Glaucoma is a pathological condition of intraocular tissues and the optic nerve, which leads to a decrease in visual acuity up to its complete absence.
If the disease is detected at an early stage, it is possible to use conservative methods of therapy to stop the progression of dystrophic conditions.
To do this, medicinal drops are selected after examination and instrumental research by a doctor. Many of them cause side effects, so self-medication is excluded.
Symptoms of glaucoma
Glaucoma is the development of pathological causes due to increased intraocular pressure. When it is exceeded to certain limits, a decrease in visual acuity and disruption of the functioning of the optic nerve occurs.
There are different types of the disease:
- open-angle – development of pathology with an open drainage system of the eyes;
- closed-angle - accumulation of intraocular fluid due to closure of the angle of the anterior chamber of the eyes;
- congenital – intrauterine formation of pathology;
- juvenile - developing at a young age;
- secondary – caused by various diseases and abnormalities in the development of eye tissue.
It is important for an ophthalmologist to determine the type of glaucoma, since each medicine eliminates the clinical symptoms of a specific type of disease. The mechanism of action is designed for only one type of disease.
The mechanism of development of the disease is associated with increased pressure inside the eyes. It increases in the chambers and puts pressure on the vitreous body and lens. These formations press against the retina, disrupting microcirculation. The cells on it die, this leads to a disruption in the nutrition of the optic nerve. A change in its functionality leads to blindness. It leads to loss of vision, up to complete blindness. Therapeutic procedures using conservative treatment methods stop the progression of development.
Intraocular pressure increases gradually. The patient may constantly experience this phenomenon, but clinical symptoms will not appear. It begins to develop when the optic nerve is compressed. This leads to partial clouding of the outer tissues, and the person begins to see poorly. Blindness occurs gradually only in the absence of therapy.
Do you know what you absolutely can’t do with glaucoma, and what you can?
Glaucoma is an insidious disease. Proceeding with almost no symptoms, it can one day lead to complete blindness .
In the article, we will look at what you should not do with glaucoma - what medications you should not take if you have high intraocular pressure, how much sleep you need, why you should not work at night with glaucoma, and other restrictions. We’ll also talk about what is quite possible.
Why is this disease so dangerous?
There is always a small amount of fluid inside the eyeball that provides nutrition to the eye. It constantly circulates, that is, it is formed and flows freely from the eye chambers. With glaucomatous changes, the outflow of fluid is disrupted. It accumulates and puts pressure on the eye from the inside, increasing intraocular pressure (IOP).
Excessive pressure inside the eyeball negatively affects vision. Over time, it leads to optic nerve atrophy. For a person, this threatens a gradual, subtle decrease in vision, up to its complete disappearance.
A feature of decreased vision in glaucoma is its decrease on the sides. Due to the fact that central vision is the last to be lost, the person himself does not feel the problem. Therefore, it is important after 40 years to regularly measure intraocular pressure .
The outcome of elevated IOP in an unfavorable case is irreversible blindness and disability.
Restrictions for increased intraocular pressure
Glaucoma is a chronic pathology and lasts for many years. It cannot be cured completely, but blindness must be prevented . A person has to live with increased pressure inside the eyeball.
In order to avoid pressure surges and decreased vision, glaucoma patients must follow some simple lifestyle rules.
Medications
Every person who has glaucoma trains himself to always study the instructions for use of the medicine. Some medications increase IOP and are therefore contraindicated for use :
- atropine;
- some antihypertensive drugs;
- oral contraceptives;
- vasodilators;
- nitrates;
- antihistamines – suprastin, diphenhydramine;
- some analgesics.
IMPORTANT ! One of the popular painkillers, aspirin, causes swelling of the lens. In this case, the outflow of fluid worsens, which provokes deterioration of vision.
It is worth mentioning separately about nasal drops for a runny nose. The most common of them are not recommended for glaucoma patients, as they cause a short-term increase in IOP. Therefore, you should not use when you have a runny nose :
- xylometazoline (Rinostop, Rinorus);
- naphazoline (Naphthyzin);
- phenylephrine (Vibrocil);
- oxymetazoline (Nazivin, Afrin).
They can be replaced by other means . Rinsing with warm sea water is effective - it moisturizes the mucous membrane and washes away mucus.
Of the permitted drops and sprays, drugs with an antihistamine component, as well as local hormonal agents, are usually used. They do not help as quickly as classic vasoconstrictors, but they are safe for the eyes of glaucoma patients :
- Allergodil;
- Nasonex;
- Aldecin.
