A working method to restore vision! You will throw your glasses in the trash in just 3 days... Restoring vision. Real life story.
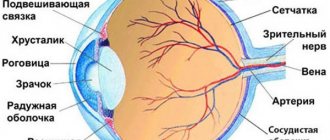
Intraocular pressure (ocular pressure) is one of the most important clinical factors in ophthalmology. For the normal functioning of the eye and its structures, it is very important to keep intraocular pressure within normal physiological values. Intraocular pressure (eye pressure) is a term that each of us has probably heard either when visiting an ophthalmologist, an optical salon or somewhere else. However, many people do not know what this term includes, what its function is, and why it is important. The importance of intraocular pressure can be compared to blood pressure, people know that increasing or decreasing it can have unpleasant consequences.
The situation with intraocular pressure is identical. Intraocular pressure maintains the constant shape of the human eye and protects it from deformation. Because the eyeball can only expand slightly, intraocular pressure is the result of a balance between the secretion and elimination of aqueous humor. Intraocular pressure may decrease when there is insufficient secretion of intraocular fluid or excessive secretion. On the other hand, high intraocular pressure is caused by excess production of intraocular fluid or insufficient permeability of the drainage channels, which are located in the corner of the anterior chamber of the eye.
Intraocular pressure range
The range of physiological values of intraocular pressure is relatively wide; for eye health, the values vary from 10 to 21 mmHg. Art. We must take into account that intraocular pressure values vary from person to person and thus we cannot consider cut-off values as a higher or lower limit for normal conditions. In other words, values “above” these limits are considered suspicious. Although we know that intraocular pressure is far from the only symptom in the diagnosis of glaucoma, it remains one of the most important. Therefore, the distinction between physiological, suspicious and pathological intraocular pressure values is vital.
The daily deviation of intraocular pressure is also individual, but for healthy normal eyes it should be from 2 to 6 mmHg. Art. Deviations higher occur in the case of ocular hypertension or glaucoma. Eye pressure values are highest in the first half of the day, especially immediately after waking up, and decrease throughout the day. However, this is only true for 80% of people, and others may have peak values in the evening that decline in the morning.
Causes of increased intraocular pressure
Intraocular pressure is an important indicator of serious disorders. The examination should always be accompanied by monitoring of the visual field and the condition of the optic nerve papilla. In the case of normotensive glaucoma, the intraocular pressure value should not be pathological, even in an advanced stage. On the contrary, in the case of ocular hypertension, when there is increased intraocular pressure, but there are no other symptoms of glaucoma. Patients suffering from this disorder often have low blood pressure.
A significant increase in intraocular pressure occurs as a result of stress and smoking. Drinking large amounts of fluid over a short period of time, drinking alcohol in small quantities in combination with smoking can lead to increased intraocular pressure. Intraocular pressure values are also influenced by body position, corticosteroid use, and eyelid conditions. In the supine position, intraocular pressure increases by approximately 2 mmHg. Art., when a person stands on his head and hands, intraocular pressure reaches its highest values.
Optimal eye pressure level
Normal intraocular pressure values range from 14 to 25 millimeters of mercury. They may vary depending on several factors:
- person's age;
- type of measuring device;
- the presence of a chronic form of hypertension;
- intensity of eye strain;
- Times of Day.
Regarding the time of day, it is worth checking separately. The highest blood pressure is observed in a person in the morning; closer to lunch it decreases. The lowest pressure measurement results can be noted in the late afternoon. These changes in intraocular pressure are normal and do not relate to pathology! Doctors warn that any deviation from the norm is an alarming signal!
Why does eye pressure rise?
Eye pressure can increase due to a variety of factors. The most common reasons are:
- ailments associated with the cardiovascular system. These include atherosclerosis, varicose veins and a huge number of other diseases that affect the normal functioning of the heart;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- diabetes;
- poisoning with substances of chemical origin;
- kidney disease: a wrinkled kidney and severe glomerulonephritis affect the retina and provoke high eye pressure;
- post-traumatic glaucoma. With glaucoma resulting from mechanical damage to the eyes, ophthalmotonus may be higher than normal;
- spending a long time in front of the display of a tablet or laptop.
