity of the equipment.
Ability to detect metastases.
Safety and effectiveness.
The scintigram obtained during diagnosis reflects changes in the kidneys much earlier than a similar x-ray examination. If the latter can note changes in an organ already significantly affected by the tumor, then scintigraphy finds abnormal zones in the kidneys a year and a half earlier than conventional studies.
Renal cell carcinoma is one of the most dangerous cancers. Every year, oncologists register up to 30 thousand cases of malignant tumors of the kidney or urinary system. In this regard, the need for early diagnosis of cancer increases. Common diagnostic methods, such as radiography and measurement of biochemical parameters, can detect malignant pathologies when more than half of the kidney cells are affected. At the same time, kidney surgery with a tumor size exceeding 4 cm has an unfavorable prognosis even with proper treatment.
Static nephroscintigraphy is a more progressive, but partially biased radiological method, in contrast to highly accurate research using dynamic nephroscintigraphy.
Preparation for dynamic renal scintigraphy
The radiologist will warn the patient about the need to administer the radiopharmaceutical by intravenous injection, which generally does not cause severe pain.
In some cases, you need to additionally drink a special solution to improve the quality of the obtained scintigram. After this, the drug spreads throughout the body within three hours, after which the diagnosis itself is carried out.
Radiopharmaceuticals used during dynamic renal scintigraphy
If a blockade (obstruction) of the kidney is suspected, a diuretic drug (Lasix) is additionally administered for examination. When evaluating hypertension, inhibitors such as Enalopril or Captopril are administered simultaneously with the administration of the radiopharmaceutical.
The radiopharmaceuticals used differ depending on the purpose of the study. For example, technetium DTPA is used to study kidney function. If a condition of the ureters or tubules is diagnosed, c99m DMSA or technetium is used. These drugs are safe and short-lived isotopes that do not harm the patient’s body.
Most radiopharmaceuticals are eliminated naturally after destruction, so one of the recommendations for patients is to drink plenty of fluids and maintain personal hygiene after the end of the diagnosis.
Method of performing dynamic renal scintigraphy
Dynamic nephroscintigraphy is performed on an outpatient basis and does not require hospitalization.
The patient is in a separate room, where a rotating gamma camera is directed at him. The diagnostic time can take up to one and a half hours, during which you need to remain motionless and silent. This must be strictly observed to avoid research errors.
The doctor is in another room, but sees and hears the patient, and also gives hints in case he needs to change position. This allows the patient to report unpredictable conditions, such as a strong heartbeat, heaviness in the head, or difficulty breathing.
If a child is diagnosed, one of the parents can be nearby, having previously protected themselves with a lead apron.
At the end of the diagnostic study, the patient can have a snack and rest, and then return to their usual lifestyle.
The advantage of scintigraphy
is not only information about the function of the organ, but also obtaining quantitative characteristics of the degree of its damage at the earliest stages.
+7 (495) 50-254-50 - innovative treatment methods
SUBMIT AN APPLICATION FOR TREATMENT
Survey history
In patient reviews you can find different feelings about the procedure. For some of them it was difficult to go through it, for others everything turned out to be simple. However, most of them have no doubt that scintigraphy is an informative and accurate method for determining various organ pathologies.
Anastasia: I didn’t feel any discomfort during the diagnosis
I had to deal with a scintigraphic study when preparing for radioiodine therapy. This treatment was prescribed to me due to diffuse toxic goiter. The disease was unsuccessfully treated with medication, but there was no effect.
Now I’ll tell you in detail how the procedure went. I went to the radiologist. The doctor gave me a small capsule to drink: outwardly, it was no different from a regular pill.
I found out that it contained a microdose of radioactive iodine 131. The drug had neither taste nor smell. I washed it down with plain water.
Throughout the day I did not experience any unpleasant sensations in my stomach. Over the course of a day, the thyroid gland gradually absorbed the dose of the medicine.
In the morning I went to the same hospital. Here they laid me on the couch. There was some kind of apparatus hanging above her that made no sounds or signals.
The doctor warned me to lie still and not move. You should also not yawn, cough, or swallow saliva. I expected that, according to the law of meanness, I would unconsciously want to do all this, but it turned out okay.
