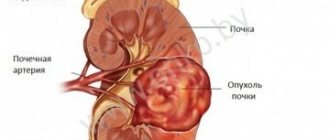
Kidney cancer is a malignant tumor with a high risk of metastasis. This term itself is a general concept. There are a significant number of both types of kidney cancer and tumor stages. Therapy in each case will depend both on the specific characteristics of the malignant neoplasm and on the capabilities of the clinic. With timely diagnosis and proper treatment, the patient's chances of full recovery vary from 79 to 100%. Surgery for kidney cancer is still the gold standard of medicine.
Classification
Blastomas are divided into 2 main types:
- Benign (isolated). They are extremely rare (in 1% of cases) and do not pose a threat to life. They grow very slowly, do not go beyond the breast gland and do not penetrate nearby structures. As they grow, they can put pressure on tissues, blood vessels and nerve endings, causing unpleasant symptoms. Easily treatable.
- Malignant (invasive). They grow into adjacent tissues, forming metastases, penetrate blood vessels and spread throughout the body.
A characteristic feature of a malignant tumor is the rapid penetration of metastases into nearby lymph nodes. Then, with the flow of lymph, malignant cells spread to the second breast, and with the bloodstream - to the lungs, liver, bones and brain.
In addition to breast blastoma, blastoma of the brain, esophagus, stomach, intestines, prostate, and bladder are known.
There are 3 types of breast blastoma:
- Erysipelas
. Occurs in most cases. Accompanied by redness of the skin in the chest area, breast enlargement, severe fever, no pain.
- Edema
. It is asymptomatic. A lump in the chest is clearly visible and can be detected during self-examination.
- Mastitis-like
. It is mainly diagnosed in young girls. The symptoms are similar to inflammation.
- Pantsirnaya
. The skin thickens, the breasts decrease in size.
Stages of the disease
In its development, breast blastoma goes through several stages:
- Zero
(in situ). Does not go beyond the boundaries of its appearance. There are no symptoms. A tumor can only be detected using ultrasound or mammography.
- First
. The malignant neoplasm increases in size and spreads to nearby tissues. Can be detected by performing self-diagnosis.
- Second
. The disease affects the axillary lymph nodes. They swell and become painful.
- Third
. The axillary lymph nodes adhere to each other and to the adipose tissue, forming plaques.
- Fourth
. Metastases penetrate to distant organs.
Kidney tumor symptoms
In some cases, with a tumor in the kidney (especially in the early stages), there may be no symptoms. The tumor is discovered accidentally during an examination carried out for other reasons. Some of the most common manifestations of tumors in the kidney are:
- hematuria (blood in the urine);
- feeling of a lump inside the abdomen;
- pain in the phalanges of the fingers and under the ribs;
- lumps in the abdomen that can be palpated manually (usually indicate late stages of the tumor, when surgical intervention is ineffective);
- weight loss;
- anemia;
- abnormalities in urine tests;
- high levels of calcium in the blood;
- low-grade fever, chills, trembling;
- feeling very tired, decreased immunity.
Causes
The most common cause (characteristic of 10% of cases) of mammary gland blastoma is a hereditary predisposition. The risk of developing a malignant tumor doubles if close relatives have been diagnosed with breast, ovarian or gastrointestinal cancer.
Other provoking factors are also known:
- Hormonal imbalance
The female hormone estrogen stimulates cell division. With high activity of the process, atypical, potentially malignant cells can be formed. Typically, the effect of estrogen is balanced by another sex hormone - progesterone, which does not allow the development of cancer. But if the hormonal balance is disturbed, activation of the malignant process is possible.
The following can cause an increase in estrogen concentration:
- early (before 10 years) onset of menstruation;
- late (after 55 years) menopause;
- late (after 30 years) first birth;
- abortion during the first pregnancy;
- absence of childbirth and breastfeeding;
- disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine gland.
- Wearing tight-fitting firm bras
Tight underwear compresses the mammary gland, limiting the outflow of lymph, which impairs the removal of toxins and toxic substances.