Some drugs used during anesthesia also have the ability to increase IOP. Therefore, if surgery is planned, you should inform the anesthesiologist about existing glaucoma. The doctor will select the type of pain relief that will not cause harm to the eyes.
Among sleeping pills there are drugs that are undesirable for people with glaucoma. They block the flow of fluid, increasing intraocular pressure.
It is better not to use Yunisom and Donormil for sound sleep - they contain doxylamine, which is prohibited in patients with glaucoma. But you can use modern sleeping pills - Ivadal or Sanval.
They contain zolpidem, which is safe for high IOP.
Exercise stress
Excessive physical stress and hard work contribute to increased blood pressure, so they are not recommended for diagnosed glaucoma. You should especially limit those activities that lead to blood flow to the head :
- washing floors;
- carpet cleaning;
- weeding;
- picking mushrooms and berries;
- planting seedlings.
Working in the garden, in addition to the unfavorable situation, is also dangerous due to the hot weather. Under these conditions, the head quickly overheats, which will cause an influx of intraocular fluid and a surge in pressure.
Therefore, gardening work in hot weather is limited to 20 minutes a day, and in cool weather to a couple of hours . Be sure to take regular breaks from work, which are necessary for the outflow of blood. During them, you should sit with your head higher than your body.
HELP : When working outdoors, it is recommended to always wear a hat - it will reduce the risk of overheating.
Moderate exercise will not harm your eyes. They will improve the condition of blood vessels and blood flow in general. You can play sports based on aerobic exercise . Swimming in the pool, athletics, cycling, etc. are useful. . When performing them, it is worth monitoring the general condition. Any symptoms of increased IOP serve as a warning to stop exercising.
It is undesirable to engage in scuba diving and deep diving - this causes an increase in pressure. It is worth completely excluding traumatic sports that easily lead to injuries and injuries to the head and eyes. Examples of sports you should not do:
- weightlifting;
- boxing;
- football, hockey, rugby.
Solar and electric light
Periodic exposure to bright light is not harmful to a person with glaucoma. But when working for a long time in an overly lit room , with a computer or tablet screen, EDV increases . Therefore, it is not recommended to work with electronic equipment for a long time without breaks.
Special unusual glasses provide protection from sunlight to eyes with high blood pressure. ideal - they protect from light and do not obscure .
Through classic dark sunglasses, everything appears in twilight, which provokes attacks of glaucoma.
Night shift work is contraindicated for glaucoma patients . At dusk, the pupil dilates, which prevents the outflow of fluid from the chambers of the eye. In such a situation, there is a threat of a jump in intraocular pressure. Therefore, if the work previously involved night shifts, it should be abandoned after diagnosis.
Sauna
Steam and high temperatures inside a sauna or bathhouse can slightly and briefly increase pressure. Therefore, staying in a sauna for a long time is undesirable.
You can safely steam in a bathhouse/sauna for no more than 15 minutes . But sudden changes in temperature are even more dangerous: jumping into the snow or dousing yourself with cold water after a bath.
These activities cause strong jumps in intraocular pressure, so this should not be done at all.
IMPORTANT ! Contrast showers and rubdowns are also undesirable. They are replaced with more gentle contrasting hand baths, if well tolerated.
Work and sleep
A person with glaucoma can work in the same way as others. But be a little more attentive to your well-being: take breaks more often and allow less nervous tension.
The workplace should be in a bright room, but away from direct light sources that irritate vision.
Sleep is recommended to be the same full, eight hours, as for healthy people.
Lack of sleep puts excessive stress on the nervous system, which can cause headaches and increased IOP in a patient with glaucoma.
It is better if the head end of the bed is higher than the foot end - this facilitates the outflow of blood from the head. If a headache appears after waking up, then the head edge is raised even higher.
Car driving
Many people ask: is it possible to continue driving? Driving with glaucoma is not contraindicated unless vision is completely impaired . In the most advanced stages, if a person has not received treatment and has lost most of their vision, they will not be allowed to drive when examined.
It is undesirable to spend a lot of time driving at dusk and at night - at this time the vision of glaucoma patients is significantly reduced.
In addition, the factor of a wide pupil and a possible jump in intraocular pressure is added. When driving, it is worth considering the possible worse vision in the periphery.