These are just the most common factors that provoke an increase in intraocular pressure. People over the age of 40 are also at risk, since the older the person, the more often the disease appears. However, children are also susceptible to the disease, so parents are obliged to closely monitor the health of children and adolescents.
How to treat illness and its prevention?
The most effective treatment for elevated intraocular pressure is surgical intervention. This is the most radical way. They resort to it if it was not possible to achieve the desired result with the help of physiotherapeutic procedures such as vacuum massage or color pulse therapy.
prophylaxis will help prevent both the operation and, in fact, the onset of illness . If you are at risk, it is incredibly important to adjust your own diet. You should limit the consumption of salt and fast carbohydrates, and enrich the menu with vegetables, red fruits, and dark chocolate.
You should also avoid clothes that have tight collars. You should not tighten your tie and unbutton the top button. In another case, the outflow of blood that comes from the veins of the head is disrupted.
It is recommended to minimize visual and physical stress. Try to avoid emotional stress and overload. As a preventive measure, it is better not to drink excessive amounts of liquid and forget about tea and coffee altogether.
Causes of increased intraocular pressure
Eye pressure levels can change for many reasons:
- Stressful state, nervous overstrain.
- Active physical activity.
- Long-term intellectual stress on the brain.
- Active strain on the eyes (for example, watching TV for a long time, working at a computer monitor for a long time).
- Disorders, failures or diseases of the cardiovascular system, which lead to an increase in both blood and intraocular pressure.
- Anatomical pathologies of the organs of vision, including those of a hereditary nature.
To protect your eyes from problems with pressure, it is recommended to avoid stress and periodically give both your eyes and body a rest during working hours. If you have diseases and pathologies, be attentive to your health, do not neglect visits to the doctor, and follow the prescribed treatment!
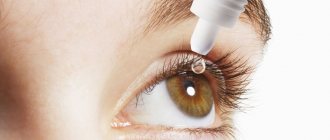
How to instill drops to relieve pressure?
Pressure lowering products are extremely easy to use. The most important rule that should be observed and which should not be neglected is cleanliness of hands. If you get an infection, then, at a minimum, you will develop conjunctivitis, which, given existing diseases, causes the most unpleasant sensations.
To apply eye drops, you should tilt your head back and drop the drug into the inner corner of the eye, after slightly moving the lower eyelid. Be careful, don't get distracted. It is very important not to let the tip of the pipette or pipette come into contact with your eye. After the procedure, you need to close your eyes for a few seconds. To store drops, choose places where there is no direct sunlight, read the manufacturer's instructions and follow the recommendations of your doctor.
Do not forget to visit your ophthalmologist in a timely manner and regularly measure the pressure inside your eyes. This approach will help you accurately select the drug and its dosage; this is extremely important for the treatment to be successful. Do not delay visiting an ophthalmologist if you experience pain or discomfort when working with documents or at the computer, or when watching TV. Regularly make an appointment with a specialist, observe the rules of personal hygiene and, if you have existing diseases, constantly monitor your well-being.
MagazinLinz.ru team
Treatment
In conservative therapy, drops are actively used to improve the nutrition of the eye and the drainage function of this organ. The dosage of the drug and the duration of treatment for the disease that provoked an increase in intraocular pressure are prescribed individually. If conservative treatment is insufficiently effective, the patient is referred for laser iridotomy or laser trabeculospasis.
The specificity of these interventions is that during laser iridictomy one or more holes are formed in the iris of the eye. Thanks to the implementation of this method, it becomes possible to improve the circulation and outflow of fluid from the eye, which ultimately normalizes increased IOP. Laser trabeculospasis is performed to improve drainage of the eye by stretching the venous sinus of the sclera. When it is implemented, the base of the ciliary body of the eye is cauterized.