The doctor approached me without a protective lead apron. I was surprised, because I read in the reviews that the specialist approached the girls only in equipment. The doctor explained that the dose was diagnostic and minimal.
This is the piece of paper I received after research
Upon completion of the procedures, I received a piece of paper with an incomprehensible design. She took it to the radiologist for interpretation.
Olga: the method helped to find out the cause of infertility
At the pregnancy planning stage, I had to undergo a bunch of tests, including hormone tests. According to the results, they were normal.
After six months of unsuccessful attempts to conceive, I found an excellent gynecologist. She recommended checking the thyroid gland in more detail, since ovulation was disrupted. The doctor also noticed that there was a “hump” on my neck.
I took a blood test for thyroid-stimulating hormones. It turned out that TSH was low, and T3 and T4 were high. The doctor called this condition hyperthyroidism.
Also, an ultrasound of the thyroid gland revealed a node in the left lobe. With the results I went to an endocrinologist. At the appointment, the doctor prescribed me a thyreostatic drug, which suppresses the production of thyroid hormones.
The next step was a fine needle aspiration biopsy. No tumor was found, thank God.
At the next appointment, the endocrinologist said that I needed to undergo gland scintigraphy. I resisted for a long time, because I had read horror stories on the Internet. But later I talked to the radiologist, who reassured me.
On day X I came to the clinic. I was greeted by a nurse in a lead apron and with a dosimeter on her chest. This made me feel creepy again: will they really be subjected to radiation?
In the office they injected me with some kind of drug. Its active substance had to be absorbed by the gland. Based on the areas of active accumulation, the doctor will determine what is wrong with the organ.
A picture was taken 15 minutes after the injection. To do this, she lay down on the platform. A lead blanket was placed on the stomach.
Then they pushed me closer to the large circle. They directed a square with a cross from the device toward my face.
She lay on the table for about 15 minutes absolutely motionless. I left the office all depressed and in tears, because it was scary. They said that I shouldn’t approach people because I emit radiation. Super.
But the study turned out to be very informative. I was diagnosed with “Autonomous functional adenoma of the left lobe of the thyroid gland with suppression of non-nodular thyroid tissue.”
Research result
The endocrinologist spoke about the disease. It turns out that for some reason that same nodule began to produce hormones in excessive quantities. This condition threatens heart disorders and problems with conception.
I was scheduled for surgery to remove the node. It will be held only in August.
Despite the horror of going through the procedure, I want to advise everyone not to delay it. If you are prescribed it, do not refuse. The advantages of diagnostics are much greater than the disadvantages.
STATIC RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY
xda.su Scintigraphy Static scintigraphy of the kidneys
Scintigraphy
is a modern radiation diagnostic method that is used to assess the functioning of various organs and tissues.
Scintigraphy
- a method of functional imaging that involves introducing radioactive isotopes into the body and obtaining an image by determining the radiation emitted by them.
Scintigraphy is a procedure performed on a gamma ray scanner - a diagnostic radiological device - after injecting a small amount of radioactive substance.
KIDNEY SCINTIGRAPHY (NEPHROSCINTIGRAPHY)
is a diagnostic test that involves injecting a small amount of radioactive medicine (a radioactive tracer) into the body and obtaining images of the kidneys using a gamma camera. The resulting images can help in the diagnosis and treatment of various kidney diseases.
Kidneys
is a paired excretory and endocrine organ that regulates the chemical homeostasis of the body through the function of urine formation. The kidneys are located in the lumbar region on either side of the spine. The right kidney is slightly lower than the left.
There are two types of nephroscintigraphy:
Static nephroscintigraphy.
Gives an image of the kidneys and urinary system, allows you to assess the condition of the kidney parenchyma, their size, correct or incorrect position, shape. This radiological examination is additional after the analysis of x-rays. Its disadvantage is that the resulting scintigram does not record functional changes in organs and does not allow obtaining a complete picture of the disease.
Dynamic scintigraphy.
After the radiopharmaceutical is introduced into the circulatory system, the gamma camera begins to record the state of the urinary system. Pictures are taken at regular intervals. Thus, it is possible to evaluate the passage of urine from the kidneys through the ureters to the bladder. This allows you to obtain a clear image of the kidneys, their parenchyma, the collecting apparatus and assess functional disorders using graphs and comparison of some indicators.