Therefore, you should be extremely careful while driving, watching the road not only in front of you, but also to the side.
Air travel
People with glaucoma usually tolerate flights well . Episodes of takeoff and landing that are associated with pressure changes may cause slight discomfort.
But these are short-term moments, after which the pressure quickly returns to normal.
To be sure, before flying, you should definitely visit an ophthalmologist - after the examination, the doctor will either allow you to fly on an airplane or advise you to abstain.
Food
The diet for glaucoma is similar to the usual diet of a healthy person. It is not recommended to frequently eat spicy and salty foods.
Preference is given to dairy and plant foods with gentle heat treatment. It is prohibited to consume foods that increase intraocular pressure: strong tea and coffee, energy drinks.
All features are discussed in a separate article about nutrition for glaucoma.
HELP : A complete abstinence from coffee and tea is not required - you just need to use no more than 1-2 cups of the drink per day. Drink in small sips, slowly.
Liquid
The total amount of fluid that a glaucoma patient should drink does not differ from standard recommendations. It’s good if you drink about 2 liters of clean water. With glaucoma, it is not advisable to drink more than 200 ml or one glass of liquid at a time . If more than 200 ml or a glass of liquid enters the body at a time, the pressure threatens to increase.
Smoking and alcohol
Cigarettes and alcoholic beverages are harmful even to a healthy person. In the case of glaucoma, if you drink alcohol, the water balance in the body is sharply disturbed.
This leads to changes in the pressure of the intraocular fluid, which complicates the course of the disease and contributes to rapid loss of vision. Smoking sharply constricts blood vessels, which also interferes with the normal circulation of intraocular fluid and impairs vision.
Contact lenses
Wearing lenses for glaucoma is not contraindicated . Therapeutic drops accumulate in the contact lens in small quantities, like in a depot, and are gradually released from it to the eye. This has a positive effect on the condition of the eyes and allows you to reduce the dosage of the medication.
Some medications prescribed for glaucoma can cause dry eyes. In order to cope with this condition, moisturizing drops and solutions are recommended. If dry eye syndrome is severe, which often happens among those who work at a computer, it is better to replace contact lenses with glasses.
Detection of increased intraocular pressure should not cause panic . Today, medications and minor surgical interventions help slow the progression of glaucoma and avoid blindness. Regular visits to the ophthalmologist, tonometry and simple lifestyle changes will help maintain clear vision for many years.
RATE THIS ARTICLE: ( 16 4.38 out of 5) Loading…
Source: //glaza.guru/bolezni-glaz/zabolevaniya/glaukoma/kak-zhit-s-glk/chto-nelzya-pri-glk.html
Groups of drops for the treatment of glaucoma
In the early stages of the disease, conservative therapy is used. Local medications are used in the form of drops that are dripped into the internal structures of the eyes. The drug helps reduce intraocular pressure. This is done using various groups of drugs:
- Beta blockers. They eliminate nerve impulses sent to the brain, which increase fluid production. These drugs include Betoptik, Timoptik.
- Prostaglandins. Hormonal substances that help remove fluid from the affected area. They have many side effects. Taflotan belongs to this category.
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. They affect the endocrine glands and reduce fluid production. Such drugs include Trusopt, Azopt.
- Alpha adrenergic receptor agonists. They have a double effect. They have an effect on nerve receptors and secretion production. Helps eliminate fluid from internal spaces.
Pharmacological properties of eye drops for glaucoma and their classification
To treat glaucoma, medications are used, the main effect of which is to normalize intraocular pressure.
Eye drops for glaucoma are divided into three groups according to their mechanism of action:
- Group No. 1: Medicines that promote the outflow of intraocular fluid.
- Group No. 2: Means for reducing the production of aqueous humor.
- Group No. 3: Combined drugs.
In drugs of the first group, the main active ingredient can be represented by:
- prostaglandins;
- sympathomimetics;
- cholinomimetics.
Among the agents that reduce the synthesis of aqueous humor are:
- carbonic anhydrase inhibitors;
- beta-adrenergic blockers;
- alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonists.
Effective anti-glaucoma drops
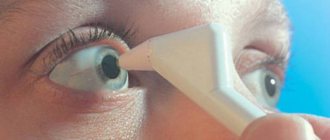
For treatment, medications are used in the form of drops. They act locally, penetrating the internal structures of the eyes. Tablets are rarely used and their effectiveness is low. The drugs are sold in pharmacies without a prescription; self-medication is unacceptable. Using products without a doctor's prescription can lead to serious side effects.