The most radical method in this situation is microsurgical technology. During goniotomy, the iridocorneal angle of the anterior chamber of the eye is dissected. Trabeculotomy is a dissection of the trabcular meshwork of the eye - the tissue connecting the ciliary edge of the iris to the posterior plane of the cornea.
Drops for eye pressure
A popular treatment for IOP is drops. Due to their properties to increase the outflow of excess fluid from the eyeball area and effectively nourish the tissues of all parts of the visual apparatus, these products have received appropriate recognition from doctors and patients. Medicines can be divided into several pharmacological groups:
- Carbanhydrase inhibitors (representatives – Azopt, Trusopt, etc.). Normalization of IOP is achieved due to the fact that they reduce the production of intraocular fluid.
- Prostaglandins (representatives - Travatan, Xalatan, Taflotan, etc.). These drugs significantly enhance the outflow of intraocular fluid.
- Beta blockers (Timolol - not in tablets, but in drops) repeatedly reduce the intensity of the synthesis of intraocular fluid. They are usually used in combination with prostaglandins.
- Miotics (Pilocarpine) are drugs that reduce the diameter of the pupil and thereby improve the outflow of intraocular fluid.
- Combined drugs (Proxofelin), the action of which helps to reduce the intensity of the synthesis of ocular fluid and increase the intensity of its outflow.
Considering that the use of antiglaucoma drops can cause complications, they should only be prescribed by an ophthalmologist.
A qualified ophthalmologist will not only prescribe drops taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s body, but will also monitor the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment.
In addition, remember that you cannot rely on only one drug - at least two are used.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Physiotherapy is a unique set of preventive and therapeutic methods that can, to a certain extent, stop the development of pathology and prevent the manifestation of various diseases that appear as complications of increased IOP.
During the procedures, a variety of physical factors are used on the body, including: carbon dioxide, magnetic field, heat, light, etc. A prerequisite for undergoing any physical procedures is a preliminary consultation with a therapist. It is he who must assess the state of a person’s health comprehensively, evaluate the presence or absence of concomitant pathology, which is a priori incompatible with physiotherapeutic methods.
Only after the therapist (together with the ophthalmologist) decides on the advisability of using physiotherapeutic treatment methods, the physiotherapist develops an individual course of treatment, determines the type of procedure, the number of sessions required, the intensity of the impact, taking into account age characteristics, the clinical specifics of the disease and the presence of complications, and as well as their degree of expression. An important advantage of all physiotherapeutic treatment procedures is the absence of even minor pain, allergic reactions and unwanted side effects.
The following conditions are absolute contraindications to physiotherapeutic measures:
- systemic diseases;
- pathologies associated with blood cells of different origins;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system of an organic nature (coronary artery disease, cardiomyopathy), as well as the presence of a pacemaker;
- infections in the acute stage - even colds;
- neurological pathologies in a state of exacerbation.
Surgery (microsurgery)
A separate and extremely important area in the treatment of pathologies of the organ of vision, as in other branches of medicine, is surgical treatment. An intervention of this nature is a last resort when other methods are not effective. However, only its use will save a person from the prospect of developing glaucoma and complete loss of vision.
Modern microsurgical technologies are the following interventions: goniotomy in combination with or without goniopuncture, as well as trabeculotomy. The choice of surgical technique is determined exclusively by an ophthalmologist after the therapist’s conclusion about the person’s health condition.
Microsurgery is usually used in cases where laser is ineffective.
Folk remedies
Treatment of high eye pressure with traditional methods has in its arsenal a lot of effective and inexpensive means. However, it is important to note that it cannot be used as the only medicine. A drug of synthetic origin must be used, or another method of influencing the human body must be implemented.
Remember that only a doctor can make a decision on the use of certain treatments, whether they belong to traditional or non-traditional medicine.
