What is central serous chorioretinopathy
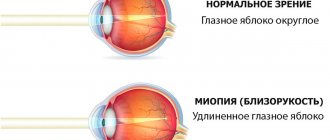
With the development of central serous chorioretinopathy (CSC), the neuroepithelium and retinal pigment epithelium peel off. Detachment can occur in different areas of the retina or be localized in certain areas of it. The pathology is activated due to the release of blood plasma from the vessels. Accumulating, this substance provokes the separation of epithelial layers among themselves.
Against the background of this disease, the nutrition of various structures of the visual apparatus is disrupted. The consequence of the described pathological processes can be serious vision problems.
According to medical statistics, CSC more often affects the population of certain territories - Asia, Spain. Residents of other countries suffer from this disorder much less frequently. The disease can cause absolute blindness and requires treatment at the initial stage of development.
Reasons for development
The exact causes of central serous chorioretinopathy are still unclear. Ophthalmologists name provoking factors leading to the development of pathology:
- regular physical overload;
- frequent stressful conditions;
- high blood sugar;
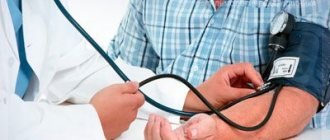
- hypertonic disease;
- circulatory disorders;
- hormonal imbalance that occurs during pregnancy.
The disease affects people who abuse alcohol, people taking steroids, undergoing a long course of treatment with antibiotics, glucocorticoids, and those susceptible to allergic reactions. Patients who have undergone a donor organ transplant and have a hereditary predisposition to CSC are prone to the disorder.
Causes of retinal detachment
The cause of rhegmactogenic retinal detachment can be various types of dystrophies: lattice dystrophy (thinning, retinal tears due to vascular obliteration), degeneration accompanied by the formation of cysts of various shapes and sizes (cystoid); separation of the retinal neuroepithelium (retinoschisis) against the background of hereditary degenerative diseases; atrophy of areas of the retina, pathological hyperpigmentation.
You may be interested in Allergic eye conjunctivitis: symptoms and treatment
Dystrophic changes occur, as a rule, in the peripheral zones of the retina, along the equator of the eyeball. They are in most cases the result of changes in the retina with age and do not manifest themselves in any way. In severe cases, the degenerative process can lead to perforation of the retina and significant detachment.
The factors that result in the development of retinal detachment are: hereditary predisposition (the presence of a similar pathology in one or more relatives), eye injuries, significant physical activity, severe forms of myopia, nutritional defects (lack of food ingredients in the diet, which are building materials for the environment). eyes, vitamins), diabetes mellitus and other diseases in which generalized vascular damage develops.
Classification of pathology
Taking into account the duration of the course, retinal disease is divided into several forms:
- Spicy.
- I'll sharpen it up.
- Chronic.
In the presence of an acute type of the disease, the main symptoms bother the patient for six months. In many cases, the pathology goes away on its own, without an intensive course of treatment. The serous exudate resolves, and the exfoliated areas of the retina return to their original position.
The subacute form of the disease lasts for 8-10 months. Unlike the previous version of CSC, there is no independent improvement, and the patient often needs surgery or laser correction.
A disease that lasts more than one year becomes chronic. This form of pathology is more often observed in people over 45 years of age and mainly affects both organs of vision. At the stage of chronic disease, mandatory surgery of the patient is necessary.
Treatment
The acute form of the pathology, as a rule, does not require therapy. Since in most cases the detachment resolves itself. But chronic and subacute chorioretinopathy must be treated without fail. To do this, conservative methods are used or surgical intervention is prescribed. The course of treatment is selected by the doctor, based on various factors (patient’s age, degree of damage, etc.).
By medication
Conservative therapy consists of taking medications. The following remedies are most effective:
- Medicines to block endothelial growth, such as Avastin or Lucentis. They are injected into the vitreous body;
- Photodynamic treatment is carried out using the drug "Visudin". Its active substance increases the sensitivity of the retina to bright light. As a result, oxygen is released, which, in “company” with radicals, clogs the blood vessels and activates the process of joining the layers.
| Conservative therapy can be combined with alternative medicine. Most often, infusions from medicinal plants (valerian, hawthorn) are used to combat choriopathy. The main thing is to remember that grandma’s recipes will not replace modern medicines and will not help eliminate the disease. |
Surgically
Surgical intervention is prescribed in the following cases:
- Destructive processes in the retina last more than four months;
- Regular relapses and loss of visual acuity;
- Urgent need to restore 100% eye functionality.