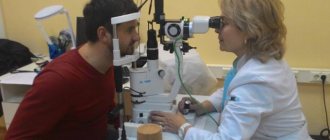
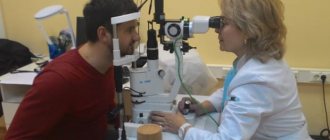
A preliminary examination is carried out by an ophthalmologist to determine the type of disease. The doctor collects anamnesis, learns about previous illnesses and medications to which the patient is allergic. Only after this is it possible to prescribe drops.
The number of instillations per day and the course of application are determined by the ophthalmologist. It is prohibited to use drugs in reduced or increased dosages. It is recommended not to instill the substance into the eyes, as this can lead to increased blood pressure.
Pilocarpine
A drug from the group of cholinomimetics. It provokes the phenomenon of accommodation, as a result of which the pupil narrows. The anterior chamber decreases in size and fluid leaks out. Normal circulation is restored. Open-angle therapy with instillation of Pilocarpine up to 6 times a day is possible.
After achieving the maximum effect, the dosage is reduced. Contact an ophthalmologist for advice.
Isoptocarbachol
A drug from a number of cholinomimetics. Carbacholine is the main substance that eliminates the effect of the disease. It is used for all types of diseases.
The product promotes eye accommodation and pupil constriction. The anterior chamber decreases in size, facilitating the release of accumulated secretions from it. During initial use, the effect of the drug appears within the first 8 hours.
The drug is used 3 times a day. The course of treatment is determined by an ophthalmologist. It is possible to use the medicine continuously while the effect is observed.
Aceclidine
A drug from the group of cholinomimetics. The accumulated secretion is eliminated by constriction of the pupil and anterior chamber of the eyes. It has a large number of negative reactions, when they occur, it is immediately canceled and replaced with an analogue.
During the first months of treatment, the drug is instilled up to 5 times a day. Once the maximum effect is achieved, the dosage is reduced.
Xalatan
A drug from the prostaglandin group. The main active ingredient of Xalatan is latanoprost. After instillation of the drug, the secreted liquid is removed from the chamber into the vascular system. The pressure drops. Instillation is carried out before bedtime 1 time per day.
Travatan
A drug from the group of prostaglandins. It is based on travoprost. The product helps remove secreted fluid through the drainage system. The pressure returns to normal. Travatan can be used for any form of glaucoma or diseases that increase pressure inside the eyes.
It is enough to use the drug once a day.
Taflotan
A drug from the group of prostaglandins. The medicine gradually accumulates in the internal structures of the eyes. Affects the lens and internal chambers. Helps eliminate accumulated secretions. The effect of the product will be achieved when used once a day.
Timolol
A drug from the group of beta-blockers. It influences internal structures, reducing the secretion of fluid, promoting its outflow. It has a small list of side effects and does not cause accommodation disturbances.
Gradual adaptation to the drug should be carried out. For initial use, use a 0.25% solution. Instillation is carried out 2 times a day. When the maximum effect is achieved, the dosage is reduced to 1 time per day.
If the effect of Timolol is not sufficient or it decreases, it is replaced with a 0.5% solution. In this case, the dosage of the product remains identical.
Trusopt
An agent from the group of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. The main substance is dorzolamide. The drug helps reduce fluid secretion. The active substance acts on the glands that produce it. The products are used 3 times a day in the morning, afternoon, and evening. Use 1 drop of the product in each eye.
Azopt
A drug from the group of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Affects the ciliary body, reducing the production of secreted fluid. Additionally, the transport of sodium ions is reduced. As a result, the pressure drops. The product is used 2 times a day, 1 drop in the area of the conjunctival sac of each eye.
Betoptik
A drug from the group of beta-blockers. The main active ingredient is betaxolol. It affects the glands in the eyes, thanks to which the flow of fluid occurs. This action is inhibited, the pressure drops. Apply the product 2 times a day, 1 drop to the eye area.
What is contraindicated for glaucoma, and what is possible?
Glaucoma is increased intraocular pressure (IOP), which compresses the optic nerve fibers and causes vision loss.
There are two types of glaucoma: open-angle and narrow-angle.
In the open-angle form, fluid flows freely through the angle created by the iris and cornea, the IOP rises because the trabecular meshwork, through which the fluid drains at an angle, is blocked.