- Wrong lifestyle
The risk of formation of blastoma in the mammary gland increases in women whose diet is dominated by fatty meat foods and almost no vegetables, fruits and seafood.
· The likelihood of a tumor occurring increases if you have bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse).
- Adverse external influences:
- work in hazardous production;
- radioactive radiation;
- action of chemicals.
Additional risk factors include:
- chest injuries;
- breast surgery;
- prolonged absence of sexual activity;
- excess weight;
- chronic diseases (diabetes mellitus, hypertension, atherosclerosis);
- presence of human papillomavirus in the body;
- weakening of the immune system;
- frequent stress;
- age over 40 years.
Where to go
To undergo surgery to treat kidney cancer, contact the NACFF clinic. We employ experienced oncourologists with thousands of successful surgical interventions behind them. Several reasons why you should contact our clinic:
- Accurate diagnosis ensures ideal treatment planning - it will be sufficient, but not excessive.
- Preference is given to organ-preserving operations.
- In the early stages, surgical interventions are performed using a minimally invasive (laparoscopic) method.
- Rapid recovery after surgery, adequate symptomatic and supportive treatment.
- The ability to successfully perform even complex operations, including tumor thrombosis of large veins, if it is necessary to remove several groups of lymph nodes.
- Complementary cancer treatments are available that provide good results even in advanced stages of the disease.
Send documents by email The possibility of treatment will be considered by the chief physician of the clinic Anton Aleksandrovich Ivanov, oncologist-surgeon, kmn
Call the phone number indicated on the website or request a call back to undergo examination and treatment at the NACFF clinic.
Clinical manifestations
At the initial stages, breast blastoma develops asymptomatically, and is usually detected by chance - during diagnosis for other diseases.
As the tumor grows, symptoms of the disease begin to appear:
- lumps or nodules in the mammary glands (may be painless or cause severe pain);
- discomfort in the chest area;
- discharge from the nipples (clear, bloody or purulent);
- the appearance on the mammary glands of wounds that do not heal for a long time, gradually transforming into ulcers;
- deformation, retraction or flattening of the nipples, changes in sensitivity;
- changes in the size, contour and shape of the mammary gland, swelling and swelling;
- redness, thickening, wrinkling, looseness and unevenness of the breast skin, the appearance of dermatitis;
- inflammation, soreness and enlargement of regional lymph nodes.
In addition to local symptoms, general ones also become noticeable: headache, increased body temperature, loss of appetite, weight loss, rapid fatigue, general weakness. They arise as a result of intoxication of the body.
Diagnostics
At the initial appointment, the doctor listens to complaints, asks about personal and family history of diseases, and palpates the mammary glands.
To confirm (or refute) the preliminary diagnosis and clarify the characteristics of the tumor, an examination is carried out, which may include:
- general and biochemical blood test - with blastoma, the number of leukocytes and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate greatly increase, and the hemoglobin concentration decreases;
- analysis for tumor markers;
- mammography - any lumps are clearly visible in the image;
- Ultrasound of the mammary gland – identifies neoplasms and examines their structure;
- biopsy - the resulting biomaterial is subjected to histological examination, which makes it possible to determine the malignancy or benignity of the tumor, and also an analysis of sensitivity to hormonal drugs is carried out.
If metastasis is suspected, additional referrals are made to:
- Ultrasound of internal organs;
- chest x-ray;
- bone tissue scintigraphy;
- computer, magnetic resonance imaging.
- PET-CT
Treatment methods
The method of treatment is selected individually for each patient, taking into account the size and type of tumor, stage of development, the presence of metastases and the degree of their spread, the condition of the lymph nodes, the hormonal level of the body, and the presence of concomitant diseases.
The main treatment method for breast blastoma is surgery. At the initial stage of the disease, a sectoral resection is performed - the tumor is dried out together with nearby tissues. In advanced cases, they resort to mastectomy - the mammary gland is removed. During a radical mastectomy, in addition to the mammary gland, lymph nodes are removed. After removal of the mammary gland, reconstructive breast surgery is recommended.