Laser treatment has a number of advantages:
- No preliminary preparation required;
- Painless. The intervention is carried out under local anesthesia;
- The operation lasts only ten minutes;
- One correction is enough to eliminate the pathology;
- Allowed during pregnancy up to thirty-two weeks.
Surgery requires maximum dilation of the pupil, so special medications are used to increase its size. The procedure has a number of contraindications, these include high blood pressure, cataracts, and inflammation of the organ of vision. Return to contents
Symptoms
Symptoms of the disease appear:
- blurring of the picture;
- deterioration of color perception;
- the appearance of cloudy, blurry spots before the eyes;
- decreased visual acuity;
- photophobia;
- worsening twilight vision;
- the appearance of scotomas (“darkened areas”) in the field of view.
Worst of all, the patient sees the central areas of surrounding objects, in place of which there may be black dots or spots.
Most patients experience pain that is worse in the morning, shortly after waking up. Some patients see objects reduced or enlarged. Often during illness there are signs of farsightedness.
Symptoms of CSC can periodically weaken, which is explained by the movement of formed areas of uneven pigmentation.
Symptoms of CSCRP
A person suffering from central serous retinopathy incorrectly perceives the size and shape of visible objects. Depending on the individual characteristics of the disease, objects may appear large or small compared to the original volume. The features are distorted, there is no clear boundary.
The patient complains of progressive loss of visual acuity. Farsightedness develops, darkened areas appear before the eyes. Moderate pain is felt in the eyes. In some cases, the field of vision narrows. Despite the normal reaction of the pupils to light sources, patients feel comfortable in twilight. The color spectrum is not distorted in case of retinal disease.
How does CSCRP manifest? Why does it occur and how is it diagnosed? All this is explained in detail and in very simple language in this video:
Diagnostics
The first steps in diagnosis are an ophthalmological examination, collection and study of anamnesis. It is possible to obtain a more accurate idea of the state of the patient’s visual system by:
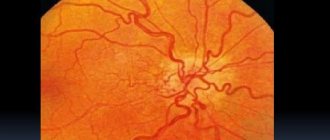
- Ophthalmoscopy, in which the doctor examines the fundus of the eye in detail.
- Electroretinography, which analyzes the condition of the retina.
- Visometry aimed at determining visual acuity.
- Biomicroscopy, which examines the ocular structures in detail.
- Fluorescein angiography, which allows you to compare the indicators of a healthy and affected organ of vision.
Some patients are prescribed optical coherence tomography, a method that can detect the slightest pathophysiological changes. These may include detachment of the pigment epithelium, dystrophic changes in the retina, and accumulation of subretinal fluid.
If central serous chorioretinopathy is suspected, differential diagnosis must be carried out. This procedure makes it possible to detect differences between CSC and choroidal neoplasms, Nagaev's disease, exudative retinal detachment, age-related macular degeneration, choroidal neovascularization, tuberculous choroiditis, Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease.
Prognosis and prevention
In general, doctors give a favorable prognosis regarding the patient’s future ability to work and life. The main problem in treating the disease is that it tends to come back. Even after restoring visual acuity, it is sometimes impossible to cope with the remaining symptoms of the disease.
To protect yourself from the appearance of chorioretinopathy, follow these simple recommendations:
- Monitor your blood pressure regularly;
- Do not ignore an examination by an ophthalmologist;
- Try to minimize the number of stressful situations;
- Distribute physical activity correctly;
- Take hormonal medications only under the supervision of your doctor.
| Take breaks every half hour when working at the computer for a long time, and do gymnastics to relax your eyes and relieve tension. |
Treatment of CSC
The acute form of the disease does not require intensive care. In the treatment of this type of pathology, a wait-and-see approach is used, which takes a period of 1 to 2 months. With a favorable course of the disease, serous detachment disappears and visual function is restored.
If the patient has confirmed subacute or chronic chorioretinopathy, a course of treatment becomes mandatory. In such cases, they turn to conservative therapy or surgery.