Normally, after the administration of a radiopharmaceutical (hippuran), after five minutes, clear photographs of the parenchyma can be taken; after one to two minutes, the contrast of the image decreases, and the drug is evenly distributed in the pyelocaliceal system.
After about fifteen minutes, the radiopharmaceutical is fixed in the bladder. Any slowdown in excretory processes or a decrease in tissue accumulation of hippuran indicates a pathology of the urinary system or kidneys.
STATIC KIDNEY SCINTIGRAPHY (NEPHROSCINTIGRAPHY)
is a scintigraphy of the kidneys in a static position, which involves several images at one point in time from different angles.
With static scintigraphy, a two-dimensional image is obtained by performing one or several scintigrams to study the anatomical and topographic state of internal organs and detect foci of pathological distribution of radiopharmaceuticals in them.
This method allows you to detect the smallest excrement in the renal pelvis and ureters. During this procedure, a small amount of radioactive medication is injected into the patient's body. In this case, the kidneys are viewed using a gamma camera. The results obtained help to more accurately see the condition of the kidneys and make a diagnosis.
Preparation for static renal scintigraphy
Depending on the purpose of this examination, in some cases the patient needs to additionally drink a special liquid, and before the actual start of the examination, empty the bladder.
During static nephroscintigraphy, the patient should not wear anything metallic.
If scintigraphy has already been carried out quite recently, then repeated examination should be abandoned for a while. Otherwise, this may lead to the accumulation of residual radioactivity, which will negatively affect the general condition of the body. In any case, you will need to follow all the doctor's instructions. After all, before you are prescribed an examination, they will definitely listen to you, after which additional studies will be prescribed. Based on the results, a diagnosis will be made, which will be used by the attending physician when drawing up a treatment regimen.
Method of performing static renal scintigraphy
The procedure lasts about one hour.
During the examination, the patient should be in a supine position. The nephroscintigram will show both kidneys located at the same distance from the spine. Doctors analyze the resulting image based on indicators such as the location of the kidneys, size, shape, and the presence of areas of uneven accumulation of radiopharmaceuticals. When specialists assess the condition of the kidneys visually, these indicators can be determined with maximum accuracy, which is a great achievement in the field of diagnosing kidney diseases. At the moment, kidney aplasia is most often diagnosed in this way. In this way, doctors avoid the more traumatic angiographic examination.
This method is suitable for diagnosing massive kidney tumors that cause severe disturbances in the functioning parenchyma. However, it should be borne in mind that nephroscintigrams clearly display areas of absence of drug accumulation that are less than twenty millimeters in diameter. In this case, such a focus should not be located on the edge of the organ.
Results of static renal scintigraphy
Based on the results of nephroscintigraphy, normal renal function can be determined taking into account the patient’s health status and age. Doctors make conclusions about the relative position, size, configuration and location of the kidneys.
Sometimes an ultrasound or computed tomography is additionally prescribed. If kidney damage or obstruction is suspected. After all, based on the results of nephroscintigraphy, it is not always possible to make an accurate diagnosis, but this largely depends on the nature of the study and the type of disease.
In some cases, the kidneys may have an irregular shape, unusual size, or unclear location, in which case additional imaging methods are prescribed.
The advantage of scintigraphy
is not only information about the function of the organ, but also obtaining quantitative characteristics of the degree of its damage at the earliest stages.
+7 (495) 50-254-50 - innovative treatment methods
SUBMIT AN APPLICATION FOR TREATMENT
Examples of radio indicators
- MIBI, sestamibi (technetril), tetrofosmin (Mioview) labeled with 99mTc is a radiopharmaceutical that is tropic to intact cardiomyocytes. Used for single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT, SPECT) of the myocardium, for the purpose of diagnosing coronary heart disease (CHD) and its complications (myocardial infarction, post-infarction cardiosclerosis, ischemic cardiomyopathy), including ECG-synchronized tomography.