Regarding effective herbal remedies:
- A decoction of meadow clover is very effective in reducing IOP. To obtain this healing infusion, the plant is infused with boiling water for two hours and taken one hundred grams before bedtime.
- The tincture made from golden mustache has proven itself to be excellent. To do this, seventeen purple knees of the plant (previously carefully crushed) are poured into half a liter of vodka and infused in a dark place for 12 days. By the way, during the cooking process you should lightly shake the container every three days to make it easier to extract all the necessary nutrients from the plant. Consume a dessert spoon of alcohol tincture half an hour before meals.
- Adding a pinch of cinnamon to kefir (at the rate of 1 teaspoon per glass - a dispersion is obtained) will make it possible to obtain a nutritional supplement, the introduction of which into the diet will greatly alleviate the condition of a patient suffering from increased intraocular pressure and enhance the healing effect of synthetic drugs.
Note!
No matter how much you use folk remedies, it is impossible to cure glaucoma on your own; on the contrary, it is so possible to lose your vision!
Best before date
The shelf life of eye drops for the treatment of glaucoma ranges from 24 to 36 months. But this expiration date applies only to the closed bottle of the drug. After opening, eye drops can be stored for 3 to 30 days. After this period, the drops lose their therapeutic properties and are not recommended for use.
Eye drops for glaucoma are medications that effectively reduce intraocular pressure, improve the outflow of fluid inside the eye and reduce the production of aqueous humor. Drops can only be used as prescribed by a doctor, since many drugs are available only by prescription and require medical advice and supervision. Timely use of drops allows you to cure glaucoma and prevent the disease from becoming chronic.
To treat glaucoma, medications are used, the main effect of which is to normalize intraocular pressure.
Eye drops for glaucoma are divided into three groups according to their mechanism of action:
- Group No. 1: Medicines that promote the outflow of intraocular fluid.
- Group No. 2: Means for reducing the production of aqueous humor.
- Group No. 3: Combined drugs.
In drugs of the first group, the main active ingredient can be represented by:
- prostaglandins;
- sympathomimetics;
- cholinomimetics.
Among the agents that reduce the synthesis of aqueous humor are:
- carbonic anhydrase inhibitors;
- beta-adrenergic blockers;
- alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonists.
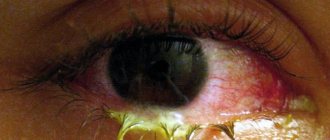
What are the symptoms of high eye pressure?
The insidiousness of intraocular pressure lies in masking the disorder under a minor ailment. A person perceives this ailment as simple overwork, and in most cases does not take any action to eliminate the problem. This allows the pathology to progress. Intraocular pressure can lead to serious changes in the organs of vision, including the development of glaucoma.
By what symptoms can you recognize increased eye pressure:
- burning;
- redness;
- insufficient moisture of the mucous membrane;
- rapid eye fatigue;
- headache;
- blurred vision, decreased clarity;
- the appearance of flies and black dots before the eyes;
- nausea.
Indications and contraindications
Indications and contraindications.
Source: osteohondrozinfo.com Only a doctor can choose which drops used for glaucoma are best suited for a particular patient.
The drug dropped into the conjunctival sac is absorbed into the blood vessels and can cause side effects, worsening existing systemic diseases.
Also, some eye drops may interact with other commonly taken medications that are prescribed to treat heart or other conditions. Only a doctor can evaluate all possible indications, contraindications and risks of prescribing one type of eye drops for glaucoma.
Many patients are interested in what nasal drops can be used for a runny nose with glaucoma. The fact is that antihistamines and decongestants (vasoconstrictors) can dilate the pupil, which leads to an increase in intraocular pressure.
In this case, without fear of a runny nose, you can use nasal drops containing hormones.
Prevention
The main recommendation regarding the prevention of the disease will be systematic clinical observation. In addition, everyone should ensure that they do not experience increased eye fatigue. First of all, this is relevant for those who work a lot at the computer. In order to maintain normal visual acuity and IOP level, do eye exercises for at least one hour a day. Mirzakarim Norbekov’s technique has proven itself very well, which is aimed not only at developing a visual analyzer, but also allows you to use VNI.