Medications
The medications used for CSC help reduce the volume of intraocular fluid and strengthen the vascular walls. The most commonly used medications are:
- Lucentis, an epithelial growth inhibitor, intended for injection into the vitreous region;
- Avastin is an antitumor drug prescribed for intraocular injection;
- Visudin, which increases the sensitivity of the retina;
- Spironolactone is a diuretic that accelerates the resorption of pathological fluid;
- Emoxipine, which improves the condition of the eye vessels;
- Diprospan is a glucocorticosteroid administered via the parabulbar route.
An auxiliary role is given to folk remedies that help relieve inflammation, strengthen blood vessels and speed up recovery. Infusions of hawthorn, valerian, and hazel bark intended for oral use are beneficial for the organs of vision.
Carrying out the operation
The main method of surgical treatment of chorioretinopathy is laser photocoagulation of the retina. Indications for the procedure are:
- Insufficient effectiveness of conservative treatment observed for 3 months or more.
- Frequent relapses of the disease.
- Extensive area of detachment.
- Severe deterioration in visual function.
The intervention is most often performed on an outpatient basis, using local anesthesia. During the operation, the doctor uses a laser to create pinpoint microburns on the retina.
To solder the peeled off areas of the retina, a krypton or argon apparatus is used. The result of the procedure is the attachment of the retinal layers to the choroid, preventing their further separation.
Primary group of retinopathy diseases
Central serous retinopathy
Until today, the exact origin of the primary group is not known, so this group refers to independent diseases that occur independently of other factors. The age range that is most often affected by central serous retinopathy is men between 20 and 40 years of age who have no physical illnesses. In their medical histories, patients refer to experiencing severe emotional and mental stress, suffering from frequent headaches that resemble migraines. In most cases, CSR affects the retina on only one side.
Central serous retinopathy is accompanied by the presence of the following 2 symptoms:
- Micropsia (Dwarf hallucinations) is a condition that causes neurological confusion. It is characterized by the appearance of disturbances in the subjective perception of objects that are far away - at the same time they seem small in size.
- Scotoma - the appearance of blind spots in the field of vision. Accompanied by partial or complete loss of visual acuity.
An important indicator of CVR is the improvement in visual acuity when wearing plus lenses.
Treatment
The most effective treatment today has been and remains laser coagulation of the retina. Perform a series of procedures that are aimed at restoring the vascular wall, reducing retinal swelling and increasing blood circulation. A therapeutic effect is applied to tissues using oxygen under high atmospheric pressure - barotherapy. In approximately 75-81% of cases, if timely treatment is provided with therapy, it is possible to stop retinal detachment and restore visual acuity to the previous level.
Acute posterior multifocal retinopathy
This subtype of retinopathy can affect the retina on both one side and the other. Accompanied by the formation of many small hemorrhages under the retina, leaving a whitish tint, while areas with lost pigmentation or pigmentary degeneration are formed. Examination of the fundus of the eye reveals swelling localized around the blood vessels and deformation of the veins.
Most patients experience opacification of the vitreous body and the development of inflammatory processes around the episcleral tissue and iris. Retinopathy is accompanied by impaired central vision, and blind spots appear in the visual field.
Treatment
Treatment is quite conservative and includes:
- Vitamin therapy - includes vitamins A, B1, B2, B6, B12 in standard dosage;
- Drugs that dilate blood vessels - Cavinton, pentoxifylline, etc.;
- Microcirculation correctors - solcoseryl;
- Retrobulbar injections - the introduction of medicinal solutions into the eye, through the skin in part of the lower eyelid;
- As practice shows, treatment with such methods for this form of retinopathy in most cases occurs without complications and produces a beneficial effect.
Possible complications
Central serous chorioretinopathy can provoke various types of complications:
- atrophic processes in the retina;
- the appearance of neoplasms in the retina area;
- secondary dystrophy of the retina of the eye.
As such phenomena progress, they inevitably lead to a severe deterioration in visual function. If chorioretinopathy has a protracted course, atypical cells and vessels appear in the affected area, and the process of vision loss may become irreversible.
It is possible to reduce the likelihood of negative consequences of the disease by timely contacting a specialist and undergoing treatment measures that help prevent chronicity of CSC.