- Mono- and bisphosphonates labeled with 99mTc (for example, pyrophosphate) are radiopharmaceuticals that are tropic to developing bone tissue. They are used in bone scintigraphy to diagnose distant blastic metastases, primary malignant bone tumors, as well as inflammatory, degenerative and traumatic changes.
- Diethylene triamine pentaacetic acid (DTPA) labeled with 99mTc is a radiopharmaceutical that targets the renal glomeruli. Used for kidney scintigraphy (dynamic nephroscintigraphy).
- Pertechnetate (99mTc) - a solution of pure technetium is used for scintigraphy of the thyroid gland.
- Macroalbumin aggregates (MAA) labeled with 99mTc are a radiopharmaceutical for lung perfusion scintigraphy.
- Hexamethylpropyleneamine oxime (HMPAO), labeled with 99mTc - radiopharmaceutical for scintigraphy (single photon emission computed tomography) of the brain
- 123I is both a vector for the thyroid gland and a radioisotope.
- Tl201 - accumulates in cardiomyocytes similarly to potassium, a marker for myocardial scintigraphy.
There are radiopharmaceuticals that are tropic to a certain pathology (including some forms of cancer) - 111ln - Octreoscan, 123I - MIBG (MIBG).
In the vast majority of studies, the tracer (radiopharmaceutical) is administered intravenously.
OSG Security
After osteoscintigraphy, it is recommended to take a warm shower using soap or gel, wash your hair with shampoo, and wash the clothes you wore during the procedure.
Cotton balls after radiopharmaceutical injection, bandages or adhesive plasters (if used) must be disposed of in radioactive waste bins located in the clinic. Hazardous medical waste should not be brought home.
Also, to speed up the process of removing radiopharmaceuticals from the body, you need to drink more fluid. For the day after the examination, it is advisable to exclude or limit as much as possible contact with pregnant women or small children.
Osteoscintigraphy is the only highly informative method for diagnosing malignant diseases of bone tissue, absolutely painless and safe for the patient. Minimal radiation exposure allows for monthly examinations. Compared to traditional radiography, the radiation dose during scintigraphy of skeletal bones, performed with modern equipment, is tens of times less.
Contraindications for scintigraphy
If the patient has certain disorders in the body, the attending physician may refuse to conduct a diagnostic test. Refusal is associated with disturbances in the patient’s body, which will lead to unpredictable consequences.
Restrictions:
- This study is not prescribed to women during pregnancy and lactation. If delivery has taken place, it will be recommended after scintigraphy to transfer the child to artificial feeding to prevent radioisotope substances from entering the baby’s body with mother’s milk. If the fetus is still in the mother’s body, then this study will harm its health.
- Diagnostics is contraindicated for patients in serious or extremely serious condition due to the length of the examination.
- The procedure is not performed while receiving treatment for cancer.
For patients with contraindications who cannot undergo scintigraphy, other methods of examining the functions and structure of the kidneys are selected.
How is recovery after the procedure?
The examination is carried out in a gamma camera, which illuminates the human body with radioactive rays, detecting radiopharmaceuticals in the bones and joints. Despite the apparent complexity, the procedure does not produce any harmful consequences and immediately after diagnosis the patient can return to their normal lifestyle. Recommendations for the rehabilitation period include monitoring sufficient fluid intake on the first day (the more, the better), as well as observing good personal hygiene measures - thorough bathing, washing all things.
Contraindications
Despite the fact that scintigraphy can be considered a relatively safe diagnostic procedure, it is prescribed for strictly limited indications. An absolute contraindication to the study is pregnancy at any stage of development.
It is also possible to carry out scintigraphy during breastfeeding, however, from the moment of taking (introducing) the radioactive drug until its final disintegration, breastfeeding should be replaced with artificial, and your own milk should be expressed and poured out. In some cases, when using “hard” iodine isotopes, close contact with the child should be minimized.
Among the side effects that occur in patients with the administration of radiopharmaceuticals are a reaction to iodine-containing drugs:
- allergy;
- increased body temperature;
- hyperemia of the face, neck or hands;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- change in blood pressure.
If the patient has a history of gastrointestinal diseases, antacids can be taken after taking iodine-containing radiopharmaceuticals. Adequate drinking regimen will also help minimize negative feelings after taking radiopharmaceuticals.