You definitely need to reconsider your diet. Add to your food as many plant-based foods as possible, enriched with vitamins and minerals, and exclude foods with high cholesterol. Carrots, blueberries, sea fish, and watermelon should dominate in the diet of a patient with increased IOP.
Physical therapy and massage are important elements in the prevention of glaucoma, but they should only be performed under the supervision of a physician.
[adsp-pro-1] [adsp-pro-2]
Hypertension
Diagnosis of high eye pressure
Only an experienced ophthalmologist can determine increased levels of eye pressure. Diagnostics is carried out in several ways:
- Palpation . The doctor palpates the eyes through the patient's closed eyelids.
- Tonometer . In ophthalmology, a special tonometer is used to determine eye pressure. First, the doctor instills anesthetic drops into the patient’s eyes, after which he measures the pressure. The tonometer is applied to the cornea of the eye, and an imprint appears on it. Next, the doctor transfers this print to an ophthalmological scale for determining the level of intraocular pressure.
- Non-contact tonometry . The most modern method of measuring eye pressure. Unlike a conventional eye tonometer, it does not require direct contact with the cornea. The patient's eyes are exposed to a stream of air supplied under pressure. Next, the doctor notes the nature of the changes occurring in the patient’s visual organs. Based on these changes, the ophthalmologist determines intraocular pressure values.
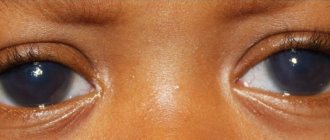
Diagnostic measures for glaucoma
Glaucoma is an ophthalmological disease that has a chronic course. During the course of this disorder, patients experience increased pressure in the organs of vision, and also develop optic neuropathy. If glaucoma is suspected, patients must be diagnosed. With its help, not only the diagnosis is confirmed, but also the development of an effective treatment regimen.
Symptoms of glaucoma
When a patient contacts a doctor, a diagnosis of glaucoma is carried out, which consists of examining the organs of vision and taking an anamnesis, which makes it possible to make a preliminary diagnosis. In order for the doctor to be able to determine the disease, the patient must talk about the symptoms that bother him.
A working method to restore vision! You will throw your glasses in the trash in just 3 days...
Restoring vision. Real life story.
Important! The early stage of open-angle glaucoma in most cases is characterized by the absence of specific symptoms.
The person’s vision is normal, and there is no pain. That is why it is quite difficult to identify the disease at this stage. Patients develop circles in front of their vision. Asthenopia phenomena may also be observed. These are nonspecific signs for this disease. Despite the fact that during this period there are no specific symptoms, damage may develop in the nerve area of the organs, which will be quite difficult to eliminate in the future.
If the diagnosis of glaucoma was not carried out in a timely manner, this provokes the occurrence of additional symptoms. This disease is characterized by deterioration of peripheral visibility. The patient can clearly see objects in front of him, but with peripheral vision he does not notice objects. Initially, the field of view narrows from the side of the nose. After a certain time, concentric seizure of the peripheral parts is observed, which can lead to complete loss of vision.
In patients, a spot appears in the area of visibility, which can be transparent or translucent. Some patients complain that their dark adaptation is worsening. People's color perception process is spoiled. The disease may be accompanied by a deterioration in the quality of visibility, which cannot be corrected. Such symptoms are observed in severe and advanced cases of the disease. At this moment, the fibers of the optic nerve gradually atrophy.
If the patient has an acute attack of the angle-closure form of the disease, then its symptoms become more pronounced. During this period, patients complain of pain in the eye area. You may also experience headaches that radiate to various areas of the cheekbones, temples and forehead.
During the course of this form of the pathological process, patients' vision may become blurred. Rainbow circles appear quite often around light sources. The disorder is sometimes accompanied by photophobia. Patients may experience redness around the eyes. Nausea and vomiting may also be present. With a complex pathological process, the number of heart contractions decreases.