In narrow-angle glaucoma, the angle narrows. The widening of the eye with this form completely covers the angle.
Both types of disease can be prevented or active development delayed if you know what is contraindicated and what restrictions need to be followed.
What drugs are contraindicated for glaucoma?
List of medications to avoid:
- Corticosteroid eye drops can worsen open-angle by damaging the already abnormal trabecular meshwork in the eye. This occurs in most people with open-angle disease who use steroid medications.
- Drugs with anticholinergic properties may have a negative effect on patients with the narrow-angle form of the disease. Medicines block the action of acetylcholine, which transmits signals from one nerve cell to another. Such drugs are used to treat asthma, urinary incontinence and gastrointestinal problems. Many medications used to treat depression can have side effects in patients with the narrow-angle form of the disease. These include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) such as Prozac (fluoxetine) and Paxil (paroxetine). Tricyclic antidepressants such as Elavil (amitriptyline) and Tofranil (imipramine).
- Antiallergy medications containing diphenhydramine put patients at risk.
- Sulfonamide-containing medications. There are certain medications that can cause angle closure in some people. Examples of medications that contain a sulfonamide include Topamax (topiramate), Diamox (acetazolamide), Sumycin (tetracycline), and Bactrim (trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole).
- Oral steroids help reduce inflammation and immune system activity. This type of medication may affect eye pressure in individuals who have open-angle glaucoma.
We recommend reading: Laser treatment of glaucoma
There are contraindications among sleeping pills. It is not recommended to use Yunisom and Donormil. Antibiotics are also not allowed to be used. If there is an infection, you should remind the doctor about the existing eye pathology to select the optimal drug.
Scuba diving
Swimming or snorkeling in shallow water will cause only minor changes in eye pressure. Patients planning to scuba dive should first consult their ophthalmologist. Patients with progressive optic nerve damage should avoid diving.
Music
Playing a wind instrument can lead to a temporary increase in IOP. Patients who play these instruments should discuss this with their ophthalmologist.
Emotional condition
Individuals are advised to lead as relaxed a lifestyle as possible. You should avoid stressful situations and maintain a calm and measured manner.
In primary open-angle glaucoma, emotional disturbances and symptoms of maladjustment are often observed. Negative emotions contribute to an increase in intraocular pressure in patients with the open-angle form of the disease.
A stressful situation, depression and a suppressed anger reaction contribute to vascular spasms and poor circulation in the brain, retina and optic nerve.
If you monitor your emotional state and correct your psychological status, you will have a positive effect on your hemodynamics.
Pregnancy
Every medicine used during pregnancy is considered potentially dangerous to the fetus. However, do not be discouraged and despair. Treatment during pregnancy is carried out and has a beneficial effect on both the condition of the mother and the future baby.
Women planning a pregnancy are advised to consult an ophthalmologist. The doctor will select the most gentle treatment that maximally protects the mother and fetus.
You can only take medications that are prescribed by your ophthalmologist. Strictly follow the dosage and treatment regimen.
sunlight
When working for a long time in an overly lit room or being outside, intraocular pressure increases. Therefore, it is recommended to take breaks from working with the PC and wear sunglasses (sold with or without diopters) when going outside.
Patients are contraindicated to work night shifts. Poor lighting forces the pupil to dilate to capture more light to transmit images to the brain. This prevents the outflow of fluid from the chambers of the eye, and there is a high risk of a jump in IOP.
Alcohol
Ethyl alcohol (ethanol) is a hyperosmotic molecule. Alcohol consumption tends to increase IOP when used regularly. The implication is that alcohol may reduce IOP in the short term (just for a couple of hours or so), but will have a negative effect in the long term.
The positive effect occurs due to the diuretic properties of alcohol and its effect on reducing the secretion of aqueous humor in the ciliary body. Neither the benefits nor harms of alcohol in glaucoma have been proven in patients with this diagnosis.
Smoking
Has an adverse effect on circulation and is a risk factor for the development of vascular diseases. Doctors and scientists have found that this habit affects the development of cataracts, and the same is expected for glaucoma.
Smoking is one of the most common causes of tissue hypoxia and the development of optic nerve atrophy. The use of nicotine is strictly contraindicated in the presence of glaucoma of any type.
TV
Watching TV is not prohibited. It is recommended to sit in front of it in a well-lit room and the light source should be behind your back.