In some cases, in addition to surgical treatment, chemotherapy, radiation, and hormonal therapy are prescribed.
Radiation therapy is most often given after surgery to destroy any remaining cancer cells. Under certain conditions, it is prescribed before surgery to reduce the size of the tumor and make it operable.
Chemotherapy helps slow down the growth of a malignant tumor, reduce its size, and prevent the formation of metastases. They are carried out both before and after surgery. For patients for whom surgery is contraindicated, it is the main method of therapy.
If the tumor has receptors for estrogen and progesterone, hormonal therapy is prescribed to block estrogen production. It is most effective during menopause.
Operating accesses
Classical open surgery to remove the kidney to treat cancer has been performed since the beginning of the 20th century. They are still in use today. Main surgical approaches:
- median laparotomy (large incision in the abdomen);
- thoracoabdominal (incision on the side) and subcostal - used for neoplasms of the upper pole of the kidney.
In recent years, laparoscopic access has been increasingly used, especially for organ-preserving operations. If it is performed by a highly qualified surgeon, then the time of surgical intervention does not increase compared to using an open approach, and the morbidity is reduced. The need for narcotic analgesics is reduced to 1-2 days, and the hospitalization time is reduced to 3-4 days. After laparoscopy, patients recover faster, suffer less pain, and lose less blood. They are less likely to develop complications.
Forecast
The main factor influencing the survival prognosis is the prevalence of the cancer process. At the first stage of the disease, the five-year survival rate reaches 90-95%, at the second - 65-80%, at the third - up to 50%. At the fourth stage, only 10% of patients manage to overcome the five-year mark.
But it is worth considering that the prognosis can vary significantly depending on the patient’s age, individual characteristics of the body, and the presence of other diseases. A positive attitude can significantly increase survival rates.
Types of operations
The following surgical interventions are used to treat kidney cancer:
Radical nephrectomy . The main treatment option for the disease. It is used for tumors with a diameter of more than 4 cm and for locally advanced processes, including cases of tumor invasion of the renal and inferior vena cava. The operation involves removal of the kidney, perinephric tissue, partial or complete removal of the adrenal gland.
Kidney resection . Kidney tumors are usually detected at an early stage. Therefore, in recent years there has been a tendency to increase the number of organ-preserving operations: in more than half of the cases, the kidney is not completely removed, but partially. At stage T1a (tumor up to 4 cm, not extending beyond the kidney), the proportion of organ-sparing operations reaches 90%.
Our expert in this field:
Ivanov Anton Alexandrovich
Medical director, oncologist-surgeon, candidate of medical
sciences Call the doctor
Call the doctor
Kidney resection occurs:
- wedge-shaped;
- planar (resection of the pole);
- atypical.
With proper patient selection, relapses occur in only 4-10% of patients. The risk of recurrence based on stage is the same as with radical nephrectomy.
Palliative nephrectomy . Performed for metastatic kidney cancer. The operation reduces symptoms, eliminates hematuria (blood in the urine) and tumor intoxication. It is often combined with immune and targeted therapy.
Lymphadenectomy . The stage of surgery involving the removal of lymph nodes. It is performed only for tumors larger than 4 cm or in case of enlarged lymph nodes (according to computed tomography).
Thrombectomy . Stage of surgery to remove blood clots from large veins. In 10-15% of patients, blood clots spread through the renal and inferior vena cava, up to the right atrium.
Prevention
The best prevention of breast blastoma is childbirth and breastfeeding. It is also necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle, give up bad habits, avoid chest injuries and stressful situations, eat right and exercise, and treat concomitant diseases in a timely manner.
Regular self-diagnosis and annual mammography will allow timely detection and removal of the tumor.
has been organizing high-quality individual medical care for many years.
Over the years of work, we have accumulated statistics on leading foreign clinics and are ready to recommend to patients for treatment of breast blastoma only those medical centers where they will truly provide the most effective care.