The manifestation of general symptoms is more striking than ocular signs. This disease is accompanied by a person’s anxiety, which leads to the occurrence of disease in the heart area. That is why most patients with the disorder suspect cardiovascular pathologies.
During an examination of the organs of vision using a slit lamp, clouding of the cornea is observed, which is explained by swelling. In patients with glaucoma, pupil dilation is diagnosed. The reaction to light may be weakened or absent altogether. Ophthalmologists palpate the eyeball, which allows them to determine its hardness.
If the above symptoms appear, the patient should immediately contact a specialist and tell them about it. This condition requires urgent assistance from a medical professional. Otherwise, vision loss may occur.
Instrumental research methods
To confirm the preliminary diagnosis, it is recommended to conduct additional examinations using special equipment. Most often patients are prescribed:
- Tonometry. This method checks eye pressure. If the patient is undergoing a pathological process, the pressure readings will be increased. Some patients are advised to instill pain-relieving drops before the procedure. The resistance of the cornea to pressure is measured with a special device - a tonometer. If the indicator is 10-21 millimeters of mercury, then eye pressure is normal. Despite this, if a person has normotensive glaucoma, then the pressure is normal, and the optic nerve is characterized by the development of damage.
- Ophthalmoscopy. This method allows you to examine the optic discs and determine the disorder. An examination is carried out with an ophthalmoscope. This instrument is used to examine the internal structure of the eye. To dilate the pupil, special drops are instilled into the person’s visual organs before the procedure. With glaucoma, there is damage to the optic nerve, as well as death of its fibers. This leads to a change in its appearance. In its shape it resembles a bowl. As its size increases, dark spots appear in the visibility zone.
- Pachymetry. Thanks to this examination method, it is possible to measure the thickness of the cornea. This indicator makes it possible to measure the level of intraocular pressure as accurately as possible. If the cornea is too thick, the pressure decreases significantly. If the cornea is thin, then the pressure in the organs of vision will be higher than what the tonometer shows.
- Perimetry. This examination method makes it possible to identify dark spots in the visibility zone. Thanks to this test, it is possible to determine not only their development, but also the location of their localization. Some spots remain invisible to the patient for a long time. The examination is carried out using a cup-shaped device - a perimeter. It is possible to test only one organ of vision at a time. That is why during the examination a bandage is applied to the second eye. The person must direct his gaze to the mark. The computer sends a signal. Flashing dots appear inside the device. If the patient sees them, then he needs to press the button. To determine the development of changes, it is recommended to conduct the study once every 8-12 months.
- Gonioscopy. Using this method, you can determine the angle of the anterior chamber of the visual organ. This research method makes it possible to find out the type of glaucoma. A simple inspection is not possible to obtain such information. The eye examination is carried out with a special mirror lens, which makes it possible to establish open-angle pathology. This disease is diagnosed when the anterior chamber angle is insufficiently functioning. This research method also determines angle-closure pathology. During the course of the disease, the angle of the anterior chamber may narrow. This pathological condition is determined using gonioscopy.
Thanks to the availability of a large number of instrumental methods, it is possible to diagnose glaucoma as accurately as possible. The doctor can not only make a correct diagnosis, but also prescribe rational therapy. The choice of certain research methods should be carried out only by a doctor.
Additional examination methods
If the need arises, then the patient is prescribed additional diagnostic methods, which makes it possible to determine the nature of the course of the disease. The most effective of them include:
- Ultrasound examination of the eye. It is an instrumental examination method that is widely used in ophthalmology. This is a non-invasive high-tech technique. Thanks to sonography in various modes, it is possible to visualize all anatomical structures of the eyeball, as well as study their sizes. This study makes it possible to determine the state of the blood flow and the vascular wall. Ultrasound is used to measure all intraorbital distances.