Watching TV for a long time is contraindicated. This leads to tension in the visual analyzer, fatigue and, as a consequence, an increase in intraocular pressure.
Sleep and rest
Lack of sleep and insufficient rest lead to overwork of the body as a whole. Sleep at least 8 hours a day.
The head is slightly elevated so that IOP does not increase during sleep and blood circulation is normal.
During the working day, take 15-minute breaks, regardless of what field the patient works in. Breaks are especially necessary when spending a long time at a personal computer.
Side effects
All of the above drugs have common side effects that occur in certain categories of patients:
- allergic reactions in the form of itching, burning, irritation, redness of the skin and mucous membranes of the eyes;
- inflammatory condition of the cornea and eyelids;
- corneal clouding;
- retinal detachment due to compression and disruption of microcirculation;
- blurred vision for a short period of time;
- increased sensitivity to bright light;
- increased secretion of tear fluid;
- neurological disorders such as headache, dizziness, insomnia, double vision;
- systemic decrease in blood pressure, especially when using antihypertensive drugs;
- poor heart function;
- narrowing of the lumen of the bronchial tree, resulting in the formation of asthma.
Combination drugs
For a more effective effect, combination drugs are used that combine the effects of several drugs.
Medicines used for ocular hypertension have a longer lasting effect. There is no need to instill drops throughout the day.
It has active ingredients contained in Pilocarpine and Timolol. The drugs belong to the group of cholinomimetics and beta-blockers. Prescribed for patients with primary and secondary glaucoma.
- For bronchial asthma;
- In the postoperative period;
- Patients under 18 years of age;
- With bradycardia;
- Diseases of the respiratory organs with obstruction.
Combines several drugs: Xalatan and Timolol. A combination type of medicine is prescribed for open-angle glaucoma, when treatment with other drugs is insufficiently effective. Not for use under 18 years of age. Contraindicated:
- With pathology of the respiratory system.
- Heart problems.
Products produced in the form of eye drops are equipped with convenient droppers that help accurately administer the medicine into the eyes. Drugs are prescribed only by a doctor, who will monitor the treatment process and determine further actions. It must be remembered that self-medication can lead to partial or complete blindness. In addition to medications, Sidorenko glasses are selected for patients with increased ophthalmotonus.
Contraindications
The drugs are contraindicated for the following conditions and diseases:
- hypersensitivity to one of the components of the product;
- serious diseases of the cardiovascular system (heart failure, arterial hypotension, blockade, arrhythmia, decreased heart rate, cardiogenic shock);
- obstructive conditions in various parts of the respiratory system (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma);
- inflammatory conditions of the anterior chamber of the eye;
- eye diseases that worsen when the pupil dilates.
Medicines to reduce aqueous humor production
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
This group of drugs acts on the ciliary body enzyme, carbonic anhydrase, inhibiting it. As a result, the secretion of intraocular fluid decreases and the pressure decreases. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors include eye drops:
- Trusopt® (INN Dorzolamide);
- Azopt® (INN Brinzolamide).
These drugs are prescribed for instillation into the eyes twice a day. They have virtually no systemic side effects on the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. Can be used in combination with prostaglandins and beta-adrenergic blockers.
Beta blockers
Eye drops based on non-selective beta-blockers (block beta-1,2-adrenergic receptors):
Eye drops based on selective beta-blockers (block beta-1 adrenergic receptors):
These drugs have systemic side effects on the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, which leads to a decrease in rhythm and bronchospasm.
Therefore, beta blockers are not recommended for patients with hypertension or asthma. Selective beta blockers have less pronounced side effects.
Alpha-2 adrenergic agonists
The peculiarity of these eye drops is their dual mechanism of action, that is, they reduce the secretion of aqueous humor and at the same time improve the outflow of intraocular fluid due to contraction of the ciliary muscle. These include clonidine derivatives - clonidine and brimonidine.
Consumer Reviews
Elena: At my last appointment with the ophthalmologist, I was diagnosed with early stage glaucoma. The doctor said that it is not advisable to perform surgery at this stage. He recommended conservative treatment with antiglaucoma drops. At first I tried Azopt, but it gave me itching and burning in my eyes. The doctor advised to replace it with Fotil. There are no negative symptoms.
Dmitriy. I have been treating glaucoma with drops for a year now. Cloudiness of the lens and increased intraocular pressure were detected. After several months of using anti-glaucoma medications, the doctor said that the pressure was under control, so she lowered the dosage. Now I have no progression of diseases.