- Optical coregent tomography. This method is used to determine the number and parameters of the optic nerve head, as well as to assess their ratio.
- Computer perimetry. Belongs to the category of high-precision hardware research methods, with the help of which the boundaries and defects of the visual field are determined. Static, kinetic and color perimetry are studied using different programs. During the examination, a person needs to concentrate his gaze on one point on the screen. When a spot appears in it, he needs to press a button.
- Elastometry. This examination method requires the use of a set of Maklakov tonometers, which are characterized by different weights. In its principle, this procedure is similar to contact tonometry. To ensure the accuracy of the indicators, it is recommended to conduct several studies at a certain interval.
Additional examination methods greatly simplify the diagnosis of glaucoma. With their help, the most effective treatment is prescribed to a sick person.
Azopt
American-made eye drops, available in 5 ml bottles. The cost of the drug is quite high - around 850 rubles. However, ophthalmologists claim that these drops perform their duties flawlessly in eliminating intraocular pressure.
The drops are based on the substance brinzolamide. For a high therapeutic effect, it is enough to drop one drop into each eye twice a day. It is important that this drug has only one contraindication - individual intolerance to the components included in the composition.
Combination drugs for glaucoma
The most famous representatives of this group are:
- Xalacom® is a combination of a non-selective beta blocker (Timolol) and a synthetic prostaglandin analogue (Latanoprost).
- Fotil® is a combination of a non-selective beta blocker (Timolol) and a cholinomimetic (Pilocarpine).
- Cosopt® is a combination of a non-selective beta blocker (Timolol) and a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor (Dorzolamide).
The combination of several medicinal substances in combination preparations can increase the effect of lowering IOP and reduce the frequency of use.
What to do to reduce blood pressure?
People suffering from ocular hypertension are interested in how to reduce eye pressure. Special drops best cope with this task, but they must be prescribed by an ophthalmologist. If it is not possible to see a doctor in the near future, then reduced with the help of a tincture of sleep grass, wild pear shoots and nettle. A decoction prepared from these herbs should be taken three times a day before meals.
Doctors also recommend instilling a solution made from onion juice and good honey into the eyes.
Betaxolol
Russian drops that have a very affordable price - a 5 ml bottle can be bought for about 140 rubles. The composition is based on the substance of the same name, betaxolol. Instill one drop twice a day.
Contraindications to the use of Betaxolol:
- bradycardia;
- diabetes;
- thyroid diseases;
- Raynaud's syndrome.
Drops can cause an allergic reaction, eye discomfort, conjunctivitis, irritation, redness of the eyes, photophobia, insomnia and even depression!
It is important to remember that this article is for informational purposes only! The presented drugs can be used in medical therapy only as prescribed by a doctor!
Antiviral
Such drops, which relieve redness of the eyes, are used when the organ of vision is affected by viral infections. Only a doctor can prescribe them after examining the patient.
Oftalmoferon
The active component of the drug is interferon. This substance affects various viruses, mostly the group of herpes viruses. These drops are indicated for relieving eye redness caused by:
- keratitis;
- conjunctivitis;
- uveitis.
Also used to treat fatigue associated with dry eye syndrome. More drops for tired eyes here.
"Ophthalmoferon" is instilled under the lower eyelid every two hours. As the inflammatory process subsides, the frequency of instillations is reduced to twice a day. When treating irritation against the background of dry syndrome, the duration is at least 45 days.
The drug has no contraindications, with the exception of individual intolerance. The cost of the medicine is about 400 rubles.
Poludan
Relatively inexpensive drops with antiviral action. Contains polyadenylic acid. The medicine is active against herpes viruses and is used to treat lesions of the mucous membrane and cornea.
Poludan is available in powder form, which must be dissolved with sterile water. The prepared solution is stored in the refrigerator for no more than 7 days. "Poludan" is dripped every two hours, the duration of treatment is 5 days.
The drug has no contraindications. The cost of the medicine is about 150 rubles.