Types of drops that reduce intraocular pressure
Drops for the treatment of glaucoma are produced in large quantities. Each of them contains certain drugs, which can be divided into several groups:
- Based on the active component, beta blockers, prostaglandins, cholinomimetics, etc. are distinguished.
- According to the mechanism for eliminating intraocular hypertension, there are drugs that reduce the synthesis of aqueous humor, drugs that improve its outflow, and combined drugs.
Prostaglandin analogues
Prostaglandins are the safest and most effective agents for the treatment of glaucoma. 2 hours after instillation of this group of medications, the pressure inside the eye begins to decrease, and the maximum effect is observed after 12 hours.
Types of drops
Ophthalmic antihypertensive drops for the treatment of cataracts and glaucoma are very common, and there are many types. The classification of medications is based on two main indicators: the basic active ingredient and the mechanism of pressure reduction. To choose the right medications, both factors must be taken into account. Schemes for providing hypotensive effects in drops are as follows:
- improving the outflow of fluid inside the eye;
- decreased secretion of intraocular fluid;
- a combination of both mechanisms.
Antihypertensive ophthalmic medications are traditionally based on one dominant chemical compound; combination drugs are rarely found. Depending on the base substance, eye drops that have the effect of reducing intraocular pressure are divided into five subtypes:
- synthetic analogs of prostaglandins F2α
- antienzyme;
- cholinomimetic;
- beta-blockers;
- mixed type.
The list of medications is approved by the doctor. Self-medication leads to complications and blindness.
Cholinomimetics
These eye drops are used for angle-closure glaucoma, since the principle of action is based on improving the outflow of ocular fluid to the corners of the eyes. The downside of the product is that its effect does not last long, so you need to instill drops 2-6 times a day. Cholinomimetics are also good medications for open-angle glaucoma. They are also used to prevent illness. In case of overdose, the drug causes dizziness and migraines, eye spasms and miosis.
Antienzyme drugs
Such eye drops for the treatment of glaucoma suppress the production of intraocular fluid, thereby improving the patient’s vision and allowing the disease to be treated both at the initial stage and in progress. Pregnant women, people with kidney disease and anemia should not take anti-enzyme medications. At the same time, these are the best and relatively safe pharmaceuticals, since the list of their side effects is minimal. The most unpleasant symptoms of overdose are burning in the eyes, bitterness in the mouth, dizziness and agranulocytosis.
Combination drugs
Medications that combine two or more active ingredients and provide a diverse effect on the intraocular fluid are better to choose if not only glaucoma in its pure form is present, but there are also associated ailments. Combined antihypertensive ophthalmic drops are suitable for cataracts and glaucoma of various origins as the main medicine. They do not prevent diseases. Self-medication is prohibited, since the wrong dosage can lead to serious side effects and complications, including loss of vision.
Ayton is often prescribed to patients by doctors for preventive purposes.
If it is necessary to carry out a preventive course for patients with several eye ailments, Indian drops "Ayton" are prescribed. They contain mainly natural ingredients - plant extracts, calcined pearls and vitamins. Ayurvedic cataract drops are safe for pregnant women. Contraindication is individual intolerance to the components and an allergic reaction to them. When using the drug for the treatment of advanced forms of glaucoma, the effectiveness of Ayton is low.
Synthetic analogs of prostaglandins F2a
The mechanism of the hypotensive action of pharmaceuticals is based on improving the outflow of intraocular fluid through additional channels, due to which they are one of the most fast-acting and effective. The therapeutic effect lasts as long as possible - from 18 to 24 hours. Disadvantages of use - the slightest overdose can lead to side effects and cause painful, unpleasant symptoms and complications. A typical negative consequence is the “red eye” effect, which occurs due to dilation of the conjunctival vessels. These eye drops for glaucoma can cause clouding of the cornea and subsequently lead to its erosion. An allergic reaction to the medication is considered to be burning and itching in the eyes. Long-term use of drops affects the patient's eye color, as it stimulates the production of melanin and causes changes in pigmentation.
Beta blockers
This type of medication has a hypotensive effect by suppressing the production of intraocular fluid. Beta blocker medications must be instilled correctly without exceeding the dosage. It is recommended to use drops once a day, maximum two. The medication should not be used by diabetics, as well as patients with diseases of the cardiovascular system, bronchial asthma and breathing disorders.